抑郁症是一种常见的情感性障碍, 临床上常表现为情绪低落、快感丧失和精力缺乏等症状[1], 并伴有发病率高、复发率高和致残率高的特点。现有抗抑郁药物存在不良反应多、药效滞后等问题[2, 3, 4]。课题组前期通过药效学实验筛选出由柴胡、当归、白术、甘草、薄荷、生姜6味药组成的复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分[5], 能够显著降低小鼠悬尾、游泳实验的不动时间, 增加慢性温和不可预知应激 (chronic unpredictable mild stress, CUMS) 大鼠糖水偏爱率、直立及穿格次数等[6], 表明其具有良好的抗抑郁作用。大鼠尿液代谢组学结果显示, 复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分能够调节在CUMS大鼠中异常变化的甘氨酸、丙酮酸、醋酸、琥珀酸、2-氧化戊二酸和柠檬酸的含量[7], 但是这些异常变化的代谢物在抑郁症发病中处于怎样的通路, 药物作用于哪些靶点而调节了这些物质最终发挥抗抑郁作用的, 即代谢组学结果只表现出已经发生的代谢紊乱, 不能解释这种变化是如何发生的, 因此抗抑郁机制尚不能阐明。本研究进一步对复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分抗抑郁作用机制进行探讨。
Hopkins于2007年提出并阐释了“网络药理学”的概念, 是在网络生物学与多向药理学的基础上提出的新思想、新策略[8], 其建立在高通量组学数据分析、计算机虚拟和网络数据库检索基础上, 通过进行“药物-靶点-疾病”多层次网络构建, 从整体角度探索药物与疾病间的关联性, 发现靶标[9]。而中药因成分复杂、系统庞大使得深入研究有难度, 该方法的提出有助于从新的角度认识复方作用机制、加速靶点的确认及生物标志物的发现[10, 11]。罗国安等[12]基于网络药理学分析方法对罗格列酮复方的作用机制进行了探讨。白钢等[13]在对清肺消炎丸进行化学成分及其吸收利用度研究的基础上, 通过网络药理学的手段研究了药物可能的作用靶标及其途径。网络药理学研究思路已逐步应用于中药复方作用机制的研究。
本研究在前期实验结果的基础上, 采用网络药理学研究思路, 预测复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分的抗抑郁靶点, 并利用CUMS抑郁模型大鼠进行体内靶点验证, 探讨复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分抗抑郁作用机制。
材料与方法 药品与试剂改良型BCA法蛋白浓度测试盒、大鼠白介素6 (IL-6) ELISA试剂盒、大鼠皮质酮/肾上腺酮 (CORT) ELISA试剂盒购自生工生物工程(上海) 股份有限公司; 磷酸环磷腺苷效应原件结合蛋白 (p-CREB) ELISA试剂盒购自美国R&D System公司。实验室前期提取的复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分[6]。
动物SD大鼠, SPF级, 180~200 g, 购自北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司, 动物许可证号SCXK (京) 2011-2012。动物自然昼夜节律光照, 适应1周后进行实验。
仪器大鼠旷场行为测试箱, 自制; Centrifuge TDL-5型离心机, Spectra Max M5多功能酶标仪均购自上海安亭科学仪器厂。
网络构建本实验室前期利用气相色谱-质谱 (gas chromatography-mass spestrometry, GC-MS) 和超高效液相色谱法 (ultra performance liquid chro-matography, UPLC) 对复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分进行了成分分析, 共鉴定出22个化合物[5]。利用TCMSP (traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology, http://lsp.nwsuaf.edu.cn/tcmsp.php) 和HIT (herbal ingredients’ targets, http://lifecenter.sgst.cn/hit/) 数据库确定了上述萃取组分药物中22个化合物的作用靶点; 利用TCMSP、Pharm GKB (the pharmaco-genomics knowledebase, https://www.pharmgkb.org/) 和Gene Cards (http://www.genecards.org/) 数据库确定和抑郁症相关的基因及蛋白。基于以上生物信息学数据采用Cytoscape分别构建药物-靶点、疾病-靶点和药物-靶点-疾病网络, 预测复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分治疗抑郁症的靶点。
