壁虎, 又名守宫, 为壁虎科无蹼壁虎、多疣壁虎、无疣壁虎和蹼趾壁虎等的全体[1]。味咸、寒, 有小毒, 归肝、肾经, 具有祛风活络、散结止痛、镇静解痉等功效[2]。壁虎在临床上对多种恶性肿瘤的疗效已引起医药界的关注[3], 且壁虎作为临床抗肿瘤药物相对于化疗药物毒副作用较小[4]。以壁虎为君药的中成药金龙胶囊可用于治疗大肠癌、食道癌、胃癌和肺癌等[5]; 含壁虎组方“消结散”配合“益气散结汤”可用于治疗食管癌[6]; 含壁虎组方“消瘤丸”可用于治疗脑肿瘤[7]; 壁虎与全蝎配伍可用于治疗颈部肿瘤[8]。由此可见, 壁虎临床用于多种肿瘤的治疗, 尤其对消化系统肿瘤应用较广。本实验室前期证明壁虎生品和炮制品均对荷肝癌H22小鼠模型具有较好的抗肿瘤活性, 并且二者活性无统计学差异[9]。为了矫味去腥和保存方便, 古法常对壁虎进行隔瓦焙制, 经现代中药炮制规范和临床使用[10, 11]整理, 归纳为焙干研末、焙黄研面、焙干焙黄、瓦片焙干和微火焙干等。但是, 对于焙制程度未做明确规定。壁虎焙制到什么程度具有较好的抗肿瘤效果呢?焙制程度与抗肿瘤活性之间有什么样的相关性呢?本文利用荷肝癌H22小鼠模型研究焙制程度对壁虎抗肿瘤活性的影响, 明确最佳焙制程度, 从而为壁虎的炮制工艺改进奠定实验基础, 最终提高壁虎的临床疗效。
材料与方法药品 无蹼壁虎(Gekkoswinhonis Guenther)鲜品, 购自山东济南市中九顶山天然养殖场, 由北京中医药大学张冰教授鉴定。
动物 ICR小鼠, 雌性, 体重23~25 g, 购自斯贝福(北京)生物技术有限公司, 动物合格证: SCXK (京) 2016-0002。相关动物实验获得北京中医药大学伦理学委员会批准。
细胞株 H22小鼠肝癌细胞, 购自北京大学医学部实验动物中心。
试剂 注射用氟尿嘧啶(5-FU, 上海旭东海普药业有限公司, 批号H31020593);生理盐水(北京高华伟业食品添加剂有限公司); SDS-PAGE凝胶制备试剂盒(北京索莱宝科技有限公司); BCA法蛋白定量试剂盒(北京兰博利德商贸有限公司)。
仪器 恒温干燥箱(上海一恒公司); 低温高速离心机(Sigma公司); 高速万能粉碎机(天津泰斯特, FW800);紫外分光光度计(Ultraviolet-2100型, 上海龙尼柯仪器有限公司); 垂直电泳槽(Bio-Rad公司); 陶土瓦片(河北宏达古建瓦业)。
壁虎焙制品的制备 鲜壁虎置于烘箱60 ℃干燥10 h后得到烘干未焙制品, 再置于瓦片上焙干, 瓦片尺寸为110 mm×100 mm×15 mm, 瓦片与火焰间距离为2 cm, 每次焙制壁虎2条, 分多次完成各组样品的焙制, 分别焙制2、4和6 min至壁虎呈现微黄色、黄色和焦黑色, 分别记为焙制品1、2、3, 再用高速万能粉碎机粉碎, 取全粉备用。
酥脆度测定 取粉碎前的焙制品, 同等力度压碎, 根据产生的碎片大小, 定义5个碎度, 由小到大计为1至5度, 1度:碎片直径小于0.2 cm; 2度:直径为0.2~0.4 cm; 3度:直径为0.4~0.6 cm; 4度:直径为0.6~0.8 cm; 5度:直径大于0.8 cm。分别计算各碎度碎片占总重量的百分比。
壁虎焙制品感官评价 取焙制品置于小盘中, 由评价员对壁虎焙制品颜色和气味分别进行打分评价, 两项分值由低到高分别计为0~10分。颜色观感很差、腥味很重计0分; 颜色观感较差、腥味较重计为1~3分; 颜色观感一般、有腥味但可以接受计为4~6分; 颜色观感好、基本无腥味计为7~9分; 颜色观感非常好、完全无腥味计为10分。评价员打分时分数为整数, 最后得分为两项平均分之和。
含水量测定 按照《中国药典》2015年版四部通则0831干燥失重测定法检测[12]。
水溶性浸出物含量测定 按照《中国药典》2015年版四部通则2201浸出物测定法下的水溶性浸出物测定法中的冷浸法测定[12]。
水溶性蛋白质浓度及多样性测定 壁虎不同程度焙制品加入浓缩胶缓冲液, 研磨成匀浆状, 超声提取, 4 ℃、10 000 r·min-1离心10 min, 收集上清再次低温离心, 收集上清作为上样样品。按照BCA法蛋白定量试剂盒说明书测定蛋白质浓度。采用SDS-PAGE法测定水溶性蛋白质多样性差异, 上样样品稀释至1 mg·mL-1, 分离胶浓度为10%, 浓缩胶浓度为5%。
H22荷瘤小鼠模型制备与动物分组 H22细胞经计数和活力测定后调整细胞浓度为每毫升2×107个[13], ICR小鼠腋下接种H22细胞悬液, 随机分为6组(n = 10), 即阴性对照组、阳性对照组、烘干未焙制品、焙制品1、焙制品2、焙制品3。各组均给予普通饲料进行喂养。阴性对照组腹腔注射生理盐水8 mL·kg-1, 灌胃生理盐水16 mL·kg-1; 阳性对照组腹腔注射剂量为3 mg·mL-1 5-FU 8 mL·kg-1, 灌胃生理盐水16 mL·kg-1。壁虎烘干未焙制品与焙制品各组按生药量24 g·kg-1灌胃给药, 腹腔注射生理盐水8 mL·kg-1。接种瘤株24 h后开始给药, 每天给药1次, 连续给药8天。末次给药后禁食不禁水24 h, 称量体重, 迅速解剖摘取脾、胸腺和肝脏, 并剥离肿瘤[14]。
