2. 贵州省高等学校天然药物药理与成药性评价重点实验室, 贵州 贵阳 550025
2. The High Educational Key Laboratory of Guizhou Province for Natural Medicinal Pharmacology and Druggability, Guiyang 550025, China
乳腺癌是威胁女性健康的主要恶性肿瘤, 目前乳腺癌的发病率逐年上升, 且发病年龄呈年轻化发展[1]。上皮细胞-间质转化 (epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT) 是指上皮细胞在形态学上发生间质细胞表型的转变过程[2]。近年来的大量研究表明, EMT广泛参与了乳腺癌的致病过程[3]。Park等[4]研究证明, 纤连蛋白 (fibronectin, FN) 与EMT密切相关, FN是细胞外基质的大分子糖蛋白, 也是乳腺上皮细胞微环境中的重要成分, 影响细胞迁移、生长、形态、分化和致癌性转变[5]。在FN作用下, 乳腺上皮细胞逐渐失去原有的极性, 从生长抑制状态转变为增殖状态, 并发生上皮间质转化, 使细胞发生胞间黏附减少、迁移和侵袭能力增强等肿瘤样行为的变化[6]。
钙蛋白酶 (calpain) 是一种Ca2+依赖性的蛋白分解酶[7], 主要有两种亚型, 钙蛋白酶-1 (calpain-1) 和钙蛋白酶-2 (calpain-2)[8]。有研究报道表明calpain能将骨桥蛋白水解为活性小分子片段, 介导丙肝病毒诱导肝细胞EMT[9]。此外, 应用同位素标记技术和串联质谱检测发现在转化生长因子-β诱导A549肺癌细胞EMT的过程中, calpain等14种与细胞骨架和运动有关的蛋白表达上调。以上研究提示, calpain蛋白表达增加可能是调控EMT的一个重要环节[10], 但calpain是否在FN诱导的EMT中发挥作用尚不清楚。本研究通过建立FN诱导的EMT体外模型, 观察钙蛋白酶抑制剂 (ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 对FN诱导的上皮间质转化的影响, 并对其作用机制进行初步探讨, 为其应用于乳腺癌的防治提供新的研究思路。
材料与方法细胞株及试剂 正常人乳腺上皮细胞株MCF-10A购自中国科学院昆明细胞库, DMEM/F12培养基、马血清 (horse serum, HS)、青霉素/链霉素 (penicillin/streptomycin)、氢化可的松 (hydrocortisone, HC)、生长因子 (epithelial growth factor, EGF)、胰岛素 (insulin)、霍乱毒素 (cholera toxin) 及胰蛋白酶 (trypsin) 购自美国HyClone公司。纤连蛋白、钙蛋白酶抑制剂 (ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 购自Sigma公司, 抗vimentin、E-cadherin、snail及calpain-2单克隆抗体购自Santa Cruze公司, 抗GAPDH抗体购自Cell Signaling公司, 羊抗兔/羊抗鼠IgG-HRP抗体购自博士德公司。
细胞培养 正常人乳腺上皮细胞MCF-10A常规培养采用DMEM/F12培养基 (含10% HS、1%青霉素/链霉素、0.1% HC、0.02% EGF、0.1%胰岛素、0.01%霍乱毒素), 在37 ℃及5% CO2的条件下进行培养, 待细胞覆盖率达90%~100%时进行传代培养。
细胞划痕实验 按照划痕修复实验法[11]将细胞随机分为4组, 分别加入无血清培养基 (control) 和含20 μg·mL-1 FN、20 μg·mL-1 FN + 10 μmol·L-1 ALLN、20 μg·mL-1 FN + 25 μmol·L-1 calpain inhibitor Ⅳ处理, 其中ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ在加入FN前预处理1 h, 置于培养箱内培养。分别于0 h和48 h在倒置显微镜下拍照。计算细胞迁移率= (0 h伤口宽度-48 h伤口宽度) / 0 h伤口宽度× 100%, 实验重复3次, 进行统计学分析。
细胞侵袭实验 培养的MCF-10A细胞覆盖率达90%后, 将培养基换成无血清DMEM, 同时按“细胞划痕实验”将细胞分为4组, 并施以相同处理。按照transwell小室侵袭实验法[12]重复3次。以control组的微孔滤膜细胞数为对照, 各组穿过Matrigel胶的细胞数与其相比所得百分率表示细胞的侵袭能力。
Western blot检测 培养的MCF-10A细胞覆盖率达90%后, 将培养基换为无血清DMEM, 同时按“细胞划痕实验”将细胞分为4组, 并施以相同处理。药物处理48 h后, 加入RIPA裂解液裂解细胞。4 ℃、12 000 r·min-1离心20 min后取样品上清液留用, 采用BCA蛋白定量法进行蛋白定量。每个泳道按40 μg蛋白质样品进行上样, 按照Western blot法[12]实验, 检测vimentin、E-cadherin、snail和calpain-2的蛋白表达。采用Bio-Rad系统进行成像, Image Lab软件分析蛋白印迹结果。
统计学处理 采用SPSS 19.0处理和分析数据, 实验结果以均值±标准差表示。组间比较采用单因素方差分析法, P < 0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
结果 1 FN对MCF-10A细胞中calpain-2蛋白表达的影响FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用MCF-10A细胞0、12、24和48 h后, 与0 h相比, calpain-2蛋白表达逐渐增加, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05)。FN使MCF-10A细胞中的calpain-2蛋白表达增加 (图 1)。
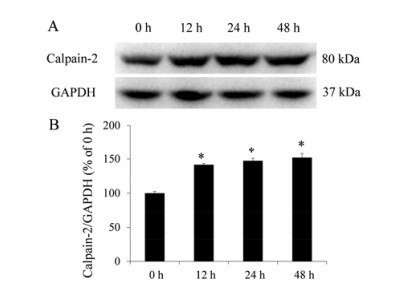
|
Figure 1 The effect of fibronectin (FN) on calpain-2 protein expression of MCF-10A cells. A: The representative photo graphs; B: The statistical analysis. n = 3, x± s. *P < 0.05 vs 0 h |
