2. 天津市畜禽分子育种与生物技术重点实验室,天津 300381;
3. 天津市畜禽健康养殖工程技术中心,天津 300381;
4. 天津嘉立荷牧业集团有限公司,天津 300404;
5. 天津天食牛种业有限公司,天津 300404
2. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Animal Molecular Breeding and Biotechnology, Tianjin 300381, China;
3. Tianjin Engineering Research Center of Animal Healthy Farming, Tianjin 300381, China;
4. Tianjin Jialihe Animal Husbandry Group Company Limited, Tianjin 300404, China;
5. Tianjin Tianshi Cattle Seed Industry Co. Ltd., Tianjin 300404, China
天津是国内首个开展奶牛生产性能测定(DHI,dairy herd improvement)的地区,通过生产性能测定全覆盖,本市奶牛泌乳性能稳居全国领先水平,据统计,2022年全市DHI测定牧场平均日产奶量35.75 kg、平均乳脂率3.93%、平均乳蛋白率3.37%、305天产奶量10 412.16 kg、平均产犊间隔392.02 d。近年来,选种选配、精细养殖等技术手段在调节和改善奶牛泌乳性方面发挥了很大的作用,但环境、季节等自然因素对泌乳性能的影响研究相对较少,有研究表明产犊季节会引起奶牛生理周期的变化,导致其泌乳或繁殖指标的相应改变[1],张俊星等[2]研究同样证实产犊季节对所有健康、乳房健康、繁殖障碍、代谢障碍均有显著影响,所有健康问题在冬季产犊的奶牛中发生风险最低,秋季是冬季的1.28倍;刘灿风等[3]也证实夏季产犊奶牛的产奶量显著低于其他季节。也有研究表明季节对产奶量和各乳成分均有显著的影响,乳蛋白率和体细胞数在夏、秋季节显著高于冬、春季节[4],童雄等[5]研究表明夏季产奶量极显著低于其他季节。母牛产犊及生产受季节影响尚且有不同表现,那么牛只受出生季节的影响也不容忽视。
不同季节出生的奶牛受温度、环境等因素影响,会引起犊牛生长发育水平参差不齐,导致牛只后续生长、生产性能相应改变,本研究拟通过积累的DHI数据分析多因素对奶牛泌乳性能的影响,进一步研究不同出生季节对奶牛各胎次泌乳性能的影响,以期获得奶牛最适宜出生季节,指导牧场繁育管理工作合理化。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据来源收集2020—2023年天津市5个牧场13 706头牛164 767条DHI测定记录,包括日产奶量、乳脂率、乳蛋白率、305天产奶量,分析中国荷斯坦牛泌乳性能的影响因素。
1.2 数据整理本研究对收集到的数据进行质量控制,要求如下:牧场连续测定2年以上,测定数量超过1 000条;日产奶量1~60 kg;乳脂率2%~8%;乳蛋白率2%~6%;乳糖率2%~6%;305天产奶量≥3 000 kg。
最终使用5个牧场9 515头中国荷斯坦牛128 346条DHI测定记录进行分析。
1.3 效应水平划分根据不同出生场牛只数据对出生场效应进行划分,出生场共5个水平;根据不同出生年份牛只数据对出生年份效应进行划分,出生年数为2012—2021年共划分为10个水平;出生季节划分为4个水平,分别为3~5月(春季)、6~8月(夏季)、9~11月(秋季)、12月~次年2月(冬季);根据不同胎次对胎次效应进行划分,胎次共划分为3个水平,分别为1胎、2胎、3胎及以上;具体水平见表 1。
|
|
表 1 效应水平划分 Table 1 Effect level partition |
不同出生季节、不同胎次、不同场、出生年份等效应对泌乳性能的影响运用SPSS22.0软件中的一般线性模型进行分析,最小二乘方差分析模型如下:
出生季节不同胎次奶牛泌乳性能的显著性采用SPSS22.0软件中单因素方差分析进行分析。
1.5 泌乳曲线拟合用SPSS非线性回归程序拟合每个胎次的泌乳曲线,本研究选择Wood模型拟合泌乳曲线: Yt=atbe-ct。式中,t为泌乳天数;Yt为对应泌乳天数的日产奶量,a、b、c是模型参数,a是泌乳潜力(初始规模因子,与泌乳初始的产奶量有关),b是泌乳高峰过后产奶量下降的速度,c是达到泌乳高峰的速度;e为自然常数。
各参数初始值a=20,b=0.1,c=0.001,利用不同出生季节各胎次泌乳曲线拟合所得参数计算二级参数:泌乳高峰日MPY=b/c,高峰产奶量PY=a*(b/c)b*e-b ,泌乳持续力Per=-(b+1)ln(c),其中e为自然常数。
2 结果 2.1 不同出生季节牛只统计由图 1可以看出,春季、夏季、秋季和冬季出生牛只分别为1 646、2 823、3 219和1 824头,秋季出生牛头数最多;由于牧场牛只使用年限较低,统计牛只以1胎、2胎牛只为主,3胎及以上牛只数量最少。
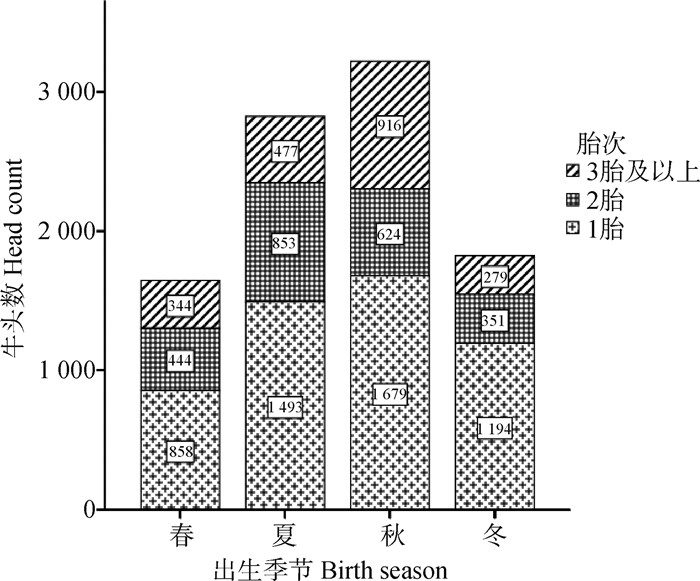
|
图 1 不同出生季节牛只统计 Fig. 1 Statistics of cattle in different birth seasons |
由表 2可见,不同出生季节、不同胎次、不同出生场及出生季节×胎次互作效应对泌乳性能均有极显著影响,不同出生年份对305天产奶量、平均乳脂率和平均乳蛋白率无显著性影响。