H22荷瘤小鼠指标检测 每日称量各组小鼠体重, 计算各组小鼠每日摄食量, 每日观察小鼠的精神状态、活动量和毛色等生理指标。分别称取各组小鼠脾、胸腺、肝脏及肿瘤重量, 计算肝指数、脾指数、胸腺指数和抑瘤率。器官指数为器官重占体重比例; 抑瘤率以阴性对照组为参照。
统计学方法 所有数据用SPSS 10.0软件进行统计分析, 用x ± s表示, 组间比较采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA), P < 0.05具有统计学意义。
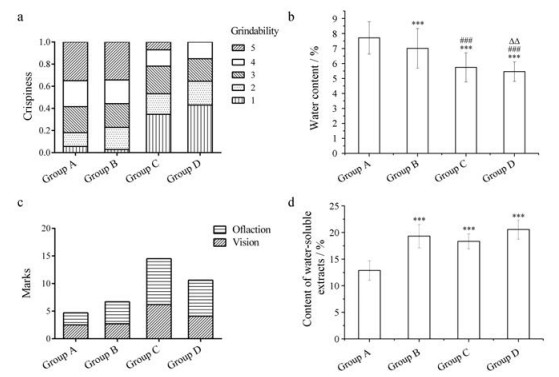
结果 1 不同程度壁虎焙制品感官评价及指标检测经过不同程度焙制, 壁虎烘干未焙制品呈青黑色, 壁虎焙制品1呈微黄色, 壁虎焙制品2呈黄色, 壁虎焙制品3呈焦黑色(图 1)。随着焙制程度的增加, 小碎片占比增加, 酥脆度增加(图 2a), 焙制品的含水量降低(图 2b)。经过感官评价, 壁虎焙制品2具有焦香味且颜色焦黄, 评分最高; 烘干未焙制品具有较刺激的腥味, 评分最低(图 2c)。壁虎焙制品水溶性浸出物含量均高于壁虎烘干未焙制品, 其中焙制品2的水溶性浸出物含量低于其他焙制品(图 2d)。

|
Figure 1 Appearance of Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling. Crude lizards were dried at 60 ℃ for 10 h and broiled over clay tiles to different extents. The size of clay tile was 110 mm×100 mm×15 mm. The distance between clay tile and fire was 2 cm. a: Group A (without broiling); b: Group B (mildly broiled); c: Group C (moderately broiled); d: Group D (heavily broiled). Group A-D were broiled for 0, 2, 4, 6 min, respectively |
|
Figure 2 Properties of Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling. a: Evaluation of crispiness. Lizards with different broiling extents were grinded respectively to fragments of different sizes. The sizes of fragments were measured and categorized into 5 levels of grindability. The levels from 1 to 5 were correspondent to the sizes of fragments from small to big. The weight of each level was weighed and the percentage relative to whole weight was calculated. b: Water content. Lizards with different extent of broiling were dried to constant weight, water content was evaluated by the ratio of weight loss to initial weight. c: Sensory evaluation of vision and olfaction. Lizards with different extent of broiling were displayed in plates respectively and marks from 0 to 10 points were graded by valuators for each standard of evaluation. d: Content of water-soluble extracts. Lizards with different extent of broiling were extracted by water overnight and supernatant was dried to constant weight. Content of water-soluble extracts was evaluated by the ratio of solid weight to initial weight. n = 3, x ± s.***P < 0.001 vs Group A, ###P < 0.001 vs Group B, △△P < 0.01 vs Group C |
经过烘干后焙制, 壁虎的含水量降低, 使药物的贮存更为方便, 壁虎的酥脆度增加, 增强了药物的适口性。壁虎的腥味可能来源于壁虎的蛋白质和油脂类成分, 经过烘干和焙制, 腥味降低, 提高了患者使用的顺应性。
