2. 扬州大学兽医学院 江苏省动物预防医学重点实验室, 扬州 225009;
3. 扬州大学兽医学院 江苏高校动物重要疫病与人兽共患病防控协同创新中心, 扬州 225009;
4. 扬州大学 教育部农业与农产品安全国际合作联合实验室, 扬州 225009
2. Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China;
3. Jiangsu Co-innovation Center for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China;
4. Joint International Research Laboratory of Agriculture and Agri-Product Safety, the Ministry of Education of China, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China
鸡传染性贫血病毒(chicken infectious anemia virus, CIAV)属圆环病毒科,是全世界范围内公认的重要禽类病原体[1-3]。CIAV在鸡群中主要以垂直传播的方式进行传播,感染后会引起鸡贫血及免疫器官发育不良,易导致疫苗免疫失败,并常与其他免疫抑制病毒同时感染鸡群[4-9]。CIAV基因组共包含3个开放阅读框[10],分别编码结构蛋白VP1和非结构蛋白VP2、VP3,VP2作为非结构蛋白被认为在VP1蛋白的组装以及VP3蛋白的磷酸化中起重要作用[11-13]。在鸡群感染CIAV后,仅需要2周就可检测到针对VP2抗体的存在,因此可以作为检测CIAV感染的重要靶标抗原[14]。
已有相关文献报道表达的重组VP2蛋白可以作为间接ELISA的检测抗原[14-15],检测感染鸡群中的VP2蛋白抗体,但特异性和灵敏性有待验证。目前,国内针对该病的检测试剂盒较少,且特异性尚有限,而国外的试剂盒价格十分昂贵,不利于大批量的检测,因此建立一种特异性好,灵敏性高的检测方法对我国CIAV的防控有重大意义。
mAb以及抗原表位的研究在疾病防控方面取得诸多成果,基于mAb建立的阻断ELISA具有高度特异性,在诸多疾病的监测中得以应用[16-18],因此制备针对CIAV VP2蛋白的mAb以及抗原表位的研究有助于CIAV防控。本研究通过原核表达VP2蛋白并免疫小鼠制备mAb,对研制mAb识别的抗原表位进行鉴定,为研究VP2蛋白在CIAV感染中的作用以及病毒检测方法的建立提供了基础材料。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料CIAV海安分离株(HA9805)、低致病性禽流感病毒(LPAIV)及其mAb 2A8、J亚群禽白血病病毒(ALV-J)及其mAb 5D3、马立克病病毒(MDV)及其mAb BA4、pET-32a载体、MDCC-MSB1细胞、DF1细胞、CEF细胞、MDCK细胞、Sf9细胞、SP2/0细胞、重组杆状病毒rBac-CIAV-VP2、pCAGSS-VP2-Flag质粒、大肠杆菌BL21 (DE3)由本实验室保存;6~8周龄BALB/c母鼠由扬州大学比较医学中心提供。Axy Prep基因组DNA小量试剂盒购自Axygen公司; 胶回收试剂盒购自QIAGEN公司;转染试剂TransIT-LT1购自Mirus公司;FITC标记山羊抗鼠IgG、HRP标记山羊抗鼠IgG均购自Sigma公司;聚乙二醇(PEG1500)购自Roche公司;蛋白Marker、高保真酶购于诺唯赞公司,ECL发光显色液购自NCM Biotech公司;mAb亚类鉴定试剂盒购自SouthernBiotech公司;RIPA裂解液(强)购自康为世纪公司。
1.2 原核表达载体构建及VP2重组蛋白的诱导表达根据CIAV的VP2(NCBI序列号:M55918.1)的序列,设计合成了1对引物(EcoRⅠ-F: 5′-CCGGAATTCATGCACGGGAACGGCG-3′, XhoⅠ-R: 5′-CCGCTCGAGCACTATACGTACCGGGG-CG- 3′),按照文献[19]的方法培养CIAV,CIAV感染MSB1细胞48~72 h后收集细胞悬液提取基因组,以基因组为模板,PCR扩增CIAV的VP2基因并克隆至原核表达载体pET-32a,转化到BL21(DE3)感受态细胞中构建表达菌株,同时设置转化pET-32a空载体组为对照。参考文献[20]进行诱导表达:将重组菌加入含有氨苄青霉素的LB液体中过夜培养,以1:100的比例接种于含有氨苄青霉素的2×YT培养基中,约3 h后(OD600 nm=0.6~0.8)加入IPTG使其终浓度为0.1 mmol·L-1诱导4 h,所得菌液离心后,使用PBS洗涤并以1:5的比例重悬,冰浴裂解5 min,分别取上清和沉淀15 μL进行SDS-PAGE分析。
1.3 蛋白样品的制备及小鼠免疫按参考文献[20]方法制备蛋白样品并免疫小鼠。主要过程:将表达的重组蛋白进行SDS-PAGE后考马斯亮蓝染色并充分脱色,切下目的蛋白条带,将目的条带置于冻干机中过夜冻干后,加入适量PBS研磨,直至样品能顺畅地通过1 mL注射器。取6周龄的雌性BALB/c小鼠进行免疫,免疫方式均为腹腔注射,第4次免疫后72 h按照常规方法,用聚乙二醇(PEG1500)融合。