大鼠p-CREB、CORT、IL-6定量分析将56只SD大鼠随机分为7组, 分别为空白对照组 (NS, 食用油)、模型组 (MS, 食用油)、阳性对照组 (YV, 文拉法辛50 mg·kg-1)、逍遥散超临界CO2萃取组分组 (XY, 46 g·kg-1生药)、复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分高剂量组 (FG, 64 g·kg-1)、复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分中剂量组 (FZ, 32 g·kg-1)、复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分低剂量组 (FD, 16 g·kg-1)。除 空白组外, 其余各组按Willner等[14]方法并加以改进进行CUMS大鼠抑郁模型的复制, 刺激因子包括4 ℃冰泳5 min、热刺激10 min、超声3 h、束缚、陌生物体24 h、足底点击5 min、禁食24 h、禁水12 h和夹尾2 min等, 每天1种刺激, 同一种刺激累计使用不超过3次, 持续28天。造模同时给药, 各组按10 mL·kg-1 i.g.相应药物 (NS和MS给予等量的食用油)。
在第28天实验结束后, 20% 乌拉坦麻醉。股动脉取血, 3 000 r·min-1离心5 min, 取上清分装于EP管中, -80 ℃保存备用。同时在冰上对大鼠进行解剖, 取海马组织于EP管中, 液氮速冻后-80 ℃保存备用。
按试剂盒对海马中p-CREB、大鼠血清中CORT和IL-6进行测定, p-CREB以海马组织匀浆液中总蛋白浓度进行归一化。
统计学分析实验数据均以平均值±标准差 (x±s) 表示, 使用SPSS 17.0软件对多组进行单因素方差分析, 以P < 0.05为具有显著性差异, P < 0.01为具有极显著性差异。
结果 1 药物-靶点网络构建通过TCMSP和HIT数据库对复方柴归方超临 界CO2萃取组分中已鉴定的22个化合物 (表 1)[5]药物靶点进行了检索, 结果见图 1。共检索到78个靶 点, 其中对应≧10个化合物的靶点共7个, 分别是前列腺素合酶2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase 2, PTGS2)、γ氨基丁酸α1受体 (gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-1, GABRA1)、毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱M1受体 (muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, CHRM1)、钠 离子依赖的去甲肾上腺素转运体 (sodium-dependent noradrenaline transporter, SLC6A2)、毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱M2受体 (muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, CHRM2)、核受体共激活剂2 (nuclear receptor coactivator 2, NCOA2) 和前列腺素合酶1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase 1, PTGS1)。
|
|
Table 1 Chemical compounds of supercritical CO2 extract from Compound Chaigui Fang. OB: Oral bioavailability; DL: Drug- likeness |
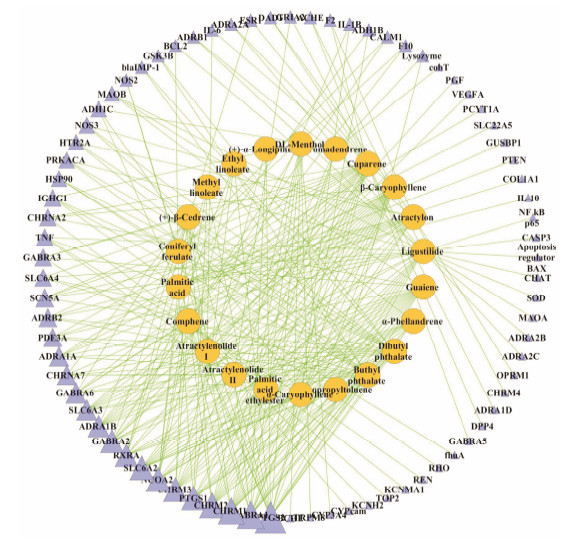 | Figure 1 Network of 22 identified compounds of supercritical CO2 extract from Compound Chaigui Fang predicted to have 78 targets. The orange circles represent the compounds, while navy triangles represent the target |