|
|
表 2 泌乳性能影响因素的显著性分析 Table 2 Significance analysis of factors affecting lactation performance |
由表 3可以看出,冬季出生牛只1胎及2胎次时日产奶量高于其它季节出生牛只,差异显著(P<0.05),夏季出生牛只1胎日产奶量均最低;平均乳脂率、平均乳蛋白率与日产奶量表现相反,春季出生牛只1胎次时平均乳脂率、平均乳蛋白率高于其它季节出生牛只,夏季出生牛只2胎、3胎及以上时平均乳脂率、平均乳蛋白率高于其它季节出生牛只,差异显著(P<0.05);秋季出生牛只2胎、3胎及以上时305天产奶量、成年当量高于其它季节出生牛只,夏季出生牛只305天产奶量、成年当量最低。
|
|
表 3 出生季节对不同胎次奶牛泌乳性能显著性分析 Table 3 Statistical analysis of lactation performance of dairy cows in different birth seasons |
由表 4可知,不同出生季节不同胎次牛只泌乳曲线各级参数表现不同。秋季出生牛只不同胎次时泌乳高峰日到来最早,秋季出生牛只2胎、3胎及以上牛只高峰奶量最高,但持续力较弱;冬季出生牛只1胎次时高峰奶量高于其它出生季节牛只;不同出生季节1胎牛泌乳高峰日普遍较2胎、3胎及以上牛只延后,1胎牛高峰奶量低于2胎、3胎及以上牛只,Wood模型拟合不同出生季节不同胎次的泌乳曲线如图 2~4所示,不同出生季节牛只各胎次泌乳曲线符合荷斯坦牛泌乳规律,一般泌乳高峰均出现在第2个测定日,在泌乳曲线图中也可以看出1胎次时冬季出生牛只高峰奶量最高,2、3胎次时秋季出生牛只高峰日到达最早、高峰奶量最高。
|
|
表 4 不同出生季节不同胎次牛泌乳曲线拟合参数表 Table 4 The fitting parameter table of lactation curve of different birth season and different parity |
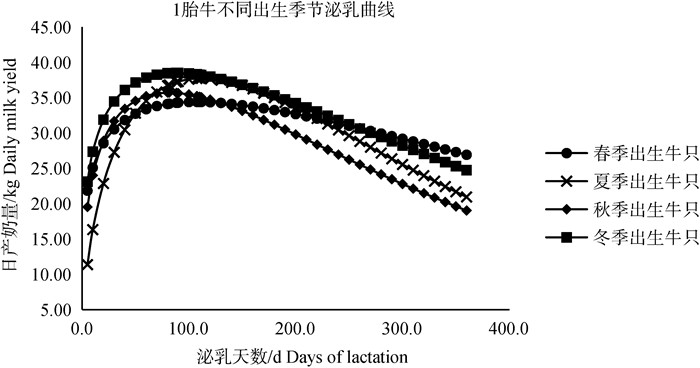
|
图 2 1胎牛只不同出生季节牛只泌乳曲线 Fig. 2 Lactation curve of cows in the first calving season |
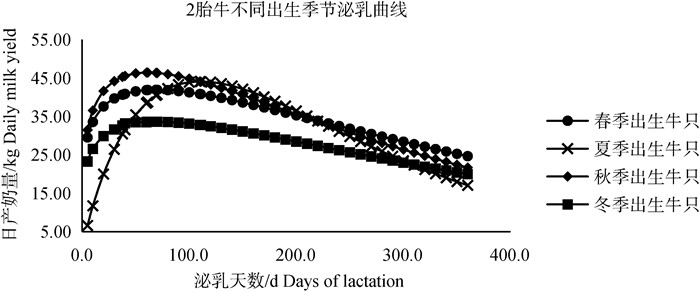
|
图 3 2胎牛只不同出生季节牛只泌乳曲线 Fig. 3 Lactation curve of cows in the second calving season |
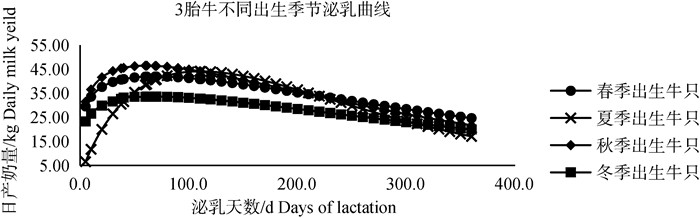
|
图 4 3胎及以上牛只不同出生季节牛只泌乳曲线 Fig. 4 Lactation curve of cows in the third and other calving seasons |
荷斯坦牛泌乳性能受遗传、营养、环境、疾病等多种因素影响,近年来泌乳性能的多因素分析大多基于不同年份[6]、不同胎次、初产月龄、产犊月龄[7]、产犊季节[8-9]、泌乳季节、泌乳阶段[10],不同体细胞水平[11]、不同产犊间隔[12]等因素,而不同“场年季”效应经常被做为多因素分析中的固定或随机效应,将出生场、出生年、出生季节作为一个影响因子进行分析。本研究结果显示,出生季节、胎次、出生场及出生季节×胎次互作效应对泌乳性能均有极显著影响(P<0.01),胎次、出生场对泌乳性能的影响与刘丽元[7]、郑雅祺[8]、梁艳[9]、林小觉[10]等的研究结果一致。胎次对泌乳性能的影响是由于不同胎次牛只身体发育水平不同,头胎牛身体发育尚不成熟,牛只在泌乳同时身体仍然在发育,从饲料中摄取的营养物质既要满足泌乳需要又要满足成长发育需要,所以泌乳性能较经产牛低,随生理成熟到3胎次时泌乳性能最佳;牛只出生场由于硬件条件、管理水平、营养调控、牛只选育等条件导致泌乳性能参差不齐。
3.2 出生季节对荷斯坦牛泌乳性能的影响出生季节对奶牛泌乳性能的影响尚未见报导。本研究发现,出生季节对奶牛泌乳性能有显著影响,分析是由于出生季节对犊牛生长发育的影响造成的。犊牛生长发育受到多个因素影响,主要包括围产期母牛的营养状况、犊牛在哺乳期和生长期营养供应、饲养管理以及外界环境等[13, 14]。
不同出生季节会引起犊牛行为、犊牛生长发育、犊牛血液生理生化指标的变化,导致牛只初配月龄、初产月龄及泌乳性能相应改变,霍小凯等[15]研究表明不同季节出生的犊牛哺乳期的体高、胸围和体斜长有一定差异,以秋季出生的发育最好;出生季节对犊牛生长发育的影响一方面可能是与温度导致的牛体舒适度相关,另一方面牛只泌乳性能的发挥首先与其母亲围产期营养状况息息相关,母牛围产期营养良好,在胎儿快速发育阶段便能提供充足的营养物质,犊牛出生后相同护理条件下便能发育更好。孙宝丽等[16]研究表明,秋季的干奶牛粪便中的有机质、全氮、全钾、铜含量均显著低于其他3个季节,说明秋季干奶牛营养物质吸收更充分,供给胎儿的营养物质更多;再者,冯亚杰等[17]研究表明炎热天气下肾上腺皮质机能亢进、糖皮质激素分泌增加,造成犊牛免疫机能抑制、采食量下降,从而导致机体白细胞增加、血钾、血钙等含量降低,影响机体发育;而冷刺激时引起机体的防御反应,提高了机体抵御外界温度变化的能力,故夏季或冬季犊牛发育会受影响。
