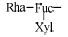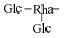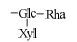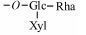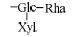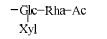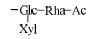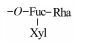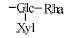2. 湖南医药学院侗医药研究湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 怀化 418000 ;
3. 香港科技大学深圳研究院, 广东 深圳 518057
2. Dong Pharmaceutical Research of Hunan Key Laboratory, Hunan University of Medicine, Huaihua 418000, China ;
3. HKUST Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen 518057, China
麦冬为百合科植物麦冬 [Ophiopogon japonicus (L.f.) Ker-Gawl.]的干燥块根,具有润肺生津、养阴清热的功能,主治热病伤津、心烦口渴等症。大量研究表明,甾体皂苷、高异黄酮和多糖是麦冬主要的固有成分[1-4]。现代中药血清药理学认为,只有被吸收入血的化学成分才是真正的效应物质[5, 6]。目前,关于麦冬药材化学成分的报道较多[7, 8],但麦冬药效部位吸收入血的系统报道较少,仅有麦冬皂苷口服吸收后薯蓣皂苷入血和参麦注射液中麦冬皂苷D血药浓度测定的报道[9-11]。
LC-MS技术兼有优秀的色谱分离能力和高灵敏度、高专属的质谱检测能力,已成为各类生物基质中化学成分最强有力的分析手段之一[12-17]。其中,LTQ-Orbitrap MS兼有高分辨率、高质量精度等诸多优点,尤其适用于复杂物质体系中化学成分的快速分析。高能诱导裂解技术 (higher energy collision dissociation,HCD) 作为一种新型的质谱裂解技术,更易获得微量成分的多级质谱图,并显著改善CID裂解中产生的低质量碎片丢失效应。本文利用UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS结合HCD裂解技术,辅以特征诊断离子判别,分析鉴定灌胃给予麦冬甾体皂苷后大鼠血浆中的移行成分,以期为进一步阐明麦冬药效物质基础提供依据。
材料与方法仪器 Accela 600 pump超高压液相色谱-LTQ- OrbitrapXL质谱联用仪: 美国Thermo Scientific公司,配有电喷雾离子源 (ESI)、在线脱气机、自动进样器、高压二元梯度泵; KQ-250DE型数控超声波清洗器: 昆山市超声仪器有限公司; TGL20M型高速冷冻离心机: 长沙湘智离心机仪器有限公司。
动物 Sprague Dawley(SD) 大鼠,体重 (200 ± 20)g,购于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,许可证号SCXK(京) 2012-0001。
药品与试剂 麦冬药材购自四川新荷花中药饮片有限公司,经北京中医药大学谭鹏副教授鉴定为百合科植物麦冬 [Ophiopogonjaponicus (L.f.) Ker-Gawl.] 的干燥块根; 乙腈、甲醇和甲酸(色谱纯): 美国Fisher公司; 色谱分析用水为Millipore超纯水; 12-hydroxy ophiogenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside(17)、ophiogenin3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside (18)、14-hydroxysprengerinin C (19)、pennogenin 3-O-[α-L-rhamno-pyranosyl-(1→2)][β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside(20)、14-hydroxydiosgenin3-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside(22)、pennogenin 3-O-[2-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→ 2)][β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside (24)、sprengerininC (29) 和ophiopogoninD (30) 等对照品均为本课题组自制,相应结构经1H NMR、13C NMR、MS确定; 纯度经HPLC-ELSD检测均大于95%。
麦冬甾体皂苷提取物的制备 取麦冬药材粗粉1 kg,加6倍量75% 乙醇回流提取2次,合并提取液,减压回收乙醇后过滤,滤液经NKA大孔吸附树脂柱吸附,先水洗至无糖反应,再依次用6倍柱体积的40% 乙醇和80%乙醇洗脱,收集80% 乙醇洗脱液,减压回收乙醇,经真空干燥后即得。
提取物供试品溶液的制备 称取上述提取物 0.2 g,精密称定,精密加入70% 甲醇25 mL,超声提取15 min,放冷,摇匀,静置后取上清液,以0.22 μm微孔滤膜滤过,即得。
对照品溶液的制备 分别精密称取上述对照品适量,加甲醇制成浓度约为100 μg·mL-1的混合溶液,即得。
生物供试品样品的制备 8只正常雄性大鼠,于实验环境下适应饲养一周。实验前禁食12h,自由饮水。以400 mg·kg-1的剂量口服灌胃给药,分别于0、0.5、1、2和4 h眼眶取血,静置30 min后,离心 (3 000 r·min-1)30 min,取上清液,以0 h作为空白血浆,剩余时间点合并后作为给药血浆。取Waters Oasis HLB (3 mL/60 mg,30 μm) 固相萃取柱,经活化平衡后,将血浆样品300 μL加入到固相萃取柱上,依次以水 4 mL和甲醇3 mL洗脱,收集甲醇洗脱液。将该洗脱液在室温下用N2吹干,残渣用甲醇50 μL复溶,涡旋后高速离心 (14 000 r·min-1) 10 min,取上清液,即得。
