糖尿病 (diabetes mellitus,DM) 是一种因胰岛素分泌不足及胰岛β-细胞功能缺陷引起的临床综合征,包括Ⅰ和Ⅱ型糖尿病。Ⅱ型糖尿病 (type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM) 属于胰岛素非依赖型糖尿病,是由于机体周边组织对胰岛素敏感性降低、胰岛素分泌不足导致的。主要病理表现为胰岛素抵抗和由胰岛细胞功能失调所致的胰岛素分泌相对不足,形成持久的高血糖,并可产生多种致命性并发症。其临床病症出现的关键是分泌胰岛素β-细胞量降低到不足以维持正常血糖代谢的水平,如果能增加β-细胞的数量就可以扭转其病程的进展。当前糖尿病临床治疗中,尚无一种药物可以增加胰岛β-细胞的数量。胰高血糖素样肽-1 (glucogan 1ike peptide-1,GLP-1) 作为一种肠促胰岛素[1, 2],是由肠道L细胞合成和分泌的,由30个氨基酸组成的多肽。GLP-1结合并激活G蛋白偶联受体GLP-1受体,通过胰腺β-细胞PKB/Akt的活化,参与葡萄糖依赖性胰岛素分泌和抗凋亡,GLP-1增加胰腺β-细胞的增殖,研究显示GLP-1还有减少食物的摄取、减慢胃的排空以及抑制胰高血糖素的分泌、促进胰岛再生等功能,且无胰岛素和磺脲类降糖药物的低血糖危险。GLP-1独特的 降血糖作用机制与众不同,是现有抗糖尿病药物无可比拟的[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]。
hGLP-I是具有广阔市场前景的新型糖尿病治疗药物,但其临床应用的最大障碍是体内半衰期短。DPP.Ⅳ介导的这种蛋白质水解作用使hGLP-1在体 内降解,失活的主要途径是通过hGLP-l受体的体内天然拮抗剂,hGLP-1在体内迅速被血浆中DPP.Ⅳ从N末端裂解His-A1a二肽,成为无活性的des(HisAla)- hGLP-1 (9-36),结果使得hGLP-1在体内的生物半 衰期很短 (< 5 min),其新陈代谢的速率为12~13 min[10, 11]。另外,由于hGLP-1只有30个氨基酸残基,分子很小,因此肾清除率较高,也是造成它体内半衰期短的一个原因[12, 13, 14]。
天然的GLP-1半衰期很短 (约2 min),无法应用于临床。天然exendin-4是从美国西南部产的大毒蜥唾液中提取的39个氨基酸多肽,exendin-4可与GLP-1受体结合,产生与GLP-1相似的生理效应,半衰期达2.5 h,每天皮下注射两次用于治疗T2DM,可得到满意的疗效。临床研究显示,exendin-4可在血糖较高 ; 时刺激胰岛素分泌,从而降低血糖; 在血糖较低时则无此作用,故不会引起低血糖。Exendin-4可显著降低T2DM患者空腹及餐后血糖、HbA1c,显著降低体重和改善脂代谢,动物研究表明exendin-4增加β-细胞数量,对Ⅱ型糖尿病有较好的疗效。但是目前exendin-4主要采用化学合成,成本高、产量低,不能满足市场需要。
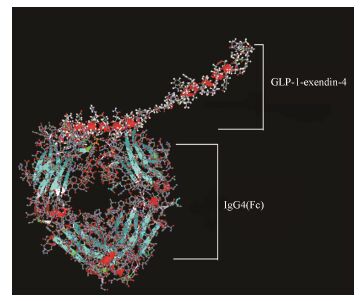
本研究构建了GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) (图 1),通过人IgG4 Fc和GLP-1-exendin-4融合,保留GLP-1和exendin-4天然活性,研究表明GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) 与GLP-1R结合,刺激INS-1细胞胰岛素分泌。CD1小鼠的药代动力学研究表明,单次腹腔注射后,该融合蛋白保持在较高的水平达1周以上。研究结果表明,GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 可以作为替代GLP-1受体激动剂用于治疗糖尿病。
|
Figure 1 Perspective structure of GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) fusion proteins |
基因片段来自南京金斯瑞基因合成,pOptiVEC™- TOPO®载体 (Dhfr+)、中华仓鼠卵巢细胞 (Dhfr gene deficient CHO/DG44cells) 细胞株,均购自Invitrogen公司,INS-1细胞购自ATCC公司,感受态菌DH5α 由上海汉骄生物科技有限公司保存。
主要试剂限制性内切酶Nhe I、Xho I和Nsb IT4 DNA连接酶,蛋白Marker (NEB公司); DNA纯化 回收试剂盒,质粒提取试剂盒 (天根生物科技公司); Lipofectamine™ 2000脂质体 (Invitrogen公司); 山羊抗人IgG(H+I) (中山金桥); 亲和层析柱ProteinG- Agarose (Roche公司); 其他试剂为国产分析纯试剂,RIA kit (Linco公司)。Ascensia XL血糖仪和Ascensia的血糖试纸 (Ascensia公司)。
培养基a-MEM(+)、a-MEM(-) 培养基 (Gibico公司); 无血清培养基CD OptiCHO™ Medium (Invitrogen公司); 透析胎牛血清 (Hyclone公司)。
动物清洁级7周雄性CD1小鼠来自上海实验动物研究中心,体重25~30 g。
细胞培养CHO/DG44细胞培养于a-MEM(+) 含10% 新生小牛血清的培养基中,于37 ℃、5% CO2的培养箱中培养。
表达载体构建用限制性内切酶Nhe I、Xho I将目的片段从克隆载体上切下,用T4 DNA连接酶将 目的片段与pOptiVEC™-TOPO®载体连接,转化感受态菌DH5α,提取质粒,Nsb I酶切GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) pOptiVEC™-TOPO®质粒使其线性化,乙醇沉淀后纯化回收,双蒸水溶解,最终质粒质量浓度为0.5 μg·μL-1。
