2. 呼吸疾病诊疗与新药研发河南省协同创新中心, 河南 郑州 450046
2. Collaborative Innovation Center for Respiratory Disease Diagnosis and Treatment and Chinese Medicine Development of Henan Province, Zhengzhou 450046, China
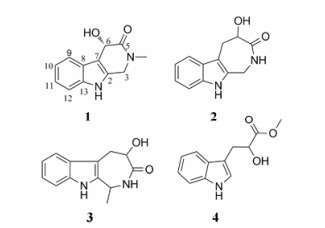
零余子为薯蓣科植物薯蓣(Dioscorea opposite Thunb.)叶腋间的珠芽[1]。据《本草拾遗》记载, 零余子味甘温、无毒、主补虚、强腰脚、食之不饥, 功能比山药还要强, 还可提高人体免疫功能和抗病能力[2]。目前, 关于零余子化学成分的研究较少, 因此, 本文采用多种柱色谱技术和手段, 从零余子中分离得到4个化合物, 分别是: 3, 4-dihydro-6-hydroxy-4-methyl-6H-pyrido[6, 5-b]indol-5(1H)-one (1)、anoectochine (2)、ginsenine (3)和吲哚乳酸酯(4), 其中, 化合物1为新化合物, 化合物2~4首次从该植物中分离得到, 结构见图 1。
|
Figure 1 Structures of compounds 1−4 |
化合物1为淡黄色无定形粉末。碘化铋钾试剂反应呈阳性, 推测该化合物可能为生物碱类成分。[α]D20 -66.014 3 (c 0.067, CH3OH:DMSO = 14:1); UV谱在232、271和289 nm处分别有最大吸收, 提示分子中含有吲哚母环结构。IR谱显示该化合物结构中含有胺基(3 450 cm-1)和酰胺羰基(1 660 cm-1)。HR-TOF-MS: m/z: 217.097 1 [M+H]+ (C12H13N2O2, 计算值为217.096 8), 提示化合物的分子式为C12H12N2O2, 计算不饱和度Ω = 7。在1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6)谱中, 在低场区δH 10.9处出现一个活泼质子信号; δ 7.06 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-10)、6.98 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-11)、7.31 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-12)、7.43 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-9)为苯环上的4个芳香氢信号; 在δH 3.16 (3H, s, N-CH3-4)出现一个N-CH3氢信号; 另外, 在δH 4.18 (2H, dd, J = 15.3, 15.2 Hz, H-3)出现一个亚甲基氢信号; 在13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 125 Hz)谱中有12个碳信号, 根据DEPT 135谱, 可知包含5个季碳、1个仲碳、一个伯碳; 其余5个均为叔碳。在化合物1的1H-1H COSY谱中, 显示出1组质子自旋体系: δH 7.43 (H-9) ↔ 7.06 (H-10) ↔ 6.98 (H-11) ↔ 7.31 (H-12), 证实化合物1中含有邻位双取代的苯环结构(图 2)。利用HSQC、HMBC谱对化合物1的1H NMR、13C NMR谱数据进行了归属(表 1)。在化合物1的HMBC谱中, δH 3.64 (H-6)与C-7 (δC 106.6)、C-2 (δC 127.0)、C-5 (δC 173.0)分别有远程相关, 说明-CHOH-连在C-5以及C-7之间; δH 3.16 (N-CH3-4)与C-3 (δC 40.4)、C-5 (δC 173.0), δH 4.18 (H-3)与N-CH3-4 (δC 48.6)、C-2 (δC 127.0)分别有远程相关(图 2), 说明化合物1中含有与吲哚母环相连的吡啶六元环。通过NOESY谱确定化合物1的相对立体构型, 在NOESY谱中, H-6和N-CH3有相关, 经查阅文献[3-14], 连在氮上的甲基为β构型, 说明H-6和CH3为β构型。综上所述, 并结合文献1, 2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2, 8-dimethyl-4H-pyrido[4, 3-b]indol-3(5H)-one的波谱数据[3], 最终确定该化合物的结构是[3, 4-dihydro-6-hydroxy-4-methyl-6H-pyrido[6, 5-b]indol-5(1H)-one], 命名为零余子碱。

|
Figure 2 1H-1H COSY and key HMBC correlations of 1 |
| Table 1 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) and 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) spectral data of compound 1 |
Bruker AVANCE Ⅲ 500型核磁共振仪(TMS内标)、Bruker maxis HD型飞行时间质谱(德国布鲁克公司); Rudolph AP-Ⅳ型旋光仪(美国鲁道夫公司); Thermo Nicolet IS10红外光谱仪、Thermo EVO300紫外分光光度计(美国热电公司); 赛谱锐思LC50型高压制备液相色谱仪(赛谱锐思北京科技有限公司); UV200型紫外检测器, YMC-Pack ODS-A色谱柱(10 mm × 250 mm.D.S-5 μm, 12 μm) (日本YMC有限公司); Waters e2695高效液相色谱仪, Waters 2998检测器。柱色谱填料Diaion HP-20、MCI Gel CHP-20 (日本三菱化学公司); Toyopearl HW-40 (日本TOSOH公司); Sephadex LH-20 (Pharmacia Biotech公司), 其他分析纯和色谱纯试剂为北京化工厂和天津第三化学试剂厂生产, 标准品购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
零余子为2017年3月采自河南省温县, 经河南中医药大学董诚明教授鉴定零余子为薯蓣科多年生草质藤本植物薯蓣(Dioscorea opposite Thunb.)叶腋间的珠芽。
1 提取与分离零余子60 kg, 50%丙酮组织破碎提取两次, 提取液减压浓缩成稠浸膏状, 稀释到适当浓度, 上Diaion HP-20柱, 依次用水、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%乙醇-水梯度洗脱得到8个洗脱组分。其中, 10%组分和20%组分用Toyopearl HW-40、Sephadex LH-20、MCI Gel CHP-20、ODS等柱色谱技术, 并结合制备液相、HPLC及重结晶方法, 得到化合物1 (6.92 mg)、2 (6.19 mg)、3 (2.49 mg)和4 (2.94 mg)。