1.4 IFA筛选阳性杂交瘤细胞用杆状病毒rBac-CIAV-VP2感染Sf9细胞,72 h后以预冷的丙酮乙醇(3:2)固定,作为IFA筛选抗原进行筛选:以杂交瘤上清为一抗,37 ℃孵育45 min,PBS洗4遍;再以FITC标记山羊抗鼠IgG(1:200稀释)为二抗,37 ℃孵育45 min,PBS洗5遍,最后滴加甘油于荧光显微镜下观察。将pCAGGS-VP2-Flag转染至DF1细胞,48 h后使用丙酮乙醇固定,用于阳性克隆的进一步验证。3次筛选后,对阳性克隆进行3次亚克隆,获得稳定分泌抗CIAV VP2蛋白的杂交瘤细胞株。取杂交瘤培养上清,按照SouthernBiotech公司的mAb亚类鉴定试剂盒对制备的mAb进行亚类鉴定。将阳性杂交瘤细胞株连续传代15代;各代次冻存6个月后复苏,并采用上述IFA检测杂交瘤细胞中的mAb。
1.5 单抗腹水制备以及效价测定取8周龄的BALB/c小鼠,腹腔注射石蜡油500 μL·只-1,2周后腹腔注射杂交瘤细胞,每天观察腹部变化,待腹部明显膨大后,采集腹水。以rBac-CIAV-VP2感染的Sf9细胞为检测抗原,将腹水倍比稀释作为一抗,进行IFA效价检测。
1.6 Western blot鉴定参考文献[21]中的方法进行Western blot的鉴定,将感染rBac-CIAV-VP2的Sf9细胞裂解产物、转染pCAGGS-VP2-Flag的DF1细胞裂解产物以及原核表达的His-VP2蛋白分别与5×SDS Loading Buffer以4:1混匀并煮沸5 min作为蛋白样品,进行SDS-PAGE并转印至硝酸纤维素膜上。转印结束后,将硝酸纤维素膜置于5%脱脂乳中,37 ℃封闭1.5 h;以杂交瘤上清(1:5稀释)为一抗,37℃孵育1 h,PBST洗4遍;再以HRP标记山羊抗鼠IgG(1:30 000稀释)为二抗,37 ℃孵育45 min,PBST洗5遍后, 经ECL发光显色液显色观察。
1.7 mAb特异性鉴定将感染ALV-J的DF1细胞、感染LPAIV的MDCK细胞、感染MDV的CEF细胞固定作为检测原,IFA鉴定mAb的特异性,同时设置针对相应病毒的抗体5D3(ALV-J)、2A8(LPAIV)、BA4(MDV)为阳性对照。
1.8 mAb识别抗原表位的鉴定参考文献[20]进行表位鉴定:以PCR扩增CIAV VP2基因的截短片段并连接入pET-32a表达载体,转入BL21(DE3)后经IPTG诱导表达截短蛋白,裂解菌体用于抗原表位的鉴定。参照“1.6”方法进行Western blot分析,鉴定截短蛋白与mAb的反应性,同时以鼠抗His标签抗体检测蛋白是否成功表达。所用到的截短蛋白引物见表 1。
|
|
表 1 截短表达CIAV VP2蛋白引物设计 Table 1 Primer sequence of CIAV VP2 truncated protein |
参照GenBank中23株国内外CIAV毒株VP2的氨基酸序列,登录号分别为AAA91822.1、AAB06180.1、AAC58476.1、AAD09422.1、BAA77832.1、AAG34179.1、AAM20897.1、AAL79913.1、AAL99895.1、AAK83006.1、ABJ90437.1、AAZ73182.1、ADJ18276.1、AEN71111.1、AFZ94856.1、AGW323371、AID81956.1、AIZ75615.1、AIV09094.1、ANA51883.1、APQ44720.1、ASL68907.1、ATG84571.1,利用DNAStar分析以上序列,对抗体识别氨基酸序列进行保守性分析。
2 结果 2.1 His-VP2融合蛋白的表达按照“1.2”中引物PCR扩增CIAV的VP2基因,经过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳验证,结果成功扩增出目的基因,大小约为648 bp(图 1A)。与pET-32a连接并转化BL21细菌,经SDS-PAGE结果显示,成功获得His-VP2融合蛋白,相对分子质量约50 ku(图 1B)。
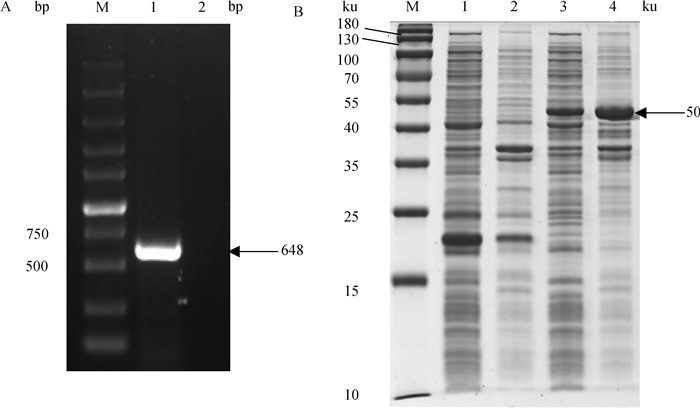
|
A. CIAV VP2基因的PCR扩增结果(M. DL10000 DNA相对分子质量标准;1. VP2基因;2. 阴性对照);B. 原核表达VP2蛋白的SDS-PAGE分析(M. 蛋白质相对分子质量标准;1. pET-32a诱导后的上清;2. pET-32a诱导后的沉淀;3. pET-32a-VP2诱导后的上清;4. pET-32a-VP2诱导后的沉淀) A. PCR amplification result of CIAV VP2 gene (M. DL10000 DNA marker; 1. VP2 gene; 2. Negative control); B. SDS-PAGE analysis of prokaryotic expression of VP2 protein (M. Protein marker; 1. Supernatant of induced pET-32a lysate; 2. Precipitation of induced pET-32a lysate; 3. Supernatant of induced pET-32a-VP2 lysate; 4. Precipitation of induced pET-32a-VP2 lysate) 图 1 CIAV VP2基因的PCR扩增及原核表达VP2蛋白的SDS-PAGE分析 Fig. 1 Amplification of CIAV VP2 and SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant protein His-VP2 expressed in E. coli |