通过TCMSP、Pharm GKB和Gene Cards数据 库对抑郁症的疾病靶点进行检索, 其中Gene Cards的筛选标准为gene score > 1, 并选择能够编码蛋白的基因, 构建的疾病-靶点见图 2。共检索到177个靶点, 根据蛋白的功能进行分类, 包括7类, 神经递质 (neurotransmitter) 转运体、代谢酶和受体; 下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺/甲状腺/性腺 (hypothalamus-pituitary- adrenal/thyroid/gonad, HPA/T/G) 轴分泌及相关激素; 信号通路 (signal pathway) 因子; 神经肽 (neuropeptide); 生长因子 (growth factor); 免疫(immune) 相关因子和其他 (other) 物质, 分别含有55、22、23、7、3、10、15个靶点。
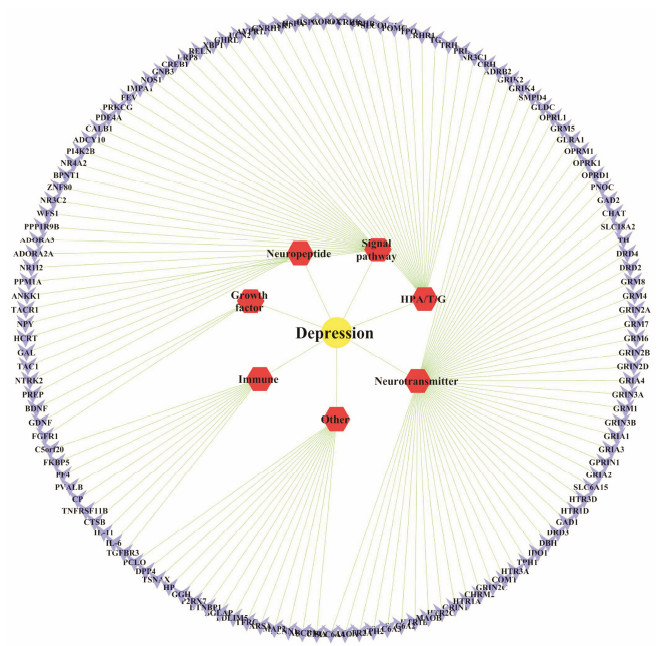 | Figure 2 Network of 177 disease targets of depression and their related metabolism. The yellow circle represents the depression, and red hexagons represent the disease targets related metabolism, while navy vees represent the target |
对检索到的药物-靶点、疾病-靶点以靶点为连接点进行药物-靶点-疾病网络构建 (图 3), 通过删除和抑郁症无共有靶标的途径, 对此网络进行精简得到新的药物-靶点-疾病网络 (图 4)。药物治疗和疾病发生共有靶点为14个, 分别是神经递质转运体、代谢酶和受体; HPA/T/G轴分泌激素; 免疫相关因子等, 并将能够调节这些靶标的复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分的化合物列于表 2, 其中藁本内酯 (ligustilide)、花侧柏烯 (cuparene) 和苍术酮 (atractylon) 分别含有8、7和6个共有靶标。
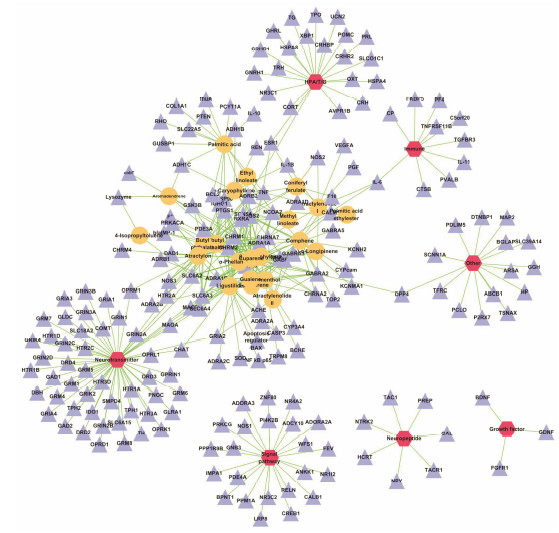 | Figure 3 Network of 22 compounds-78 drug targets-177 disease targets-7 depression targets related metabolism. The orange circles represent the compounds, and navy triangles represent the drug and disease target, while red hexagons represent the disease targets related metabolism |
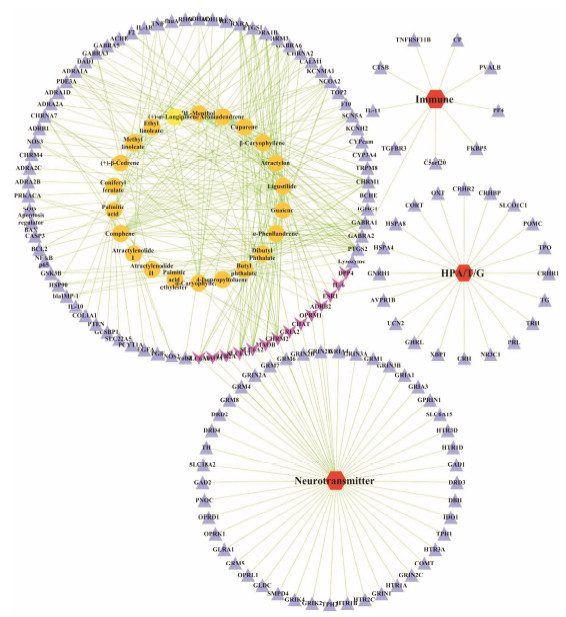 | Figure 4 Network of 22 compounds-78 drug targets-130 disease targets-3 depression targets related metabolism. The orange circles represent the compounds, and navy triangles represent the drug and disease target, and the pink vees represent the common targets of drug and disease targets, while red hexagons represent the disease targets related metabolism |
|
|
Table 2 Common targets of drug-treatment and depression-development. LL: Ligustilide; BP: Butyl phthalate; DP: Dibutyl phthalate; CE: Cuparene; α/βCE: α/β-Caryophyllene; GE: Guaiene; AO: Atractylon; PE: α-Phellandrene; IE: 4-Isopropyltoluene; AL I/II: Atractylenolide I/II; AE: Aromadendren; CeE: (+)-β-Cedrene; CoE: Comphene; MO: DL-Menthol; CF: Coniferyl ferulate |
