中药天麻是兰科植物天麻 (Gastrodia elata Blume) 的干燥块茎,主要用来治疗头痛、眩晕、癫痫、脑卒中以及肢体麻木等病症,已知天麻具有益 智以及改善痴呆的功效。近年研究[1, 2]发现天麻提取物具有神经保护作用,可显著缩短东莨菪碱模型动物在水迷宫实验中的潜伏期,并改善模型动物在被动回避实验中的表现。天麻对阿尔兹海默氏症 (Alzheimer’s disease,AD) 模型大鼠的水迷宫空间学习记忆以及海马中的Aβ沉积均具有改善作用[3]。
天麻素 (gastrodin,Gas) 是天麻的主要成分之 一,其含量是目前天麻的一项质控标准。然而天麻素对改善学习记忆障碍的效果并不理想,往往需要大剂量、 连续多日给药[4, 5, 6]。由于天麻在传统用药中多采用水煎剂的形式给药,因此本课题组研究了其水溶性成分派立辛 (parishin) 和parishin C改善学习记忆障碍的效果,并与天麻素进行对比。如图 1所示,parishin类成分在结构上与天麻素紧密相关,均为天麻素与柠檬酸的酯,parishin由柠檬酸的1,2,3位羧基各与一分子天麻素4位的羟基聚合而成,parishin B由柠檬酸的中间羧基及任意末端羧基与两分子天麻素4位羟基聚合而成,parishin C由柠檬酸两端的羧基与两分子天麻素聚合而成。Parishin B与parishin C为同分异构体,但parishin B结构不稳定,易转化成parishin或parishin C,故不单独进行研究。本所前期研究[7, 8]结果表明,天麻中parishin类提取成分 (包括parishin、parishin B和parishin C,含量 > 50%) 对东莨菪碱所致学习记忆障碍以及血管性痴呆造成的学习记忆障碍等具有显著改善作用。
海马脑区的长时程增强 (long-term potentiation,LTP) 是学习记忆的主要电生理机制及分子机制之一,也是突触可塑性的重要表现形式[9]。病理因素导致的学习记忆障碍会导致LTP的抑制。胆碱能系统参与学习记忆的过程,其功能障碍是AD的重要病理特征之一[10, 11]。东莨菪碱是M胆碱能受体的阻断剂,可引起认知功能障碍,其电生理机制与LTP的抑制有关[12]。
因此,本课题组采用东莨菪碱造成的学习记忆障碍模型,采用水迷宫的行为学实验以及在体LTP记录的手段,研究天麻素及其衍生物parishin、parishin C在改善学习记忆障碍方面的作用,并比较其构效关系。
材料与方法 动物水迷宫实验采用SPF级雄性ICR小鼠,体重23~26 g,LTP实验采用SPF级Wistar大鼠,体重240~260 g,均购于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司 [实验动物许可证号: SCXK (京) 2012-0001],自由进食进水, 室温保持在 (24 ± 1) ℃,每天照明12小时 (8∶00~20∶00),实验过程均符合北京协和医学院动物保护委员会的相关规定。
药品天麻素、parishin和parishin C均由中国医学科学院药物研究所石建功教授提供(HPLC纯度 > 98%)。东莨菪碱 (scopolamine,Scop) 购于美国Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Incorporation,多奈哌齐购于中国食品药品检定研究院。
Morris水迷宫实验实验开始之前注射药物 (东莨菪碱除外) 2天,第3天开始水迷宫实验。实验动物随机分为9组,每组14~29只: 正常对照组; 1 mg∙kg-1东莨菪碱模型组; 3 mg∙k g-1多奈哌齐组; 50和150 mg∙kg-1 parishin组; 15和50 mg∙kg-1 parishin C组; 50和150 mg∙kg-1天麻素组。药物均采用腹腔注射 (ip) 给药,药物剂量根据之前研究以及小鼠与大鼠之间体表面积比值进行换算,以保证实验的一致性[8]。在进行水迷宫实验前1 h给予各组药物,前30 min给予东莨菪碱,对照组给予生理盐水。
实验器材由圆形水池及自动录像分析系统两部分组成。圆形水池直径120 cm,高60 cm,池中注水,水温控制在 (23 ± 1) ℃,安全岛直径10 cm,位于水面下1 cm深度处。训练期间安全岛固定于任一象限中央,记录动物寻找安全岛的潜伏期。
实验程序按照Morris等[13]方法进行,分为定位航行实验和探索实验两部分。定位航行实验: 小鼠每天接受两次训练寻找平台,两次分别半随机地从对侧象限中点头朝池壁入水,记录60 s内寻找平台的潜伏期。如果60 s内未找到平台,潜伏期以60 s计算。无论是否在60 s内找到平台,小鼠都在平台上停留30 s以强化记忆。定位航行实验结束后进行探索实验,移去安全岛,小鼠自由游泳60 s,记录其在每个象限停留时间。数据收集和处理由水迷宫系统软件完成。

|
Figure 1 Structures of gastrodin,parishin,parishin B and parishin C |
大鼠用乌拉坦麻醉 (20%,1.3 g∙kg-1,ip) 后固定于立体定位仪上。本实验记录的是海马齿状回-穿通纤维的突触传递,记录电极埋置于海马齿状回 (坐标位置: 前囟后3.8 mm,中缝旁开2.0 mm,深度约3.5 mm),刺激电极埋置于穿通纤维 (坐标位置: 前囟后7.5 mm,中缝旁开4.2 mm,深度约3.5 mm)。参比电极固定于颅骨或组织处。给予固定强度的刺激,调整刺激电极或记录电极的位置,直到记录到最大群峰电位 (population spike,PS) 时将电极固定。
