禽腺病毒(fowl adenovirus, FAdV)分为5个种(A~E),12个血清型[1]。临床上与FAdV感染相关的主要是FAdV-4引起的心包积液综合征(HPS)及FAdV-8b引起的包涵体肝炎(IBH),给我国养禽业造成了巨大的经济损失[2-4]。纤突蛋白(Fiber)是FAdV的主要结构蛋白,能够编码中和抗原表位,参与体液免疫,使动物产生中和抗体[5-7]。其中,FAdV-4有两个Fiber(Fiber1和Fiber2),FAdV-8b只有一个Fiber[8-10]。Gupta等[11]研究表明重组fiber蛋白临床保护率可达到82.7%,能够很好地阻止包涵体肝炎的发生,对预防由FAdV-8b引起的包涵体肝炎具有很好的防制效果。Luca等[9]研究表明FAdV-8b的Fiber蛋白免疫后对子代有一定的保护效果。研究证实重组fiber2蛋白作为免疫原对FAdV-4引起的心包积液综合征的防控具有很好的效果[12-14],可作为FAdV亚单位疫苗的候选蛋白,具有很好的应用前景。我们前期将制备的FAdV-4和FAdV-8b单因子血清进行细胞交叉中和试验,结果表明FAdV-4和FAdV-8b的血清不能相互中和[15]。目前,尚未见有关禽腺病毒FAdV-4和FAdV-8b二价亚单位疫苗的研究,研发针对FAdV-4和FAdV-8b的二价疫苗具有重要的应用价值。本研究将FAdV-4 fiber2和FAdV-8b fiber的全长蛋白、截短蛋白及二价融合蛋白成功在大肠杆菌中表达,并对其免疫原性进行了评价,以期为禽腺病毒FAdV-4和FAdV-8b二价亚单位疫苗的研发奠定基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 主要材料与试剂1.1.1 主要试剂 Ⅰ群禽腺病毒FAdV-4和FAdV-8b为青岛农业大学预防兽医实验室分离、鉴定并保存;pCold-TF载体,大肠杆菌DH5ɑ、BL21(DE3),FAdV-4和FAdV-8b阳性血清均由青岛农业大学预防兽医实验室保存;T3 Super PCR Mix购自北京擎科生物科技有限公司;T4 DNA连接酶购自TaKaRa公司;His-Tagged蛋白纯化试剂盒购自康为世纪生物科技有限公司;HRP标记兔抗鸡IgG抗体、7号白油、BCA蛋白浓度试剂盒均购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;反转录试剂盒、SYBR Green Pro Taq HS预混型qPCR试剂盒购自湖南艾科瑞生物工程有限公司。
1.1.2 实验动物 150枚SPF鸡胚购自北京勃林格殷格翰维通生物技术有限公司;SPF雏鸡由SPF鸡胚自行孵化并在负压隔离器中饲养至所需日龄。
1.2 重组表达质粒的构建及鉴定根据FAdV-4 fiber2和FAdV-8b fiber基因序列设计截短片段(FP和BP)、融合片段(BP-FP)及全长(FL和BL)引物,引物送生工生物工程有限公司合成,引物序列见表 1。
|
|
表 1 FAdV-4 fiber-2和FAdV-8b fiber基因扩增引物 Table 1 Primers of FAdV-4 fiber-2 and FAdV-8b fiber gene |
以实验室保存的FAdV-4和FAdV-8b毒株的DNA为模板,使用FP、FL、BP、BL引物扩增目的基因,PCR反应程序为95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸90 s,35个循环;72 ℃终延伸10 min。PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶回收。使用BP-F和F-Linker引物、Linker-F2和FP-R引物分别进行PCR扩增,PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳回收后各取1 μL混合当模板,使用BP-F和FP-R引物扩增BP-FP目的基因,PCR反应程序同上,进行琼脂糖凝胶回收。将FP、FL、BP、BL、BP-FP回收产物和pCold-TF空载体用Xba Ⅰ和Hind Ⅲ双酶切,用T4 DNA连接酶连接纯化回收的酶切产物,转化DH5ɑ感受态细胞,提取转化子质粒,进行酶切验证和测序鉴定。
1.3 重组蛋白的表达及纯化将测序正确的5个重组质粒转化BL21(DE3)感受态细胞,涂布于氨苄抗性的LB平板,37 ℃过夜培养。挑单菌落接种于氨苄抗性的LB培养基中,37 ℃、220 r·min-1培养至OD600 nm为0.6左右,加入1 mol·L-1的IPTG,16 ℃诱导表达12 h。收集表达后的菌体沉淀,冰浴超声破碎菌体,12 000 r·min-1离心5 min,SDS-PAGE分析蛋白表达情况。超声破碎后菌体上清按照His-Tagged蛋白纯化试剂盒说明书进行目的蛋白纯化。
1.4 重组蛋白的Western blot鉴定纯化后的蛋白经SDS-PAGE电泳后湿转至PVDF膜,使用FAdV-4和FAdV-8b阳性血清为一抗,HRP标记兔抗鸡IgG抗体为二抗,对纯化蛋白进行Western blot鉴定,用ECL化学发光后,凝胶成像系统观察并拍照。
1.5 重组蛋白免疫效果评价1.5.1 动物分组及处理 将纯化后的蛋白与油相1∶2混合。108只1日龄SPF鸡随机分成9组。1~6组(FL、FP、BP-FP4、BP-FP8b、BL、BP)为免疫组,7日龄皮下注射疫苗100 μg·只-1,14日龄进行二免;7~8组(C4、C8b)为攻毒对照组,9组(C)为空白对照组。二免后7 d,FL、FP、BP-FP4、C4组肌肉注射FAdV-4(107.5 TCID50·mL -1),BL、BP、BP-FP8b、C8b组肌肉注射FAdV-8b(107.5 TCID50·mL -1),攻毒剂量为0.2 mL·只-1。在免疫前,免疫后7、14、21 d心脏采血并分离血清;攻毒后3、7 d采集攻FAdV-8b组的泄殖腔拭子;攻毒后7 d采集各组鸡肝脏样品。
