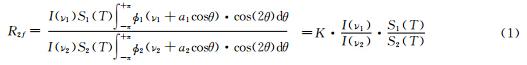航空航天发动机燃烧流场参数(温度、组分浓度等)的测量对改进发动机设计、提高燃烧效率、以及计算流体动力学(Computational Fluid Dynamics,简称CFD)的建模及数值仿真结果的验证等方面至关重要。可调谐二极管激光吸收光谱(Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy,简称TDLAS)技术可用于测量燃烧场温度、组分浓度和流场速度等[1, 2],具有对流场无扰动、高响应速率和测量系统小巧紧凑等优势。目前,国内外相关研究单位利用TDLAS技术实现对航空航天发动机(超燃冲压发动机、涡轮/涡扇发动机、脉冲爆震发动机)燃烧流场在线监测和燃烧控制等方面的文献不断见诸报导[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],并有望利用该技术制成小型光学传感器,安装于发动机各测量点上,用于监测和控制发动机状态[10]。
TDLAS技术在测量方法上主要分为直接吸收法和二次谐波法。直接吸收法能够将谱线的线型还原出来,测量原理较为直观,可以消除燃烧场压强变化对测量的影响,但灵敏度较低,测量易受散射颗粒、湍流 以及现场振动的影响[11];二次谐波法是基于锁相检测的原理,能够有效抑制其它频段噪声对测量的影响,具有测量灵敏度高和抗干扰能力强的优点[2, 11]。 二次谐波法的主要缺点是不能直观地反映谱线线型信息,测量过程中需要对测量系统进行标定。近几年也有相关文献报道通过一次谐波信号还原谱线线型[12, 13]或采用一次谐波信号归一化二次谐波信号等方法实现免标定的二次谐波测量技术[14],但前者数据过程较为复杂,后者实验系统较为复杂,不易研制发动机现场实时在线监测的TDLAS二次谐波法测量系统。本文采用同步监测激光光强并结合HITEMP数据库谱线参数[15]及调制参数计算标定常数的方法实现TDLAS技术二次谐波法测温,并在西北工业大学直联式超燃冲压发动机试验台氢气和乙烯燃烧时不同位置处开展TDLAS技术二次谐波法测量试验,对该技术的工程应用可行性进行了考核。 1 测量原理
TDLAS二次谐波法中,二极管激光器的输出波长除了以一个锯齿波的形式进行扫描外,在每个扫描周期内还受一个频率更高的正弦波调制。由于介质的吸收系数对波长响应是非线性的(Voigt函数),所以经过吸收介质后的激光光强变化的频率将包含很多谐波成分。二次谐波法便是通过测量激光经过燃烧场后调制信号的二次谐波信号实现对燃烧参数的测量,图 1为TDLAS二次谐波法原理示意图。
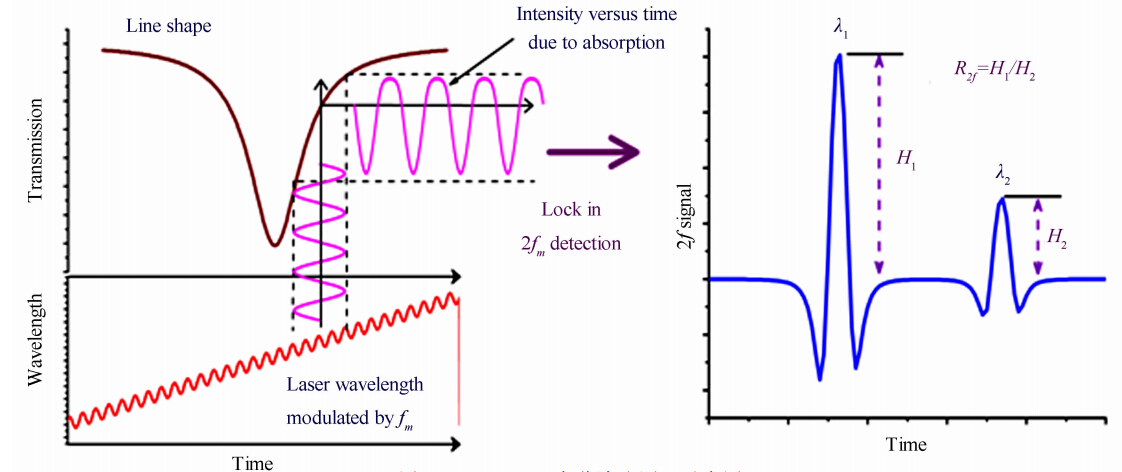 |
| 图 1 TDLAS二次谐波法原理示意图Fig. 1 Principle diagram of TDLAS second harmonic technique |
燃烧场温度测量一般是通过双线法,即通过2条吸收线谱线强度S(T)的比值 是温度的单值函数来反演出燃烧场温度。对于二次谐波法,2条 吸收线的二次谐波信号高度(中心频率处值)的比值可表示成:
对于常压燃烧场来说,K是与谱线参数及调制参数有关的常量。根据谱线强度S(T)的表达式得到二次谐波法温度计算公式为:
式中:S(T0)是在参考温度T0下的谱线强度,h是普朗克常量(J·s),c 是光速(cm·s-1),k是波尔兹曼常量(J·K-1),E"是吸收谱线下能级的能量(cm-1)。(2)式中的R2f通过测量获得,K通过具体的谱线参数和调制参数计算获得,I(ν2)/I(ν1)通过同步监测光强的方式获得。 2 测量装置及布局
图 2为TDLAS二次谐波法测量系统示意图。主要由中心波长位于1397.8nm的二极管激光器及其控制器、锁相放大器、探测器以及带有多功能数据采集卡的计算机组成。
 |
| 图 2 TDLAS测量系统示意图Fig. 2 Schematic of TDLAS measurement system |
首先利用激光控制器调节二极管激光器的温度和注入电流,使其输出波长为1397.8nm,然后将从多功能数据采集卡产生的锯齿波与正弦波的叠加信号加到二极管激光器的注入电流上。其中,频率较低的锯齿波信号用来调谐激光输出波长,使其反复地扫过选定的2条水吸收线,扫描频率为250Hz;频率较高的正弦波信号用来在每个扫描周期内调制激光输出波长。输出的激光经过光纤准直器后(光束直径约2mm)单次穿过待测的燃烧场,由探测器测量激光经过燃烧场后光强变化,将其转化为电信号后输入到锁相放大器中进行锁相检测并输出二次谐波信号。最后通过多功能数据采集卡进行信号采集并由计算机进行数据处理和测量结果实时显示。
