2. 广西大学化学化工学院, 广西 南宁 530007
2. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530007, China
Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr. (Orchidaceae) is a medicinal and edible herb in Southeast Asia which has been used to treat the cough and throat swelling for a long history[1]. Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr. had antitumor[2],antiviral[3],analgesic[4] and anti-inflammatory[5] activities. Extensive chemical studies of this herb led to the isolation of flavonoids,terpenes,sterols and amino acids[6, 7]. In this work,we reported two new flavonoid glycosides named as nervilifordin K and nervilifordin L (Figure 1) which were isolated from Nervilia fordii.
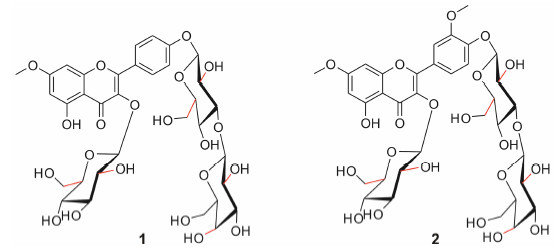 | Figure 1 Structures of compounds 1 and 2 |
Compound 1 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder. The UV absorption maximum of 1 were at 267 and 331 nm,which are the characteristic signals of a flavonoid. The IR spectrum showed absorption bands for the hydroxyl group (s) (3 400 cm-1),carbonyl group (s) (1 657 cm-1),and aromatic ring (s) (1 600,1 500,and 1 446 cm-1). Its molecular formula was deduced as C34H42O21 from its positive mode HR-ESI- MS [m/z 809.211 9 ([M+Na]+ C34H42O21Na+,Cacld. for 809.211 6)],and NMR data (Table 1). The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in DMSO-d6 showed a proton signal at δ 12.56 (1H,s),suggesting that there was a hydroxyl group at C-5. The spectrum also showed four aromatic protons at δ 8.14 (2H,d,J = 9.0 Hz,H-2',H-6') and 7.17 (2H,d,J = 9.0 Hz,H-3',H-5'),which consisted an AA'BB' system. Additionally,the 1H NMR spectrum of 1 also displayed two meta-coupled alkene protons at δ 6.79 (1H,d,J = 2.2 Hz,H-8) and 6.40 (1H,d,J = 2.2 Hz,H-6). The acid hydrolysis combined with high- performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis[8],which proved the presence of D-glucose and D-galactose in the ratio of 2: 1. The proton signals at δ 5.54 (1H,d,J = 7.8 Hz,H-1"),5.04 (1H,d,J = 7.4 Hz,H-1"') and δ 4.26 (1H,d,J = 7.9 Hz,H-1"") were attributed to three sugar moieties in the 1H NMR spectrum of 1,which further confirmed that the three sugar residues were β-pyranosyl configurations. One β-D-glucosyl moiety was linked to the aglycone at C-3 indicated by the HMBC correlation (Figure 2) from δ 5.54 (H-1") to δ 134.5 (C-3). The HMBC correlations from δ 5.04 (H-1"') to δ 161.5 (C-4'),from δ 5.04 (H-1"') to δ 80.7 (C-3"'),from δ 4.26 (H-1"") to δ 80.7 (C-3"') and from δ 3.36 (H-3"') to δ 103.7 (C-1"") established that the remaining β-D-glucosyl unit was attached to C-4',and that the β-D-galactosyl moiety was linked to C-3"'. The HMBC correlation from a methoxyl proton signal δ 3.87 (3H,s) to δ 165.8 (C-7) revealed that a methoxyl unit was linked to aglycone at C-7. On the basis of the above evidences,the structure of compound 1 was determined to be rhamnocitrin-3-O-β-glucopyranosyl- 4'-O-β-galactosyl-(1→3)-glucopyranoside and named as nervilifordin K.
