2. 中国科学院西北生态环境研究院沙漠与沙漠化重点实验室,兰州 730070
2. Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730070
抗菌肽(Antimicrobial peptides,AMPs)是在外界条件刺激下,动物免疫防御系统产生的一类对外源病原体的致病作用具有免疫活性的多肽物质,是动物非特异性免疫防御的重要组成部分[1]。它是广泛分布于细菌、植物、软体动物、两栖动物、鱼类、鸟类和哺乳动物体内的小分子多肽,由20-60个氨基酸残基组成[2]。自然抗菌肽不仅抗菌,而且还有细胞凋亡、伤口愈合和免疫调节的功能[3]。多黏菌素和短杆菌素是第一个用于临床上黏膜感染的阳离子抗菌多肽,具有治疗炎症性皮肤疾病及改善伤口感染愈合的功能。近年来,国内外对抗菌肽的研究有了重大突破。例如,从吴郭鱼(Oreochromis mossambicus)获得的抗菌肽tilapia hepcidin 1-5和循环虾抗内毒素因子(Cyclic shrimp anti-lipopolysaccharide factor,CSALF)能有效杀死石斑鱼神经坏死病毒(GNNV)[4-5];从日本鲎血细胞中提取到的抗菌肽Tachyplesin 1可有效抗贝类病原菌[6];与现有已确定抗菌肽无结构同源性的水母抗菌肽对革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性菌的抑制作用[7]。抗菌肽的杀菌机制为:带正电的抗菌肽通过作用于细菌质膜磷脂分子上的负电荷,使膜发生去极化或形成“孔洞”,进入到细胞内作用于DNA或RNA,直接杀死细菌,从而产生抗菌活性[8]。有研究表明,影响抗菌肽的最关键因素是疏水性和两亲性,而肽链长度、电荷数并不起决定性作用[9]。抗菌肽的这种特殊抑菌机制很难使致病菌产生抗性和交叉抗性。
鱼类的鳃、皮肤和胃肠道是病原微生物侵入的主要途径,它能够有效抵制感染的原因在于这些部位含有的丰富抗菌肽。例如,从泥鳅中分离到的misgurin,从冬季比目鱼中分离到的pleurocidin和hepcidin,从豹鳎鱼中分离到的paradaxins,从石斑鱼中分离到的epinecidin,从杂交条纹鲈鱼中分离到的moronecidin和piscidin 4,从八目鳗鱼中分离到的hagfish intestinal antimicrobial peptides,从黑鲈鱼中分离到的dicentracin,从鲶鱼中分离到的parasin和从大西洋八目鳗鱼中分离到的hfiap-1等[10-13]。两栖动物长期暴露的皮肤也含多种抗菌活性物质,如从蛙类皮肤腺体上提取到的受交感神经控制的多种药理活性抗菌肽:使血管舒张增加通透性的速激肽(tachykinins)、具有心脏保护作用的缓激肽(bradykinins)、促甲状腺激素释放激素(thyrotropinreleasing hormone、bombesin-like)和作为免疫系统中重要的调节因子阿片样肽(opioid peptides)[14-17]等。雨蛙(Hylachinensis)产生的雨蛙肽caeruleins,形成两亲性螺旋结构,是一种常见的功能和组成上类似于胆囊收缩素(Cholecystokinin,CCK)的宿主防御肽,能够刺激胃、胆管和胰腺分泌,降低高血压和缓解肾绞痛、胆囊痛等[18]。这两类动物体内或体表存在的抗菌肽迅速在先天固有免疫领域成为最新最热门的研究。本文重点阐述鱼类中的鲈鱼、石斑鱼、豹鳎鱼、泥鳅抗菌肽及两栖动物中的臭蛙抗菌肽的抗菌谱,提出这几类抗菌肽能在毕赤酵母中成功异源表达的可能性,探讨这几类抗菌肽的应用前景。通过归纳总结这5类抗菌肽的相关基础理论可以为后续该类研究应用提供参考依据。
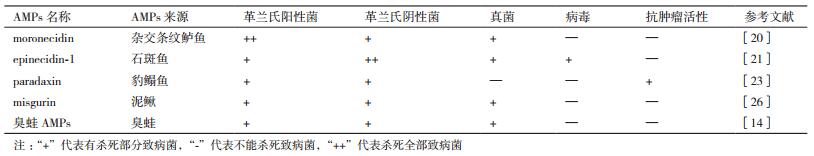
1 鲈鱼、石斑鱼、豹鳎鱼、泥鳅和臭蛙抗菌肽的抗菌谱 1.1 鲈鱼抗菌肽的抗菌谱Moronecidin是从杂交条纹鲈鱼(Hybrid striped bass)鳃和皮肤中分离得到的含23个氨基酸残基,经圆二色谱分析结构呈α-螺旋结构的抗菌肽[19]。预测信号肽(79个氨基酸)包括3个结构域:1个信号肽(22个氨基酸),1个C末端prodomain区域(35个氨基酸)和成熟肽(22个氨基酸),该基因有3个内含子和4个外显子[20]。Moronecidin抗革兰氏阴性菌、革兰氏阳性菌、丝状真菌(Filamentous fungi)和酵母,包括耐抗生素细菌,如铜绿假单胞菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)、耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(Methicillin-resistant S.aureus)和耐万古霉素粪肠球菌(Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis)。Moronecidin对单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌(Listeria monocytogenes)、表皮葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus epidermidis)、大肠杆菌(E. coli)、阴沟肠杆菌(Enterobacter cloacae)、肺炎克雷伯菌(Klebsiella pneumoniae)、卡他莫拉菌(Moraxella catarrhalis)、猪霍乱沙门菌(Salmonella choleraesuis)、小肠结肠炎耶尔森氏菌(Yersinia enterocolitica)、白色念珠菌(Candida albicans)、热带假丝酵母(Candida tropicalis)均具有较强抗菌活性。