1.5.2 抗体水平检测 用间接ELISA进行抗体水平检测,采用浓度为1 μg·mL-1的BP-FP蛋白包被过夜,用1% BSA 37 ℃封闭1 h,洗后加入1∶1 000稀释的血清37 ℃孵育1 h,洗后加入1∶5 000稀释的兔抗鸡IgG-HRP 37 ℃孵育1 h,洗后加入显色液避光孵育30 min,终止显色后读取OD450 nm值。
1.5.3 免疫攻毒保护 攻毒后每天观察鸡的健康状况,记录死亡数量,计算存活率。
1.5.4 排毒量检测 所有攻FAdV-8b的鸡在攻毒3、7 d后取泄殖腔拭子置于含有抗生素的无菌生理盐水中,提取DNA,经qPCR检测排毒量。根据FAdV-8b Hexon基因与其它血清型禽腺病毒差异显著的保守区域设计引物,引物序列为F 5′-CTACGGCAACAGCTGGGGCAA-3′;R 5′-TGTGCAGTGGTGTCTAAC-3′,引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。反应体系:模板1 μL,上、下游引物各0.4 μL,2×SYBR Mix 10 μL,加水至20 μL。反应程序:95 ℃预变性30 s;95 ℃5 s,60 ℃30 s,40个循环;熔解曲线反应条件为95 ℃10 s,65 ℃ 60 s,97 ℃1 s。每个样本设3个重复。按照公式拷贝数(拷贝·μL -1)=6.02×1023(拷贝·mol-1)×质粒浓度(ng·μL -1)×10-9/[(载体分子量+插入片段分子量)×660](g·mol -1)绘制标准曲线。
1.5.5 细胞因子mRNA表达水平检测 根据文献[16-17]合成IL-4、TNF-α、IFN-γ和内参基因β-actin引物。取攻毒7 d后所有鸡的肝脏进行研磨,提取RNA,经RT-PCR反转录成cDNA,以β-actin作为内参基因经qPCR检测IL-4、IFN-γ和TNF-α mRNA表达水平。qPCR反应程序同“1.5.4”。
1.6 数据分析抗体水平、排毒量及细胞因子mRNA表达水平检测数据均用Prism 5.0软件进行统计分析,使用t检验法进行差异性显著分析,P<0.05代表差异显著。
2 结果 2.1 重组表达载体的构建及鉴定如图 1所示,重组质粒经双酶切后,均出现载体片段和目的片段,FL、FP、BP-FP、BL和BP基因大小与预期一致,表明原核重组质粒构建成功。经测序进一步确定重组表达质粒构建成功。

|
M.相对分子质量标准;1.FL;2.FP;3.BP-FP;4.BL;5. BP M. Standard molecular weight; 1.FL; 2.FP; 3.BP-FP; 4.BL; 5.BP 图 1 重组表达质粒的双酶切鉴定 Fig. 1 Results of double digestion of recombinant expression plasmids |
经SDS-PAGE检测,结果如图 2A所示,成功表达出大小为104.9、70.6、92.3、100.3和69.2 ku的重组蛋白,且均在上清中以可溶性形式表达。将BP-FP、BL、BP、FL和FP蛋白上清用蛋白纯化试剂盒纯化,纯化后的蛋白样品进行SDS-PAGE分析(图 2B)。

|
M.标准分子质量;1.BL沉淀;2.BL上清;3.BP沉淀;4.BP上清;5.BP-FP上清;6.BP-FP沉淀;7.FL上清;8.FL沉淀;9.FP上清;10.FP沉淀;11.FP;12.FL;13.BP-FP;14.BL;15.BP M. Standard molecular weight; 1.BL precipitation; 2.BL supernatant; 3.BP precipitation; 4.BP supernatant; 5.BP-FP supernatant; 6.BP-FP precipitation; 7.FL supernatant; 8.FL precipitation; 9.FP supernatant; 10.FP precipitation; 11.FP; 12.FL; 13.BP-FP; 14.BL; 15.BP 图 2 各样品中重组蛋白(A)及其纯化后(B)的SDS-PAGE分析 Fig. 2 SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant proteins in each sample (A) and their purified proteins (B) |
重组蛋白Western blot鉴定结果如图 3,FP、FL、BP-FP、BP、BL蛋白条带大小分别为69.2、100.3、92.3、70.6、104.9 ku,与预期大小一致,表明重组蛋白在原核系统中成功表达。

|
A.FAdV-4阳性血清作一抗;B.FAdV-8b阳性血清作一抗;M.标准分子质量;A1~A3.FP、FL和BP-FP;B1~B3.BP、BL和BP-FP A. FAdV-4 positive serum as primary antibody; B. FAdV-8b positive serum as primary antibody; M.Standard molecular weight; A1-A3.FP, FL, and BP-FP; B1-B3.BP, BL, and BP-FP 图 3 重组蛋白的Western blot Fig. 3 Western blot of recombine protein |