取免疫后的小鼠脾细胞与SP2/0细胞融合,经过多次IFA筛选,结果成功筛选到1株稳定分泌针对CIAV VP2蛋白mAb的杂交瘤细胞株,命名为CIAV-VP2-4A12。该细胞株分泌的mAb可以与转染pCAGGS-VP2-Flag的DF1细胞以及感染杆状病毒rBac-CIAV-VP2后表达VP2蛋白的Sf9细胞反应(图 2)。经过亚类鉴定试剂盒鉴定mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12重链为IgG1型,轻链为kappa链。经测定,腹水的IFA效价为1:12 800。
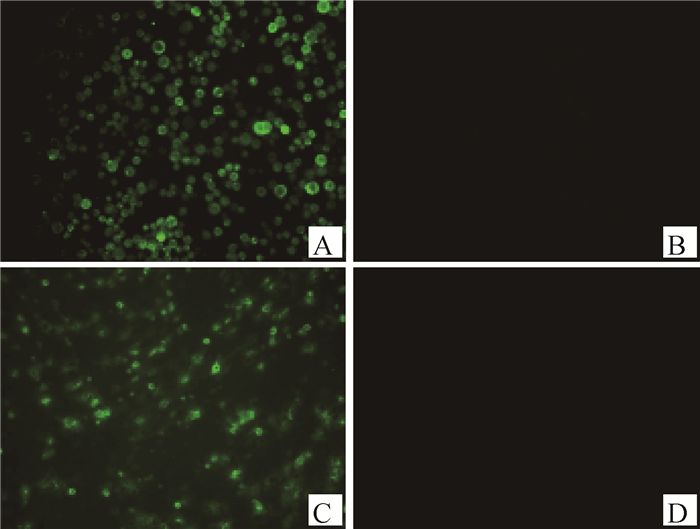
|
A. 感染rBac-CIAV-VP2的Sf9细胞;B. 感染野生型杆状病毒的Sf9细胞;C. 转染pCAGGS-VP2-Flag的DF1细胞;D. 转染pCAGGS的DF1细胞 A. Sf9 cells infected with rBac-CIAV-VP2; B. Sf9 cells infected with wild baclovirus; C. DF1 cells transfected with pCAGGS-VP2-Flag; D. DF1 cells transfected with pCAGGS 图 2 mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12的IFA鉴定(400×) Fig. 2 IFA Identification of mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12(400×) |
Western blot结果显示,mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12能与原核表达、杆状病毒系统表达以及转染DF1细胞表达的VP2蛋白反应,产生特异性条带(图 3),杆状病毒表达的VP2蛋白经过加工修饰大小约为38 ku,转染pCAGGS-VP2-Flag(Flag标签大小为0.9 ku)的DF1细胞所表达的VP2大小约为35 ku。

|
M. 蛋白质相对分子质量标准;1. pET-32a空载体表达产物;2. pET-32a-VP2表达产物;3. 感染野生型杆状病毒的Sf9细胞;4. 感染重组杆状病毒rBac-CIAV-VP2的Sf9细胞;5. 转染pCAGGS空载体的DF1细胞;6. 转染pCAGGS-VP2-Flag的DF1细胞 M. Protein marker; 1. Induced pET-32a; 2. Induced pET-32a-VP2; 3. Sf9 cells infected with wild baclovirus; 4. Sf9 cells infected with rBac-CIAV-VP2; 5. DF1 cells transfected with pCAGGS; 6. DF1 cells transfected with pCAGGS-VP2-Flag 图 3 mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12的Western blot鉴定 Fig. 3 Western blot identification of mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12 |
将LPAIV、ALV-J、MDV感染的细胞经过固定后以mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12以及针对各自病毒的mAb为一抗,进行IFA鉴定,结果显示,阳性对照组均出现了特异性荧光,而mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12不与3种病毒反应(图 4),说明mAb的特异性较好。

|
阳性对照所用抗体为2A8(LPAIV)、5D3(ALV-J)和BA4(MDV) The antibodies used in positive control were 2A8 (LPAIV), 5D3(ALV-J) and BA4(MDV) 图 4 mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12特异性鉴定(200×) Fig. 4 Specific identification of mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12(200×) |
