组蛋白修饰是一种常见的表观遗传调控分子机制,与植物的生长发育和胁迫反应具有一定的关系,不同的环境胁迫均可导致组蛋白修饰的改变。组蛋白修饰包括组蛋白乙酰化、甲基化、泛素化及磷酸化等过程,目前对组蛋白乙酰化的研究较为清楚和深入。该过程是动态和可逆的,包括乙酰化和去乙酰化两个过程,分别由组蛋白乙酰转移酶(HATs)和组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDACs)催化完成[1]。
组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDACs)是一个超基因家族,在真核生物(包括酵母、哺乳动物和植物)中广泛存在。自从1996年第一个组蛋白去乙酰化酶HDAC1从人类淋巴T细胞中克隆出来,其在真菌、动植物中也被相继鉴定出来。目前,通常采用HDAC特异性抑制剂(SAHA、trichostatin A或butyrate)处理植物或在转基因植物中使HDAC基因过度或反义表达等方法来研究HDACs的功能。植物HDACs代表了一个多基因大家族,不同的亚细胞定位和表达谱意味着其功能的多样性,越来越多的数据表明HDACs在植物生长发育中发挥关键作用,其中包括花发育[2]、种子发育[3]、根发育[4]以及器官生长过程中细胞的增殖[5]和死亡[6, 7]等,同时响应生物和非生物胁迫,如干旱[8]、盐胁迫[9]、低温[10]、ABA[9]等。除此之外,HDAC还与基因沉默、细胞周期进程等有关。目前对植物中HDACs的功能研究主要集中在拟南芥等背景和基因组比较小的草本植物中,木本类植物相对较少;而且主要集中在干旱、盐渍等方面,对于其在低温中的作用研究还有待于进一步探讨。本文主要就HDACs的分类以及在植物发育和胁迫反应中的作用进行了综述,旨在为进一步研究HDAC在植物中的表观遗传调控机理以及培育抗逆新品种奠定理论基础。
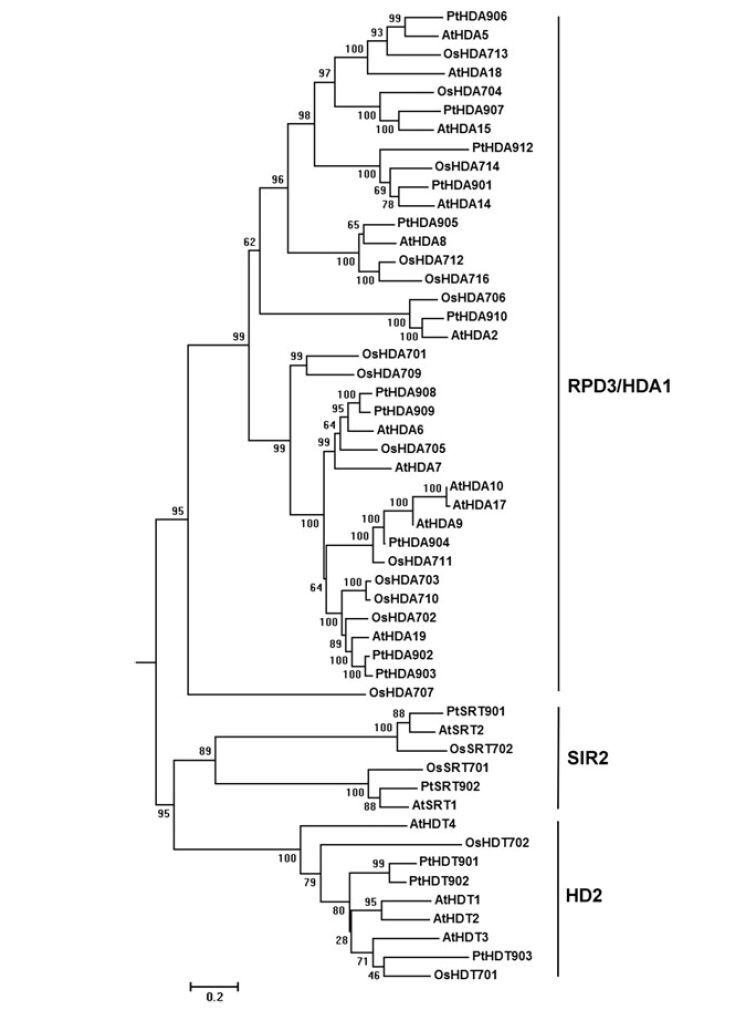
1 HDAC家族分类HDACs广泛分布于动物、酵母以及植物中,基于酵母HDAC序列的同源性分析,植物HDACs可分为3个亚家族:RPD3/HDA1家族,SIR2家族以及HD2家族[11](图 1)。RPD3/HDA1家族与酵母RPD3和HAD-1相关,SIR2-like与酵母SIR2同源,HD2最初是在玉米中发现的,该家族是植物特有的一类蛋白,目前在动物中还没有发现[12, 13]。HDACs定位于细胞核、细胞质,或在细胞核和细胞质之间穿梭。除此之外,HDACs也分布在叶绿体、线粒体、内质网等细胞器中。HDACs不同的细胞定位与其细胞功能有关,调节组蛋白结构和功能的HDACs主要定位于细胞核中。RPD3/HDA1亚家族成员分布在细胞核、细胞质和一些细胞器中,不同的成员其在细胞中的定位有所不同[14]。与RPD3/HDA1亚家族不同,HD2特定定位于核仁中,这可能与它参与调节核糖体的结构和功能有关。SIR2-like亚家族成员及其同源物主要位于细胞的核仁内[15]。
1.1 RPD3/HDA1-like家族RPD3/HDA1是HDACs家族中最大的一个亚家族,该家族依赖于Zn2+,其家族成员与酵母RPD3和HDA-1同源,且该家族成员都包含有一个典型的组蛋白去乙酰化酶结构域。第一个RPD3/HDA1的cDNA是从玉米中分离获得的,目前在拟南芥中发现了12个该亚家族成员。此类亚家族的酶活性受到TSA和Sodium butyrate的抑制[16]。
1.2 HD2家族HD2是植物特有的一类HDAC亚家族,该家族成员结构与其他真核生物中已确定的HDAC结构不同,且在酵母和动物中均未发现[17]。该亚家族的存在反映了植物在发育调控和胁迫反应等方面可能与哺乳动物和酵母存在一定的区别。HD2亚家族的一些成员定位于核仁,其他一些在胚珠和种子发育中发挥作用[18]。HD2蛋白由3个结构域组成:具有保守五肽序列的N末端结构域、高电荷的中央酸性结构域和可变的C末端结构域[19]。HD2最初是通过对玉米胚乳体外纯化得到的,其活动形式是一种磷酸化蛋白。进一步鉴定结果表明HD2可以被酪蛋白激酶Ⅱ在体外磷酸化,如果将HD2溶解液中的磷酸盐去除会大幅降低其活性[20]。
1.3 SIR2-l ike家族植物SIR2-like家族(又被称为sirtuins)是与酵母SIR2同源的一类HDAC,该亚家族成员可被烟酰胺(nicotinamide)、splitomicin和sirtinol等所抑制[21],但却不受TSA和Sodium butyrate的影响。蛋白结构域分析表明,该家族蛋白包含7个保守结构域,保守结构域在不同家族成员的组成及分布位置存在多样性。对SIR2家族成员分析发现,此类家族成员从原核到真核生物都比较保守,并以NAD+为辅酶以行使组蛋白去乙酰化酶的活性[22]。
2 HDAC家族在植物中的作用 2.1 HDACs在植物生长发育中的作用对HDACs在植物生长发育中的作用研究主要集中在拟南芥中。最近对玉米、辣椒和番茄也有相关报道。
