脂肪酸是一类重要的营养成分,对人体起着十分重要的作用,尤其是高度不饱和脂肪酸(Highlyunsaturated fatty acid,HUFA),能降低心脑血管疾病[1],抗衰老[2],促进婴幼儿发育,增强记忆力[3],同时对能量代谢、维持细胞膜结构与功能以及信号转导等生命活动有着至关重要的作用[4]。脂肪酸去饱和酶和碳链延长酶是HUFA 合成过程中的关键酶[5, 6]。动物脂肪酸去饱和酶主要有4 种,包括△9去饱和酶、△5 去饱和酶、△6 去饱和酶和△4 去饱和酶,其中△6 去饱和酶为第一限速酶。这种膜结合的蛋白酶催化HUPA 生物合成的第一步,能分别将亚油酸(C18 :2n-6)和亚麻酸(C18 :3n-3)催化为C18 :3n-6 和C18 :4n-3[7, 8]。除此之外,有研究表明△6 去饱和酶是EPA 和花生四烯酸合成过程中的限速关键酶[9, 10]。△6 去饱和酶在水产动物,尤其是水产脊椎动物上的研究较多。研究者们分别从虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)[11]、斑马鱼(Daniorerio)[12]、鲤鱼[13]、大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)[14]、军曹鱼(Rachycentron canadum)[15]等多种脊椎鱼类中克隆得到△6 去饱和酶基因全长。然而这在甲壳动物中研究甚少,仅在中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheirsinensis)[16]有过报道。
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus) 俗称梭子蟹,属甲壳纲,十足目,梭子蟹科,是我国重要的经济海水蟹类,其营养丰富,滋味独特,深受人们的喜爱。其中,HUFA 在三疣梭子蟹中发挥十分重要的生理功能,能够促进蟹类生长及性腺发育[17, 18, 19]。现在水产养殖业中,对经济蟹类的营养需求方面多集中在中华绒螯蟹上,对三疣梭子蟹脂肪酸需求,特别是对HUFA 需求报道甚少。鉴于此,我们试从分子学角度入手,首次克隆三疣梭子蟹△6去饱和酶基因全长,同时进行相关生物学分析,并构建其组织表达谱,旨在为进一步研究三疣梭子蟹△6 去饱和酶功能,探明三疣梭子蟹HUFA 合成机理奠定分子基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料实验中所用三疣梭子蟹,雌雄(雌126±10 g,雄212±10 g)各3 只,均购自上海芦潮港水产市场。解剖三疣梭子蟹,取其肝胰腺、胸神经节、心脏、肌肉、眼柄、肠道、胃、鳃共8 种组织存于-80℃冰箱作为实验样品。
实验室所用的试剂均来自日本TaKaRa 公司(RNAisoTM Plus、Reverse Transcriptase、dNTPs、rTaq聚合酶、DNA Marker、pMD19-T Simple 载体试剂盒、IPTG、X-Gal、SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM、琼脂糖)、天根生化科技有限公司(氨苄青霉素、TOP10 感受态细胞、琼脂糖凝胶DNA 回收试剂盒)、Clontech 公司(SMARTTM RACE cDNA Amplification Kit、Advantage2 PCR Kit);、生工生物工程有限公司(无菌去离子水、DEPC 水、50×TAE buffer、5×TBE buffer)、上海赛百盛基因技术有限公司(核酸染料Gold view)及国药集团化学试剂有限公司(酒精、三氯甲烷等)。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 核酸的提取和反转录参照RNAisoTM Plus(TaKaRa)操作说明书,取三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺样品提取总RNA,经1% 琼脂糖凝胶电泳和紫外分光光度计(Q5000)检测RNA 完整度及浓度。根据PrimscriptTM Reverse Transcriptase(TaKaRa)说明书,取1.0 μg 三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺总RNA 反转录成模板第一链cDNA。
1.2.2 引物设计及序列验证根据实验室所构建的三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺cDNA 文库,通过NCBI blast比对发现,有一预测的Δ6 去饱和酶基因序列片段与中华绒螯蟹的Δ6 去饱和酶(GenBank 登录号JX946434)相似度十分高。根据已知片段序列设计一对上下游引物(表 1),PCR 扩增,按照琼脂糖凝胶DNA 回收试剂盒(天根)回收纯化,并送上海工程生物工程公司测序,对已知序列进行验证。