将截短表达CIAV VP2蛋白作为抗原,以mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12和His标签抗体为一抗进行Western blot鉴定。结果显示,当VP2蛋白分为两段(aa1~aa130和aa111~aa216)表达时,mAb可以识别aa111~aa216(图 5);将该区域分成两段,发现mAb识别的区域为aa111~aa170,而不与aa156~aa216反应(图 5),说明mAb识别表位的N端位于aa111~aa156;再将VP2蛋白N端从aa111逐步截短表达,进一步确定mAb识别表位的N端位于aa147~aa156片段(图 5)。为精确定位mAb识别序列的N端位置,将VP2蛋白N端从aa148开始逐个缺失表达,结果发现, mAb与片段aa155~aa216仍可以反应(图 5),由上述结果可知, mAb不与aa156~aa216反应,故mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12识别表位的N端为aa155;之后将VP2蛋白C端从aa165逐个截短表达,发现mAb可以识别截短片段aa1~aa159而不识别aa1~aa158,说明mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12识别的最短序列aa155~aa159,该区域的氨基酸序列为155KTVRW159(图 5)。
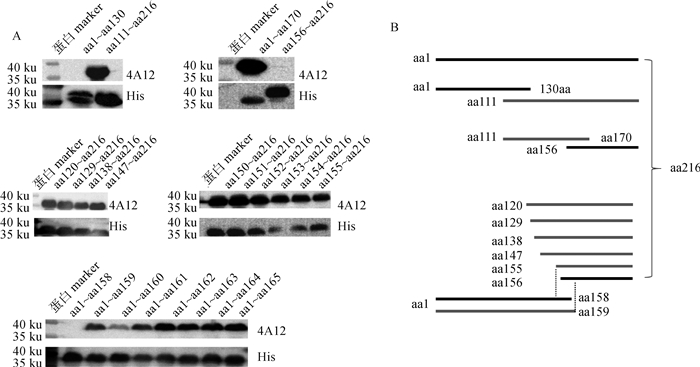
|
A. Western blot分析;B. 截短片段示意图 A. Western blot analysis; B. Schematic diagram of the truncated fragments 图 5 mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12识别表位的定位 Fig. 5 Identification of antigen epitope recognized by mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12 |
在GenBank下载国内外的23株CIAV VP2氨基酸序列,并使用DNAStar软件分析mAb识别区域在不同毒株中的保守性,结果显示, CIAV的VP2蛋白在aa155~aa159处没有发生氨基酸突变(图 6),表明mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12识别的氨基酸序列在各毒株间高度保守。

|
图 6 mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12识别表位的保守性分析 Fig. 6 Conservative analysis of antigen epitope recognized by mAb CIAV-VP2-4A12 |
CIAV是一种重要的禽类免疫抑制病,自1979年被发现以来,包括我国在内的多个国家陆续分离到该病原体[22-25],目前商品化疫苗防止该病的效果有限,且没有特效药可用于CIAV的治疗,对于该病及时准确的监测是防控中的重要环节[26-27]。
近年来,mAb以及抗原表位的研究成为疾病的防控的热门研究领域。通过病毒抗原及其mAb建立的阻断ELISA,相比于常规的ELISA,不会受到血清中的细胞因子等杂质的影响,极大提高了检测的特异性[16-18]。因此制备针对病毒蛋白的mAb并对其进行表位研究具有应用前景。CIAV目前只有1个血清型,在病毒的3个蛋白中,VP2蛋白在不同毒株中具有较高的保守性[28],是建立检测方法的理想抗原。鉴于CIAV生长速度缓慢,难以获得滴度较高的病毒,利用外源表达的病毒蛋白免疫小鼠制备mAb是制备CIAV mAb的主要途径[29-31]。本研究在制备VP2蛋白mAb时选择原核表达的VP2重组蛋白为免疫原,并尝试使用切胶纯化直接免疫小鼠,省去了变性纯化等步骤,节约了时间与成本。在筛选mAb时,为了避免非特异性抗体的产生,不同于陆桂丽等[30]和陈延飞[31]使用原核表达的抗原进行间接ELISA筛选,本研究采用真核系统表达的VP2蛋白进行IFA筛选,提高了筛选方法的特异性,最终获得了高效价的特异性mAb。
目前,与VP2蛋白抗原表位的相关研究较少,陈延飞等[31]和王晓燕等[32]制备了VP2蛋白的mAbs并初步定位识别表位,发现所制备mAbs的识别区域分别位于VP2蛋白的aa21~aa36、aa111~ aa126、aa121~aa136以及aa20~aa40,但均未精确定位具体识别的氨基酸。为了研究已制备的mAb针对的抗原表位与先前报道是否存在差异,本研究通过逐步截短表达VP2蛋白,采用Western blot方法检测与不同截短蛋白的反应性,对表位进行精确定位,确定该mAb识别抗原表位为aa155~aa159,发现了不同于前人鉴定的新的抗原表位并定位至5个氨基酸,经过同源性比较分析,发现国内外不同毒株在该识别区域十分保守,具有潜在应用前景。
4 结论成功制备针对CIAV VP2蛋白的mAb,确定其识别表位为155KTVRW159,为VP2蛋白结构与功能的研究以及CIAV检测方法的建立奠定了基础。
| [1] |