HDAC基因表达的改变会影响植物的生长发育和表型的改变。拟南芥中反义抑制或T-DNA的插入会引起AtHD1/AtHDA19(AtHD1或AtRPD3A)表达下调,最终导致植株早期衰老、叶片呈锯齿状、花器官一致性上的缺陷和晚开花等一系列发育缺陷[18]。在胚胎发育过程中AtHD1/AtHDA19也可能和TPL(a transcriptional co-repressor)配合促使根与芽的分化[23]。AtHDA6,是AtHDA19的同源物,在拟南芥中通过抑制FLC(flowering locus C)的表达来控制开花时间,从而参与花的发育。Probst等[24]研究表明AtHDA6的突变体有明显的延迟开花的现象。此外,HDA7在拟南芥雌配子体和胚胎的发育中起到了关键作用[25],而HDA18功能的缺失导致了拟南芥根表皮细胞结构的改变[26]。
HDACs也参与种子的发育。拟南芥中AtHD2A的反义表达会导致种子发育的终止[3],AtHD2A基因的过度表达引起叶和花的形态缺陷并且延迟开花,此外还中止种子发育[27]。Grozinger等[28]用sirtuin家族基因抑制剂sirtinol处理拟南芥发现,处理过的拟南芥植株下胚轴明显变短而且没有主根,说明了sirtuin家族基因参与了植株的生长发育。在水稻中,OsHDA704的下调表达引起了植株的矮小致死和种子粒厚的减小[29]。
玉米中ZmHDA101的超表达和反义表达都会使转基因玉米呈现生长缓慢和开花晚的现状,而且成年转基因植物也显示出表型改变的情况,如改变花序形态和分化,花药异常开裂并降低了生育能力[30]。李涛等[31]在对辣椒发育过程中的HDAC家族各成员进行了研究发现,CaHDA1在果皮和胎座成熟过程中的表达量逐渐升高,意味着该基因可能参与了辣椒后期果实的发育过程。Zhao等[32]通过酵母双杂交分析研究发现番茄RPD3/HDA1亚 家族成员SlHDA1、SIHDA3 和SlHDA4与番茄生殖发育相关的两个蛋白相互作用,表明了这些基因可能参与番茄生殖发育的基因调控。
2.2 HDACs在逆境胁迫反应中的作用植物在生长过程中会经受各种生物和非生物胁迫,在这个过程中植物中的组蛋白通过乙酰化和甲基化等过程发生改变。最近的研究表明组蛋白去乙酰化酶参与了植物对胁迫相关激素以及各种胁迫(盐、干旱、低温和病原菌等)的反应。
HDACs参与生物和非生物胁迫,在脱落酸(ABA)信号和非生物胁迫中发挥作用。拟南芥中AtHD2C的表达受到ABA的抑制,AtHD2C在转基因拟南芥株系中的过量表达影响几个ABA响应基因的表达。高盐处理20 d,大约60% AtHD2C转基因植物叶片成 活,而野生型叶片成活率只有5%[33]。与此相反,AtHD2C的 T-DNA插入突变体(hd2c-1和hd2c-3)在种子发芽期间对ABA和盐更敏感[9]。此外,用ABA处理大麦6 h后HvHDAC2-2基因的表达受到抑制[34]。
拟南芥AtHDA19通过调节组蛋白去乙酰化来参与植物生长发育和响应环境胁迫。损伤、病原体感染以及乙烯均能诱导AtHDA19的表达[35]。AtHDA19的过表达可以增加ERF1(乙烯反应因子1)的表达量,提高转基因植株对病原体的抗性。而Choi等[36]研究表明AtHDA19在S A-依赖的信号途径的基础防御中起到了负面作用。T-DNA插入的AtHDA19突变体hda19-1对盐胁迫和ABA极为敏感,且在突变体植株中ABA应答基因的表达量有所下降;NaCl和ABA处理下,突变体种子的发芽率比野生型低得多[37]。AtHDA6也参与病原体反应和环境胁迫,ABA和JA诱导AtHDA6基因的表达。AtHDA6突变体和HDA6-RNAi植物比野生型植株对ABA和盐胁迫表现更加敏感,且在ABA和非生物胁迫下应答基因的表达有所下降[38]。最近一份研究报告表明,低温(2 ℃ )处理下拟南芥AtHDA6的转录上调,与野生型相比,经过低温驯化后hda6的突变体axe1-5对低温(-18 ℃ )高度敏感[39]。
水稻中HDT701、HDT702及HDA707的表达受水杨酸、脱落酸和茉莉酸的影响;而HDA714、SRT702和SRT701的表达则受寒冷、盐渍和甘露醇等非生物胁迫的调节[40]。研究显示水稻SRT1基因超表达后可以增强水稻的氧化胁迫抗性[41]。玉米HDACs(ZmHDAC101、ZmHDAC102、ZmHDAC103、ZmHDAC106、ZmHDAC108 和ZmHDAC110)在低温胁迫下高度诱导,同时TSA处理抑制了ZmDREB1和ZmCOR413等冷反应基因的诱导,说明了HDAC活性是低温应激反应必须的,而且可以激活低温诱导基因的转录[10]。此外,玉米HDACs是植物抵抗真菌病原菌所必需的,并且可以和植物病原菌相互作用。大麦中HD2基因与植物胁迫相关激素如JA、ABA、SA有关,意味着这些基因参与了植物非生物胁迫反应[34]。
3 展望组蛋白去乙酰化是一种十分重要的表观遗传修饰,其参与的基因表达调控是一个复杂的过程,既涉及与组蛋白乙酰转移酶的共同作用,也涉及与DNA甲基化的相互作用。通过对拟南芥等植物的研究,人们对组蛋白去乙酰化酶有了一定了解。目前,HDAC基因家族已在拟南芥、水稻和玉米等多种植物中被鉴定,其在植物基因调控和生长发育中的作用已经在拟南芥中得到深入研究。另外,在玉米、大麦等植物中也有报道,但是其在木本植物中的研究却相对较少。HDAC基因家族参与生物和非生物胁迫,如ABA、乙烯、盐渍引起的相关基因表达,但对其在低温等其他非生物胁迫中的作用研究相对较少。对HDAC基因家族在植物生长发育、逆境胁迫等方面的作用进行了大量的研究,但对其具体的调控机制还不清楚。
