肺离子细胞[1-2](pulmonary ionocyte)是2018年在人和小鼠肺中发现的一种新型细胞,在肺纤维化的形成机制和修复中发挥关键作用,对ATP6V0D2具有独有的免疫反应性[2]。牦牛虽长期处于高原低氧环境下,但其肺却无低氧造成的肺纤维化现象[3-4]。现有的肺离子细胞的相关研究仅限于人和小鼠,尚无其他动物的研究报道,也无ATP6V0D2在低氧环境中生活动物的研究报道。因此,本研究拟通过免疫组织化学、qPCR和Western blot技术检测ATP6V0D2在不同年龄牦牛肺中的分布和表达,确定ATP6V0D2在牦牛肺中的动态分布和表达情况、探讨ATP6V0D2在高原低氧适应动物肺结构形成和功能保持方面的可能作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料健康牦牛肺采自甘南藏族自治州(初生1~7日龄)、青海省西宁市马家肴屠宰场(幼年1~2岁和老年7~10岁)、甘肃省临夏自治州(成年3~6岁),每年龄段各3头。颈动脉放血处死,迅速采集肺组织固定于4%多聚甲醛溶液和液氮中。
1.2 免疫组织化学石蜡切片4 μm,按SP试剂盒(北京博奥森生物科技有限公司)说明书处理。ATP6V0D2抗体(Rabbit Anti-ATP6V0D2,bs-12548R,同上)1∶300稀释,空白对照用0.01 mol·L-1的PBS代替一抗,DAB显色,苏木精复染。深棕黄色为强阳性表达,浅棕黄色为阳性表达,接近背景色或无色为阴性。Olympus DP71显微照相系统进行拍摄。
1.3 Western blot称0.1 g各年龄组牦牛肺组织,加入1 mL RIPA裂解液和10 μL PMSF,摇床冰浴2.5 h,4 ℃,12 000 r·min-1离心10 min,吸上清,-20 ℃保存。将提好的蛋白按比例配制,金属浴变性,进行SDS-PAGE电泳。一抗(Mouse Anti-ATP6V0D2,ab236375,abcam;Anti-β-actin Mouse,N21123,北京全式金生物技术有限公司),二抗1∶5 000[Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L),N21009,同上]。Image J软件分析目的条带,根据所测灰度值计算出蛋白相对表达量,SPSS 19.0软件进行分析。
1.4 qRT-PCRNCBI数据库中检索牦牛β-actin (NM 173979.3)、ATP6V0D2 (NM 001046101.1)序列,Primer 6软件设计引物。目的片段197 bp,引物序列:F: 5′-ACCCCTAGCTCCGTTCTTTC-3′;R: 5′-TGATGATAAAAGCACGCCGG-3′,内参片段141 bp,引物序列:F: 5′- GCAATGAGCGGTTCC-3′;R: 5′-CCGTGTTGGCGTAGAG-3′。按照TRIzol试剂(Invitrogen,美国)总RNA提取试剂盒提取4个年龄组牦牛肺组织的总RNA,Promega试剂盒进行反转录。使用Lightcycler96(Roche,美国)进行qPCR。
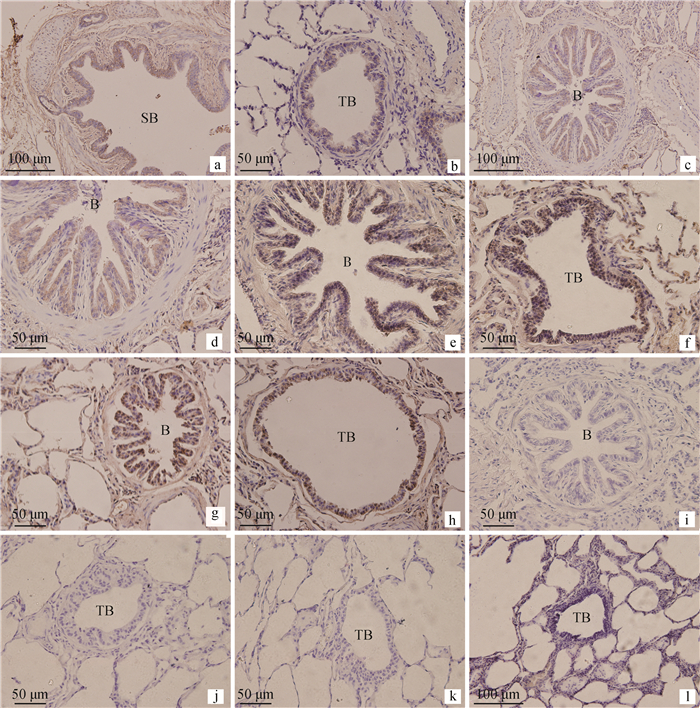
2 结果 2.1 免疫组织化学结果ATP6V0D2主要分布于肺内支气管及其分支管壁上皮黏膜层的纤毛细胞和克拉拉细胞内(图 1)。在各年龄组均呈阳性表达,以成年组和老年组表达强阳性。
|
a、b.初生组;c、d.幼年组;e、f.成年组;g、h.老年组;i~l.各年龄空白对照。SB.小支气管;B.细支气管;TB.终末细支气管 a, b. Newborn group. c, d. Juvenile group. e, f. Adult group. g, h. Elderly group. i-l. Blank control of the newborn, juvenile, adult, and elderly groups. SB. Small bronchiole; B. Bronchiole; TB. Terminal bronchiole 图 1 不同年龄段牦牛肺内ATP6V0D2的分布 Fig. 1 Distribution of ATP6V0D2 in the yak lungs at different ages |