脂质体法转染CHO/DG44细胞及阳性克隆的筛选采用Invitrogen公司的脂质体转染技术 (参考试剂说明书)。按照转染试剂Lipofectamine™ 2000说明书将线性化的重组质粒转染CHO/DG44 细胞。同时设置空载体组和未转染组细胞。转染24 h后加入a-MEM-培养基进行筛选。12天后表达质粒组和空载体组可见有阳性克隆形成,阴性细胞组全部死亡,用克隆环套取单克隆,胰酶消化,选出20个生长旺盛的单克隆扩大培养,在扩大培养的基础上重复选取20个单克隆扩大培养、冻存和检测。
GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 目的基因的扩增、诱导表达与纯化在每个单克隆扩大培养稳定生长达到70%~80%时,分别用浓度为50、100、250、500和1 000 nmol·L-1的MTX进行加压筛选,加入a-MEM(-) 筛选培养基使细胞生长达到70%~80% 后,离心除去杂质,超滤法浓缩细胞上清液,将浓缩后的细胞上清液用ProteinG-Agarose纯化,最后分别收集在pH 9.0的预冷2 mol·L-1中和缓冲液 (neutralization buffer) 中。
表达产物Western blot检测分别收集质粒表达组、空载体组及未转染对照组CHO-DG44细胞培养上清。ProteinG-Agarose纯化后,用10% 分离胶和5% 浓缩胶进行SDS-PAGE电泳。电泳完毕后,电转印至硝酸纤维素膜,5%脱脂牛奶封闭,TBST洗膜后孵育二抗,山羊抗人IgG,稀释倍数为1∶2 500~1∶50 000显色,曝光。
胰岛素分泌实验INS-1细胞接种于24孔培养板,细胞数为2.56×105个/孔,在含10% FBS的RPMI 1640培养基中。第二天,将培养基更换为新鲜的克-林二氏重碳酸盐缓冲液 (KRB) 缓冲缺乏葡萄糖120 min。将细胞用2.8或16.8 mmol·L-1葡萄糖和不同浓度的0.01、0.1、1.0和5.0 mmol·L-1纯化的GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 融合蛋白在KRB缓冲液中培养 2 h。胰岛素水平使用大鼠胰岛素放射免疫测定 (RIA) 试剂盒测定。
GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 在小鼠体内的药代动力学雄性CD1小鼠腹腔内注射组 (n = 3) GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 使用剂量为1 mg·kg-1。血清样品于0、0.5、24、96、120、168和192 h后收集。从眼球后静脉处取静脉血样本,exendin-4 (Heloderma suspectum) RIA kit测定不同时间点血清exendin-4水平。Exendin-4和GLP-1分别腹腔注射0.12和0.1 mg·kg-1,前者于给药0、0.25、0.5、1、2、4和6 h 后经小鼠眼球后静脉处取静脉血,exendin-4 RIA Kit测定不同时间点血清exendin-4水平,后者于给药0、1、2、4、8和15 min后经小鼠眼球后静脉处取静脉血,GLP-1 RIA kit测定不同时间点血清GLP-1水平。
GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 抗小鼠糖尿病作用评估GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 是否有抗糖尿病的作用,使用多次低剂量链脲霉素(STZ,50 mg·kg-1·d-1,连续4次腹腔注射) 诱导糖尿病 (CD1) 小鼠,分为实验组、对照组、exendin-4组和GLP-1组,每组各 5只。实验组在喂养过程中每三天腹腔注射GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) (1 mg·kg-1),第1次给药时间是STZ给予前一天,exendin-4组和GLP-1组腹腔注射0.12和0.1 mg·kg-1,给药时间和方法同实验组,对照组腹腔注射磷酸盐缓冲液 (PBS),在指定时间测定血糖水平。
统计学分析采用SPSS14软件对数据进行统计处理,实验结果用均数 ± 标准差 (x ± s) 表示,参数统计采用重复测量的方差分析,P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
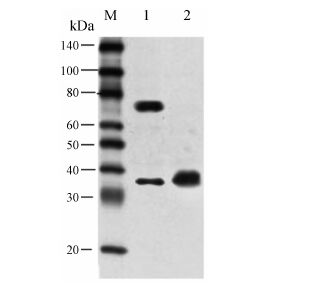
结果 1 GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 基因表达产物实验组细胞培养上清液经Western blot分析发现,质粒转染组有一个分子质量约为70 kDa的GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 二聚体和35 kDa的GLP-1- Exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 单体特异性条带与山羊抗人IgG特异结合。结果表明,在不加二硫苏糖醇 (DTT) 非还原条件下蛋白形成稳定的二聚物的70 kDa (条带1); 在加DTT还原条件下,形成单体结构 (条带2) (图 2)。
|
Figure 2 The expression of fusion protein GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) by Western blot. M: Maker; 1: Sample without DTT; 2: Sample add DTT |
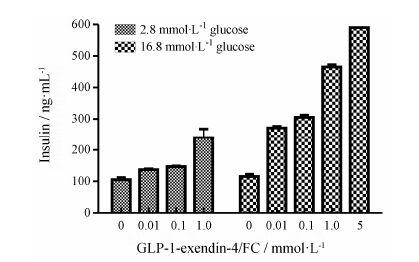