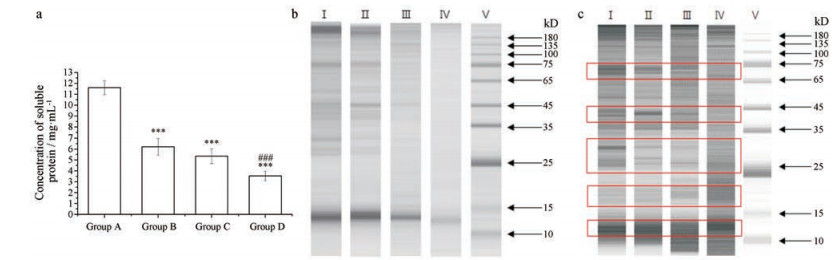
2 壁虎不同程度焙制品可溶性蛋白质浓度及多样性测定随着焙制程度的加深, 壁虎可溶性蛋白质含量降低(图 3a、b), 但壁虎的可溶性蛋白分子量大小有明显差异, 红框中标记位置各样品均出现对应差异条带区域(图 3c)。生药量相同时, 蛋白质条带随着焙制程度的增加而减少, 溶出的蛋白质含量降低, 焙至焦黑组基本无法溶出蛋白。蛋白质条带主要在以下几个区域集中: 180 kDa以上、75~100 kDa、25~45 kDa及10~15 kDa。其中, 180 kDa以上和10~15 kDa的蛋白质溶出随着焙制程度减弱最为明显。将蛋白质浓度调整至相同后, 发现可溶出蛋白质的组成发生变化。随焙制程度增加, 75~100 kDa和25~35 kDa区域蛋白条带减少, 而15~25 kDa蛋白条带增加, 另外, 焙至微黄组的35~45 kDa区域的蛋白量最高。焙制可能促进壁虎中某些蛋白质成分溶出, 而使另一部分蛋白质固化, 不易溶出。
|
Figure 3 Concentration and component difference of soluble proteins in Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling. a: Concentration of soluble proteins. Lizards with different extent of broiling were extracted by ultrasonic extraction. The concentration of soluble proteins in supernatant was tested under the instruction of BCA kit. Soluble proteins concentration (b) and component difference (c) were evaluated by SDS-PAGE, Ⅰ-Ⅴ were group A-D and protein marker, respectively. The numbers on the right side were molecule weight of protein marker bands. The loading samples for b had the same crude drug content, while for c had the same soluble protein concentration. Band difference was marked by red boxes. n = 3, x ± s.***P < 0.001 vs Group A, ###P < 0.001 vs Group B |
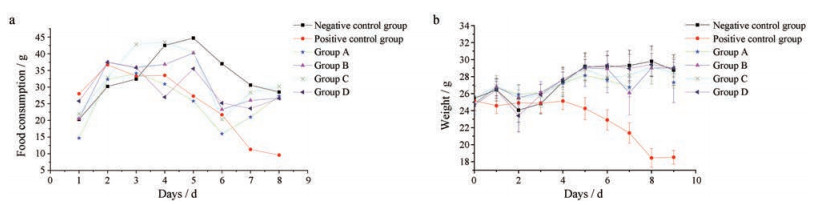
H22荷瘤小鼠摄食量在壁虎不同程度焙制品作用后与阴性对照组相比没有显著差别, 阳性对照组摄食量明显减少(图 4a)。壁虎不同程度焙制品作用后的H22荷瘤小鼠体重与阴性对照组相比没有显著差别(P > 0.05), 且阴性对照组与各焙制品组小鼠体重均有增加, 而阳性对照组小鼠体重明显下降(图 4b)。5-FU作用后小鼠较阴性对照组食欲明显减退, 活动量减少, 体重明显降低, 生存质量下降; 壁虎不同程度焙制品作用后小鼠正常摄食, 正常活动, 生存状态良好。壁虎焙制品在治疗肿瘤的过程中, 对个体的不良反应小于阳性对照药, 使个体能维持较高的生存质量。
|
Figure 4 Life quality of mice after treated with Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extents of broiling on each day. Life quality was assessed by food consumption (a) of each group and average weight (b) of mice after treatment on each day. Mice were injected with H22 cells on day 0, treated with Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling on day 1-8, and dissected on day 9. Negative control group was given a gavage (ig) of normal saline (NS) and intraperitoneal injection (ip) of NS. Positive control group was given NS (ig) and 3 mg·mL-1 fluorouracil (5-FU) 8 mL·kg-1 (ip). Group A-D were given 24 g·kg-1 lizards without broiling, mildly broiled, moderately broiled or heavily broiled lizards respectively (ig) and NS (ip). n = 10, x ± s |