1.2.3 △6 去饱和酶基因的克隆
根据已验证的序列,设计3'-FAD RACE 上游引物和5'-FAD RACE下游引物( 表 1)。利用SMARTTM RACE cDNAAmplification Kit(Clontech)试剂盒反转录合成3'-cDNA 第一链和5'-cDNA 第一链,作为基因3' 和5' 端序列快速扩增的模板,并按照SMARTTM RACEcDNA Amplification Kit 说明书上的反应体系及反应条件进行三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因的扩增。
PCR 反应体系:3'-cDNA(5'-cDNA) 模板2.5 μL,10 μmol/L 的 3'-FAD(5'-FAD) 引物1.0μL,10 mmol/L dNTP Mix 1.0 μL,50× Advantage 2Polymerase Mix 1.0 μL,10×Advantage 2 PCR buffer缓冲液5.0 μL,UPM 通用引物5.0 μL,加无菌去离子水至总体积50.0 μL。反应条件:94℃ 30 s,72℃3 min,5 个循环;94℃ 30 s,70℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min,5 个循环;94℃ 30 s,68℃ 30 s,72℃ 3 min,25 个循环。RACE PCR 产物进行胶回收、克隆并送上海生工生物工程公司测序。
1.2.4 目的基因序列分析利用NCBI Vecscreen网站去除测序结果的载体序列,然后进行片段的拼接。开放阅读框的寻找利用ORF(Open readingframe)finder 软件;序列翻译和蛋白质相似性分析利用ClustalW 及DNAMAN 等软件;相对分子量和蛋白质等电点的计算使用Compute pI/Mw(http ://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/);系统进化树构建用MEGA6.0 软件的邻接法(Neighbor-Joining,NJ)进行。
1.2.5 Δ6 去饱和酶基因在各组织中的表达将已获得的各组织cDNA 作为模板,通过克隆得到的全长序列设计荧光定量PCR 引物(表 1)。根据Livak等[20]提出的相对标准曲线法 2-ΔΔCt,以三疣梭子蟹β-actin 基因(GenBank 登录号FJ641977.1)为内参,雌雄各3 只,每个组织分别3 个重复。利用CFX96仪器进行标准曲线的制作及不同组织荧光定量PCR的扩增。标准曲线的制作以肝胰腺cDNA 为模板,以5 倍梯度进行稀释,分别进行Δ6 去饱和酶基因和β-actin 基因引物的荧光定量PCR,得出各稀释模板Ct 值,制作标准曲线,反应体系:SYBR Premix ExTaqTM(2×)12.5 μL,上下游引物各0.25 μL,cDNA模板2 μL,加去离子水至终体积为25 μL ;反应程序为:95℃ 30 s ;95℃ 5 s,62℃ 30 s,40 个循环,65℃至熔解曲线。利用SPSS 17.0 软件进行统计分析,数据均用平均值± 标准差(x-±s)表示。
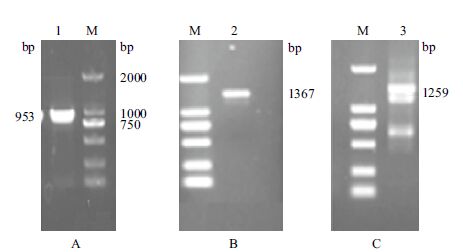
2 结果 2.1 Δ6去饱和酶基因cDNA的序列分析从三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺中提取总RNA,反转为模板,设计验证引物扩增获得三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因部分片段,大小为953 bp,与实验室基因库中预测结果相符(图 1-A),初步确定为三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因。根据已验证的引物设计RACE 引物,经过3'-RACE PCR 和5'-RACE PCR 扩增后分别获得1 367 bp(图 1-B)和1 259 bp(图 1-C)片段,与预期片段大小基本一致。拼接测序结果,该基因全长2 875 bp,其中包括465 bp 的5' 非编码区(UTR),1 078 bp 的3' 非编码区(UTR),开放阅读框(ORF)长1 332 bp,编码443 个氨基酸,同时具有加尾信号(AATAAA)以及Poly-A 尾(图 2)。分析序列表明,编码理论等电点为8.52,分子量为50.62 kD 的氨基酸。同时,该序列具有典型的组氨酸簇保守区域,HNXFH( 第186-190 位)、HALSHH( 第214-219 位)和HTLHH(第378-382 位),属于典型的去饱和酶结构[16, 22]。经BLASTn、BLASTp 等比对表明,此序列与中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)Δ6去饱和酶基因序列具有高度的相似性,由此初步确定此序列为三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶序列。
