2. 广东药科大学 广东省生物活性药物研究重点实验室, 广东 广州 510006
2. Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Bioactive Substances, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China
卵巢癌是妇科三大恶性肿瘤之一, 其发病率高, 预后差, 五年存活率不足30%, 对患者生命造成极大威胁[1]。由于缺乏明确有效的治疗靶点及相应药物, 当前的治疗手段仍以细胞毒性药物进行化疗为主。因此, 急需探索全新的分子靶标及进行相应的药物开发。维甲酸相关孤儿核受体α (retinoid acid receptor related orphan receptor α, RORα)是一类广泛分布于机体各组织的核受体超家族成员之一, 参与调节昼夜节律、炎症与免疫反应及糖脂代谢等多种生理活动[2-7]。由于RORα基因定位于常见的脆性区域而经常发生丢失, 因此, 普遍认为其具有抑制肿瘤的功能[8]。尽管研究发现RORα在卵巢癌细胞系中的表达明显下调, 但其在卵巢癌中的作用迄今尚无研究报道。
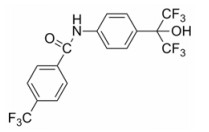
N-[4-[2, 2, 2-三氟-1-羟基-1-(三氟甲基)乙基]苯基]-4-(三氟甲基)苯甲酰胺(SR1078) (图 1)是第一个合成的RORα激动剂, 能够提高RORα的活性, 促使RORα与目的基因启动子上的ROR调控元件(ROR response element, RORE)结合, 刺激RORα目的基因的表达。因此, 本文以卵巢癌为研究对象, 通过利用SR1078处理卵巢癌细胞系实验探讨RORα在卵巢癌细胞中的作用及其调控机制, 为寻求治疗卵巢癌的临床有效药物靶点提供实验依据。
|
Figure 1 Chemical structure of SR1078. SR1078: N-[4-(1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3-Hexafluoro-2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]-4-(trifluoro-methyl)benzamide |
试剂 SR1078 (溶于DMSO, 母液10 mmol·L-1)购自美国MCE公司; Pifithrin-α/β(PFT-α/β)粉剂购自美国Selleck公司, 溶于DMSO; MTS购自美国Promega公司; 凋亡试剂盒购自北京四正柏公司; 二甲基亚砜(DMSO)和碘化丙啶(propidiun iodide, PI)购自美国Sigma公司; 总RNA提取试剂盒购自OMEGA公司; Takara逆转录试剂盒购自大连宝生物工程有限公司; RORα抗体购自美国GeneTex公司; GAPDH和Noxa抗体购自美国Abcom公司; p-p53、p53和β-actin抗体购自武汉博士德公司; ECL购自美国Pierce公司。
细胞培养 上皮性卵巢癌细胞HeyA8和Hey购自中国科学院上海分院细胞库[9]。细胞培养在含有10%胎牛血清、100 μmol·L-1青霉素和链霉素的DMEM培养基(美国Gibco公司)中, 培养条件为含5% CO2的37 ℃培养箱。
药物处理 当HeyA8和Hey细胞贴壁长至培养瓶底部80%即处于对数生长期时, 将细胞消化后按一定浓度接种到孔板中, 待帖壁长至70%~80%时去除旧培养基, 予以分组加入不同浓度的SR1078进行处理。
实时荧光定量PCR(Real-time PCR)检测
细胞总RNA提取 用1×PBS溶液洗涤细胞2次后, 将RNAiso plus液1 mL加入6孔板中, 充分吹打混匀, 收集。加入氯仿200 μL, 涡旋混匀, 冰上孵育10 min。12 000 r·min-1, 4 ℃下离心15 min, 取上清液, 加入1/3体积的乙醇, 涡旋混匀, 将上清液转至2 mL RNeasy Mini spin column, 吸附柱置于2 mL column中, 室温, 1 000×g离心1 min。依次加入300 μL和400 μL wash buffer 1以及500 μL wash buffer 2至column, 清洗RNA沉淀, 室温, 1 000 ×g离心1 min。加入30 μL无菌DEPC水于吸附柱的薄膜上, 放置2 min, 室温, 最高转速离心1 min, 将RNA洗脱下来。核酸蛋白分析仪检测RNA浓度及纯度, OD260/280 = 1.8~2.1, 表明提取的RNA纯度较高。1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳图显示两个条带且条带亮度28S: 18S = 2: 1, 无弥散, 表明提取的RNA纯度高且无降解。
RNA逆转录成cDNA 按照逆转录试剂盒说明书将RNA逆转录成cDNA。引物设计引物由Invitrogen公司设计合成, h-RORαF:5'-AAGCAATGCCACCTACTCCT-3'; R:5'-CAGCATCTCGAGACATCCCT-3'。
Q-PCR反应 反应体系20 μL, SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM 10 μL, 去离子水6.4 μL, 上下游引物各0.8 μL, 模板cDNA 2 μL。两步法反应过程如下: 95 ℃预变性30 s, 进入循环, 95 ℃变性5 s, 60 ℃退火和延伸50 s, 循环次数40次。以GAPDH作为内参, 将所得Ct值按照2-ΔΔCt的方法进行处理。
Western blot检测 SR1078 (终浓度为5.0和10 μmol·L-1)处理HeyA8和Hey细胞48 h后, 收集细胞并提取蛋白。样品经SDS-PAGE电泳分离, 湿电转移至硝酸纤维素膜, 膜在室温下用封闭液封闭2 h, 加入5% BSA稀释的GAPDH抗体(1: 8 000)、RORα (1: 1 000)、p-p53和Noxa抗体(1: 2 000)、p53和β-actin抗体(1: 400), 4 ℃过夜, 洗膜3次, 加入封闭液稀释的二抗稀释液(1: 2 000), 室温1 h。用ECL solution显色, 最后进行显影, 定影。用Bankscan软件进行灰度分析, 分析目标基因的表达水平时用GAPDH和β-actin为内源对照。
