2. 江苏省食品药品监督检验研究院, 江苏 南京 210019;
3. 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司, 上海 201206;
4. 中国药科大学, 江苏 南京 211198
2. Jiangsu Institute of Food and Drug Control, Nanjing 210019, China;
3. Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation, Shanghai 201206, China;
4. China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, China
环维黄杨星D是从黄杨科植物小叶黄杨(Buxus microphylla Sieb. et Zucc. var. sinica Rehd.et Wils.)及其同属植物经酸性醇提、碱化、有机溶剂萃取、粗品重结晶所得的生物碱[1, 2]。具有抗心律失常、抗心肌缺血、舒张血管、降血压等作用[3]。以环维黄杨星D为原料加适量辅料所制的黄杨宁片由我国于上世纪80年代自主研制开发, 在治疗冠心病、心律失常、心绞痛等方面有较好的疗效[4]。除环维黄杨星D外, 小叶黄杨中还含有结构极为相近的环常绿黄杨碱C、环黄杨碱D等有关物质, 且目前生产的黄杨宁片原料难以使环维黄杨星D的含量高达90%以上[2], 而自2000版中国药典始收载此药起, 连续四版均采用非水滴定法测定原料中环维黄杨星D含量, 但实际测定的是总生物碱含量, 缺乏专属性[1, 5]。
黄杨宁片原料中含有的环维黄杨星D及有关生物碱是一类由三萜-孕甾烷衍生出的C-19和C-9相连的特殊生物碱, 部分此类生物碱并不具有紫外特征吸收甚至某些不具有末端吸收[6]。环维黄杨星D为其主要成分, 为4, 4, 14-三甲基孕甾烷生物碱, 具紫外末端吸收[7, 8], 因此有学者采用HPLC紫外末端检测法进行分析, 如反相离子对色谱法[9], 但部分有关物质无末端吸收, 因而难以得到全面的有关物质信息。为获取全面的有关物质信息, 也有学者采用柱前衍生化法进行紫外检测, 或采用ELSD检测[10-12], 但前者对衍生化后物质的全面性无从验证且增加了操作繁琐性, 而后者又局限于痕量物质的检测灵敏度不高, 因此难以兼顾有关物质的全面性和定量准确性。CAD是一种新型非挥发性通用型液相色谱检测器, 检测原理是将液相洗脱液雾化蒸发后对带电粒子信号电流进行检测, 其响应与分析物颗粒质量有关[13], 灵敏度是ELSD的30~55倍[14], 可有效弥补黄杨生物碱UV检测信号不全、微量有关物质无法准确定量等问题。此外, 在等度洗脱或者反相梯度补偿下的梯度洗脱时, CAD对非挥发性物质的响应具有均一性[15, 16], 可实现采用一种易得对照品来准确定量其他母核相同物质, 解决黄杨宁片原料中未知有关物质缺少相应对照品而无法准确定量问题。因此, 本文新建立的HPLC-CAD法, 可同时具有黄杨宁片原料中物质信号齐全、微量物质信号灵敏度高、可一标多测的三大优势, 兼顾了定性和定量的准确性, 且操作简单易行, 是目前黄杨宁片原料分析方法中可靠和较为前沿的方法。
材料与方法仪器 美国Thermo-Fisher UltiMate3000高效液相色谱仪, 美国Thermo-Fisher Corona Veo RS电喷雾式检测器(HPLC-CAD); 美国Thermo-Fisher UltiMate3000高效液相色谱仪, 美国Thermo-Fisher四级杆-静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱(HPLC-Q Exactive); KH-600DE型超声仪(功率是720 W, 频率是40 kHz); 电子天平(瑞士Mettler Toledo XSE205型、XPR2型、德国Sartorius BS21S型); Merck Millipore超纯水制备系统, DELTA 320型pH计。
试药与试剂 环维黄杨星D对照品(批号: 110888-200503, 纯度: 93.20%), 购自中国食品药品检定研究院。黄杨宁片原料样品共13批:分别由安徽新陇海药业有限公司、东台市康宁植物素有限公司、南京小营药业提供。乙腈(Merck公司)、甲酸、甲酸铵均为色谱纯, 水为超纯水。