色谱条件 色谱柱为ACQUITY UHPLC BEH C18 (1.7 μm,2.1 mm × 50 mm,美国Waters公司); UHPLC流动相: A为0.1% 甲酸水溶液,B为乙腈-甲醇 (3∶1) 混合溶剂;线性梯度洗脱程序: 0~2 min,5% B; 2~17 min,5%~50% B; 17~23 min,50%~60% B; 23~30 min,60%~95% B; 30~35 min,95% B。流速0.3 mL·min-1,柱温25℃,进样量3 μL。
质谱条件 电喷雾离子源 (ESI),负离子全扫描检测模式,扫描范围为m/z 100~1 400。喷雾电压3.0 kV,毛细管温度300℃,鞘气30 arb,辅助气10 arb。
分析时采用FT全扫描采集一级质谱,扫描分辨率为30 000,然后采用HCD碰撞方式采集二级质谱,动态数据依赖扫描,碰撞能量45%。利用Xcalibur 2.1工作站进行数据采集与处理。
结果 1 目标成分的分子式预测结合甾体皂苷的定义以及目前已知的麦冬甾体皂苷类成分,设定高分辨质谱数据处理参数: 最大分子质量误差为3 ppm,H-C比例小于5,不饱和度 (Ω) 范围为8~20,C原子数目范围为35~60,H原子数目范围为60~95,O原子数目范围为10~30。
2 甾体皂苷类成分HCD裂解诊断离子的确定中药化学成分多具有相似的母核骨架或亚结构,在质谱裂解过程中一般会发生相似的质谱裂解反应,并产生一系列特征诊断离子[18, 19],可用于中药化学成分类似物的分析鉴定。实验首先对麦冬皂苷D、sprengerininC等8种对照品的HCD质谱裂解规律进行了分析,并总结相应的特征诊断离子。
由于碰撞能量对于质谱碎片提供的信息 (种类和强度) 具有至关重要的作用,实验首先考察了甾体皂苷准分子离子峰在不同HCD碰撞能量下的碎裂状态。以麦冬皂苷D为例,当HCD碰撞能量低于35% 时,其准分子离子几乎没有发生碎裂; 随着HCD碰撞能量的增强,得到的碎片离子的信息也随之增多; 但是,当碎裂碰撞能量高于45% 时,得到的碎片离子过多,反而增加了后续结构解析的难度。因此,实验最终选择HCD碰撞能量为45%。根据各甾体皂苷类成分的碎片离子信息,可发现甾体皂苷负离子检测模式下的质谱裂解碎片多来源于糖苷键的碎裂,由此确定该类成分的特征诊断离子为 [M-H]-、[M-H- n×Sugar]-(n = 1~4,Sugar:葡萄糖/木糖/阿拉伯糖/岩藻糖等)、[M-H-CH2CO]-(乙酰化的甾体皂苷) 等。
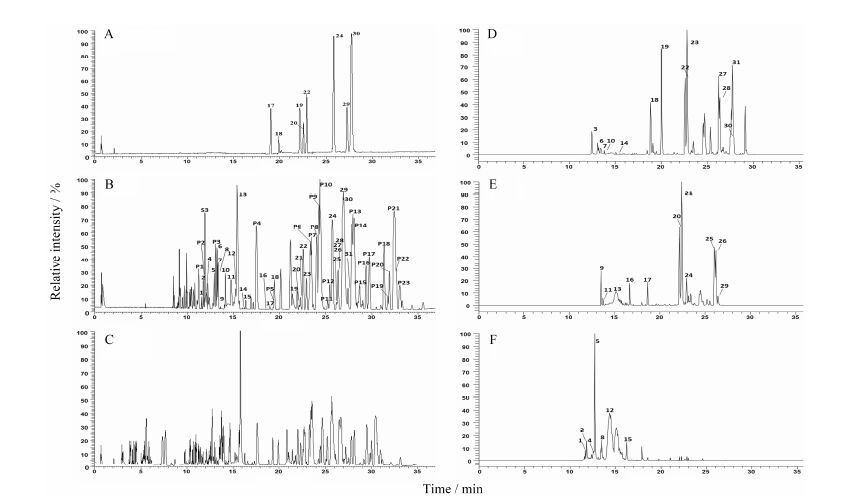
3 给药大鼠血浆中移行成分的快速鉴定应用高分辨提取离子流 (HRMS-EIC) 数据挖掘方法,通过对比给药后大鼠血浆、大鼠空白血浆、麦冬甾体皂苷提取物以及对照品之间的色谱和质谱信息,辅以特征诊断离子判别,最后从麦冬总皂苷提取物中筛选甾体皂苷类成分54个,其中有31个甾体皂苷可在给药大鼠血浆中被鉴定,结果见图 1和表 1。给药大鼠血浆移行成分的化学结构见表 2,3。
|
Figure 1 The TIC chromatograms of reference standards (A),total steroidal saponins (B) and blank plasma (C); high-resolution EIC chromatograms of steroidal saponins absorbed into rat plasma (D: m/z 737.410 7,753.405 6,769.400 5,779.421 2,853.458 0, 923.463 5,1 049.516 3; E: m/z 869.452 9,901.442 8,911.463 5,1 031.505 7,1 033.521 4,1 045.521 4,1 195.574 2; F: m/z 933.469 0, 1 061.516 3, 1 063.532 0, 1 079.526 9,1 177.563 6,917.474 0). The peak numbers were in accordance with those in Table 1 |
| Table 1 Identification of steroidal saponins absorbed into rat plasma using UHPLC/LTQ-Orbitrap MS. ΔCompounds identified by comparison with reference standards. P: Detected in total steroidal saponins and not detected in rat plasma |
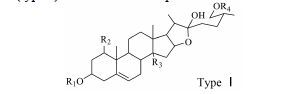
| Table 2 The structures of steroidal saponins (type I) absorbed into rat plasma |
| Table 3 The structures of steroidal saponins (type Ⅱ) absorbed into rat plasma |
该类甾体皂苷最明显的结构特征是F环断裂,并在26位碳原子上连接糖基。根据准分子离子峰[M-H]-的精确质量数、质谱裂解碎片以及相应的特征诊断离子,对血中移行成分1~13进行结构鉴定。以4为例,其在ESI-MS谱给出m/z 1 061.515 1 [M-H]-,可推断其分子式为C51H81O23, 误差为-1.13 ppm。通过对比分析其碎片离子的种类和相对离子强度,可进一步确定呋甾烷醇母核上糖基的种类和数量: 中性丢失一分子己糖残基 (162 u) 后产生的ESI-MS2谱基峰离子m/z 899,表明其分子结构中可能存在葡萄糖残基; 而其他主要碎片离子如m/z 915、m/z 753、m/z 735、m/z 573,表明其分子中除了一个葡萄糖基 外,还至少含有一个鼠李糖基/岩藻糖基和葡萄糖基。结合文献中已报道的麦冬甾体皂苷类成分[7],对其结构进行了鉴定。其他呋甾烷醇型甾体皂苷的结构鉴 定见表 2。