因此,植物HDAC基因家族仍有待深入和广泛的研究。在草本植物研究的基础上,增加对木本植物中HDAC基因家族的作用研究,探究其在不同的种属之间是否存在功能差异。同时,探索HDAC参与生长发育和胁迫反应的表观遗传调控机理(包括其上游调节基因),以及开展相关胁迫基因功能的鉴定工作,这对于培育优良的抗逆新品种将具有重大意义。
| [1] | Ma XJ, Lv SB, Zhang C, et al. Histone deacetylases and their functions in plants. Plant Cell Rep , 2013, 32 : 465–478. DOI:10.1007/s00299-013-1393-6 |
| [2] | Li C, Huang L, Xu C, et al. Altered levels of histone deacetylase OsHDT1 affect differential gene expression patterns in hybrid rice. PLoS One , 2011, 6 : e21789. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0021789 |
| [3] | Wu KQ, Tian LN, Malik K, et al. Functional analysis of HD2 histone deacetylase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal , 2000, 22 : 19–27. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00711.x |
| [4] | Xu CR, Liu C, Wang YL, et al. Histone acetylation affects expression of cellular atterning genes in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA , 2005, 102 : 14469–14474. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0503143102 |
| [5] | Nelissen H, Flemy D, Bruno L, et al. The elongate mutants identify a functional Elongator complex in plants with a role in cell proliferation during organ growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , 2005, 102 (21) : 7754–7759. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0502600102 |
| [6] | Huang L, Sun Q, Qin F, et al. Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2-related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice. Plant Physiol , 2007, 144 : 1508–1519. DOI:10.1104/pp.107.099473 |
| [7] | Bourque S, Dutartre A, Hammoudi V, et al. Type-2 histone deacetylases as new regulators of elicitor-induced cell death in plants. The New Phytologist , 2011, 192 : 127–139. DOI:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03788.x |
| [8] | Sridha S, Wu K. Identification of AtHD2C as a novel regulator of abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J , 2006, 46 : 124–133. DOI:10.1111/tpj.2006.46.issue-1 |
| [9] | Luo M, Wang YY, Liu X, et al. HD2C interacts with HDA6 and is involved in ABA and salt stress response in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot , 2012, 63 (8) : 3297–3306. DOI:10.1093/jxb/ers059 |
| [10] | Hu Y, Zhang L, Zhao L, et al. Trichostatin A selectively suppresses the coldinduced transcription of the ZmDREB1 gene in maize. PLoS One , 2011, 6 : e22132. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0022132 |