利用TDLAS技术二次谐波法分别对发动机出口、扩张段以及燃烧室3个位置,燃料分别为乙烯与氢气进行了测量试验。图 3为测量位置示意图,不同测量段处x轴与y轴的定义如图中所示,TDLAS激光的传播方向与x-y平面垂直。其中,x1轴的0点对应于发动机出口边沿,y1轴的0点对应于发动机出口上沿;x2-o-y2与x3-o-y3坐标系原点分别为相应光学窗口的右上角顶点。
 |
| 图 3 测量位置及坐标示意Fig. 3 Sketch map of measurement positions and coordinates |
采用高温高压标定炉作为测量对象,对建立的TDLAS测量系统进行了测温验证。标定炉的最高工作温度为1400K,温度控制精度为±1K,温度不均匀性<±3K。图 4为在一个大气压情况下TDLAS测量结果。可以看出,在1000K以下时,TDLAS测量结果与炉温实际值基本一致,最大偏差为22K;在1000K以上时,TDLAS测量结果与炉温实际值差别较大,最大偏差为74K,其主要原因是在高温情况下,炉膛的热辐射对TDLAS探测器造成干扰(标定炉的升温时间约2小时,炉膛的热辐射会使探测器温度升高,使其性能变差)。文中使用的1397.8nm两条吸收线在800~2200K温度范围内有着较好的信号强度和测温灵敏度[16],标定炉的验证实验表明利用公式(2)反演流场温度是可靠的。
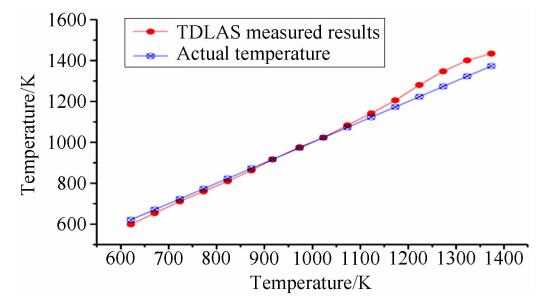 |
| 图 4 标定炉温度测量结果Fig. 4 Measured temperatures in calibration burner by TDLAS technique |
发动机出口与扩张段处燃烧场相对简单,燃烧比较充分也比较稳定,因此采用电控平移台同步扫描的方式,分别测量了氢气和乙烯燃烧时温度随y轴位置变化情况。
图 5为发动机出口处氢气和乙烯燃烧时温度随y1轴位置的变化(x1=30mm)。可以看出,随着沿 y1坐标增加,温度逐渐升高,该现象与同一实验获得的OH基的荧光图像一致;发动机出口处氢气与乙烯燃 烧状况基本相同,在y1=-2.5mm左右处,两者温度均达到最高,约为1600K。图 6为发动机扩张段处氢气和乙烯燃烧时温度随y2轴位置变化(x2=40mm)。与发动机出口结果类似,在发动机扩张段处氢气与乙烯的燃烧温度基本一致,表明该位置氢气 与乙烯的燃烧均比较充分,同时y2轴上半部分比下半部分燃烧剧烈。
 |
| 图 5 发动机出口处温度随y1轴位置变化Fig. 5 Measured temperatures as a function of y1 at engine exit |
 |
| 图 6 发动机扩张段处温度随y2轴位置变化Fig. 6 Measured temperatures as a function of y2 in expansion section |
OH荧光图像表明,发动机燃烧室内部燃烧比较剧烈,分已燃区和未燃区,其中已燃区主要集中在燃烧室的上部。因此选取在x3=45mm,y3=-15mm位置处测量了氢气和乙烯燃烧时温度随点火时间变化。图 7与8分别为氢气与乙烯燃烧时TDLAS测量结果。从图中可以看出:(1)氢气的燃烧时间约为6s(与燃料注入时间长度一致),燃烧过程相对稳定,整个燃烧过程温度基本处于2100K左右;氢气燃烧时测量信号的抖动比较小,表明其燃烧流场比较干净,所以燃烧相对比较充分;(2)乙烯的燃烧时间约为11s(与燃烧注入时间一致),燃烧过程不稳定,从点火至燃烧结束温度从2000K左右逐渐降至1250K左右;乙烯燃烧时原始测量信号的随机抖动比较大,由于实验中采用大感光面积(Φ5mm)探测器,燃烧场折射率变化引起的光线扰动对测量影响非常小。而燃烧场中的散射颗粒会引起光强信号的随机变化,导致测量信噪比下降,所以测量信号的随机抖动大表明燃烧场中散射颗粒较多,燃烧不充分。
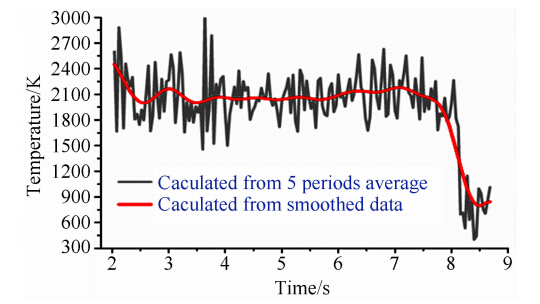 |
| 图 7 发动机燃烧室处(x3=45mm,y3=-15mm)氢气燃烧测量结果Fig. 7 Measured result for hydrogen in engine combustor (x3=45mm,y3=-15mm) |
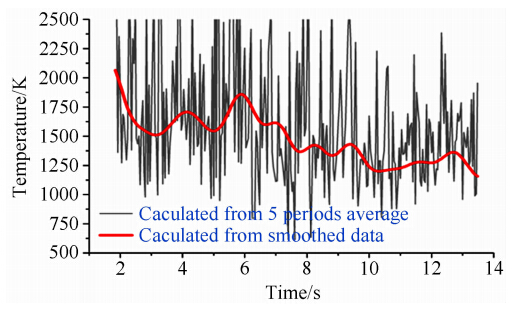 |
| 图 8 发动机燃烧室处(x3=45mm,y3=-15mm)乙烯燃烧测量结果Fig. 8 Measured result for ethylene in engine combustor (x3=45mm,y3=-15mm) |