SCHAT K A. Chicken anemia virus[M]//DE VILLIERS E M, HAUSEN H. TT Viruses. Berlin: Springer, 2009.
|
| [2] |
YUASA N, TANIGUCHI T, YOSHIDA I. Isolation and some characteristics of an agent inducing anemia in chicks[J]. Avian Dis, 1979, 23(2): 366-385. DOI:10.2307/1589567 |
| [3] |
YUASA N, IMAI K, WATANABE K, et al. Aetiological examination of an outbreak of haemorrhagic syndrome in a broiler flock in Japan[J]. Avian Pathol, 1987, 16(3): 521-526. DOI:10.1080/03079458708436401 |
| [4] |
OTAKI Y, NUNOYA T, TAJIMA M, et al. Isolation of chicken anaemia agent and Marek's disease virus from chickens vaccinated with turkey herpesvirus and lesions induced in chicks by inoculating both agents[J]. Avian Pathol, 1987, 16(2): 291-306. DOI:10.1080/03079458708436376 |
| [5] |
OTAAKI Y, NUNOYA T, TAJIMA M, et al. Depression of vaccinal immunity to Marek's disease by infection with chicken anaemia agent[J]. Avian Pathol, 1988, 17(2): 333-347. DOI:10.1080/03079458808436452 |
| [6] |
ROSENBERGER J K, CLOUD S S. The effects of age, route of exposure, and coinfection with infectious bursal disease virus on the pathogenicity and transmissibility of chicken anemia agent (CAA)[J]. Avian Dis, 1989, 33(4): 753-759. DOI:10.2307/1591156 |
| [7] |
MCNULTY M S. Chicken anaemia agent: a review[J]. Avian Pathol, 1991, 20(2): 187-203. DOI:10.1080/03079459108418756 |
| [8] |
TONGKAMSAI S, LEE M S, CHENG M C, et al. Persistent infection with chicken anemia virus in 3-week-old chickens induced by inoculation of the virus by the natural route[J]. Pathogens, 2019, 8(2): 48. DOI:10.3390/pathogens8020048 |
| [9] |
邵红霞, 王平平, 武敏, 等. 鸡传染性贫血病毒海安分离株感染雏鸡的病原动态分析[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2012, 20(5): 1-7. SHAO H X, WANG P P, WU M, et al. Pathogenesis of chicken anemia virus Haian strain in chicks[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2012, 20(5): 1-7. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-6422.2012.05.002 (in Chinese) |
| [10] |
NOTEBORN M H M, VERSCHUEREN C A J, ZANTEMA A, et al. Identification of the promoter region of chicken anemia virus (CAV) containing a novel enhancer-like element[J]. Gene, 1994, 150(2): 313-318. DOI:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90444-8 |
| [11] |