细胞用2.8或16.8 mmol·L-1葡萄糖和不同浓度的纯化GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 融合蛋白于KRB缓冲液中,胰岛素分泌RIA结果表明GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) 刺激的INS-1细胞胰岛素分泌量与葡萄糖浓度呈依赖方式。人体正常血糖浓度为3.9~6.1 mmol·L-1,本实验设计低于正常血糖浓度的2.8 mmol·L-1葡萄糖浓度和高于正常血糖浓度的16.8 mmol·L-1葡萄糖浓度。当葡萄糖浓度为2.8 mmol·L-1,融合蛋白浓度为0.01、0.1 mmol·L-1均无效果,1 mmol·L-1高浓度 融合蛋白时,胰岛素分泌量变大; 当葡萄糖浓度为16.8 mmol·L-1,融合蛋白为0.01 mmol·L-1时,胰岛素分泌量明显变大,随着融合蛋白浓度的增高,INS-1细胞胰岛素分泌增多,说明随着葡萄糖浓度的变化,GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 融合蛋白对INS-1细胞可调节胰岛素分泌,对糖尿病有调节血糖浓度作用。见图 3。
|
Figure 3 Stimulation of insulin secretion by GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) in INS-1 cells |
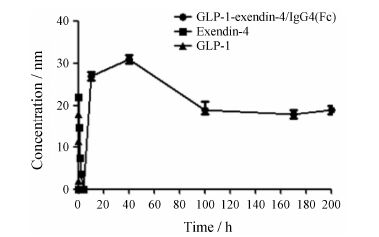
药代动力学数据显示,注射单一剂量GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 20~60 min后,CD1小鼠GLP-1的浓度明显增加。24 h时蛋白检测达到峰值,其后逐渐下降,200 h后仍然可以被检测到。而天然exendin-4的体内半衰期为 (1.39 ± 0.28) h,GLP-1体内半衰期为4 min。GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 半衰期与exendin-4和GLP-1比较具有非常显著差异 (P < 0.01)。见图 4。
|
Figure 4 Pharmacokinetic study of GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) fusion protein |
4个连续的腹腔注射低剂量STZ (50 mg·kg-1) 诱导小鼠糖尿病高血糖,各组每三天给药1次。PBS对照组在实验第10天血糖浓度持续升高保持在17 mmol·L-1左右; GLP-1和exendin-4组血糖浓度持续升高,exendin-4组血糖浓度低于GLP-1组; GLP-1- exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 组小鼠血糖水平保持相对恒定,维持在7.5 mmol·L-1左右,血糖浓度明显低于其他3组 (P < 0.01)。见图 5。
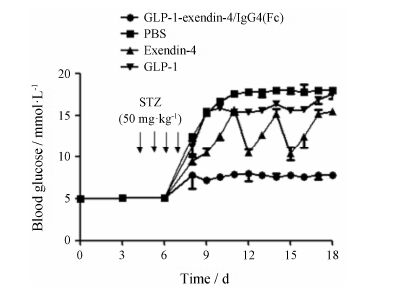
|
Figure 5 GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) improves glucose regulation in MDSD mice. STZ: Streptozotocin |
Exendin-4在毒蜥唾液中含量非常低,因此通过提取天然exendin-4不可能实现其临床应用,由于其半衰期较短,需每日皮下注射两次,给患者带来极大痛苦。IgG4Fc为大分子二聚体结构,在体内有较长的半衰期,本研究通过对GLP-1和exendin-4进行结构改造,采用基因工程方法获得了exendin-4与GLP-1及IgG4(Fc)融合的长效类似物,IgG4(Fc)显著延长了exendin-4与GLP-1半衰期,增强了其生物学效应。
为抵制DPP-N对hGLP-1的剪切作用,获得更稳定长效的hGLP-1,作者将hGLP-1第2位的Ala替换为Gly,获得活性更高的hGLP-1,在22位Phe替换为Glu,并使之与Fc进行融合。为了减少Fc融合对GLP- 1-exendin-4活性的影响,在exendin-4与IgG4Fc之间加入了一个柔性的连接肽 (GGGGS)3。由 于hGLP-1降血糖的作用具有血糖浓度依赖性,血糖正常时不促进胰岛素分泌。RIA结果表明GLP-1-exendin-4/ IgG4(Fc) 刺激的INS-1细胞胰岛素分泌量与葡萄糖浓度呈依赖方式。CD1小鼠的药代动力学研究表明,单次腹腔注射,该融合蛋白保持在较高的水平 (1周以上)。GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 对STZ诱导小鼠 具有抗糖尿病作用,控制血糖效果明显好于GLP-1和exendin-4。研究结果表明,GLP-1-exendin-4/IgG4(Fc) 可以作为替代GLP-1受体激动剂用于治疗糖尿病。
| [1] | Meier JJ, Nauck MA. Glucagon-like peptide 1(GLP-1) in biology and pathology[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2005, 21:91-117. |
| [2] | Holst JJ, Gromada J. Role of incretin hormones in the regulation of insulin secretion in diabetic and nondiabetic humans[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2004, 287:E199-E206. |