2.4.1 抗体水平检测 ELISA抗体检测结果如图 4所示,BL、FL、BP-FP、BP和FP组在免疫后7~14 d各组抗体均呈上升趋势,免疫后14~21 d抗体水平没有明显变化,免疫组抗体水平显著高于阴性对照组(P<0.05),但免疫组抗体水平无显著差异(P>0.05)。

|
“**”表示差异显著,无标注表示差异不显著。下同 "**"means significant difference, and no mark means insignificant difference. The same as below 图 4 鸡免疫后血清抗体水平 Fig. 4 Serum antibody levels of chickens after immunization |
2.4.2 免疫攻毒保护 攻毒后各组SPF鸡的存活情况如图 5所示,C4组存活率为25%,BP-FP4组存活率为58.3%,其它组鸡存活率均为100%。

|
图 5 攻毒7 d后鸡存活率 Fig. 5 Survival rate of chickens at 7 d post-challenge |
2.4.3 排毒量测定 以log(X)为X轴,Ct值为Y轴绘制标准曲线,结果如图 6,标准曲线为y=-2.956 1x+38.826,R2=0.99。

|
图 6 FAdV-8b实时荧光定量PCR标准曲线 Fig. 6 The standard curve for Real-time PCR of FAdV-8b |
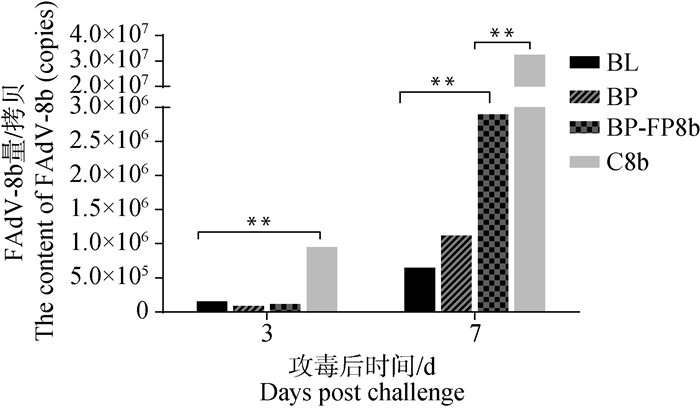
排毒量检测结果如图 7,在攻毒3、7 d后,C8b组排毒量分别为9.48×105和3.24×107拷贝·μL -1, BL、BP和BP-FP8b组排毒量显著低于C8b组(P<0.05)。攻毒后7 d BL和BP组排毒量分别为6.4×105和1.1×106拷贝·μL -1,显著低于BP-FP8b组(P<0.05),BP与BL组之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
|
图 7 FAdV-8b攻毒后泄殖腔拭子排毒量 Fig. 7 Viral loads of cloacal swabs challenged with FAdV-8b |
2.4.4 细胞因子mRNA表达水平测定 qPCR检测肝脏中IL-4、IFN-γ和TNF-α mRNA表达水平,结果如图 8。免疫组细胞因子mRNA表达水平均显著高于阴性对照组(P<0.05),FP组IL-4和IFN-γ mRNA表达水平分别为5.7和8.5,显著高于FL组(P<0.05);BP组IL-4 mRNA表达水平为10.4,显著高于BL组(P<0.05);BL组和BP组TNF-α mRNA表达水平分别为5.73和4.45,二者差异不显著(P>0.05)。

|
A~C.不同免疫组FAdV-4攻毒;D~F.不同免疫组FAdV-8b攻毒 A-C. Different immune groups post FAdV-4 challenge; D-F. Different immune groups post FAdV-8b challenge 图 8 各免疫组攻毒后细胞因子mRNA表达水平 Fig. 8 mRNA expression level of cytokines in different immune groups post challenge |
2.4.5 肝脏组织病理观察 肝脏病理组织切片如图 9所示,C4组肝细胞严重充血、水肿,肝细胞空泡变性、坏死,存在嗜碱性包涵体和严重的炎性细胞浸润,C8b组肝细胞中存在包涵体和大量空泡变性。C组无病变。FL组与BL组未见明显空泡变性,无炎性灶。FP组与BP组有轻微炎性细胞浸润。BP-FP4与BP-FP8b组肝细胞能观察到轻微空泡变性。

|
A.FL组;B.FP组;C.BP-FP4组;D: BL组;E.BP组;F.BP-FP8b组;G.C4组;H.C8b组;I.C组 A. FL group; B. FP group; C. BP-FP4 group; D: BL group; E. BP group; F. BP-FP8b group; G. C4 group; H. C8b group; I. C group 图 9 肝组织病理观察(100×) Fig. 9 Histopathological observation in liver (100×) |
近年来,由FAdV-4引起的HPS和FAdV-8b引起的IBH在肉鸡中有流行暴发趋势[18-21],给养禽业带来了巨大的经济损失。不同血清型FAdV混合感染的情况在养殖场普遍存在。疫苗是防控疫病的有效手段之一,目前我国还未有同时防控HPS和IBH的商品化疫苗,研制防控FAdV-4和FAdV-8b的二价疫苗具有重要意义[22-24]。