3.2 (异)螺甾醇型 (Type Ⅱ) 麦冬甾体皂苷的结构鉴定异螺甾醇型或螺甾醇型甾体皂苷的区别 在于C25是S或R构型。由于质谱难以区分,因此本文未标注C25的构型。根据准分子离子峰 [M-H]-的 精确质量数、质谱裂解碎片以及诊断碎片离子,对血中移行成分14~31进行结构鉴定 (表 3)。以19、20和23为例,三者在电喷雾负离子检测模式下,均产生m/z 869 [M-H]- 的准分子离子峰,可推断分子式为C44H69O17。通过分析三者的质谱碎片离子的种类和相对离子强度,可归属m/z 737为 [M-H-Rha]-、m/z 591为 [M-H-Rha-Xyl]-、m/z 429为 [M-H-Rha-Xyl-Glc]-,由此可确定它们分子结构中均含有1个鼠李糖基、1个木糖基和1个葡萄糖基。通过对照品比对,将19和20准确鉴定为14-hydroxy sprengerinin C和pennogenin 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)][β-D- xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside。而23由于难以确定母核的信息,暂将其鉴定为前两者的同分异构体。同理,14~18、21、22及29~31的结构也可依次被鉴定。
同时,在 (异) 螺甾醇型移行成分的鉴定过程中,还发现了一类含有乙酰基的甾体皂苷,如24~28。其多级质谱裂解特征为准分子离子易中性丢失乙烯酮基而产生ESI-MS2谱的基峰离子 [M-H-CH2CO]-,同时会伴有 [M-H-CH2CO-H2O]-离子产生。通过对照品比对,分别将三者准确鉴定为diosgenin 3-O-[4-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)][β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside、diosgenin 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)][2-O-acetyl-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside和pennogenin 3-O-[2-O- acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)][β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside。同理,26和27的结构也可依次被鉴定。
讨论采用0.1% 甲酸作为流动相改性剂,可获得良好的甾体皂苷色谱峰形和质谱信号响应值。同时实验对比了不同种类流动相(甲醇-0.1% 甲酸溶液、乙腈- 0.1% 甲酸溶液以及乙腈-甲醇-0.1% 甲酸溶液) 对甾体皂苷的色谱分离效果,最终选择乙腈-甲醇 (3∶1) 为有机相,0.1% 甲酸溶液为水相进行色谱分离。
实验中分别考察了提取溶剂、溶剂倍量以及提取时间对提取物中甾体皂苷提取率的影响,最终确定以70% 甲醇25 mL超声提取15 min制备供试样品溶液。
在生物供试品溶液制备过程中,分别考察了甲醇沉淀、乙腈沉淀以及固相萃取 (SPE) 方法对于基质的去除和目标成分的保留效果,最终选择固相萃取的处理方法。
由于甾体皂苷类化学成分在负离子检测模式下的电离效果较好,因此选择负离子模式对给药后大鼠血浆中的移行成分进行检测。
本研究从大鼠血浆中共鉴定31个移行成分,其中有8个化学成分可被准确鉴定。这些移行成分均为原形成分,未找到相关的代谢产物,究其原因可能有: ① 麦冬甾体皂苷的Ⅰ和Ⅱ相代谢产物入血浓度过小而无法被检测到,这与人参皂苷、柴胡皂苷、薯蓣皂苷等的体内代谢特征类似[20, 21]; ② 麦冬甾体皂苷可能在药物代谢酶的作用下发生水解反应,生成次生苷代谢产物,而这些产物与麦冬药材中原有的甾体皂苷相同而无法被分辨; ③ 本实验未检测到薯蓣皂苷元等代谢产物,可能是由于文献报道多是大剂量给予麦冬甾体皂苷单体后得到的结果。
本研究结果还表明,麦冬甾体总皂苷中的呋甾烷醇型和 (异) 螺甾醇型皂苷在反相色谱柱上的色谱行为具有很明显的差异: 整体上前者较后者极性大,更容易被洗脱下来。
结论本研究应用UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS结合HCD裂解技术,从复杂物质体系中快速剔除干扰信号而快速筛选目标成分,并结合特征诊断离子鉴定给药后的大鼠血浆中的麦冬甾体皂苷移行成分(呋甾烷醇型和螺甾醇型皂苷),从而为阐明麦冬药效物质基础提供依据。本研究建立的基于UHPLC-HR-MSn分析方法可以达到准确、快速鉴别复杂物质体系中化学成分的目的。
| [1] | Li N, Zhang L, Zeng KW, et al. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Ophiopogon japonicas[J]. Steroids , 2013, 78 :1–7. DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2012.10.001 |
| [2] | Li N, Zhang JY, Zeng KW, et al. Anti-inflammatory homoi-soflavonoids from the tuberous roots of Ophiopogon japonicas[J]. Fitoterapia , 2012, 83 :1042–1045. DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2012.05.011 |
| [3] | Tada A, Kasai R, Saitoh T, et al. Studies on the constituents of Ophiopogonis tuber. V. Isolation of a novel class of homoi-soflavonoids and determination of their structures (1)[J]. Chem Pharm Bull , 1980, 28 :1477–1484. DOI:10.1248/cpb.28.1477 |