色谱条件 色谱柱为XBridge Amide色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm); 流动相为乙腈-100 mmol·L-1甲酸铵溶液(85:15) (混合溶液用甲酸调pH 2.8);流速1.1 mL·min-1; CAD雾化温度35 ℃; 气压: 62.2 psi; 柱温30 ℃。精密吸取10 μL进样, 以外标一点法计算环维黄杨星D和有关物质含量。
质谱条件 离子源为电喷雾离子源(ESI), 分析模式为正离子模式, 质量扫描范围m/z 50~500, 喷雾电压3 800 V(+), 鞘气体积流量为30个流量单位, 辅助体积流量为10个流量单位, 毛细管温度320 ℃, 透镜电压50 kPa, ,质量分辨率70 000。
对照品溶液的制备 取环维黄杨星D对照品适量, 精密称定, 加流动相制成浓度为0.500 8 mg·mL-1对照品溶液(1)、1.199 6 mg·mL-1的对照品溶液(2)、0.150 0 mg·mL-1对照品溶液(3)和0.629 4 mg·mL-1对照品溶液(4) (必要时超声)。
供试品溶液的制备 取原料样品适量, 精密称定, 加流动相制成0.6 mg·mL-1的溶液(必要时超声)。
阴性溶液的制备 取流动相溶液作为阴性溶液。
定量测定和定性分析 取样品每批制备2份供试品溶液, 每份测定2针, 以浓度相对应的环维黄杨星D对照品溶液按外标一点法分别计算环维黄杨星D和有关物质含量。采用HPLC-Q-Exactive技术对HPLC-CAD中出现的有关物质色谱峰进行定性分析。
方法学验证
专属性 取对照品溶液(1)、供试品溶液、阴性溶液, 分别注入液相色谱仪, 比较色谱图。
精密度 精密吸取对照品溶液(1), 连续进样6次, 记录峰面积, 计算RSD。
线性关系 依次将环维黄杨星D对照品溶液(2)稀释85%、50%、35%、25%、10%, 将对照品溶液(3)稀释80%、40%、30%、10%、4%, 分别进样。以进样量(μg)为横坐标, 峰面积为纵坐标, 分别计算高浓度回归方程(用于环维黄杨星D的线性范围考察)和低浓度回归方程(用于有关物质的线性范围考察)。
检测限和定量限 取对照品溶液(4), 用流动相逐步稀释至信噪比约为3和10时的溶液, 计算此时的溶液浓度。
稳定性 精密吸取供试品溶液(批号: 140901), 分别在0、2、4、6、8、12、16、20、24、30 h进样, 记录峰面积, 计算RSD, 考察供试品溶液在30 h内的稳定性。
重复性 称取同一批号样品(批号: 141101) 6份, 按供试品溶液制备方法平行制备6份, 测定含量。
加样回收率 取已知含量的样品(批号: 141101) 6份, 每份3 mg, 精密称定, 精密加入环维黄杨星D对照品溶液(1) 5 mL, 按供试品制备方法制备, 测定, 计算回收率。
结果 1 方法学验证 1.1 专属性测得样品色谱图如图 1所示。结果阴性溶液未出现与环维黄杨星D对照品及原料中的有关物质峰保留时间相一致的色谱峰, 表明阴性溶液对主成分和有关物质均无干扰。
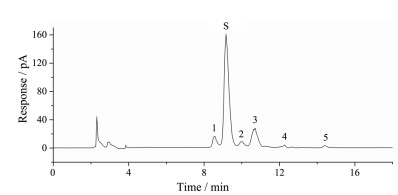
|
Figure 1 The HPLC-CAD chromatograms of API sample solution. S: Cyclovirobuxine D; 1-5: Related substances 1-5, respectively |
环维黄杨星D峰面积RSD值为1.09% (n = 6), 表明仪器精密度良好。
1.3 线性关系环维黄杨星D高浓度溶液的回归方程为Y = 7.353 8 X + 9.130 9, r = 0.999 3 (n = 6), 线性范围1.118 0~11.179 9 μg; 低浓度溶液的回归方程为Y = 12.287 6 X + 0.227 8, r = 0.999 8 (n = 6)。线性范围0.055 9~1.398 0 μg。
1.4 检测限和定量限结果检测限为12.588 ng, 定量限为28.323 ng。
1.5 稳定性环维黄杨星D峰面积RSD为1.10% (n = 20), 表明供试品溶液在30 h内稳定。
1.6 重复性环维黄杨星D含量的RSD为1.79% (n = 6), 平均含量为84.81%, 表明重复性良好。