2 结构鉴定化合物1 无定形淡黄色粉末, 碘化铋钾试剂反应呈阳性, 推测该化合物可能为生物碱类成分。[α]D20 -66.014 3 (c 0.067, CH3OH:DMSO = 14:1); UV (MeOH:DMSO = 49:1) λmax (logε): 232 (4.17)、271 (4.16)、289 (4.07) nm; IR (MeOH) νmax: 3 450、1 660 cm-1; HR-TOF-MS: m/z: 217.097 1 [M+H]+ (计算值为217.096 8, C12H12N2O2); 1H NMR和13C NMR数据见表 1。
3 化合物抗肿瘤活性测定采用MTT法, 参照文献[15], 对4个化合物进行了细胞毒活性评价, 结果表明, 所有化合物对人肝瘤细胞HepG2和乳腺癌细胞MDA-231的IC50值均大于100 μmol·L-1, 无明显细胞毒活性。本研究不仅丰富了零余子化学成分的类群, 也为进一步开发利用零余子提供了实验基础。
| [1] | Zhao B. New Cultivation Techniques of Chinese Yam (山药栽培新技术)[M]. Beijing: Golden Shield Press, 1998. |
| [2] | Sheng W, Xue JP, Xie BJ. Study on antioxidant activity of extracts from bulbil of Dioscorea opposite[J]. Food Sci, 2009, 30: 92–94. |
| [3] | Wu TS, Chang FC, Wu PL, et al. Constituents of leaves of Tefradium glabrifolium[J]. J Chin Chem Soc, 1995, 42: 929–934. DOI:10.1002/jccs.v42.6 |
| [4] | Luo JP, Zhang LP, Yang SL, et al. Seperation and structure elucidation of alkaloids from Chinese drug buzhaye, Folium Microcos[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2009, 44: 150–153. |
| [5] | Yamasaki K, Fujita K. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of ephedra alkaloids in Eohedrae Herba by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1979, 27: 43–47. DOI:10.1248/cpb.27.43 |
| [6] | Lao AN, Tang ZJ, Xu RS. Study on the chemical constituents of Stephania longa L. (Menispermaceae) (Ⅱ)[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 1981, 16: 940–942. |
| [7] | Hou CY, Xue H. Study on the chemical constituents of Menispermum dauricum DC[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 1984, 19: 471–472. |
| [8] | Lin WH, Cai MS, Ying BP, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of Croomia japonica MIQ[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 1993, 28: 202–206. |
| [9] | Guo YY, Lin LB, Shen J. Study on the chemical constituents of Tinospora hainanesis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 1998, 33: 350–354. |
| [10] | Chaudhuri PK. Echinozolinone, an alkaloid from Echinops echinatus[J]. Phytochemistry, 1987, 26: 587–589. DOI:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)81466-1 |
| [11] | Abdjul DB, Yamazaki H, Ukai K, et al. Two new indole derivatives from a marine sponge Ircinia sp. collected at Iriomote Island[J]. J Nat Med, 2015, 69: 416–420. DOI:10.1007/s11418-015-0891-y |
| [12] | Wang L, Sun L, Liu HY, et al. Chemical constituents of Gelsemium elegans[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2017, 48: 2028–2032. |
| [13] | Zhang DB, Yang Y, Song ZX, et al. Study on alkaloids from Ervatamia hainanensis[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2017, 48: 1286–1291. |
| [14] | Hong B, Li WJ, Zhao CJ. Chemical constituents of Rauvolfia verticillata[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2012, 47: 764–768. |
| [15] | Zhang Z, Wang S, Qiu H, et al. Waltonitone induces human hepatocellular carcinoma cells apoptosis in vitro and in vivo[J]. Cancer Lett, 2009, 286: 223–231. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.05.023 |
 2018, Vol. 53
2018, Vol. 53