 | Figure 2 Key HMBC (H→C) correlations of compounds 1 and 2 |
Compound 2 was a yellowish amorphous powder,and its molecular formula was determined to be C35H44O22 by its negative mode HR-ESI-MS spectrum [(m/z 815.224 8 [M-H]- C35H43O22-,Cacld. for 815.224 6)] and NMR data (Table 1). The IR spectrum showed absorption bands for hydroxyl (3 400 cm-1) and carbonyl group(s) (1655 cm-1) and aromatic ring(s) (1 600,1 500 and 1 453 cm-1). The UV spectrum revealed absorption bands at 267 and 343 nm,which suggested a flavonol skeleton. The 1H and 13C NMR data of compound 2 highly resembled those of 1,except for the presence of an additional methoxyl unit. The HMBC correlation (Figure 2) from the methoxyl proton signal δ 3.84 (3H,s) to δ 148.7 (C-3') proved that the methoxyl group was attached to C-3'. The acid hydrolysis combined with HPLC analysis[8],which certified the presence of D-glucose and D-galactose in the ratio of 2: 1. The 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2 also showed signals corresponding to three anomeric protons at δ 5.48 (1H,d,J = 7.6 Hz),5.02 (1H,d,J = 7.4 Hz) and δ 4.26 (1H,d,J = 7.8 Hz),which further confirmed that the three sugar residues were β-pyranosyl configurations. One glucosyl moiety was established by the HMBC,and the correlation between δ 5.48 (H-1") with δ 134.5 (C-3),suggesting that the glucosyl moiety was linked at C-3. The HMBC correlations from δ 5.02 (H-1"') to δ 149.2 (C-4'),from δ 5.02 (H-1"') to δ 80.7 (C-3"'),from δ 3.38 (H-3"') to δ 103.7 (C-1"") identified that another β-D-glucosyl residue was attached to C-4',and that the β-D-galactosyl unit was linked to C-3"'. Therefore,compound 2 was established to be 7,3'-di-O-methylquercetin-4'-O-[β-galactosyl-(1→3)- β-glucopyranosyl]-3-O-β-glucopyranoside,and named as nervilifordin L.
|
|
Table 1 The NMR data of compound 1 and 2 in DMSO-d6 (600MHz for 1H and 150 MHz for 13C) (J in Hz) |
UV spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu UV mini-1240 spectrophotometer. IR spectra were obtained on a Perkin Elmer Spectrum One FT-IR spectrometer with KBr pellets. 1D and 2D NMR spectra were performed on the Bruker ARX-600 spectrometer in DMSO-d6 with TMS as an internal standard. HR-ESI-MS data was obtained on a Waters API QSTAR Pular-1 mass spectrometer,and a Waters Synapt G2 MS mass spectrometer. Sugar analysis by HPLC: Shimadzu LC-20A. Preparative HPLC: Shimadzu LC-6AD pump,Shimadzu SPD-20A UV detector,YMC ODS-A (20 mm × 250 mm,10 μm),flow rate 8.0 mL·min-1,detection at UV 365 nm. Column chromatography was performed using D101 macroporous resin (Cangzhou Bon Adsorber Technology Co.,Ltd.,P. R. China),and reversed-phase C18 silica gel (Merck,Germany). Fractions were monitored by TLC [silica gel G plates (Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory,P. R. China) and polyamide film plates (Taizhou Luqiao Sijia Biochemical Plastics Company,Zhejiang,P. R. China)],and spots were detected with 10% H2SO4 in ethanol followed by heating. Standard substances: D-glucose and D- galactose (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd). The reagents were analytical grade.
Plant materialNervilia fordii were collected from Yulin county of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region,P. R. China,in March 2013,and was authenticated by TCM-Pharmacist Jia-fu Wei from Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Food and Drug Administration. A voucher specimen (No. 20130301) was deposited in the Laboratory of Natural Products of the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Guangxi Medical University.
Extraction and isolationThe air-dried herb (8 kg) of Nervilia fordii was extracted with 10-fold of 95% EtOH under reflux. Then the plant residue was extracted with 10-fold of distilled water. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to afford a crude extract (1 022 g). The distilled water extract was chromatographed on a D101 macroporous resin column using gradient of H2O-EtOH (100: 0,90: 10,70: 30,50: 50,30: 70 and 0: 100) to yield six fractions (Fr.1-6). Fraction 5 (357 g) was chromatographed on a RP C18 silica gel eluted with gradient of H2O-MeOH (100: 0,90: 10,70: 30,50: 50,30: 70 and 0: 100) to afford six subfractions (Fr.51-56). Fraction 54 (4.8 g) was purified by preparative HPLC to afford 1 (30 mg) and 2 (25 mg).