行为学结果显示, 与空白组比较, 模型组大鼠体重增长缓慢、糖水偏爱率、穿格次数和直立次数显著减少 (P < 0.01, P < 0.05), 表明CUMS造模程序对大鼠造成了显著的抑郁行为, 模型复制成功; 连续给药28 天后, 给药组大鼠行为学指标均显著调节趋近空白组, 表现出良好的抗抑郁作用[7]。根据以上研究预测的复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分的抗抑郁靶标进行体内验证, 即对复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分干预抑郁症模型大鼠后海马组织中神经递质及其受体介导的信号通路转录因子p-CREB和血清中CORT和IL-6含量进行了测定。
与空白对照组比较, 模型组大鼠海马组织中p-CREB含量显著降低、血清中CORT和IL-6含量显著升高; 而复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分高、中、低剂量组表现出不同程度的调节作用, 其中以高剂量调节作用最佳, 并对p-CREB的调节优于阳性对照药文拉法辛和逍遥散; 低剂量对IL-6含量具有下调趋势, 但没有统计学意义 (图 5)。结果表明, 复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分通过作用于神经递质传递、HPA/T/G轴激素分泌和免疫相关因子含量而发挥抗抑郁作用。
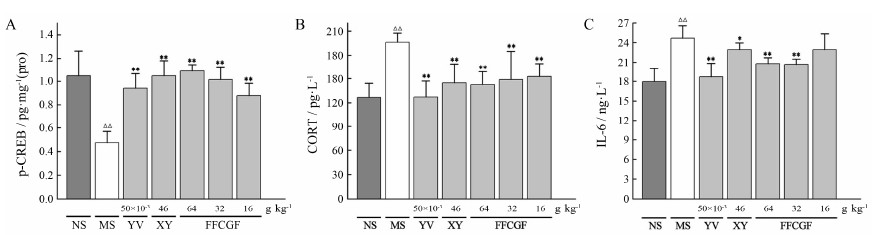 | Figure 5 The relative levels of p-CREB (A), CORT (B) and IL-6 (C) in the normal control group (NS), the CUMS model group (MS), the venlafaxine group (YV), the Xiaoyaosan group (XY), the high/medium/low dose of supercritical CO2 extract from Compound Chaigui Fang (FFCGF). n = 8, x±s. △△P < 0.01 vs NS group; P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs MS group |
本研究利用网络药理学的思路与方法预测了复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分的抗抑郁靶点。预测的14个潜在抗抑郁靶点分别是神经递质转运体、代谢酶和受体; HPA/T/G轴分泌激素; 免疫相关因子等。其中11个与神经递质作用及代谢相关, 与单胺类神经递质的代谢最为相关。此外, 雌激素受体 (ESR1) 和IL-6和二肽基肽酶4 (DPP4) 可能也是复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分的抗抑郁作用靶点。
针对预测的靶点及其相关代谢途径, 通过给予CUMS抑郁模型大鼠复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分后进行体内验证。神经递质需要通过与其受体结 合而发挥效应, 而11个靶点中多为单胺类神经递质的转运体、代谢酶及受体, 5-羟色胺 (5-hydroxyl tryptamine, 5-HT) 受体[15]; 肾上腺素能受体、多巴胺受体、毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体和阿片受体均是G蛋白耦联受体[16, 17], 其介导的信号转导通路大多数最终作用于p-CREB。因此, 对于与神经递质代谢相关的抗抑郁作用靶点, 选择了通过检测大鼠海马中神经递质受体介导的信号通路转录因子p-CREB的表达量进行验证。此外, 还发现了药物治疗和疾病发生的共有靶点中有与三大分泌轴 (HPA/T/G) 代谢相关的ESR1, 而HPA轴分泌失调学说是抑郁症经典的发病机制之一, 因此检测了大鼠血清中HPA轴终端分泌激素CORT的含量和IL-6含量。
复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分高、中、低剂量组均不同程度调节了在模型组中含量异常的p-CREB、CORT、IL-6, 提示其可能通过调控神经递质受体介导的信号转导通路及HPA/T/G轴和炎性因子代谢而发挥抗抑郁作用。此外, 研究表明, 在22个已指认的化合物中含有共有靶点最多的藁本内酯具有较好的神经保护作用[18], 能够显著上调低钾处理的大鼠小脑颗粒神经元中p-CREB的水平[19], 剂量依赖地下调脂多糖引起的小胶质细胞内升高的促炎性细胞因子水平[20], 因此, 藁本内酯可能是复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分发挥抗抑郁作用的重要成分。