NOTEBORN M H, VERSCHUEREN C A, KOCH G, et al. Simultaneous expression of recombinant baculovirus-encoded chicken anaemia virus (CAV) proteins VP1 and VP2 is required for formation of the CAV-specific neutralizing epitope[J]. J General Virol, 1998, 79(12): 3073-3077. DOI:10.1099/0022-1317-79-12-3073 |
| [12] |
PETERS M A, JACKSON D C, CRABB B S, et al. Chicken anemia virus VP2 is a novel dual specificity protein phosphatase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(42): 39566-39573. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M201752200 |
| [13] |
PETERS M A, CRABB B S, WASHINGTON E A, et al. Site-directed mutagenesis of the VP2 gene of Chicken anemia virus affects virus replication, cytopathology and host-cell MHC class I expression[J]. J General Virol, 2006, 87(4): 823-831. DOI:10.1099/vir.0.81468-0 |
| [14] |
IWATA N, FUJINO M, TUCHIYA K, et al. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant chicken anemia virus proteins expressed in a baculovirus vector system[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2001, 60(2): 175-180. |
| [15] |
LAI G H, LIN M K, LIEN Y Y, et al. Expression and characterization of highly antigenic domains of chicken anemia virus viral VP2 and VP3 subunit proteins in a recombinant E. coli for sero-diagnostic applications[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2013, 9(1): 161. DOI:10.1186/1746-6148-9-161 |
| [16] |
向文杰, 李德栋, 林俊, 等. 牛传染性鼻气管炎病毒单克隆抗体的制备及阻断ELISA方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2020, 42(1): 33-39. XIANG W J, LI D D, LIN J, et al. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies against bovine infectious rhinotracheitis virus and development of a blocking ELISA[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 42(1): 33-39. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
王宁, 谨瑾, 刘璐, 等. 猪肺炎支原体P97蛋白单克隆抗体的制备、表位鉴定及其初步应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2020, 51(5): 1110-1118. WANG N, JIN J, LIU L, et al. Preparation, identification of the B-cell epitope and preliminary application of a monoclonal antibody against P97 protein of Mycoplasma hypneumoniae[J]. Acta Veterinariaet Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(5): 1110-1118. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