1.7 加样回收率环维黄杨星D的加样回收率为95.74%, RSD为1.79%, 表明该方法的准确度良好。结果见表 1。
| Table 1 Results of recovery |
样品中环维黄杨星D含量在79.94%~88.49%, 平均值82.20%。5个有关物质总含量为15.99%~22.15%, 平均值20.10%, 有关物质1~5含量分别在4.78%~7.26% (峰1)、1.80%~3.78% (峰2)、7.52%~13.03% (峰3)、0.58%~1.72% (峰4)、0.05%~0.27% (峰5, 其中6批未检出), 结果见表 2。
| Table 2 Results of different batches of samples (n = 4). "-" Not detected |
通过正负离子模式比较, 选择了信息更丰富的正离子模式(图 2)。在一级质谱图中, 发现除[M+H]+峰外还有[1/2M+H]+峰, 且[1/2M+H]+为优势离子峰, 故将[1/2M+H]+作为母离子进行二级质谱分析。根据一级、二级质谱的裂解特征, 结合Xcalibur质谱工作站和ACD/Spectrus数据库平台, 推测出5个有关物质分别为环常绿黄杨碱C (峰1)、环黄杨碱D双键加氢产物(峰2和峰4)、环黄杨碱D (峰3)、cyclobuxamine H (峰5), 其中峰1和峰3为两个主要有关物质, 见表 3。
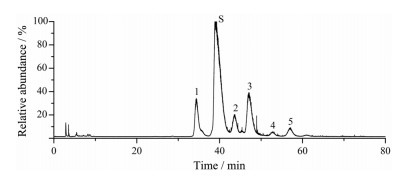
|
Figure 2 Total ion chromatogram (TIC) of cyclovirobuxine D and its related substances extract in positive ion mode |
| Table 3 The structures and MS characteristics of the related substances |
本实验首次建立了采用HPLC-CAD方法对黄杨宁片原料中环维黄杨星D及有关物质的定量研究, CAD检测器具有对低含量物质检测灵敏度高的优势, 可提高微量有关物质定量的准确性; 其检测信号全面, 可有效解决黄杨生物碱因有些有紫外末端吸收而有些没有末端吸收在UV检测器上出现的信号不全问题; 其响应信号具有均一性, 可仅以一种易得对照品来(该方法中是主成分环维黄杨星D)定量其他有关物质, 解决黄杨宁片原料有关物质缺少相应对照品而无法准确定量问题。本方法操作简单、无需衍生化处理, 为分析黄杨宁片原料中环维黄杨星D和有关物质研究提供一种新的方法和思路。
前期考察了水、甲酸、甲酸铵以及乙酸铵作为水相, 甲酸铵、乙酸铵缓冲盐可使环维黄杨星D与有关物质较好的分开, 且缓冲盐浓度较高时峰型较好。此外, 改变缓冲盐pH值可使保留时间发生改变, 随着pH值减小, 保留时间减小, 最终选择100 mmol·L-1甲酸铵(甲酸调节至pH 2.8)作为水相。本研究采用具有HILIC模式的XBridge Amide色谱柱, HILIC是一种以极性固定相(硅胶或衍生硅胶)及高比例有机相为流动相的色谱模式, HILIC利用被测组分与硅胶表面硅羟基的相互作用, 实现不加离子对试剂的洗脱液就可对极性范围大的生物碱进行分离[17], 且避免了离子对色谱难以与质谱兼容的问题[18]。同时, 对于通过蒸发去除流动相的电喷雾检测器, HILIC系统中高比例有机相有利于检测灵敏度的提高[19, 20]。此外, 本法在保留时间为3.8 min时(图 1C)还可以观察到延宽的色谱峰, 含量约在0.2%, 通过质谱验证, 还含有多个其他有关物质, 有待今后对优化流动相作进一步研究考证。
本实验建立的HPLC-CAD方法对黄杨宁片原料中环维黄杨星D及有关物质的定量研究同时还采用了HPLC-Q-Exactive对黄杨宁片原料中有关物质进行定性研究。Q-Exactive质量分析器分辨率高达50万[21], 具有稳定的质量精度, 可大大提高黄杨宁片原料中结构相近有关物质的鉴别准确度; 同时所带有的Xcalibur质谱工作站对推测的分子式的准确性也有强大的支撑作用。
| [1] |
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (中华人民共和国药典)[S]. 2015ed. Vol 1. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2015: 406.