徐明等[18]进一步研究显示,犊牛哺乳期生长发育状况显著影响犊牛成年后各胎次的峰值奶量和峰值日;也有研究表明,犊牛哺乳期平均日增重与成年后305天产奶量呈正相关趋势,哺乳期日增重达到1 kg·d-1,头胎牛的胎次产奶量增加1 100~1 500 kg[19-21]。犊牛哺乳期一般为60 d左右,秋季出生犊牛在断奶后即迎来寒冷的冬季,受气候环境影响,犊牛转育成阶段采食量即要满足身体生长发育又要抵御低温,故日增重变缓,Krpálková等[22]研究表明,5~14月龄犊牛平均日增重0.850~0.949 kg(中等组)时其头胎牛产奶量、峰值奶量最佳。本研究发现,秋季出生牛只经产后各项生产性能与以上研究结果一致,但头胎牛各项生产性能指标未见明显规律,应该是与牧场对育成牛的饲养管理有关。
4 结论天津地区荷斯坦牛出生季节、胎次、出生场及出生季节×胎次互作效应对泌乳性能均有极显著影响;秋季出生牛只2、3胎次时305天产奶量最高、泌乳高峰到来最早、高峰奶量最高。
| [1] |
王欣荣, 刘婷, 苏东伟, 等. 胎次、犊牛性别和初生重及产犊季节对奶牛繁殖性能的影响[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2017, 38(3): 52-55. WANG X R, LIU T, SU D W, et al. Effect of parity, calves' gender, birth weight and calving season on reproductive traits of Holstein cows[J]. Acta Ecologae Animalis Domastici, 2017, 38(3): 52-55. (in Chinese) |
| [2] |
张俊星, 张海亮, 韩丽云, 等. 宁夏地区荷斯坦泌乳牛健康性状影响因素分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(6): 2389-2401. ZHANG J X, ZHANG H L, HAN L Y, et al. Analysis on the influencing factors of wellness traits in Holstein lactating cows in Ningxia[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(6): 2389-2401. (in Chinese) |
| [3] |
刘灿风, 王澳, 马龙刚, 等. 宁夏地区荷斯坦牛泌乳曲线拟合及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2023, 59(3): 95-102. LIU C F, WANG A, MA L G, et al. Fitting of Holstein lactation curve and its influencing factors in Ningxia[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2023, 59(3): 95-102. (in Chinese) |
| [4] |
韩晓晖, 周震, 吴泽标, 等. 胎次、泌乳阶段和季节对华南地区荷斯坦奶牛产奶量和乳成分的影响[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2021, 42(4): 52-56. HAN X H, ZHOU Z, WU Z B, et al. Effects of parity, lactation stage and season on milk yield and milk composition of Holstein cows in South China[J]. Acta Ecologae Animalis Domastici, 2021, 42(4): 52-56. (in Chinese) |
| [5] |
童雄, 王秀娟, 李大刚, 等. 华南地区荷斯坦牛泌乳性能在季节、胎次、泌乳时期影响下的变化规律[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2018, 39(2): 16-22. TONG X, WANG X J, LI D G, et al. Variation in milk performance of Holstein dairy cows under the effects of season, parity and lactation stage in South China[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2018, 39(2): 16-22. (in Chinese) |
| [6] |
叶东东, 张孔杰, 热西提·阿不都热合曼, 等. 影响荷斯坦奶牛305d产奶量的因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(1): 148-152. YE D D, ZHANG K J, REXITI A, et al. Analysis of factors influencing 305-days milk yield of Holstein dairy cow[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(1): 148-152. (in Chinese) |
| [7] |