MTS检测 用0.25%胰酶消化处于对数生长期的HeyA8和Hey细胞并接种于96孔培养板, 每孔加入2×103个细胞, 培养液100 μL, 每组设3个复孔。共分4组, 分别以终浓度为1.25、2.5、5.0和10 μmol·L-1 SR1078处理为实验组, 加入等体积的DMSO作为阴性对照, 36和72 h后, 每孔加入MTS 20 μL, 37 ℃孵育1~2 h。490 nm测定吸收度(A)值的变化并计算细胞存活率。细胞存活率(%) = (A实验组–A空白组/A对照组–A空白组) × 100%。
细胞周期和凋亡检测
流式细胞仪检测细胞周期 SR1078 (终浓度5.0和10 μmol·L-1)处理HeyA8和Hey细胞, 以DMSO处理组为阴性对照组, 72 h后收集细胞。加入预冷的70%乙醇进行固定, -20 ℃过夜。离心去上清, 用PBS润洗2次。PBS 100 μL重悬细胞并加入RNA酶2 μL, 于37 ℃孵育15 min, 再以PBS润洗并以100 μL重悬, 加入PI 5 μL混匀, 避光, 室温孵育5 min, 上机检测前加入PBS调整细胞数为每毫升1×106个, 混匀。
流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡 凋亡检测的实验分组同检测周期, 72 h后收集细胞, PBS润洗2次, 离心去上清, 加入1×binding buffer 100 μL重悬, 再加入Alexa Flour 647 Annexin-Ⅴ试剂4 μL, 混匀, 室温避光孵育10 min。再加入PI 7 μL, 最后加入1×binding buffer 200 μL调整细胞数为每毫升1×106, 上机检测。
p53 RNAi实验 p53 siRNA由广州锐博生物科技有限公司合成, 序列如下: si-h-TP53-001, GACTC CAGTGGTAATCTAC; si-h-TP53-002, GTAATCTA CTGGGACGGAA。取HeyA8和Hey细胞以每毫升1×105个接种于12孔板, 加入含10% FBS的DMEM培养基至800 μL体积。将siRNA (siRNA 1+2, 终浓度100 nmol·L-1, 100 μL)稀释于opti-MEM 100 μL中, 轻轻混匀; 另外, 将lipofectamine RNAi MAX 2 μL稀释于opti-MEM 100 μL中, 室温放置5 min后将两种稀释液混合, 轻轻混匀室温孵育20 min后, 将lipofectamine RNAi MAX/siRNA混合液加入培养孔中, 混合后培养箱中培养48 h, 补加10% FBS的DMEM培养基至1 mL, 加入终浓度为10 μmol·L-1 SR1078处理细胞72 h后, 检测细胞凋亡。
PFT-α和PFT-β抑制实验 将PFT-α和PFT-β溶于DMSO, 配制为50 mmol·L-1工作液。取HeyA8和Hey细胞以每毫升2×105个接种于6孔板, 加入含10% FBS DMEM培养基2 mL。将PFT-α和PFT-β工作液分别稀释到10和25 mmol·L-1, 加入培养孔中, 至终浓度分别为10和25 μmol·L-1, 处理细胞5 h后, 加入终浓度为10 μmol·L-1 SR1078, 混匀后培养箱中培养72 h。
统计学分析 使用Graphpad Prism 5软件进行数据分析, 数据用x±s表示。组间均数比较采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)进行t检验。
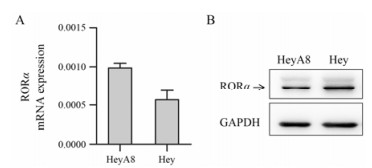
结果 1 MTS比色法检测SR1078对HeyA8和Hey细胞活性的影响Q-PCR和Western blot检测结果显示, HeyA8和Hey细胞中均表达RORα mRNA和蛋白(图 2A, B), 且Hey细胞的RORα蛋白表达水平高于HeyA8细胞。
|
Figure 2 The expression RORα mRNA (A) and protein (B) in Hey and HeyA8 cells |
细胞增殖实验结果显示, SR1078呈时间及剂量依赖性抑制Hey (图 3A)和HeyA8 (图 3B)的细胞活性。5.0和10 μmol·L-1 SR1078分别处理细胞36和72 h后, 细胞活性显著下降(P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001)。这些结果提示, RORα激活剂SR1078能有效抑制卵巢癌细胞HeyA8和Hey的细胞活性。

|
Figure 3 Effect of SR1078 on cell viability of Hey (A) and HeyA8 (B) cells. n = 3, x±s. Hey and HeyA8 cells were treated with different dose of SR1078 for 36 and 72 h, and then cell viability was detected by MTS assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs control group (36 h); ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs control group (72 h) |
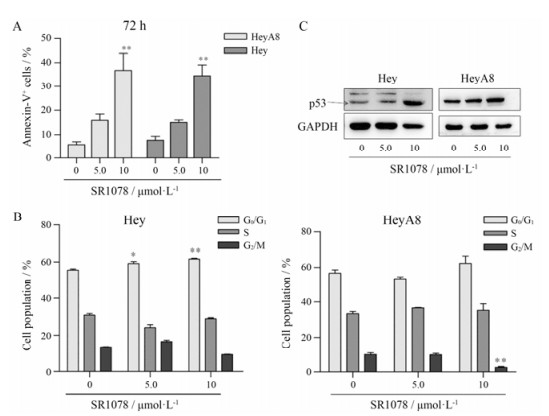
流式细胞术检测结果显示, 5.0 μmol·L-1 SR1078对HeyA8和Hey细胞凋亡有一定的促进作用, 而处理浓度为10 μmol·L-1时能够诱导细胞发生显著的凋亡(图 4A, P < 0.01)。细胞周期检测结果显示(图 4B), 10 μmol·L-1 SR1078明显引起HeyA8细胞发生G0/G1周期阻滞, 而对Hey细胞的周期分布并无明显影响。
|