| [11] | Kyproμla D, Aliki K, Konstantinos B, et al. Epigenetic chromatin modifiers in barley:Ⅱ. Characterization and expression analysis of the HDA1 family of barley histone deacetylases during development and in response to jasmonic acid. Plant Mol Biol Rep , 2010, 28 : 9–21. DOI:10.1007/s11105-009-0121-4 |
| [12] | Clemente S, Franco L, Lopez-Rodas G. Distinct site specificity of two pea histone deacetylase complexes. Biochemistry , 2001, 40 : 10671–10676. DOI:10.1021/bi0100844 |
| [13] | Lusser A, Brosch G, Loidl A, et al. Identification of maize histone deacetylase HD2 as an acidic nucleolar phosphoprotein. Science , 1997, 277 : 88–91. DOI:10.1126/science.277.5322.88 |
| [14] | Alinsug MV, Chen FF, Luo M, et al. Subcellular localization of class Ⅱ HDAs in Arabidopsis thaliana:nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HDA15 is driven by light. PLoS One , 2012, 7 : e30846. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0030846 |
| [15] | Guarente L. Sir2 links chromatin silencing, metabolism, and aging. Genes Dev , 2000, 14 : 1021–1026. |
| [16] | Hollender C, Liu Z. Histone deacetylase genes in Arabidopsis development. J Integr Plant Biol , 2008, 50 : 875–885. DOI:10.1111/jipb.2008.50.issue-7 |
| [17] | Pandey R, Muller A, Napoli C A, et al. Analysis of histoneacetyl transferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res , 2002, 30 : 5036–5055. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkf660 |
| [18] | Chen ZJ, Tian L. Roles of dynamic and reversible histone acetylation in plant development and polyploidy. Biochim Biophys Acta , 2007, 1769 : 295–307. DOI:10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.04.007 |
| [19] | Dangl M, Brosch G, Haas H, et al. Comparative analysis of HD2 type histone deacetylases in higher plants. Planta , 2001, 213 : 280–285. DOI:10.1007/s004250000506 |
| [20] | K?lle D, Brosch G, Lechner T, et al. Different types of maize histo-ne deacetylases are distinguished by a highly complex substrate and site specificity. Biochemistry , 1999, 38 : 6769–6773. DOI:10.1021/bi982702v |