记录刺激采用波宽0.1 ms、0.033 Hz,强度为引起最大PS强度的40% 进行记录。LTP的诱发采用 100 Hz、10 串,间隔300 ms重复10次的高频刺激 (high-frequency stimulation,HFS)。刺激强度加倍,波宽不变。然后采用HFS前的记录条件继续记录1 h。
给药之前PS稳定记录15~20 min,给药后 10 min腹腔注射东莨菪碱,东莨菪碱注射后30 min给予HFS。对照组注射生理盐水。
数据分析及统计水迷宫实验中,采用two-way ANOVA进行分析。LTP实验中,计算PS的幅度值,并采用Matlab v7.1 (Mathworks) 软件进行统计[14]。具体方法为,每5 min的PS幅度统计均值为1个 时间点,统计所有HFS前后的时间点。以HFS前 30 min PS值的平均值为baseline,PS相对值为与baseline的比值 × 100%。HFS后PS增幅超过30% 即为LTP诱发成功。本文中所提PS数值均为HFS后55~60 min时的数值。组间LTP效果的比较采用repeated measures ANOVA进行,结合 Dunnett’spost hoc test检验,P < 0.05认为具有显著性差异。
结果 1 天麻素及parishin、parishin C对东莨菪碱诱导空间学习记忆障碍的改善作用水迷宫实验主要反映动物海马依赖的空间学习记忆能力[13, 15]。如图 2所示,随着训练时间的增加,1 mg∙kg-1东莨菪碱组动物找到平台的潜伏期与正常组相比差距明显加大 (P < 0.01)。3 mg∙kg-1多奈哌齐显著改善这一状况 (P < 0.05,图 2D)。50和150 mg∙kg-1天麻素仅表现出改善的趋势 (图 2C),15和50 mg∙kg-1parishin C,以及150 mg∙kg-1 parishin可显著改善东莨菪碱致空间学习记忆能力障碍,缩短寻找平台的潜伏期 (P < 0.05,图 2A和图 2B)。探索实验代表长时间记忆的能力,结果表明,高剂量的parishin C,即50 mg∙kg-1组可显著延长动物在目标象限的停留时间 (P < 0.05,图 2E)。
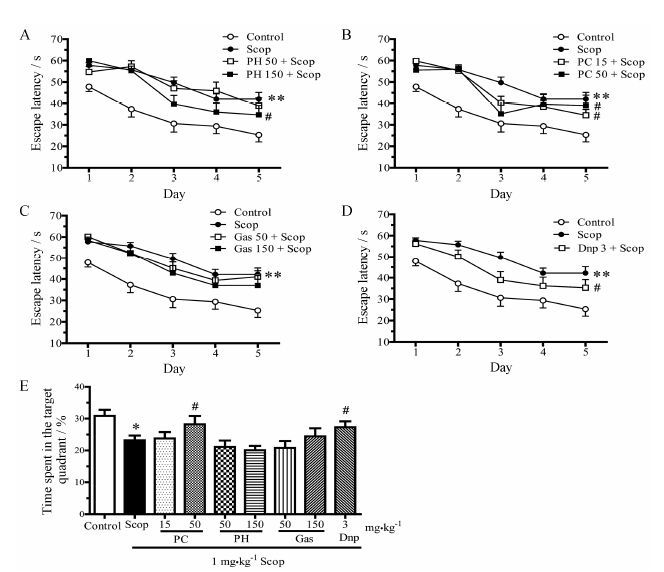
|
Figure 2 Effects of parishin (PH),parishin C (PC),gastrodin (Gas) and donepezil (Dnp) on the escape latency of the Morris water maze task. A-D: For training days,scopolamine (Scop,1 mg∙kg-1) significantly prolonged escape latency. 150 mg∙kg-1 PH,15 and 50 mg∙kg-1 PC and 3 mg∙kg-1 Dnp ameliorated memorydeficits induced by Scop significantly. E: Probe trials showed that Scop significantly decreased the time spent in the target quadrant,and 50 mg∙kg-1 PCand 3 mg∙kg-1 Dnp significantly prolonged it. n = 14-29,$\overline{x}$± s. P < 0.05,**P < 0.01 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs Scop group |
Parishin C的分子结构是长链结构,仅在柠檬酸的两端羧基上与天麻素聚合成酯。水迷宫的结果提 示,parishin C可在比parishin剂量低时起效,且对长时间记忆有效。因此,根据之前的实验结果与最大给药剂量[8],本研究首先观察parishin C的3个剂量 (5、10和20 mg∙kg-1) 对在体LTP的影响。从图 3中可以看到,东莨菪碱可显著抑制LTP的诱发 (150.2% ± 5.5% vs control 190.5% ± 7.8%,n = 7~8,P < 0.05),说明东莨菪碱可损伤神经突触传递效率。5 mg∙kg-1parishin C无显著改善效果 (155.6% ± 9.0% vs Scop group,n = 5,P > 0.05,图 3A),10 mg∙kg-1 parishin C (192.0% ± 10.6% vs Scop group,n = 6,P < 0.05,图 3B) 和20 mg∙kg-1 parishin C (202.6% ± 18.4% vs Scop group,n = 6,P < 0.01,图 3C) 均可显著改善东莨菪碱引起的LTP诱发抑制。Parishin C可剂量依赖性地改善东莨菪碱造成的LTP诱发抑制,以上结果与水迷宫结果一致。

|