Figure 4 Effect of SR1078 on apoptosis (A), cell cycle (B) and the p53 protein expression (C) of HeyA8 and Hey cells. A, B: Hey and HeyA8 cells were treated with different dose of SR1078 (5.0 and 10 μmol·L-1) for 72 h and then cells went apoptosis and cell cycle were detected by flow cytometry; C: Hey and HeyA8 cells were treated with different dose of SR1078 (5.0 and 10 μmol·L-1) for 48 h and then the p53 protein expression were evaluated by Western blot. n = 3, x±s. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs control group |
Western blot结果显示, 不同浓度SR1078处理HeyA8和Hey细胞48 h后, p53的表达上调(图 4C)。
3 p53在SR1078诱导卵巢癌细胞HeyA8和Hey凋亡中的作用为验证p53在SR1078诱导卵巢癌细胞凋亡中的作用, 采用p53抑制剂PFT-α和PFT-β抑制p53活性后观察对SR1078诱导HeyA8和Hey细胞凋亡的影响。流式细胞仪检测结果显示, 10 μmol·L-1SR1078诱导细胞发生显著的凋亡(P < 0.001), 而抑制p53后SR1078诱导的细胞凋亡明显减少, 尤其PFT-β (25 μmol·L-1)的作用更为显著(图 5A, P < 0.001)。

|
Figure 5 Role of p53 in RORα-induced apoptosis of HeyA8 and Hey cells. A: HeyA8 and Hey cells were treated with PFT-α (10 μmol·L-1) and PFT-β (25 μmol·L-1) for 4 h, followed by treated with 10 μmol·L-1SR1078 for 72 h, and then the apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. B: Hey cells were transfected with si-p53 for 48 h, and then the expression of p53 protein was detected by Western blot. C: Hey cells were transfected with si-p53 for 48 h, treated with 10 μmol·L-1 SR1078 for 72 h, and then the apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. n = 3, x±s. ***P < 0.001 vs control group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs SR1078 group. si-NC: si-Negative control |
另外, 为进一步验证p53的作用, 采用RNAi的方法抑制p53表达, 观察对SR1078诱导细胞凋亡的影响。Western blot结果显示(图 5B), 针对p53的siRNA可以明显降低Hey细胞中p53蛋白的表达。流式细胞术检测结果显示(图 5C), 10 μmol·L-1SR1078能够明显诱导Hey细胞凋亡(P < 0.001), 抑制p53表达后SR1078诱导的细胞凋亡显著降低(P < 0.01)。
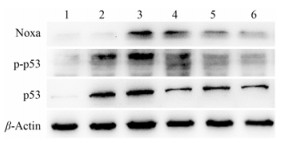
同时, 为了研究p53介导SR1078诱导细胞凋亡的分子机制, Western blot检测SR1078、PFT-α和PFT-β单独或联合作用对p53及其调控的促凋亡蛋白表达的影响。结果显示, SR1078处理Hey细胞后p53、p-p53及Noxa蛋白的表达水平明显上调, 而抑制p53后明显地抑制SR1078对这些蛋白的促进作用(图 6)。
|
Figure 6 Effect of SR1078 on expression of p53, p-p53 and Noxa protein in Hey cells. Hey cells were treated with PFT-α (10 μmol·L-1) and PFT-β (25 μmol·L-1) for 4 h, followed by treated with 10 μmol·L-1SR1078 for 48 h, and then the p53, p-p53 and Noxa protein expression were evaluated by Western blot. 1: Control; 2: PFT-α; 3: SR1078; 4: PFT-β; 5: SR1078+ PFT-α; 6: SR1078+PFT-β |
肿瘤的发生和发展往往与抑癌基因突变或失活密切相关, 靶向肿瘤形成与恶化过程中发生变化的基因治疗肿瘤成为一种可能。研究已经发现, RORα在多种肿瘤中表达下调或失活, 过表达RORα能够抑制乳腺癌细胞的生长和侵袭, 并促进胃癌细胞凋亡[8, 10-12]。同样, RORα激活剂激活RORα也能够抑制前列腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭, 并且通过调节糖代谢阻止肝癌细胞的生长及诱导肝癌细胞凋亡[13-15]。这些结果说明, 恢复RORα基因的表达或激活其蛋白活性可以起到抗癌的作用。在本研究中, RORα激动剂SR1078通过激活RORα显著降低卵巢癌HeyA8和Hey细胞活性和诱导其发生细胞凋亡, 提示RORα具有成为卵巢癌治疗药物靶点的潜能。