本研究通过软件分析得到FAdV-4 fiber2和FAdV-8b fiber亲水性和抗原性较好的区域位于后半段,与knob-s区域所在位置一致。因此选取了fiber2基因片段850~1 440 bp和fiber基因片段937~1 566 bp,并通过(GGGGS)3 15个氨基酸的linker串联表达。5种重组蛋白均能在上清液中稳定可溶表达,避免了包涵体复性对蛋白结构的影响。BP和FP的表达量明显高于BL和FL,表明截短的蛋白比全长蛋白更易表达,这可能与所选基因片段的长度有关,这些结果与Fingerut等[25]研究结果一致。本研究基于大肠杆菌表达的FL、FP、BP-FP、BL、BP 5个蛋白制备了亚单位疫苗,攻毒免疫保护显示,除BP-FP4组存活率为58.3%,其它组存活率均为100%;肝脏病理切片观察发现,攻毒组肝脏病变最严重,FP组与BP组次之,FL组与BL组无明显病变,表明截短蛋白和全长蛋白免疫保护效果优于二价融合蛋白。FAdV-8b泄殖腔拭子排毒量结果显示,BP-FP8b排毒量显著高于BL和BP,但仍显著低于FAdV-8b攻毒对照组,表明BP-FP重组蛋白的保护效果弱于单价蛋白。BP-FP4组的存活率为58.3%,低于单价蛋白,但高于对照组,表明BP-FP重组蛋白可诱导一定程度的免疫保护。
间接ELISA法检测重组蛋白免疫后鸡的抗体水平,具有特异性强、灵敏度高、重复性好等优点[26-27]。5种重组蛋白均能有效诱导体液免疫反应,仅经过首免即可获得较高水平的抗体,具有良好的免疫原性。与对照组相比,5种重组蛋白抗体水平均显著升高,免疫组在受免后14 d血清抗体水平下降,与第二次免疫后抗体水平相似。抗体水平达到峰值后,依次为FL>FP>BP-FP>BL>BP, BL组与BP组差异不显著。由此可见,全长蛋白刺激SPF鸡产生抗体的能力优于截短蛋白,这可能与全长蛋白具有其他重要的表位有关。Th1细胞主要分泌IFN-γ和TNF-ɑ等细胞因子,参与调节细胞免疫,介导细胞免疫应答;Th2细胞主要分泌IL-4和IL-10,可以激活B细胞,促进中和抗体的产生[28-29]。研究表明,FAdV-4灭活苗可刺激动物机体产生较高水平的IL-4和IFN-γ且显著高于阴性对照组[30]。本研究结果显示,免疫组均显著高于阴性对照组,表明全长蛋白、截短蛋白和二价融合蛋白均能诱导产生细胞免疫,FP组IL-4和IFN-γ mRNA表达水平显著高于FL组,表明FP蛋白刺激机体产生IL-4和IFN-γ的水平高于FL蛋白。
4 结论FAdV-4 fiber2和FAdV-8b fiber截短蛋白和全长蛋白免疫保护效果优于二价融合蛋白,截短蛋白可替代全长蛋白用于禽腺病毒亚单位疫苗的制备。
| [1] |
EL-SHALL N A, EL-HAMID H S A, ELKADY M F, et al. Epidemiology, pathology, prevention, and control strategies of inclusion body hepatitis and hepatitis-hydropericardium syndrome in poultry: a comprehensive review[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9: 963199. DOI:10.3389/fvets.2022.963199 |
| [2] |
LIU A J, ZHANG Y, CUI H Y, et al. Advances in vaccine development of the emerging novel genotype fowl adenovirus 4[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 916290. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2022.916290 |
| [3] |
WANG Z, ZHAO J. Pathogenesis of hypervirulent fowl adenovirus serotype 4:the contributions of viral and host factors[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(8): 741. DOI:10.3390/v11080741 |
| [4] |
王白玉, 黄庆, 乔麒龙, 等. 表达FAdV-8b Fiber蛋白重组FAdV-4的构建与鉴定[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2022, 42(2): 230-236. WANG B Y, HUANG Q, QIAO Q L, et al. Construction and identification of recombinant fowl adenovirus 4 expressing the fiber gene of fowl adenovirus 8b[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2022, 42(2): 230-236. (in Chinese) |
| [5] |
SOHAIMI N M, HAIR-BEJO M. A recent perspective on fiber and hexon genes proteins analyses of fowl adenovirus toward virus infectivity-A review[J]. Open Vet J, 2021, 11(4): 569-580. DOI:10.5455/OVJ.2021.v11.i4.6 |
| [6] |