| [4] | Wu XM, Dai H, Huang LX, et al. A fructan, from Radix Ophiopogonis, stimulates the proliferation of cultured lym-phocytes: structural and functional analyses[J]. J Nat Prod , 2006, 69 :1257–1260. DOI:10.1021/np060033d |
| [5] | Zhou W, Tam KY, Meng JJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics screening for multi-components absorbed in the rat plasma after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine Flos Lonicerae Japonicae-Fructus Forsythiae herb couple by sequential negative and positive ionization ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometric detection[J]. J Chromatogr A , 2015, 1376 :84–97. DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.12.018 |
| [6] | Liang Y, Hao HP, Xie L, et al. Development of a systematic approach to identify metabolites for herbal homologs based on liquid chromatography hybrid ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry: gender-related difference in metabolism of Schisandra lignans in rats[J]. Drug Metab Dispos , 2010, 38 :1747–1759. DOI:10.1124/dmd.110.033373 |
| [7] | X ie, T, Liang Y, Hao HP, et al. Rapid identification of ophiopogonins and ophiopogonones in Ophiopogon japonicus extract with a practical technique of mass defect filtering based on high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A , 2012, 1227 :234–244. DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.01.017 |
| [8] | Guo Z, Chen L, Liang QL, et al. Identification of homo-isoflavonoids in Ophiopogon japonicus alcohol extract by an LC-MS based on precise mass and tandem mass spectrometer[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药) , 2011, 42 :844–847. |
| [9] | Xia CH, Wang GJ, Sun JG, et al. Simultaneous determination of ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rd, Rb1 and ophiopogonin D in rat plasma by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometric method and its application to pharmacokinetic study of ‘SHENMAI’ injection[J]. J Chromatogr B , 2008, 862 :72–78. DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.11.020 |
| [10] | Wu Y. Studies on Chemical Composition Analysis and Phar-macokinetics of Radix Ophiopogonis Based on LC-MS/MS Technology (基于液质联用技术的麦冬化学成分分析与药代动力学研究)[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2015: 89-96. |
| [11] | Shen L, Feng Y, Xu DS, et al. Determining metabolite dios-genin of Ophiopogon japonicus saponin in vivo by HPLC-MS[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med (中成药) , 2006, 28 :1178–1181. |
| [12] | Zhang JY, Zhang Q, Li N, et al. Diagnostic fragment-ion-based and extension strategy coupled to DFIs intensity analysis for identification of chlorogenic acids isomers in Flos Lonicerae Japonicae by HPLC-ESI-MS[J]. Talanta , 2013, 104 :1–9. DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.11.012 |