刘丽元, 田佳, 温万, 等. 宁夏地区荷斯坦牛产奶量和产犊间隔影响因素分析[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(9): 68-74. LIU L Y, TIAN J, WEN W, et al. Factors influencing milk yield and calving interval of Holstein dairy cow in Ningxia area[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(9): 68-74. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
郑雅祺, 吴通, 严彦平. 西安地区胎次和季节对奶牛泌乳性能的影响[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2023, 19(6): 137-140. ZHENG Y Q, WU T, YAN Y P. Effect of parity and season on lactation performance of dairy cows in Xi'an[J]. The Chinese Livestock and Poultry Breeding, 2023, 19(6): 137-140. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
梁艳, 张强, 唐程, 等. 影响荷斯坦牛305d泌乳性能的因素分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(4): 56-59, 65. LIANG Y, ZHANG Q, TANG C, et al. Analysis of factors affecting 305-days milking traits of Holstein cows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56(4): 56-59, 65. (in Chinese) |
| [10] |
林小觉, 刘德武, 邓铭, 等. 影响华南华北地区奶牛泌乳性能的非遗传因素研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2023, 59(5): 143-149. LIN X J, LIU D W, DENG M, et al. Study on non-genetic factors affecting lactation performance of dairy cows in north and South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2023, 59(5): 143-149. (in Chinese) |
| [11] |
余诗强, 李留学, 赵小博, 等. 不同泌乳阶段和体细胞水平的中国荷斯坦奶牛泌乳性能差异和相关性研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(3): 1003-1014. YU S Q, LI L X, ZHAO X B, et al. Differences and correlations of lactation performance in Chinese Holstein dairy cows at different lactation stages and somatic levels[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2023, 54(3): 1003-1014. (in Chinese) |
| [12] |
黄锡霞, 热西提·阿不都热依木, 田月珍, 等. 非遗传因素对荷斯坦牛305天产奶量的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2009, 36(10): 115-118. HUANG X X, ABUDUREYIMU R, TIAN Y Z, et al. Analysis of non-genetic factors influencing 305-day milk yield in Holstein[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2009, 36(10): 115-118. (in Chinese) |
| [13] |
CANTOR M C, STANTON A L, COMBS D K, et al. Effect of milk feeding strategy and lactic acid probiotics on growth and behavior of dairy calves fed using an automated feeding system[J]. J Anim Sci, 2019, 97(3): 1052-1065. |
| [14] |