CHEN L, YIN L J, ZHOU Q F, et al. Epidemiological investigation of fowl adenovirus infections in poultry in China during 2015-2018[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2019, 15(1): 271. DOI:10.1186/s12917-019-1969-7 |
| [7] |
HARAKUNI T, ANDOH K, SAKAMOTO R I, et al. Fiber knob domain lacking the shaft sequence but fused to a coiled coil is a candidate subunit vaccine against egg-drop syndrome[J]. Vaccine, 2016, 34(27): 3184-3190. DOI:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.005 |
| [8] |
GUARDADO-CALVO P, LLAMAS-SAIZ A L, FOX G C, et al. Structure of the C-terminal head domain of the fowl adenovirus type 1 long fiber[J]. J Gen Virol, 2007, 88(9): 2407-2416. DOI:10.1099/vir.0.82845-0 |
| [9] |
DE LUCA C, SCHACHNER A, MITRA T, et al. Fowl adenovirus (FAdV) fiber-based vaccine against inclusion body hepatitis (IBH) provides type-specific protection guided by humoral immunity and regulation of B and T cell response[J]. Vet Res, 2020, 51(1): 143. DOI:10.1186/s13567-020-00869-8 |
| [10] |
郭瑞珍, 苏冰倩, 王棋, 等. 禽腺病毒血清4型Fiber2蛋白单克隆抗体制备及其抗原表位鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52(7): 2000-2012. GUO R Z, SU B Q, WANG Q, et al. Preparation of the monoclonal antibody against the serotype 4 fowl adenovirus fiber2 protein and identification of the antigenic epitope[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(7): 2000-2012. (in Chinese) |
| [11] |
GUPTA A, AHMED K A, AYALEW L E, et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of virus-like particles and recombinant fiber proteins in broiler-breeder vaccination against fowl adenovirus (FAdV)-8b[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(20): 2716-2722. DOI:10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.075 |
| [12] |
SCHACHNER A, MAREK A, JASKULSKA B, et al. Recombinant FAdV-4 fiber-2 protein protects chickens against hepatitis-hydropericardium syndrome (HHS)[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(9): 1086-1092. DOI:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.12.056 |
| [13] |
LI P H, ZHENG P P, ZHANG T F, et al. Fowl adenovirus serotype 4:epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostic detection, and vaccine strategies[J]. Poult Sci, 2017, 96(8): 2630-2640. DOI:10.3382/ps/pex087 |
| [14] |
JIA Z P, PAN X H, ZHI W J, et al. Probiotics surface-delivering fiber2 protein of fowl adenovirus 4 stimulate protective immunity against hepatitis-hydropericardium syndrome in chickens[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 919100. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2022.919100 |