早期文献[2, 16]报道, RORα作为一种转录调节因子, 通常以经典方式与靶基因启动子上的RORE结合, 调节目的基因及其下游基因的表达而发挥作用。在乳腺癌中, RORα可以直接转录调节SEMA3F (transcription regulator of semaphorin 3F)基因的表达抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖与侵袭[11]。另一方面, RORα也能够通过非转录激活作用发挥功能。如RORα在结肠癌中通过与β-catenin蛋白的相互结合而抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路, 调节细胞增殖和肿瘤进展[17]。此外, p53通路是机体应对DNA损伤的天然防护屏障, 研究发现, DNA损伤可诱导RORα活化, 进而抑制p53蛋白的泛素化而增强p53稳定性, 最终激活p53的转录活性, 促进肿瘤细胞凋亡[18, 19]。有意思的是, RORα的人工合成配体SR1078同样能够通过活化RORα增强p53蛋白稳定性而诱导肝癌细胞发生凋亡[13, 20]。在本研究中, RORα激活剂SR1078处理卵巢癌细胞后, p53及其下游调控的促进凋亡蛋白Noxa同样明显增多, 而p53抑制剂和p53 siRNA均能显著削弱其作用, 表明p53是介导SR1078诱导卵巢癌细胞凋亡的关键分子。由于p53在抑制肿瘤形成过程中发挥着至关重要的作用, SR0178能够增强p53蛋白稳定性的结果提示RORα小分子激动剂将是一种潜在肿瘤治疗策略[21]。需要指出的是, 虽然p53 siRNA同样能够显著抑制SR1078的作用, 但是其抑制效果却明显低于p53抑制剂PFT-β (图 5C), 这与p53 siRNA并不能完全抑制p53蛋白的表达所造成的(图 5B)。
综上, RORα激活剂SR1078通过激活p53信号通路诱导细胞凋亡发挥抗卵巢癌的作用。由于晚期卵巢癌易发生转移及产生耐药, 因此, 深入研究SR1078对卵巢癌细胞转移和药物敏感性方面的影响及相关机制, 必将有助于进一步将RORα开发成为卵巢癌治疗药物新靶点。
| [1] | Cress RD, Chen YS, Morris CR, et al. Characteristics of long-term survivors of epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Obstet Gynecol, 2015, 126: 491–497. DOI:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000981 |
| [2] | Giguère V, Tini M, Flock G, et al. Isoform-specific amino-terminal domains dictate DNA-binding properties of ROR alpha, a novel family of orphan hormone nuclear receptors[J]. Gene Dev, 1994, 8: 538–553. DOI:10.1101/gad.8.5.538 |
| [3] | Kang HS, Okamoto K, Takeda Y, et al. Transcriptional profiling reveals a role for RORα in regulating gene expression in obesity-associated inflammation and hepatic steatosis[J]. Physiol Genomics, 2011, 43: 818–828. DOI:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00206.2010 |
| [4] | Lau P, Fitzsimmons RL, Raichur S, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor, RORα, regulates gene expression that controls lipid metabolism:staggerer (SG/SG) mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity[J]. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283: 18411–18421. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M710526200 |
| [5] | Wong SH, Walker JA, Jolin HE, et al. Transcription factor RORα is critical for nuocyte development[J]. Nat Immunol, 2012, 13: 229–236. DOI:10.1038/ni.2208 |
| [6] | Zhao X, Han C, Yu RT, et al. Nuclear receptors rock around the clock[J]. EMBO Rep, 2014, 15: 518–528. DOI:10.1002/embr.201338271 |
| [7] | Byun JK, Choi YK, Kang YN, et al. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha reprograms glucose metabolism in glutamine-deficient hepatoma cells[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61: 953–964. DOI:10.1002/hep.v61.3 |
| [8] | Zhu Y, Mcavoy S, Kuhn R, et al. RORα, a large common fragile site gene, is involved in cellular stress response[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25: 2901–2908. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1209314 |
| [9] | Buick RN, Pullano R, Trent JM. Comparative properties of five human ovarian adenocarcinoma cell lines[J]. Cancer Res, 1985, 45: 3668–3676. |