Structure elucidation Compound 1Yellow,amorphous powder,UV (MeOH) λmax/nm (logε) 331 (3.08),267 (3.26). IR (KBr) νmax 3 400,2 922,1 657,1 600,1 500,1 446,1 215,1 167,841 and 526 cm-1. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6,600 MHz) and 13C NMR (DMSO-d6,150 MHz) spectral data,see Table 1. HR-ESI-MS (positive): m/z 809.211 9 [M+Na]+ C34H42O21Na+,Cacld. for 809.211 6.
Compound 2Yellow,amorphous powder,UV (MeOH) λmax/nm (logε) 343 (3.14),267 (3.25). IR (KBr) νmax 3 400,2 920,1 655,1 600,1 500,1 453,1 425,1 214,1 166,804 and 643 cm-1. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6,600 MHz) and 13C NMR (DMSO-d6,150 MHz) spectral data,see Table 1. HR-ESI-MS (negative): m/z 815.224 8 [M-H]- C35H43O22-,Cacld. for 815.224 6.
Analytical acid hydrolysisCompound 1 and compound 2 (each 1 mg) were hydrolyzed with 2 mol·L-1 HCl (1 mL) at 85 ℃ for 1 h. The mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (2×1 mL). The aqueous layer was evaporated to dryness,and dissolved in pyridine (1 mL),then L-cysteine methyl ester hydrochloride (1 mg) was added,and the mixture was heated at 60 ℃ for 1 h. After that,O-tolyl isothiocyanate (20 μL) was added,and the mixture was heated at 60 ℃ for another 1 h. An aliquot (2 mL) of the supernatant was removed and directly subjected to HPLC analysis under the following conditions: flow rate 1.0 mL·min-1,column temperature 35 ℃,detection wavelength 245 nm,AQ C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm,5 μm,Welch,Potamac,MA,USA). The acetonitrile- 0.1% formic acid (25: 75,V/V) was employed as a
mobile phase for 60 min. The sugar residues of compounds 1 and 2 were identified by comparing the retention times of the corresponding derivative with the standard D-glucose (tR = 27.40 min) and D-galactose (tR = 30.67 min).
Acknowledgments: The authors thank Mr Si-min Zhang of Guangxi Institute of Analysis for measuring the NMR and MS data and Ms Li-li He of Guangxi Institute of Medicinal Plant for her kind help in measuring HR-ESI-MS.
| [1] | Editorial Committee of Chinese Materia. Chinses Materia Medica (中华本草)[M]. Shanghai:Shanghai Scientific and Technical Puberlishers, 1999, 24:740-741. |
| [2] | Lu CL, Wang H, Zhou GX, et al. Studies on chemical constituents of petroleum ether extract with anti-tumor activity from Nervilia fordii[J]. J Jinan Univ Nat Sci (暨南大学学报自然科学版), 2009, 30:556-559. |
| [3] | Wang ZH, Du Q, Zhang FX. Study on the antiviral action of Nervilia fordii against influenza virus[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (时珍国医国药), 2007, 18:2940-2941. |
| [4] | Fang WC, Mei QX, Gao YQ. Experimental studies on analgesic effects of 12 Guangdong native heat-clearing and detoxicatong herbs[J]. Pharm Today (今日药学), 2010, 20:12-15. |
| [5] | Zhou GX, Lu CL, Wang HS, et al. An acety flavonol from Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr.[J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2009, 11:498-502. |
| [6] | Qiu L, Xu LY, Miao JH, et al. Study advances on chemical constituents from Nervilia fordii (Hance) Schltr. and its bioactivities[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (时珍国医国药), 2011, 22:2258-2260. |
| [7] | Zhang L, Zhu CC, Zhao ZX, et al. Simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in Nervilia fordii with HPLC[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2011, 46:1237-1240. |
| [8] | Tanaka T, Nakashima T, Ueda T, et al. Facile discrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC[J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 2007, 55:899-901. |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51