| [15] |
邹开宇, 高倩文, 江之瑶, 等. 我国Ⅰ群禽腺病毒主要流行血清型间交叉中和作用的初步研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018(11): 150-153. ZOU K Y, GAO Q W, JIANG Z Y, et al. Study on the cross-neutralization between the main serotypes of group Ⅰ fowl adenovirus in China[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2018(11): 150-153. (in Chinese) |
| [16] |
吴志金. 鸡传染性支气管炎病毒广西分离株的致病性研究和细胞因子实时荧光RT-PCR相对定量检测方法的建立[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2013. WU Z J. Pathogenicity of infectious bronchitis virus Guangxi isolates and development of real-time RT-PCR assays for chicken cytokines[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2013. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
MENG K, YUAN X Y, YU J, et al. Identification, Pathogenicity of novel fowl adenovirus serotype 4 SDJN0105 in Shandong, China and immunoprotective evaluation of the newly developed inactivated oil-emulsion FAdV-4 vaccine[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(7): 627. DOI:10.3390/v11070627 |
| [18] |
YIN L J, CHEN L, LUO Y Y, et al. Recombinant fiber-2 protein protects Muscovy ducks against duck adenovirus 3 (DAdV-3)[J]. Virology, 2019, 526: 99-104. DOI:10.1016/j.virol.2018.10.011 |
| [19] |
ZHANG X H, ZHONG Y J, ZHOU Z H, et al. Molecular characterization, phylogeny analysis and pathogenicity of a Muscovy duck adenovirus strain isolated in China in 2014[J]. Virology, 2016, 493: 12-21. DOI:10.1016/j.virol.2016.03.004 |
| [20] |
TIAN K Y, GUO H F, LI N, et al. Protection of chickens against hepatitis-hydropericardium syndrome and newcastle disease with a recombinant Newcastle disease virus vaccine expressing the fowl adenovirus serotype 4 fiber-2 protein[J]. Vaccine, 2020, 38(8): 1989-1997. DOI:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.01.006 |
| [21] |
SONG Y P, WEI Q, LIU Y C, et al. Development of novel subunit vaccine based on truncated fiber protein of egg drop syndrome virus and its immunogenicity in chickens[J]. Virus Res, 2019, 272: 197728. DOI:10.1016/j.virusres.2019.197728 |
| [22] |
程增青, 范根成, 窦小龙, 等. 1群4型禽腺病毒的分离鉴定及Fiber-2蛋白的免疫效果分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2020, 51(10): 2463-2471. CHENG Z Q, FAN G C, DOU X L, et al. Isolation and identification of group Ⅰ type 4 avian adenovirus and analysis in immune effect of fiber-2 protein[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(10): 2463-2471. (in Chinese) |