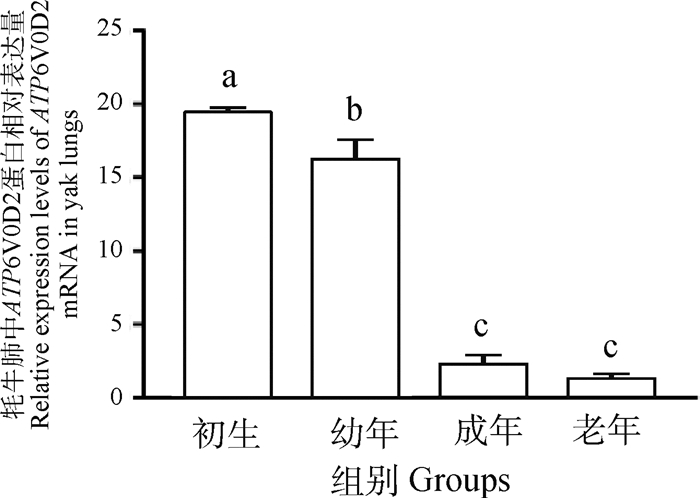
ATP6V0D2在初生组表达量最高,与其他各组比较,差异性均显著(P<0.05);幼年组表达次之,和其他各组比较,差异性均显著(P<0.05);成年组和老年组之间表达差异性不显著(P>0.05)(图 2)。
|
不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05), 相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),下同 Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), the same letter means no significant difference (P>0.05), the same as below 图 2 不同年龄牦牛肺中ATP6V0D2 mRNA相对表达量 Fig. 2 Relative expression levels of ATP6V0D2 mRNA in yak lungs at different ages |
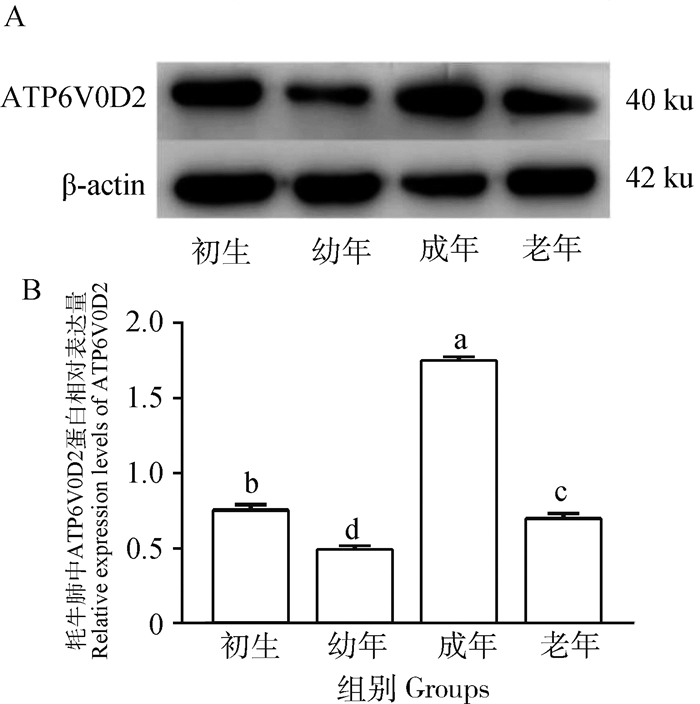
ATP6V0D2在不同年龄组牦牛肺中均能检测到不同程度的表达(图 3)。成年组表达量显著高于其他3组(P<0.05),其他3组两两比较,差异性均显著(P<0.05)(图 3 B)。
|
A.ATP6V0D2免疫印迹蛋白条带; B. ATP6V0D2灰度值分析 A. Western blot strip of ATP6V0D2; B. ATP6V0D2 gray value analysis 图 3 不同年龄牦牛肺中ATP6V0D2蛋白的表达 Fig. 3 Expression of ATP6V0D2 protein in yak lungs at different ages |
本试验结果显示,ATP6V0D2在牦牛肺中普遍分布于肺内支气管分支的上皮细胞中,并没有特定的仅表达于某一种细胞中,这与Plasschaert等[1]仅在肺离子细胞中表达结论相悖。但也有研究证明,ATP6V0D2会在培养的肺II型细胞[5]、破骨细胞[6]和一些癌细胞[7]中的某个阶段表达。Nishi等[8]从小鼠(D2)中分离出编码亚型D的cDNA,在肺、心和脾中也检测到表达。ATP6V0D2在牦牛肺内细支气管及其分支上皮黏膜层的纤毛细胞和克拉拉细胞中均有不同程度的分布,可能具有类似肺离子细胞的部分功能,与肺离子细胞可能具有相关性。本试验结果显示,ATP6V0D2在各年龄组牦牛肺支气管分支上皮中均有分布,但表达量有所不同,其蛋白以成年组表达量最高。这可能与牦牛肺对低氧环境的适应过程和适应能力相关:初生到幼年阶段牦牛肺尚未完全发育,生理机能尚不健全,处于对低氧环境的适应过程中;成年时肺上皮细胞增生、细胞代谢能力和抗损伤等能力达到顶峰,ATP6V0D2的表达在成年组中达到最大值;之后随着年龄增长,生理机能下降,ATP6V0D2的表达也开始出现下降的趋势。ATP6V0D2可能在牦牛肺适应高原低氧环境、防止气道损伤或修复方面发挥重要作用,其作用机理仍需进一步研究。
4 结论ATP6V0D2在不同年龄牦牛肺内支气管分支管壁的上皮细胞内均有不同程度分布和表达,以成年组表达最高,主要分布于黏膜层的纤毛细胞和克拉拉细胞。牦牛气道纤毛细胞和克拉拉细胞与肺离子细胞可能具有功能上的相关性。ATP6V0D2在牦牛肺适应高原低氧环境、防止肺损伤和肺纤维化、肺修复方面可能发挥重要作用。
| [1] | PLASSCHAERT L W, ŽILIONIS R, CHOO-WING R, et al. A single-cell atlas of the airway epithelium reveals the CFTR-rich pulmonary ionocyte[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 377–381. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0394-6 |