1.2 石斑鱼抗菌肽的抗菌谱Epinecidin-1是从条带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)的鳃和肠道中分离到,含21个氨基酸残基保护鱼类免受病原菌感染的一种抗菌肽。完整的epinecidin-1 cDNA 518 bp,预测含67个氨基酸的信号肽,包括3个领域:22个氨基酸的信号肽,25个氨基酸的成熟肽,和20个氨基酸的羧基末端pro区域,epinecidin-1基因含有3个内含子和4个外显子[21]。一种酰胺化的成熟肽epinecidin-1具有很强的抗菌活性,对大多数水产病原菌如副溶血性弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)、溶藻弧菌(Vibrio alginolyticus),创伤弧菌(Vibrio vulnificus),多杀巴斯德氏菌(Pasturella multocida),温和气单胞菌(Aeromonas sobrio),摩氏摩根氏菌(Morganella morganii)、嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)、脑膜脓毒性黄杆菌(Flavobacterium meningosepticum)和大肠杆菌DH5α均有很强的杀菌能力,最低杀菌浓度小于5 μmol。Pan等[22]发现,石斑鱼抗菌肽在已注射嗜盐弧菌(Vibrio vulnificus)的石斑鱼和罗非鱼(Tilapia)中存活率显著增高。
1.3 豹鳎鱼抗菌肽的抗菌谱Paradaxin是最早从豹鳎鱼(Pardachirus marmoratus)体内分离得到的两亲性阳离子a-螺旋结构并具有穿膜作用的抗菌肽,含33个氨基酸残基,具有抗肿瘤活性,该抗菌肽为离子型神经毒素[23-24]。Paradaxin分为ParadaxinI、ParadaxinⅡ两种,是通过离子交换层析、反相高压液相色谱法获得的两种抗菌肽。ParadaxinI和ParadaxinⅡ分别占豹鳎鱼腺体分泌蛋白的10%和8%,ParadaxinI的细胞毒性是ParadaxinⅡ的5-10倍。Paradaxin对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均有抗菌活性,对绵羊红细胞有溶血活性。
1.4 泥鳅抗菌肽的抗菌谱Misgurin是由泥鳅(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)产生的强碱性抗菌肽,含21个氨基酸残基,其中含极性带正电荷的4个赖氨酸和5个精氨酸残基。泥鳅抗菌肽含有1个亲水性甘氨酸对革兰阴性菌的杀菌能力非常有效。此类抗菌肽由于不含半胱氨酸可折叠成疏水或双亲性α-螺旋结构。泥鳅抗菌肽的等电点为11.84,当pH < pI时该蛋白质带正电荷,正电荷的引入使抗菌肽的活性增强,而负电荷的引入可以使抗菌肽的活性减弱,适当的加酸可使抗菌肽的活性增强[25]。泥鳅抗菌肽浓度在10 μg/mL以下的时候对绵羊红细胞没有溶血活性。泥鳅抗菌肽能够杀死大部分革兰阳性菌,部分革兰阴性菌及真菌,这种广谱抗菌的特性是传统抗生素无法比拟的。据Park[26]研究表明,misgurin及合成型misgurin的最低抑菌剂浓度相同,当泥鳅抗菌肽浓度为4 μg/mL时可抑制真菌酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae);当泥鳅抗菌肽浓度为8 μg/mL时可抑制革兰氏阳性菌如枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)、肺炎链球菌(Streptococcus pneumoniae)、恶臭假单胞菌(Pseudomonas putida),同时可以抑制革兰氏阴性菌如大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)、鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium),还可抑制真菌如新型隐球菌(Cryptococcus neoformans);当泥鳅抗菌肽浓度为16 μg/mL时可抑制变形链球菌(Streptococcus mutans)、沙雷氏菌(Serratia sp.)、白色念珠菌(Candida albicans)。