| [13] | Zhang JY, Wang ZJ, Liu Y, et al. A strategy for comprehensive identification of sequential constituents using ultra-high per-formance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer, application study on chlorogenic acids in Flos Lonicerae Japonicae[J]. Talanta , 2016, 147 :16–27. DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.039 |
| [14] | Zhang JY, Cai W, Zhou Y, et al. Profiling and identification of the metabolites of baicalin and study on their tissue distri-bution in rats by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer[J]. J Chro-matogr B , 2015, 985 :91–102. DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.01.018 |
| [15] | Cai W, Zhang JY, Dong LY, et al. Identification of the metabolites of ixerin Z from Ixeris sonchifolia Hance in rats by HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry[J]. J Pharm Biomed , 2015, 107 :290–297. DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2015.01.004 |
| [16] | Zhang JY, Cai W, Li Y, et al. Rapid characterization of chlorogenic acids analogues in Artemisia younghusbandii using HPLC/LTQ-Orbitrap MSn coupled with MDF data mining technology[J]. J Chin Mass Spectrom Soc (质谱学报) , 2015, 36 :321–327. |
| [17] | Zhang JY, Tu PF. The establishment and application of natural product liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-database (LC-MS-DS)[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报) , 2012, 47 :1187–1192. |
| [18] | Zhang JY, Li C, Che YY, et al. LTQ-Orbitrap-based strategy for traditional Chinese medicine targeted class discovery, iden-tification and herbomics research: a case study on phenyletha-noid glycosides in three different species of Herba Cistanches[J]. RSC Adv , 2015, 5 :80816–80828. DOI:10.1039/C5RA13276B |
| [19] | Zhang JY, Wang ZJ, Zhang Q, et al. Rapid screening and identification of target constituents using full scan-parent ions list-dynamic exclusion acquisition coupled to diagnostic product ions analysis on a hybrid LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer[J]. Talanta , 2014, 124 :111–122. DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.025 |
| [20] | Yang XW. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity and Activity of the Chemical Constituents in Traditional Chinese Medicines (中药成分的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄、毒性与药效)[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2006 : 973 -1052. |
| [21] | Li K, Tang Y, Fawcett JP, et al. Characterization of the pharmacokinetics of dioscin in rat[J]. Steroids , 2005, 70 :525–530. DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2004.11.014 |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51