陆相龙, 苏衍菁, 杨志强, 等. 犊牛生长发育影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程技术, 2020, 40(35): 88-89. LU X L, SU Y J, YANG Z Q, et al. Analysis of influencing factors on growth and development of calves[J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2020, 40(35): 88-89. (in Chinese) |
| [15] |
霍小凯, 王加启, 王建平, 等. 不同出生季节对犊牛体尺发育的影响[J]. 中国奶牛, 2008(12): 35-37. HUO X K, WANG J Q, WANG J P, et al. The effects of different seasons on the growth of body measurements in calves[J]. Chinese Cows, 2008(12): 35-37. (in Chinese) |
| [16] |
孙宝丽, 陈汝能, 吴银宝, 等. 不同季节、不同生理阶段奶牛粪便的特性[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(8): 187-190. SUN B L, CHEN R N, WU Y B, et al. Characteristics of dairy manure in different seasons and physiological stages[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(8): 187-190. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
冯亚杰, 张子敬, 施巧婷, 等. 季节变化对夏南牛血液生理生化指标的影响[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2016(5): 41-43. FENG Y J, ZHANG Z J, SHI Q T, et al. Effects of seasonal variation on blood physiological and biochemical indexes of Xianan cattle[J]. Shanghai Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2016(5): 41-43. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
徐明, 吴东霖, 王鹏宇, 等. 犊牛生长发育对成年奶牛高峰奶产量和峰值日的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58(10): 178-185. XU M, WU D L, WANG P Y, et al. Effects of growth and development of calves on peak milk yield and peak day in adult dairy cows[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58(10): 178-185. (in Chinese) |
| [19] |
HOSEYNI F, MAHJOUBI E, ZAHMATKESH D, et al. Effects of dam parity and pre-weaning average daily gain of Holstein calves on future milk production[J]. J Dairy Res, 2016, 83(4): 453-455. |
| [20] |
SOBERON F, RAFFRENATO E, EVERETT R W, et al. Preweaning milk replacer intake and effects on long-term productivity of dairy calves[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2012, 95(2): 783-793. |
| [21] |
SOBERON F, VAN AMBURGH M E. The effect of nutrient intake from milk or milk replacer of preweaned dairy calves on lactation milk yield as adults: A meta-analysis of current data[J]. J Anim Sci, 2013, 91(2): 706-712. |
| [22] |
KRPÁLKOVÁ L, CABRERA V E, VACEK M, et al. Effect of prepubertal and postpubertal growth and age at first calving on production and reproduction traits during the first 3 lactations in Holstein dairy cattle[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2014, 97(5): 3017-3027. |
(编辑 郭云雁)