| [21] | Michael DJ, Manning TS, Norman JO, et al. Mechanism of nicotinamide inhibition and transglycosidation by Sir2 histone/protein deacetylases. Journal of Biological Chemistry , 2003, 278 : 50985–50998. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M306552200 |
| [22] | Frye RA. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications , 2000, 273 : 793–798. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3000 |
| [23] | Fong PM, Tian L, Chen ZJ. Arabidopsis thaliana histone deacetylase 1(AtHD1)is localized in euchromatic regions and demonstrates histone deacetylase activity in vitro. Cell Res , 2006, 16 : 479–488. DOI:10.1038/sj.cr.7310059 |
| [24] | Probst AV, Fagard M, Proux F, et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 is required for maintenance of transcriptional gene silencing and determines nuclear organization of rDNA repeats. Plant Cell , 2004, 16 : 1021–1034. DOI:10.1105/tpc.018754 |
| [25] | Cigliano RA, Cremona G, Paparo R, et al. Histone deacetylase AtHDA7 is required for female gametophyte and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol , 2013, 163 : 431–440. DOI:10.1104/pp.113.221713 |
| [26] | Liu C, Li LC, Chen WQ, et al. HDA18 Affects Cell Fate in Arabidopsis root epidermis via histone acetylation at four kinase genes. Plant Cell , 2013, 25 : 257–269. DOI:10.1105/tpc.112.107045 |
| [27] | Zhou C, Labbe H, Sridha S, et al. Expression and function of HD2-type histone deacetylase in Arabidopsis development. Plant J , 2004, 38 : 715–724. DOI:10.1111/tpj.2004.38.issue-5 |
| [28] | Grozinger CM, Chao ED, Blackwell HE, et al. Identification of a class of NAD-dependent deacetylases small molecule phenotypic inhibitors of the sirloin family of byscreening. J Biol Chem , 2001, 276 : 38837–38843. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M106779200 |
| [29] | 秦付军. 水稻组蛋白甲基转移酶和去乙酰化酶基因的功能研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2010. http://epub.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=31&CurRec=1&recid=&FileName=2010271866.nh&DbName=CDFD0911&DbCode=CDFD&pr= |
| [30] | Rossi V, Locatelli S, Varotto S, et al. Maize histone deacetylase hda101is involved in plant development, gene transcription, and sequence-specific modulation of histone modification of genes and repeats. Plant Cell , 2007, 19 : 1145–1162. DOI:10.1105/tpc.106.042549 |
| [31] | 李涛, 徐小万, 黎振兴, 等. 辣椒组蛋自去乙酞化基因家族分离鉴定及表达分析. 辣椒杂志 , 2015, 1 : 1–7. |