虽然本研究利用网络药理学的方法预测了复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分潜在的14个抗抑郁靶点, 并对其相关代谢中的因子表达水平进行了体内实验验证, 但是仍存在一些不足。首先, 由于复方组分中化学成分复杂, 而实验前期仅利用GC-MS和UPLC对其化学成分进行了分析, 仍然存在化学成分不完全明确的问题, 有待于后期继续结合其他分析手段进一步分析指认; 其次, 仅对数据库中检索到的药物治疗和疾病发生的共有靶点进行了寻找, 尚未对其进行靶点互作分析, 有待利用软件及数据库进行分析; 最后, 本文仅有目的性的选取了3个指标进行了ELISA检测, 并未对共有靶点的转录及蛋白表达水平进行验证, 因此, 从p-CREB、CORT、IL-6 ELISA结果中并未发现复方柴归方超临界CO2萃取组分和阳性药文拉法辛抗抑郁机制的区别, 需要进行更为深入的验证。
| [1] | Belmaker RH, Agam G. Major depressive disorder[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 358:55-68. |
| [2] | Monteggia LM, Malenka RC, Deisseroth K. Depression:the best way forward[J]. Nature, 2014, 515:200-201. |
| [3] | Blendy JA. The role of CREB in depression and antidepressant treatment[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2006, 59:1144-1150. |
| [4] | Crawford AA, Lewis S, Nutt D, et al. Adverse effects from antidepressant treatment:randomised controlled trial of 601 depressed individuals[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2014, 231:1-11. |
| [5] | Zuo YM. Quality, Chemical and Formulation of Supercritical CO2 Extraction Component From Fufang Chaigui (复方柴归超临界CO2萃取组分的化学、质量及制剂研究)[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi University, 2014. |
| [6] | Guo XQ. Investigation on the Anti-depression of Active Fractions and Pesticide Effect From Fufang Chaigui (复方柴归方抗抑郁有效组分筛选及其药效学评价研究)[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi University, 2013. |
| [7] | Chen L, Zheng XF, Gao XX, et al. Anti-depressant effect and mechanism of supercritical CO2 extract from Compound Chaigui Fang[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2014, 39:2744-2750. |
| [8] | Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology:the next paradigm in drug discovery[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2008, 4:682-690. |
| [9] | Liu ZH, Sun XB. Network pharmacology:new opportunity for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2012, 47:696-703. |