通过在西北工业大学直联式超燃冲压发动机试验台不同位置处开展测量试验,对TDLAS技术的工程应用可行性进行了考核,试验结果表明:(1)相对于其它诊断技术,TDLAS技术具有测量系统小巧紧凑、抗干扰能力强、数据处理速度快等优势,可用于研制集成化的燃烧场温度传感器;(2)TDLAS技术可以实现高重复频率测量(文中的重复频率为250Hz),能够反映瞬态流场变化细节。但是在本轮试验中TDLAS技术给出的是路径积分测量结果,空间分辨率较差,下一步拟针对实验室正在研制的CT-TDLAS测量系统进行集成和算法改进。
致谢: 本文为国家自然科学基金资助课题(51176159),同时感谢西北工业大学动力与能源学院宋文艳教授课题组对本工作的支持。
| [1] | Davidson D F, Hong Z K, Pilla G L, et al. Multi-species measurements behind reflected shock waves in hydrocarbons using laser absorption[R]. AIAA-2010-198, 2010. |
| [2] | Rieker G B, Jeffries J B, Hanson R K, et al. Calibration-freewavelength-modulation spectroscopy for measurements of gas temperature and concentration in harsh environments[J]. Applied Optics, 2009, 48(29): 5546-5560. |
| [3] | Caswell A W, Roy S. High-bandwidth H2O absorption sensor for measuring pressure, enthalpy, and mass flux in a pulsed-detonation combustor[R]. AIAA-2012-0471, 2012. |
| [4] | Liu J T C, Rieker G B, Jeffries J B, et al. Near infrared diode laser absorption diagnostic for temperature and water vapor in a scramjet combustor[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44: 6701-6711. |
| [5] | Li Fei, Yu Xilong, Gu Hongbin, et al. Measurement of temperature, velocity and water vapor concentration in a scramjet combustor based on near infrared diode laser absorption[R]. AIAA-2011-2214, 2011. |
| [6] | Meyers J M, Fletcher D. Diode laser absorption sensor design and qualification for CO2 hypersonic flows[J]. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2011, 25(2): 193-201. |
| [7] | 王广宇, 洪延姬, 潘虎, 等. 二极管激光吸收传感器测量超声速流场的温度和速度[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(9): 0912009. Wang Guangyu, Hong Yanji, Pan Hu, et al. Diode laser absorption sensor for measurements of temperature and velocity in supersonic flow[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(9): 0912009. |
| [8] | 陶波, 胡志云, 王晟, 等. TDLAS技术测量燃烧流场温度研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2014, 35(2): 401-404. Tao Bo, Hu Zhiyun, Wang Sheng, et al. Study on the measurement of combustion temperature based on TDLAS technique[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2014, 35(2): 401-404. |