| [32] | Zhao L, Lu J, Zhang J, et al. Identification and characterization of histone deacetvlases in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum). Front Plant Sci , 2014, 5 : 760. |
| [33] | Sunandini S, Wu KQ. Identification of AtHD2C as a novel regμlator of abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J , 2006, 46 : 124–133. DOI:10.1111/tpj.2006.46.issue-1 |
| [34] | Demetriou K, Aliki K, Alessandro T, et al. Epigenetic chromatin modifiers in barley:I. Cloning, mapping and expression analysis of the plant specific HD2 family of histone deacetylases from barley, during seed development and after hormonal treatment. Physiologia Plantarum , 2009, 136 : 358–368. DOI:10.1111/ppl.2009.136.issue-3 |
| [35] | Zhou CH, Zhang L, Duan J, et al. HISTONE DEACETYLASE 19 is involved in jasmonic acid and ethylene signalling of pathogen response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell , 2005, 17 : 1196–1204. DOI:10.1105/tpc.104.028514 |
| [36] | Choi SM, Song HR, Han SK, et al. HDA19 is required for the repression of salicylic acid biosynthesis and salicylic acid-mediated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J , 2012, 71 (1) : 135–146. DOI:10.1111/tpj.2012.71.issue-1 |
| [37] | Chen LT, Wu KQ. Role of histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA19 in ABA and abiotic stress response. Plant Signaling & Behavior , 2010, 5 : 1318–1320. |
| [38] | Chen LT, Luo M, Wang YY, et al. Involvement of Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA6 in ABA and salt stress response. Journal of Experimental Botany , 2010, 61 : 3345–3353. DOI:10.1093/jxb/erq154 |
| [39] | To TK, Kim JM, Matsui A, et al. Arabidopsis HDA6 regulates locus-directed heterochromatin silencing in cooperation with MET1. PLoS Genet , 2011, 7 : e1002055. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002055 |
| [40] | Guarente L. Sir2 links chromatin silencing, metabolism, and aging. Genes Dev , 2000, 14 : 1021–1026. |
| [41] | Zhong X, Zhang H, Zhao Y, et al. The rice NAD-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRTI targets preferentially to stress-and metabolism-related genes and transposable elements. PLoS One , 2013, 8 (6) : e66807. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0066807 |