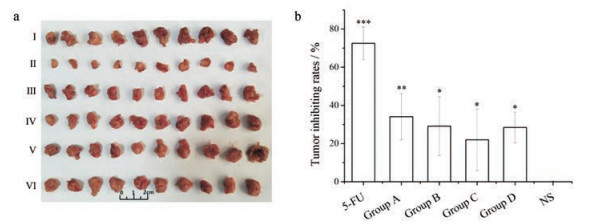
阳性对照组的抑瘤率为72.49%, 壁虎各焙制品组抑瘤率与阴性对照组比较有显著性差异(图 5)。壁虎不同程度焙制品对H22荷瘤小鼠肿瘤均有抑制作用, 各焙制品之间抑瘤效果也有显著性差异, 抑制肿瘤生长活性顺序为:烘干未焙组活性最好(34.11%), 其次是焙至微黄组(29.14%)和焦至黑组(28.43%), 焙黄组活性最差(21.98%)。
|
Figure 5 Tumor inhibiting rates of Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling. a: Excised tumors. Tumors were excised from dissected mice and each group was displayed by sizes, Ⅰ-Ⅵ were excised tumors from mice of negative control group, positive control group, group A, group B, group C and group D, respectively. b: Tumor inhibiting rates were calculated by the ratio of weight difference to negative control (NS) group. n= 10, x ± s. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs NS group |
与阴性对照组相比, 阳性药5-FU作用后的H22荷瘤小鼠脾和胸腺器官指数显著降低, 但经壁虎不同程度焙制品作用后的脾和胸腺器官指数没有显著性差异; 与5-FU组比较, 各焙制品组器官指数明显增大, 且各组之间无显著性差异。各组肝的器官指数无显著性差异(表 1)。说明壁虎各焙制品对小鼠的脾、胸腺和肝没有生长抑制作用, 不会降低小鼠的免疫力, 且焙制程度对其影响不大。
| Table 1 Organ index of mice after treated with Gekkoswinhonis Guenther with different extent of broiling. n = 10, x ± s.###P < 0.001 vs NS group; ***P < 0.001 vs 5-FU group |
动物药的炮制方法和工艺对其活性影响较大[15]。本文比较了壁虎烘干未焙制品与烘干后不同程度焙制品的各项指标与抗肿瘤活性。结果表明, 焙制工艺对壁虎抗肿瘤活性影响较大。随着焙制程度的加深, 壁虎样品含水量下降, 使壁虎药材更易保存; 酥脆度增加, 提高了壁虎药材的适口性; 焙制后产生的焦香味, 提高了壁虎临床使用的顺应性。但焙制后壁虎的抗肿瘤活性降低, 推测对壁虎进行焙制时, 使可能造成腥味的成分逸散或破坏, 对壁虎进行焙制的目的是为了矫嗅、矫味。虽然焙制品提高了感官评价, 但壁虎作为临床抗肿瘤药物, 需以临床疗效为指标, 最佳的炮制加工方法为烘干不焙制。
本实验室前期发现壁虎中抗肿瘤活性成分为大分子蛋白类物质[16], 本研究结果显示, 经过焙制, 壁虎可溶性蛋白质分子质量大小有显著差异并且蛋白质浓度降低, 且抗肿瘤活性降低, 进一步验证了壁虎抗肿瘤活性物质与蛋白质类物质有关。另外, 壁虎经焙制后仍保留抗肿瘤活性, 推测活性蛋白应为耐热蛋白, 可以耐受一定程度的高温作用。后期实验室将考虑以动物模型体内抑瘤实验结合体外细胞形态观察, 对壁虎中的活性蛋白进行深入研究, 并探讨其可能的抑瘤机制。
致谢: 感谢北京中医药大学胡慧华老师在烘干与焙制方法方面提供的参考资料和指导意见。
| [1] | Zhang BG, Zhang DL. Animal Medicine (动物药)[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2003: 398. |
| [2] | Li SZ. Compendium of Materia Medica (本草纲目)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1982: 2389. |
| [3] | Jiang GX, Wang CM, Geng D. Research progress and mechanism research on anti-tumor material finding from Gecko[J]. J Tradit Chin Med (中华中医药杂志), 2013, 28: 1037–1040. |