赵少若, 郝丽影, 王同燕, 等. 猪瘟病毒E2蛋白单克隆抗体的制备及阻断ELISA抗体检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2020, 52(11): 60-66. ZHAO S R, HAO L Y, WANG T Y, et al. Development of monoclonal antibody against E2 protein of classical swine fever virus (CSFV) and establishment of a blocking ELISA for detection of antibodies[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 52(11): 60-66. (in Chinese) |
| [19] |
刘岳龙. 鸡贫血病毒中国株基因序列比较、病毒编码蛋白的表达及分子克隆化病毒的构建[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2001. LIU Y L. Sequence comparsion of Chinese isolates of chicken anemia virus (CAV), expression of three virus-encoding proteins and construction of the molecularly cloned virus[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese) |
| [20] |
朱敏, 王琳, 许默儒, 等. 鸡IRF7原核表达及多克隆抗体制备[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2018, 26(4): 76-81. ZHU M, WANG L, XU M R, et al. Prokaryotic expression and preparation of polyclonal antibodies of chicken IRF7[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2018, 26(4): 76-81. (in Chinese) |
| [21] |
闫泽一. 禽白血病病毒单克隆抗体识别抗原表位的鉴定与分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020. YAN Z Y. Identification and analysis of antigen epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibody of avian leukosis virus[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese) |
| [22] |
MCNULTY M S, CONNOR T J, MCNEILLY F, et al. Chicken anemia agent in the United States: isolation of the virus and detection of antibody in broiler breeder flocks[J]. Avian Dis, 1989, 33(4): 691-694. DOI:10.2307/1591146 |
| [23] |
CONNOR T J, MCNEILLY F, FIRTH G A, et al. Biological characterisation of Australian isolates of chicken anaemia agent[J]. Austr Vet J, 1991, 68(6): 199-201. DOI:10.1111/j.1751-0813.1991.tb03192.x |
| [24] |
WICHT J D, MAHARAJ S B. Chicken anaemia agent in South Africa[J]. Vet Rec, 1993, 133(6): 147-148. |
| [25] |
ZHOU W P, YANG B, SHEN B, et al. A Serologic survey of antibody against chicken infectious anemia virus by indirect immunofluorescent assay in domestic poultry in China[J]. Avian Dis, 1996, 40(2): 358-360. DOI:10.2307/1592232 |
| [26] |
邵红霞, 王平平, 武敏, 等. 家禽活疫苗中鸡传染性贫血病毒PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国家禽, 2012, 34(21): 28-30. SHAO H X, WANG P P, WU M, et al. A rapid PCR approach for detecting the Contamination of chicken anemia virus in avian live vaccines[J]. China Poultry, 2012, 34(21): 28-30. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-6364.2012.21.007 (in Chinese) |