与对照组相比, FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用48 h后, calpain-2蛋白表达显著增加, 差异具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05); (FN + ALLN) 和 (FN + calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 组与FN组相比, calpain-2蛋白表达显著降低, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05)。钙蛋白酶抑制剂 (ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 能显著抑制FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞中calpain-2蛋白表达上调 (图 2)。
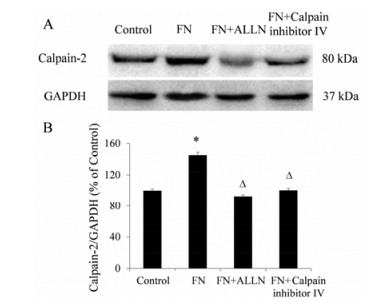
|
Figure 2 The effect of calpain inhibitors on calpain-2 expression of MCF-10A cells induced by FN. A: The representative photographs; B: The statistical analysis. n = 3, x± s. *P < 0.05 vs control; △P < 0.05 vs FN |
FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用MCF-10A细胞48 h后, 对照组细胞形态为鹅卵石状, 细胞之间黏附力较强, 结构紧密。与对照组细胞相比, FN组细胞拉长呈纺锤形, 细胞之间黏附力降低, 结构松散, 形态接近成纤维细胞; 与FN组细胞相比, (FN + ALLN) 和 (FN + calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 组细胞之间黏附力增强, 结构紧密, 细胞形态接近鹅卵石状 (图 3)。以上结果说明, 钙蛋白酶抑制剂ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ能够逆转FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞形态变化。
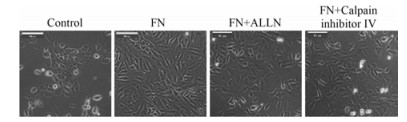
|
Figure 3 The effect of calpain inhibitors on morphology of MCF-10A cells induced by FN. Scale bar= 40 μm |
划痕修复实验结果表明, 与对照组相比, FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用48 h后, 细胞的迁移率增加到 (188.9 ± 1.8) %, 差异具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05); (FN + ALLN) 和 (FN + calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 组与FN组相比, 细胞的迁移率分别降低到 (92.3 ± 6.1) %和 (98.8 ± 1.7) %, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05) (图 4)。钙蛋白酶抑制剂ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ对FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞迁移有明显的抑制作用。
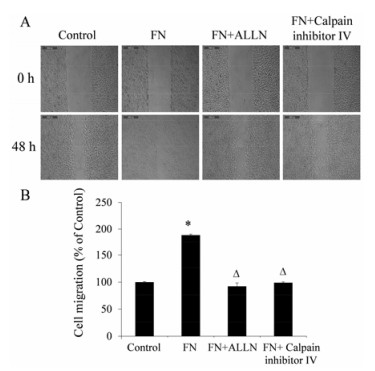
|
Figure 4 The effect of calpain inhibitors on MCF-10A cells migration induced by FN. A: The representative photographs, scale bar = 400 μm; B: The statistical analysis. n = 3, x± s. *P < 0.05 vs control; △P < 0.05 vs FN |
基质胶包被的transwell小室实验结果表明, FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用48 h后, 侵袭细胞数增加到 (234.5 ± 9.4) %, 与对照组相比, 差异具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05); (FN + ALLN) 和 (FN + calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 组侵袭细胞数分别降低到 (102.4 ± 6.1) %和 (116.7 ± 7.3) %, 与FN组相比, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05) (图 5)。钙蛋白酶抑制剂ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ对FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞侵袭有明显的抑制作用。

|
Figure 5 The effect of calpain inhibitors on MCF-10A cells invasion induced by FN. A: The representative photographs, scale bar = 200 μm; B: The statistical analysis. n = 3, x± s. *P < 0.05 vs control; △P < 0.05 vs FN |
与对照组相比, FN (20 μg·mL-1) 作用48 h后, vimentin和snail蛋白表达显著增加, E-cadherin蛋白表达显著降低, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05); (FN + ALLN) 和 (FN + calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 组与FN组相比, vimentin和snail蛋白表达显著降低, E-cadherin蛋白表达显著增加, 差异均具有统计学意义 (P < 0.05) (图 6)。钙蛋白酶抑制剂ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ能显著抑制FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞中vimentin和snail蛋白表达上调及E-cadherin蛋白表达下调。