Figure 3 Effects of PC on long-term potentiation (LTP) suppression induced by Scop. After baseline recordings of 15 min,rats were injected ip with PC (5,10 or 20 mg∙kg-1) followed (10 min later) by injection of Scop (1 mg∙kg-1) as indicated by arrows. High-frequency stimulation (HFS) was given 30 min later. All drugs had no effects on basic synaptic transmission. n = 5-8,$\overline{x}$± s. P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05,##P < 0.01 vs Scop group. PS: Population spike |
水迷宫实验中,高剂量的parishin可显著改善 东莨菪碱导致的空间学习记忆障碍。因此本研究从10 mg∙kg-1开始至100 mg∙kg-1观察parishin对LTP的 作用。从图 4中可以看到,东莨菪碱可显著抑制LTP的诱发 (153.4% ± 6.4% vs control 185.8% ± 6.6%,n = 6,P < 0.05)。10 mg∙kg-1 parishin对东莨菪碱造成的LTP抑制无改善作用 (158.2% ± 7.9% vs Scop group,n = 5,P > 0.05,图 4A); 30 mg∙kg-1 parishin仅有一定改善的趋势 (168.3% ± 9.1% vs Scop group,n = 5,P > 0.05,图 4B); 100 mg∙kg-1 parishin可显著逆转东莨菪碱导致的LTP诱发抑制 (188.7% ± 16.0% vs Scop group,n = 5,P < 0.05,图 4C)。综上所述,parishin也可剂量依赖性地改善东莨菪碱抑制的LTP诱发,但是有效剂量至少为parishin C的10倍。

|
Figure 4 Effects of PH on LTP suppression induced by Scop. After baseline recordings of 15 min,rats were injected ip with PH (10,30 or 100 mg∙kg-1) followed (10 min later) by injection of Scop (1 mg∙kg-1) as indicated by arrows. HFS was given 30 min later. All drugs had no effects on basic synaptic transmission (P > 0.05). n = 5-6,$\overline{x}$± s. P < 0.05 vs control group,#P < 0.05 vs Scop group |
在与parishin和parishin C相同的条件下,本研究观察了天麻素的作用。10 mg∙kg-1天麻素对东莨菪碱所致LTP抑制无效 (160.5% ± 11.3% vs Scop group 154.0% ± 4.4%,n = 5~6,P > 0.05,图 5A),30 mg∙kg-1 (177.1% ± 11.3% vs Scop group,n = 5~6,P > 0.05,图 5B) 和100 mg∙kg-1 (168.7% ± 11.5% vs Scop group,n = 5~6,P > 0.05,图 5C) 天麻素仅有改善的趋势。以上结果与水迷宫结果一致。

|
Figure 5 Effects of Gas on LTP suppression induced by Scop. After baseline recordings of 15 min,rats were injected ip with Gas (10,30 or 100 mg∙kg-1) followed (10 min later) by injection of Scop (1 mg∙kg-1) as indicated by arrows. HFS was given 30 min later. Gas had no effects on basic synaptic transmission. n = 5-6,$\overline{x}$± s. *P < 0.05 vs control group |
本研究采用东莨菪碱造成的学习记忆障碍模型,研究了天麻中结构相关的3个主要的单体化合物天麻素、parishin和parishin C的构效关系。发现天麻素经过与柠檬酸结合后形成的化合物效果比天麻素单体强,其中,parishin C的改善作用比parishin高约10倍,比天麻素高约20~30倍。
胆碱能系统在记忆的存储以及追溯等过程中起重要的作用[16]。东莨菪碱造成的学习记忆障碍可模拟AD患者的胆碱能系统功能的下降,因此东莨菪碱模型在AD研究中可作为早期促认知药物筛选的模型[17]。本实验选用胆碱酯酶抑制剂多奈哌齐作为水迷宫实验的阳性对照,结果表明3 mg∙kg-1多奈哌齐可以显著改善东莨菪碱造成的空间学习记忆能力损伤。水迷宫实验中,15和50 mg∙kg-1 parishin C组,&nbs p;以及150 mg∙kg-1 parishin组都可显著改善动物在定位航行实验中的潜伏期,而探索实验中,50 mg∙kg-1 parishin C组可显著改善东莨菪碱引起的工作记忆障碍。以上结果表明,parishin C以及parishin都对短期记忆有改善作用,但是对长期工作记忆,parishin C的作用优于parishin。LTP实验中,东莨菪碱造成的LTP诱发抑制可被10和20 mg∙kg-1 parishin C显著改善,parishin在100 mg∙kg-1时亦有改善作用,天麻素仅有改善趋势。因此,相同条件下,化合物结构中含两分子天麻素的parishin C效果最好,结合了3分子天麻素的parishin次之,天麻素的作用明显较弱。