1.5 臭蛙抗菌肽的抗菌谱臭蛙抗菌肽是从臭蛙皮肤上产生的含26个氨基酸残基的生物活性肽,含带负电荷的1个天冬氨酸和1个谷氨酸,含带正电荷的3个赖氨酸和3个精氨酸。Conlon[27]认为蛙的皮肤表面分布大概250多种颗粒腺体,大部分集中在背部区域,合成和分泌多种抗菌活性的多肽,并认为这些多肽是多种基因复制的结果,形成两性α-螺旋结构。蛙类抗菌肽家族十分庞大,包括brevinin-1、brevinin-2、esculentin-1、esculentin-2、ranalexin、ranatuerin-1、ranatuerin-2和temporin peptides等。
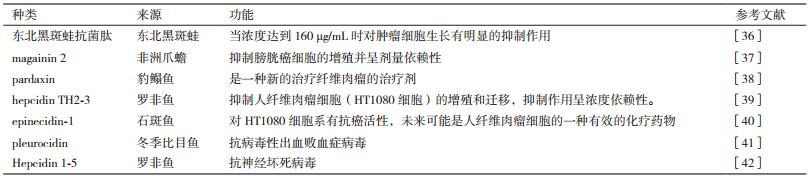
五种抗菌肽的抗菌谱及性质,如表 1、表 2所示。源于鱼类和两栖动物具有抗肿瘤和抗病毒活性的抗菌肽见表 3。
毕赤酵母是一种以甲醇为唯一碳源和能源的酵母,含有甲醇代谢所必须的酶,如醇氧化酶(Alcohol oxidase,AOX)、二羟丙酮合成酶和过氧化氢酶[28],利用毕赤酵母表达时使用最多的是pPIC9K载体,含强有力的启动子AOXI,能快速筛选高拷贝整合转化株,属于表达外源蛋白最高的载体系列[29]。抗菌肽基因编码根据毕赤酵母偏爱密码子设计并用化学方法合成,基因克隆到表达载体再通过电击法转入到毕赤酵母,诱导并已成功表达的有:从冬季比目鱼(Winter flounder)分离到的抗菌肽Pleurocidin[30],从墨西哥鳄梨果实中分离抗菌肽PaDef[31],从鸡中分离到的Fowlicidin-2[32],从巨大天蚕中分离到的Cecropin B[33],合成天蚕素杂合肽Cecropin A(1-8)-Melittin(1-18)[34-35],杂合抗菌肽CA和CB[9]等。鲈鱼、石斑鱼、豹鳎鱼、泥鳅和臭蛙抗菌肽已在本实验室用毕赤酵母成功表达。毕赤酵母表达抗菌肽,筛选表达量高的菌株,通过BMMY培养基加甲醇诱导获得。通过对抗菌肽的研究,将有利于开发抗菌肽类药物,缓解水产养殖遇到的急慢性疾病,避免抗生素带来的直接或间接耐药性。
3 结语泥鳅、鲈鱼和石斑鱼均属于经济鱼类,集约化水产养殖造成的高密度生物量降低了它们抵抗疾病的能力进而引起巨额损失。虽然目前有几种不同的疫苗已被开发,包括肌肉或腹腔注射重组蛋白、合成肽、灭活病毒、DNA疫苗、病毒样颗粒来控制病情。但是,在大多数情况下,鱼类感染病毒通常发生在早期阶段(幼虫和幼鱼时),注射疫苗非常困难。因此,开发新的药物来预防或治疗病毒感染迫在眉睫。抗菌肽作为预防病原菌侵染的重要措施,不同的物种分泌的AMPS抗菌谱有所差异,可用于寻找新的治疗耐病原体的药物[43]。Li等[44]认为部分海洋无脊椎动物抗菌肽为多肽,通过研究删除类似物的效果,发现许多有抗菌潜力抗菌肽局限于较小天然肽区。鱼类和两栖类抗菌肽大部分属于小分子天然肽,因此活性相对较高并具有广谱的抗菌活性,开发利用更具有实际价值。从鱼源中分离的抗氧化剂和抗菌肽可作为食品配方中的功能成分,以促进消费者的健康和提高食品的保质期[45]。通过对抗菌肽的研究,未来将会减少渔业抗生素滥用、鱼肉质量低、渔业养殖病害等问题。抗菌肽作为新型的免疫活性物质应用于环境、食品、医药及水产养殖方面有巨大的潜力,有助于改善当前药物的耐药性、抗生素滥用、环境污染和食品污染等问题。
目前研究抗菌肽有待解决的问题:探索抗菌肽基因表达是否受病原体信号的调节,这种调节机制与皮肤上潜在的有益微生物竞争或抑制病原体的生长之间的微妙平衡是如何完成的;对于酵母重组表达的抗菌肽而言,pH、盐浓度、温度、消化酶是如何影响抗菌肽活性的;如何采用针对性的方法规模化生产和纯化抗菌肽,提高抗菌肽在体内的稳定性并应用于食品配料、医药和水产养殖方面。充分解决上述问题才能更好地应用市场发挥作用。
| [1] |
杨学明, 江林源, 蒋和生. 水生动物抗菌肽及其基因工程研究[J]. 生物技术通讯, 2006, 17(1): 109-111. |
| [2] |
罗琳, 蔡雪峰. 抗菌肽作为水产饲料添加剂的应用前景[J]. 科学养鱼, 2009(2): 65-66. |
| [3] |
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z. APD3:the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(Database issue): D1087-D1093. |
| [4] |
Wang YD, Kung CW, Chen JY. Antiviral activity by fish antimicrobial peptides of epinecidin-1 and hepcidin 1-5 against nervous necrosis virus in medaka[J]. Peptides, 2010, 31(6): 1026-1033. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.02.025 |
| [5] |
Chia TJ, Wu YC, Chen JY, et al. Antimicrobial peptides(AMP)with antiviral activity against fish nodavirus[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 28(3): 1-4. |