|
| [2] |
Hu GQ, Xu QT, Zhang BG, et al. An improved separation method of cyclovirobuxine D from the total alkaloids of Buxus[J]. Chin J Nat Med (中国天然药物), 2004, 2: 30-31. |
| [3] |
Guo Q, Guo J, Yang R, et al. Cyclovirobuxine D attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by suppression of oxidative damage and mitochondrial biogenesis impairment[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2015, 2015: 151972-151983. |
| [4] |
Duan SS, Xie Y, Hu T. Effect of cyclovirobuxine D on plasma N-terminal pro-brainnatriuretic peptide level and exercise tolerance in patients with congestive myocardial failure caused by coronary heart disease[J]. Cent South Pharm (中南药学), 2009, 7: 308-310. |
| [5] |
Liu J, Hang TJ, Zhang ZX. HPLC determination of cyclovirobuxinum D and its related alkaloids in Huangyangning[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal (药物分析杂志), 2006, 26: 446-449. |
| [6] |
Liang BW, Zhang ZX, Fang TH, et al. Buxus Alkaloids and Cardiovascular Disease (黄杨碱与心脑血管疾病)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011: 118.
|
| [7] |
Lv X, Yv X, Guo Q, et al. Progress on study of Buxus alkaloids[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2012, 18: 315-321. |
| [8] |
Xie Y, Yu ZG, Xu XS, et al. IP-HPLC determination of cyclovirobuxium D[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal (药物分析杂志), 2006, 26: 888-890. |
| [9] |
Xu XJ, Zhang ZX, Sheng LS, et al. Determination of cyclovirobuxine D by RP-HPLC with precolumn fluorescence derivatization[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2002, 37: 359-361. |
| [10] |
Lv X, Hu MT, Yang C, et al. Determination of cyclovirobuxium D in Huangyangning tablets by HPLC-ELSD[J]. Res Pract Chin Med (现代中药研究与实践), 2014, 28: 52-54. |
| [11] |
Yang C, Guo Q, Wolf C, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of cyclovirobuxine D and impurities in active pharmaceutical ingredient of Huangyangning tablets by RP-HPLC with pre-column derivatization[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal (药物分析杂志), 2017, 37: 1013-1022. |
| [12] |
Liu L, Gao X, Yang YJ. Application of HPLC-charged aerosol detection[J]. Chin J Pharm (中国医药工业杂志), 2012, 43: 227-231. |
| [13] |
Long Z, Guo Z, Acworth I N, et al. A non-derivative method for the quantitative analysis of isosteroidal alkaloids from Fritillaria by high performance liquid chromatography combined with charged aerosol detection[J]. Talanta, 2016, 151: 239-244. DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.01.027 |
| [14] |
Eckardt M, Kubicova M, Simat TJ. Universal response quantification approach using a Corona Charged Aerosol Detector (CAD)-application on linear and cyclic oligomers extractable from polycondensate plastics polyesters, polyamides and polyarylsulfones[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2018, 19: 187-202. |
| [15] |
Górecki T, Lynen F, Szucs R, et al. Universal response in liquid chromatography using charged aerosol detection[J]. Anal Chem, 2006, 78: 3186-3192. DOI:10.1021/ac060078j |
| [16] |
Qiu MH, Nie RL. Buxus alkaloids and its plant resources[J]. Nat Product Res Dev (天然产物研究与开发), 1992, 4: 41-57. |
| [17] |
Li RP, Huang JX. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography and its applications in the separation of basic drugs[J]. Prog Chem (化学进展), 2006, 18: 1509-1513. |
| [18] |
Wang Y, Gu HX, Lu X, et al. Development of hydrophilic interaction chromatographic hyphenated techniques and their applications[J]. Chin J Chromatogr (色谱), 2008, 26: 649-657. |
| [19] |
Cao CC, Liang JJ, Wang M, et al. Separation of amino acids and their initial Maillard reaction intermediates by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography[J]. Food Sci (食品科学), 2016, 37: 63-71. |
| [20] |
Mitchell CR, Bao Y, Benz NJ, et al. Comparison of the sensitivity of evaporative universal detectors and LC/MS in the HILIC and the reversed-phase HPLC modes[J]. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2009, 877: 4133-4139. DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.10.027 |
| [21] |
Zhang JX, Hu Q, Yu H, et al. Rapid and intelligentized identification of the constituents in Gualoupi injection by HILIC/ESI-Orbitrap HRMS combined with Compound Discoverer software[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2018, 53: 1705-1712. |
 2019, Vol. 54
2019, Vol. 54