| [10] | Jun D, Ren X. RORα, a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic target of breast cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13: 15755–15766. DOI:10.3390/ijms131215755 |
| [11] | Xiong G, Wang C, Evers BM, et al. RORα suppresses breast tumor invasion by inducing SEMA3F expression[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72: 1728–1739. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2762 |
| [12] | Wang Z, Xiong F, Wang X, et al. Nuclear receptor retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha promotes apoptosis but is reduced in human gastric cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 8: 11105–11113. |
| [13] | Wang Y, Solt LA, Kojetin DJ, et al. Regulation of p53 stability and apoptosis by a ROR agonist[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7: e34921. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0034921 |
| [14] | Moretti RM, Montagnani MM, Motta M, et al. Role of the orphan nuclear receptor ROR alpha in the control of the metastatic behavior of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2002, 9: 1139–1143. |
| [15] | Moretti RM, Marelli MM, Motta M, et al. Activation of the orphan nuclear receptor RORα induces growth arrest in androgen-independent DU 145 prostate cancer cells[J]. Prostate, 2001, 46: 327–335. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0045 |
| [16] | Zhang Y, Luo XY, Wu DH, et al. ROR nuclear receptors:structures, related diseases, and drug discovery[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2015, 36: 71–87. DOI:10.1038/aps.2014.120 |
| [17] | Kim H. RORα attenuates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by PKCα-dependent phosphorylation in colon cancer[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 37: 183–195. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.022 |
| [18] | Kim H, Lee JM, Lee G, et al. DNA damage-induced RORα is crucial for p53 stabilization and increased apoptosis[J]. Mol Cell, 2011, 44: 797–810. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.023 |
| [19] | Wang YJ, Sun H, Liu GD, et al. Advances in the study of p53 in response to DNA damage[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2011, 46: 1413–1419. |
| [20] | Wang Y, Kumar N, Nuhant P, et al. Identification of a synthetic agonist for the orphan nuclear receptors RORα and RORγ, SR1078[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2010, 5: 1029–1034. DOI:10.1021/cb100223d |
| [21] | Li T, Kon N, Jiang L, et al. Tumor suppression in the absence of p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and senescence[J]. Cell, 2012, 149: 1269–1283. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.026 |
 2018, Vol. 53
2018, Vol. 53