| [6] |
Morvan A, Iwanaga S, Comps M, et al. In vitro activity of the limulus antimicrobial peptide tachyplesin i on marine bivalve pathogens[J]. J Invertebr Pathol, 1997, 69(2): 177-182. DOI:10.1006/jipa.1996.4642 |
| [7] |
Ovchinnikova TV, Balandin SV, Aleshina GM, et al. Aurelin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from jellyfish Aurelia aurita with structural features of defensins and channel-blocking toxins[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 348(2): 514-523. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.078 |
| [8] |
Jin LL, Geng YJ, Wang QY. Overview of the membrane-associated methods of antibacterial mechanism of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Journal of Liaoning University, 2014, 41(4): 356-360. |
| [9] |
Jiang X, Gen MA, Zheng-Chao XU, et al. Secreted expression and activity detection of two hybrid antimicrobial peptides in Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Sichuan University, 2007, 3: 673-678. |
| [10] |
Wang X, Yue T, Lee TC. Development of Pleurocidin-poly(vinyl alcohol)electrospun antimicrobial nanofibers to retain antimicrobial activity in food system application[J]. Food Control, 2015, 54: 150-157. DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.02.001 |
| [11] |
Uzzell T, Stolzenberg ED, Shinnar AE, et al. Hagfish intestinal antimicrobial peptides are ancient cathelicidins[J]. Peptides, 2003, 24(11): 1655-1667. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2003.08.024 |
| [12] |
Terova G, Cattaneo AG, Preziosa E, et al. Impact of acute stress on antimicrobial polypeptides mRNA copy number in several tissues of marine sea bass(Dicentrarchus labrax)[J]. BMC Immunology, 2011, 12(1): 1-19. DOI:10.1186/1471-2172-12-1 |
| [13] |
Noga EJ, Silphaduang U, Park NG. Piscidin 4, a novel member of the piscidin family of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2009, 152(4): 299-305. DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.12.018 |
| [14] |
Barra D, Simmaco M. Amphibian skin:a promising resource for antimicrobial peptides[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 1995, 6: 205-209. |
| [15] |