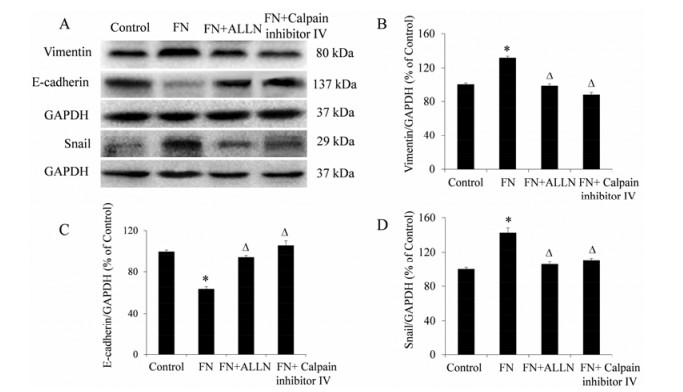
|
Figure 6 The effects of calpain inhibitors on vimentin, E-cadherin and snail protein expression of MCF-10A cells induced by FN. A: The representative photographs; B-D: The statistical analysis. n = 3, x± s. *P < 0.05 vs control; △P < 0.05 vs FN |
上皮间质转化是肿瘤细胞自身塑形的重要标志[13], EMT在乳腺癌的发展、浸润和转移方面有着密切联系[14]。当细胞发生EMT时, 细胞极性消失, 转变为有间质细胞形态和特性的细胞[15]。这种转变使细胞间的黏附能力减弱、细胞的运动和侵袭能力增强, 使细胞获得可塑性、迁移、侵袭、对抗凋亡的能力及干细胞样特征[16], 从而促进肿瘤的发生和发展。EMT为细胞的恶变和转移提供了基础, 调控EMT的发生可能是防治肿瘤的一个靶点[17]。乳腺肿瘤源于乳腺上皮细胞的恶变, 抑制乳腺上皮细胞EMT可能有效控制肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移以及降低乳腺癌患者的死亡率。
Park等[4]研究证明, 乳腺肿瘤组织中的FN水平与肿瘤的恶性程度呈正相关, 与乳腺癌患者的存活率呈负相关。本研究发现FN能够诱导MCF-10A乳腺上皮细胞形态向间质细胞形态发生改变。此外, 通过划痕修复实验和transwell小室侵袭实验, 发现FN能够显著增强MCF-10A乳腺上皮细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。Western blot法检测结果显示, FN能够明显上调MCF-10A细胞中vimentin和snail的蛋白表达及明显下调E-cadherin的蛋白表达, 表明FN能够诱导乳腺上皮细胞发生间质转化。钙蛋白酶抑制剂通过模拟calpain底物结构, 竞争性地与calpain相互作用, 从而阻止calpain对底物的水解来发挥作用[18]。Calpain抑制剂是抗肿瘤药物开发的重要方向, 抑制calpain的活性可能会成为抑制肿瘤细胞转移的重要手段[19]。Čáslavský等[20]研究证明, calpain能使细胞从静态的上皮表型转变为具有运动和侵袭性的间质表型, 提示calpain表达增加及其活性的发挥可能在EMT中扮演着一个重要的角色。本研究发现FN能够使MCF-10A细胞中calpain-2蛋白表达上调。两种钙蛋白酶抑制剂 (ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ) 均能显著抑制FN诱导的MCF-10A细胞中calpain-2蛋白的表达, 并显著抑制细胞的形态变化、迁移和侵袭能力增强。此外, ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ能够显著抑制MCF-10A细胞中vimentin和snail蛋白表达上调及E-cadherin蛋白表达下调。
综上所述, FN能够诱导上皮细胞发生间质转化, 钙蛋白酶抑制剂ALLN和calpain inhibitor Ⅳ能够抑制FN诱导的乳腺上皮细胞EMT, 有望应用于乳腺癌的预防。
| [1] | Umar A, Dunn BK, Greenwald P. Future directions in cancer prevention[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2012, 12: 835–848. DOI:10.1038/nrc3397 |
| [2] | Zhu T, Zhang X. Research progress on the role of epithe-lial-mesenchymal transition in pathogenesis of endometriosis[J]. J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci) (浙江大学学报医学版), 2016, 45: 439–445. |
| [3] | Ma Y, Liu H, Zhang H, et al. The TGF-β signaling pathway induced EMT in breast cancer[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2015, 50: 385–392. |
| [4] | Park J, Schwarzbauer JE. Mammary epithelial cell inter-actions with fibronectin stimulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33: 1649–1657. DOI:10.1038/onc.2013.118 |
| [5] | Helleman J, Jansen MP, Ruigrok-Ritstier K, et al. Associa-tion of an extracellular matrix gene cluster with breast cancer prognosis and endocrine therapy response[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14: 5555–5564. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0555 |
| [6] | Moon PG, Lee JE, Cho YE, et al. Fibronectin on circulating extracellular vesicles as a liquid biopsy to detect breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7: 40189–40199. |
| [7] | Storr SJ, Thompson N, Pu X, et al. Calpain in breast cancer:role in disease progression and treatment response[J]. Pathobiology, 2015, 82: 133–141. DOI:10.1159/000430464 |