| [4] | Chen G, Li W. Editorial preface for targeted cancer therapy[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2018, 8: 501–502. DOI:10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.003 |
| [5] | Cui YL. Doctor Li Jiansheng's experience on treatment of esophageal carcinoma[J]. Beijing J Tradit Chin Med (北京中医), 2005, 24: 269–270. |
| [6] | Xu MS, Li ZB. Yiqi Sanjie decoction and Xiaojie powder in the treatment of 80 cases of a dvanced esophageal cancer pain[J]. Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med (陕西中医), 2003, 24: 612–613. |
| [7] | Qiao YS, Zhou SH. Experience of diagnosing and treating cerebral tumor from Zhou Chang'an[J]. China Med Pharm (中国医药科学), 2013, 3: 99–101. |
| [8] | Luo HD. Three treatments and tests of neck tumor[J]. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med (四川中医), 2001, 19: 39–40. |
| [9] | Hou XN, Geng D, Cai A, et al. Comparative research on anticancer activity between fresh and processed Gekkosubpalmatus[J]. J Chin Med Mater (中药材), 2008, 31: 957–959. |
| [10] | Drug Administration of the People's Republic of China. National Standard for Processing Traditional Chinese Medicine (全国中药炮制规范)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1988: 332. |
| [11] | Zhou GR. Clinical observation on treatment of 8 cases of fistula with Gecko powder[J]. Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm (中国民族民间医药杂志), 2000, 44: 137. |
| [12] | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (中华人民共和国药典: 四部)[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2015. |
| [13] | Wang BB, Wang XH, Liu K, et al. Enhanced radiosensitivity of H22 ascitic tumor to 12C6+ ions radiation in ultra-filtration extract mixture from Astragalus mongholicus-treated mice[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2015, 50: 1596–1602. |
| [14] | Fang XY. Medical Experimental Zoology (医学实验动物学)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1995: 104-116. |
| [15] | Ouyang LD, Ma L, Xiao XH. Analysis on the status quo and countermeasures of processing animal medicine of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med (中成药), 2017, 39: 1034–1037. |
| [16] | Hou XN. Anti-tumor Activity Study of Gecko (壁虎抗肿瘤研究)[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2008. |
 2019, Vol. 54
2019, Vol. 54