| [9] | 许振宇, 刘文清, 刘建国, 等. 基于可调谐半导体激光器吸收光谱的温度测量方法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(23): 234204. Xu Zhenyu, Liu Wenqing, Liu Jianguo, et al. Temperature measurements based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Acta Physics Sinica, 2012, 61(23): 234204. |
| [10] | Sappey A D, Sutherland L, Owenby D, et al. Flight-ready TDLAS combustion sensor for hypersonic[R]. AIAA-2009-7234, 2009. |
| [11] | Zhou Xin. Diode-laser absorption sensors for combustion control[D]. California: Mechanical Engineering of Stanford University, 2005: 11-29. |
| [12] | Ruxton K, Chakraborty A L, Johnstone W, et al. Tunable diode laser spectroscopy with wavelength modulation: Elimination of residual amplitude modulation in a phasor decomposition approach[J]. Sens Actuat A: Chem, 2010, 150: 367-375. |
| [13] | Li L, Arsad N, Stewart G, et al. Absorption line profile recovery based on residual amplitude modulation and first harmonic integration methods in photoacoustic gas sensing[J]. Optical Communication, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2010.08.038. |
| [14] | 屈东胜, 洪延姬, 王广宇, 等. 基于免标定波长调制光谱技术的气体温度和组分浓度测量[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(12): 123001. Qu Dongsheng, Hong Yanji, Wang Guangyu, et al. Measurements of gas temperature and component concentration based on calibration free wavelength modulation spectroscopy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(12): 123001. |
| [15] | Rothman L S, Gordon I E, Burber R J, et al. HITEMP, the high-temperature molecular spectroscopic database[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 2010, 111: 2139-2150. |
| [16] | An Xinliang, Caswell A W, Lipor J J, et al. Determining the optimum wavelength pairs to use for molecular absorption thermometry based on the continuous-spectral lower state energy[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Transfer, 2011, 112: 2355-2362. |