| [10] | Wang YH, Yang L. Systems pharmacology-based research framework of Traditional Chinese Medicine[J]. World Chin Med (世界中医药), 2013, 8:801-808. |
| [11] | Liu AL, Du HH. Network pharmacology:new guidelines for drug discovery[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2010, 45:1472-1477. |
| [12] | Bai Y, Fan XM, Sun H, et al. The mechanism of rosiglitazone compound based on network pharmacology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2015, 50:284-290. |
| [13] | Cheng BF, Hou YY, Jiang M, et al. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of Qingfei Xiaoyan Wan studied with network pharmacology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2013, 48:686-693. |
| [14] | Willner P, Benton D, Brown E, et al. "Depression" increases "craving" for sweet rewards in animal and human models of depression and craving[J]. Psychopharmacology, 1998, 136:272-283. |
| [15] | Chen X. Study on the Immune Regulation Function of 5-HT Receptor (五羟色胺受体免疫调节功能研究)[D]. Taiyuan:Northwest A&F University, 2012. |
| [16] | Dong JH. β-Adrenergic Receptors Effect on the Metabolism of Lactate in Astrocyte and Content of Somatostain (β-肾上腺素受体对星型胶质细胞lactate代谢及胰岛素Somatoaststin合成的调控及机制)[D]. Jinan:Shandong University, 2014. |
| [17] | Li F, Shu SY, Bao XM. Structure and function of dopamine receptors[J]. Chin J Neurosci (中国神经科学杂志), 2003, 19:405-410. |
| [18] | Li J, Wang N, Wang GY, et al. Research progress studies on pharmacology of ligustilide in neuroprotective[J]. Asia Pac Tradit Chin (亚太传统医学), 2015, 11:55-57. |
| [19] | Li NJ, Wang Y, Wang LF, et al. Protective effect of ligustilide against low potassium induced apoptosis in cultured rat cerebellar granule neuros[J]. J Sichuan Univ (四川大学学报), 2015, 46:42-46. |
| [20] | Zhu MD, Zhao LX, Wang XT, et al. Ligustilide inhibits microglia-mediated proinflammatory cytokines production and inflammatory pain[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2014, 109:54-60. |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51