| [8] | Seinfeld J, Baudry N, Xu X, et al. Differential activation of calpain-1 and calpain-2 following kainate-induced seizure activity in rats and mice[J]. eNeuro, 2016, 3: ENEURO. 0088-15.2016. |
| [9] | Igbal J, McRae S, Banaudha K, et al. Mechanism of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced osteopontin and its role in epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288: 36994–37009. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.492314 |
| [10] | Keshamouni VG, Jagtap P, Michailidis G, et al. Temporal quantitative proteomics by iTRAQ 2D-LC-MS/MS and corresponding mRNA expression analysis identify post-transcriptional modulation of actin-cytoskeleton regulators during TGF-beta-Induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. J Proteome Res, 2009, 8: 35–47. DOI:10.1021/pr8006478 |
| [11] | Wang HJ, Shang DD, Zhu ZX, et al. The effects of fulvestrant on invasion ability and matrix metalloproteinase expression induced by estrogen in breast cancer cell MCF-7[J]. J Guiyang Med Coll (贵阳医学院学报), 2014, 39: 633–637. |
| [12] | Shang D, Li Z, Zhu Z, et al. Baicalein suppresses 17-β-estradiol-induced migration, adhesion and invasion of breast cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2015, 33: 2077–2085. |
| [13] | Zhao XN, Sun ML, Wei MJ. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer stem cells[J]. Prog Anat Sci (解剖科学进展), 2013, 19: 354–357. |
| [14] | He ZY, Wu SG, Peng F, et al. Up-regulation of RFC3 promotes triple negative breast cancer metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis via EMT[J]. Transl Oncol, 2016, 10: 1–9. |
| [15] | Comaills V, Kabeche L, Morris R, et al. Genomic instabil-ity is induced by persistent proliferation of cells undergoing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Cell Rep, 2016, 17: 2632–2647. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.022 |
| [16] | Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50: 1464–1474. DOI:10.1002/hep.23221 |
| [17] | El-Ghonaimy EA, Ibrahim SA, Youns A, et al. Secretome of tumor-associated leukocytes augment epithelial-mesenchymal transition in positive lymph node breast cancer patients via activation of EGFR/Tyr845 and NF-κB/p65 signaling pathway[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37: 14333. DOI:10.1007/s13277-016-5137-4 |
| [18] | Yoshida M, Miyasaka Y, Ohuchida K, et al. Calpain inhibitor calpeptin suppresses pancreatic cancer by disrupting cancer-stromal interactions in a mouse xenograft model[J]. Cancer Sci, 2016, 107: 1443–1452. DOI:10.1111/cas.2016.107.issue-10 |
| [19] | Mataga MA, Rosenthal S, Heerboth S, et al. Anti-breast cancer effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors and calpain inhibitor[J]. Anticancer Res, 2012, 32: 2523–2529. |
| [20] | Čáslavský J, Klímová Z, Vomastek T. ERK and RSK regulate distinct steps of a cellular program that induces transition from multicellular epithelium to single cell phenotype[J]. Cell Signal, 2013, 25: 2743–2751. DOI:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.024 |
 2017, Vol. 52
2017, Vol. 52