Pintado CO, Pinto FM, Pennefather JN, et al. A role for tachykinins in female mouse and rat reproductive function[J]. Biology of Reproduction, Biology of 2015, 69(3): 940-946. |
| [16] |
Mansi M, Wu MA, et al. Angioedema and the role of bradykinins:new treatments and implications in patients with heart failure[J]. G Ital Cardiol(Rome), 2016, 17(12): 966-971. |
| [17] |
Guzzo LS, Romero TRL, Queiroz-Junior CM, et al. Involvement of endogenous opioid peptides in the peripheral antinociceptive effect induced by the coffee specific diterpene kahweol[J]. Pharmacological Reports Pr, 2015, 67(5): 1010-1015. DOI:10.1016/j.pharep.2015.02.009 |
| [18] |
Bowie JH. Chapter 48 -Caeruleins[J]. Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2013, 338-341. |
| [19] |
Shin SC, Ahn IH, et al. Characterization of two antimicrobial pepti-des from antarctic fishes(Notothenia coriiceps and Parachaenich-thys charcoti)[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(1): e0170821. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0170821 |
| [20] |
Lauth X, Shike H, Burns JC, et al. Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 7: 5030-5039. |
| [21] |
Yin ZX, He W, Chen WJ, et al. Cloning, expression and antimicrobial activity of an antimicrobial peptide, epinecidin-1, from the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides[J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 253(1): 204-211. |
| [22] |
Pan CY, Chen JY, Cheng YS, et al. Gene expression and localization of the epinecidin-1 antimicrobial peptide in the grouper(Epinephelus coioides), and its role in protecting fish against pathogenic infection[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2007, 6: 403-413. |
| [23] |
Lazarovici P, Primor N, Loew LM. Purification and pore-forming activity of two hydrophobic polypeptides from the secretion of the Red Sea Moses sole(Pardachirus marmoratus)[J]. J Biol Chem, 1986, 261(35): 16704-16713. |
| [24] |
Rahamim E, Barenholz Y, Zlotkin E, et al. Paradaxin alters the morphology of vertebrate red blood cells:A scanning electron microscopy study[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1985, 2: 167-167. |
| [25] |
胡功铃. 杂合抗菌肽HMCM的原核表达及其抗菌活性的初步鉴定[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011.