| [3] | Moens K, Heimberg H, Flamez D, et al. Expression and functional activity of glucagon, glucagon-like activity peptide 1, and glucose-dependent insulinotrophic peptide receptors in rat pancreatic islet cells[J]. Diabetes, 1996, 45:257-261. |
| [4] | Mayo KE, Miller LJ, Bataille D, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXXV. The glucagons receptor family[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2003, 55:167-194. |
| [5] | Trumper A, Trumper K, Trusheim A, et al. Glu-cose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is a growth factor for beta(INS-1) cells by pleiotropic signaling[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2001, 15:1559-1570. |
| [6] | Wrede CE, Dickson LM, Lingohr MK, et al. Protein kinase B/Akt prevent fatty acid-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta- |
| [7] | Wang Q, Li L, Xu E, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 regu-lates proliferation and apoptosis via activation of protein kinase B in pancreatic INS beta-cells[J]. Diabetologia, 2004, 47:478-487. |
| [8] | Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the islet beta-cell:augmentation of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis[J]. Endocrinology, 2003, 144:5145-5148. |
| [9] | Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system:gluca-gon-like prptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes[J]. Lancet, 2006, 368:1696-1705. |
| [10] | Kumar M, Hunag Y, Glinka Y, et al. In vivo expression of GLP-1/IgG-Fc fusion protein enhances beta-cell mass and protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetes[J]. Gene Ther, 2007, 14:162-172. |
| [11] | Kumar M, Hunag Y, Glinka Y, et al. In vivo expression of GLP-1/IgG-Fc fusion protein enhances beta-cell mass and protects against streptozotocin-induced diabetes[J]. Gene Ther, 2007, 14:162-172. |
| [12] | Walsh NA, Yusta B, DaCambra MP, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor activation in the rat intestinal mucosa[J]. Endocrinology, 2003, 144:4385-4392. |
| [13] | Trumper A, Trumper K, Trusheim A, et al. Glu-cose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is a growth factor for beta(INS-1) cells by pleiotropic signaling[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2001, 15:1559-1570. |
| [14] | Baggio LL, Kim JG, Drucker DJ. Chronic exposure to GLP-1R agonists promotes homologous GLP-1 receptor desensitization in vitro but does not attenuate GLP-1R-dependent glucose homeostasis in vivo[J]. Diabetes, 2005, 53:S205-S214. |
 2015, Vol. 50
2015, Vol. 50