| [2] | MONTORO D T, HABER A L, BITON M, et al. A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 319–324. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0393-7 |
| [3] |
陈秋生, 冯霞, 姜生成. 牦牛肺脏高原适应性的结构研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(10): 2107–2113.
CHEN Q S, FENG X, JIANG S C. Structural study on plateau adaptability of yak lung[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(10): 2107–2113. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2006.10.024 (in Chinese) |
| [4] |
何俊峰, 余四九, 崔燕. 不同年龄高原牦牛肺脏的组织结构特征[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2009, 40(5): 748–755.
HE J F, YU S J, CUI Y. Characteristics of lung structure in different age Plateau yak[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2009, 40(5): 748–755. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2009.05.023 (in Chinese) |
| [5] | FENG N H, LIN H I, WANG J S, et al. Differential expression of a V-type ATPase C subunit gene, Atp6V1C2, during culture of rat lung type Ⅱ pneumocytes[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2005, 12(6): 899–911. DOI: 10.1007/s11373-005-9020-3 |
| [6] | SMITH A N, FRANCIS R W, SORRELL S L, et al. The d subunit plays a central role in human vacuolar H+-ATPases[J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2008, 40(4): 371–380. DOI: 10.1007/s10863-008-9161-y |
| [7] | YANG J G, GUO F H, YUAN L L, et al. Elevated expression of the V-ATPase D2 subunit triggers increased energy metabolite levels in KrasG12D-driven cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(7): 11690–11701. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.28448 |
| [8] | NISHI T, KAWASAKI-NISHI S, FORGAC M. Expression and function of the mouse V-ATPase d subunit isoforms[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(47): 46396–46402. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M303924200 |