|
| [26] |
Park CB, Lee JH, Park IY, et al. A novel antimicrobial peptide from the loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus[J]. Febs Letters, 1997, 411(2-3): 173-178. DOI:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00684-4 |
| [27] |
Conlon JM, et al. Antimicrobial peptides from ranid frogs:taxonomic and phylogenetic markers and a potential source of new therapeutic agents[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2004, 1: 1-14. |
| [28] |
欧阳立明, 张惠展, 等. 巴斯德毕赤酵母的基因表达系统研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2000(2): 151-154. |
| [29] |
蔡鹏, 姜宁, 张爱忠, 等. 毕赤酵母表达系统应用于抗菌肽表达的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2015(11): 56-60. |
| [30] |
Burrowes OJ, Diamond G, Lee TC. Recombinant expression of pleurocidin cDNA usingthe Pichia pastoris expression system[J]. Biomed Research International, 2004, 2005(4): 374-384. |
| [31] |
Meng DM, et al. Recombinant expression, purification and antimicrobial activity of a novel antimicrobial peptide PaDef in Pichia pastoris[J]. Protein Exp Purifi, 2017, 130: 90-99. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2016.10.003 |
| [32] |
Xiao Y, Herrera AI, Bommineni YR, et al. The central kink region of fowlicidin-2, an alpha-helical host defense peptide, is critically involved in bacterial killing and endotoxin neutralization[J]. Journal of Innate Immunity, 2009, 1(3): 268-280. DOI:10.1159/000174822 |
| [33] |
Florack D, Allefs S, et al. Expression of giant silkmoth cecropin B genes in tobacco[J]. Transgenic Res, 1995, 2: 132-141. |
| [34] |
Diazachirica P, Ubach J, Guinea A, et al. The plasma membrane of Leishmania donovani promastigotes is the main target for CA(1-8) M(1-18), a synthetic cecropin A-melittin hybrid peptide[J]. Biochemical Journal, 1998, 330(1): 453-460. DOI:10.1042/bj3300453 |
| [35] |
Feng X, Jing LI, Song X, et al. Study on recombinant expression of antimicrobial peptides FAPs in Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2013, 44(9): 68-72. |
| [36] |
郝镯, 王雅丽, 李楠, 等. 蛙皮抗菌肽的提取及抗肿瘤活性检测[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2015(5): 169-171. |
| [37] |
Lehmann J, Retz M, Sidhu SS, et al. Antitumor activity of the antimicrobial peptide magainin Ⅱ against bladder cancer cell lines[J]. European Urology, 2006, 50(1): 141-147. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.043 |
| [38] |
Wu SP, Huang TC, Lin CC, et al. Pardaxin, a fish antimicrobial peptide, exhibits antitumor activity toward murine Fibrosarcoma in vitro and in vivo[J]. Marine Drugs, 2012, 8: 1852-1869. |
| [39] |
Chen JY, Lin WJ, Lin TL. A fish antimicrobial peptide, tilapia hepcidin TH2-3, shows potent antitumor activity against human fibrosarcoma cells[J]. Peptides, 2009, 30(9): 1636-1642. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2009.06.009 |
| [40] |
Lin W, Chien YC, Lin T, et al. Epinecidin-1, an antimicrobial peptide from fish(Epinephelus coioides)which has an antitumor effect like lytic peptides in human fibrosarcoma cells[J]. Peptides, 2009, 30(2): 283-290. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2008.10.007 |
| [41] |
Falco A, Ortega-Villaizan M, Chico V, et al. Antimicrobial peptides as model molecules for the development of novel antiviral agents in aquaculture[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2009, 10: 1159-1164. |
| [42] |
Chia TJ, Wu YC, Chen JY, et al. Antimicrobial peptides(AMP)with antiviral activity against fish nodavirus[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 28(3): 1-6. |
| [43] |
Rajanbabu V, Chen JY. Applications of antimicrobial peptides from fish and perspectives for the future[J]. Peptides, 2011, 32: 415-420. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.11.005 |
| [44] |
Li W, Tailhades J, O'Briensimpson NM, et al. Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides:potential therapeutics against antibiotic-resistant bacteria[J]. Amino Acids, 2014, 10: 2287-2294. |
| [45] |
Najafian L, Babji AS. A review of fish-derived antioxidant and antimicrobial peptides:their production, assessment, and applications[J]. Peptides, 2011, 33(1): 178-185. |