| [27] |
任志浩, 房立春, 栾怀彪, 等. 鸡传染性贫血病毒荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及其在疫苗污染检测中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2016, 47(7): 1459-1464. REN Z H, FANG L C, LUAN H B, et al. Development and application of a quantitative PCR for detection of chicken infectious anemia virus contamination in attenuated vaccines[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2016, 47(7): 1459-1464. (in Chinese) |
| [28] |
ISLAM M R, JOHNE R, RAUE R, et al. Sequence analysis of the full-length cloned DNA of a chicken anaemia virus (CAV) strain from bangladesh: evidence for genetic grouping of CAV strains based on the deduced VP1 amino acid sequences[J]. J Vet Med, Ser B, 2002, 49(7): 332-337. DOI:10.1046/j.1439-0450.2002.00581.x |
| [29] |
史静柯, 王鹏, 霍臣智, 等. 鸡传染性贫血病毒VP3蛋白的原核表达及其单克隆抗体的研制[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2020, 28(3): 55-60. SHI J K, WANG P, HUO C Z, et al. Prokaryotic expression of vp3 protein of chicken infectious anemia virus and preparation of monoclonal antibodies[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2020, 28(3): 55-60. (in Chinese) |
| [30] |
陆桂丽, 高玉龙, 高宏雷, 等. 鸡传染性贫血病毒VP2蛋白单克隆抗体的制备与鉴定[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2007, 37(5): 396-400. LU G L, GAO Y L, GAO H L, et al. Preparation and identification of monoclonal antibodies against chicken infectious anemia virus VP2 protein[J]. Veterinary Science in China, 2007, 37(5): 396-400. (in Chinese) |
| [31] |
陈延飞, 覃尧, 李夏莹, 等. 鸡传染性贫血病毒VP2蛋白单克隆抗体的制备及鉴定[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2015, 51(4): 3-6, 9. CHEN Y F, QIN Y, LI X Y, et al. Development and identification of monoclonal antibodies against chicken infectious anemia virus(CIAV) VP2[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 51(4): 3-6, 9. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2015.04.001 (in Chinese) |
| [32] |
WANG X Y, GAO H L, GAO Y L, et al. Mapping of epitopes of VP2 protein of chicken anemia virus using monoclonal antibodies[J]. J Virol Methods, 2007, 143(2): 194-199. DOI:10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.03.016 |
(编辑 白永平)