文献[18]表明,天麻素可以改善环己酰亚胺造成的学习记忆损伤。但天麻素多为大剂量 (100 mg∙kg-1或者更高) 连续给药1~2周[1, 3, 5],而本实验中天麻素、parishin和parishin C均为一次性给药,或者提前给药2天。因此推测,天麻素可能需要连续大剂量给药才能起效,提示parishin和parishin C效果更强。其原因有可能是parishin C的独特长链结构,既比天麻素更伸展,又没有parishin结合3个分子天麻素造成的分子内拥挤。这样独特的结构可能使parishin C和目标靶蛋白更好地结合。其次,根据文献[19]研究,天麻素在给药后20 min内在脑中达到峰值浓度,60 min后大部分被代谢,血药浓度下降到极低水平[19, 20]。Tang等[21]针对天麻素、parishin及天麻提取物进行了药物代谢研究,发现parishin及含有parishin的天麻提取物代谢时间比天麻素长。以上研究提示天麻素在给药后快速代谢消除,血药浓度降低,影响药效,而parishin和parishin C可能在代谢方面比天麻素具有优势。
综上所述,本研究比较研究了天麻素、parishin和parishin C在东莨菪碱造成的学习记忆障碍模型中的作用,并分析了它们的构效关系以及可能的电生理机制。Parishin和parishin C的作用优于天麻素本身,parishin C优于parishin。因而parishin C有可能成为新一代抗痴呆药的先导物。
| [1] | Wu CR, Hsieh MT, Huang SC, et al. Effects of Gastrodia elata and its active constituents on scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats[J]. Planta Med, 1996, 62:317-321. |
| [2] | Chen PJ, Liang KC, Lin HC, et al. Gastrodia elata Bl. attenuated learning deficits induced by forced-swimming stress in the inhibitory avoidance task and Morris water maze[J]. J Med Food, 2011, 14:610-617. |
| [3] | Huang GB, Zhao T, Muna SS, et al. Therapeutic potential of Gastrodia elata Blume for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2013, 8:1061-1070. |
| [4] | Xu X, Lu Y, Bie X. Protective effects of gastrodin on hypoxia-induced toxicity in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons[J]. Planta Med, 2007, 73:650-654. |
| [5] | Yong W, Xing TR, Wang S, et al. Protective effects of gastrodin on lead-induced synaptic plasticity deficits in rat hippocampus[J]. Planta Med, 2009, 75:1112-1117. |
| [6] | Zhao X, Zou Y, Xu H, et al. Gastrodin protect primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons against amyloid-beta peptideinduced neurotoxicity via ERK1/2-Nrf2 pathway[J]. Brain Res, 2012, 1482:13-21. |
| [7] | Wang K, Shi J, Liu Y, et al. Gastrodia elata plant extract for preventing senile dementia and its preparing method:China, CN200510128785.1[P]. 2005-12-02. |
| [8] | Wang K, Shi J, Zhao L, et al. Application of gastrodiaelata blume parishin extractive in preparation of medicament for protecting brain:China, CN102727506A[P]. 2012-07-04. |