| [23] |
GUO X, CHANG J, LU S Y, et al. Multiantigen epitope fusion recombinant proteins from capsids of serotype 4 fowl adenovirus induce chicken immunity against avian Angara disease[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2023, 278: 109661. DOI:10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109661 |
| [24] |
GRAFL B, PROKOFIEVA I, WERNSDORF P, et al. Infection with an apathogenic fowl adenovirus serotype-1 strain (CELO) prevents adenoviral gizzard erosion in broilers[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2014, 172(1-2): 177-185. DOI:10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.05.020 |
| [25] |
FINGERUT E, GUTTER B, GALLILI G, et al. A subunit vaccine against the adenovirus egg-drop syndrome using part of its fiber protein[J]. Vaccine, 2003, 21(21-22): 2761-2766. DOI:10.1016/S0264-410X(03)00117-8 |
| [26] |
SHAH M S, ASHRAF A, KHAN M I, et al. Fowl adenovirus: history, emergence, biology and development of a vaccine against hydropericardium syndrome[J]. Arch Virol, 2017, 162(7): 1833-1843. DOI:10.1007/s00705-017-3313-5 |
| [27] |
UGWU C C, HAIR-BEJO M, NURULFIZA M I, et al. Efficacy, humoral, and cell-mediated immune response of inactivated fowl adenovirus 8b propagated in chicken embryo liver cells using bioreactor in broiler chickens[J]. Vet World, 2022, 15(11): 2681-2692. |
| [28] |
PAN Q, YANG Y C, GAO Y L, et al. An inactivated novel genotype fowl adenovirus 4 protects chickens against the hydropericardium syndrome that recently emerged in China[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9(8): 216. DOI:10.3390/v9080216 |
| [29] |
刘玲, 焦鹏涛, 王萌, 等. 鸡干扰素γ与白介素2对外周血中Th1细胞分化相关细胞因子的影响[J]. 生物工程学报, 2012, 38(9): 3329-3343. LIU L, JIAO P T, WANG M, et al. Effects of chicken interferon γ and interleukin-2 on cytokines related to Th1 cell differentiation in peripheral blood[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2012, 38(9): 3329-3343. (in Chinese) |
| [30] |
SARFRAZ M, SULEMAN M, TIKOO S K, et al. Immune responses to in ovo vaccine formulations containing inactivated fowl adenovirus 8b with poly[di(sodium carboxylatoethylphenoxy)] phosphazene (PCEP) and avian beta defensin as adjuvants in chickens[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(6): 981-986. DOI:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.12.023 |
(编辑 白永平)