| [9] | Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory:long-term potentiation in the hippocampus[J]. Nature, 1993, 361:31-39. |
| [10] | Schliebs R, Arendt T. The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Neural Transm, 2006, 113:1625-1644. |
| [11] | Cuello AC, Bruno MA, Allard S, et al. Cholinergic involvement in Alzheimer's disease. A link with NGF maturation and degradation[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2010, 40:230-235. |
| [12] | Ebert U, Kirch W. Scopolamine model of dementia:electroencephalogram findings and cognitive performance[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 1998, 28:944-949. |
| [13] | Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 1984, 11:47-60. |
| [14] | Li PP, Wang WP, Liu ZH, et al. Potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate promotes long-term potentiation in A β1-42-injected rats and APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2014, 35:869-878. |
| [15] | Vorhees CV, Williams MT. Morris water maze:procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory[J]. Nat Protoc, 2006, 1:848-858. |
| [16] | Deutsch JA. The cholinergic synapse and the site of memory[J]. Science, 1971, 174:788-794. |
| [17] | Lenz RA, Baker JD, Locke C, et al. The scopolamine model as a pharmacodynamic marker in early drug development[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2012, 220:97-107. |
| [18] | Hsieh MT, Wu CR, Chen CF. Gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol facilitate memory consolidation and retrieval, but not acquisition, on the passive avoidance task in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 1997, 56:45-54. |
| [19] | Wang Q, Chen G, Zeng S. Distribution and metabolism of gastrodin in rat brain[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2008, 46:399-404. |
| [20] | Wang Q, Chen G, Zeng S. Pharmacokinetics of gastrodin in rat plasma and CSF after i.n. and i.v[J]. Int J Pharm, 2007, 341:20-25. |
| [21] | Tang C, Wang L, Liu X, et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of gastrodin in rats after intragastric administration of free gastrodin, parishin and Gastrodia elata extract[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 176:49-54. |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51