|
| 图 1 三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因PCR 扩增产物 M :DL2000 DNA Marker ;1 :Δ6 去饱和酶基因部分片段PCR 扩增结果; 2 :Δ6 去饱和酶基因3' RACE PCR 扩增结果;3 :Δ6 去饱和酶基因5' RACE PCR 扩增结果 |

|
| 图 2 三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸全长cDNA 序列及推测的氨基酸序列 实线框表示起始密码子及终止密码子;虚线框表示Ploy(A)加尾信号AATAAA ;下划线表示3 个保守的组氨酸簇结构域 |
使用ClustalX 软件将三疣梭子蟹去饱和酶氨基酸序列与其他代表性的脊椎动物与无脊椎动物进行Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸多序列比对。结果(图 3)表明,三疣梭子蟹的Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸与中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)、大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)、罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)、利什曼原虫(Leishmaniadonovani)以及线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)的Δ6去饱和酶氨基酸都具有一个血红素结合的HPGG 保守结构域,相似性分别为66%、37%、37%、24%和40%。与人(Homo sapiens)的Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸相似性要高于与Δ5 去饱和酶氨基酸的相似性,分别为39% 和32%。

|
| 图 3 三疣梭子蟹与其他物种Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸序列比较 |
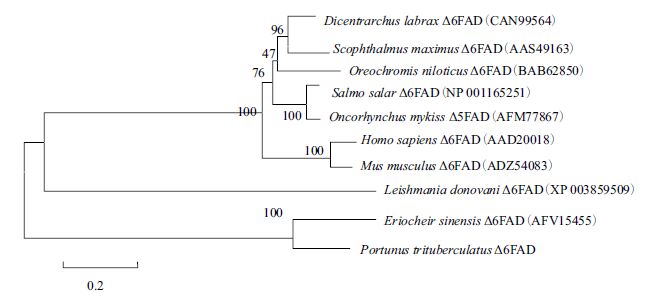
利用MEGA6.0 软件的邻接法(Neighbor-Joining)将相关代表脊椎动物和无脊椎动物的Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸序列构建发育树。此外,该发育树还包括可能存在于脊椎动物中的另一种与Δ6 去饱和酶相似度较大的膜结合蛋白Δ5 去饱和酶。脊椎动物中,包括鱼类的很多Δ6 去饱和酶已经被确定,但是在无脊椎动物中被确定较少。因此选择所做的鱼类和其他脊椎动物发育树的分支比无脊椎动物的分支要宽广,共同聚成一大支。同时,三疣梭子蟹的Δ6 去饱和酶与中华绒螯蟹的Δ6 去饱和酶同聚一小支,形成单独的一体,表明这两个物种亲缘关系接近。
2.3 三疣梭子蟹Δ6去饱和酶mRNA不同组织的表 达分析图 4绘制得到的Δ6 去饱和酶基因和β-actin 基因的标准曲线分别为:y=-3.260x+33.59,R2=0.997,扩增效率E 为102.6% ;y=-3.203x+30.72,R2=0.992,扩增效率E 为105.2%,因此满足2-ΔΔCt 法。
|
| 图 4 基于Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸序列的NJ 系统进化树 |
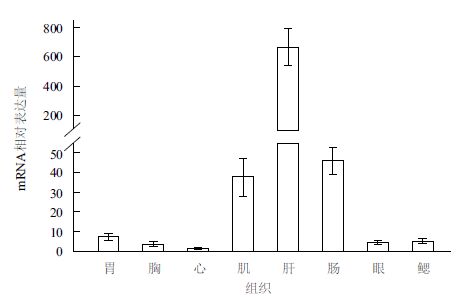
取三疣梭子蟹成蟹的肠、胃、心脏、肝胰腺、胸神经节、肌肉、眼柄和鳃8 个组织,利用荧光定量PCR 方法研究三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶mRNA 的组织表达特征,设定三疣梭子蟹在心脏中的表达量为1,根据Δ6 去饱和酶在各个组织中的相对表达量作柱形图。结果(图 5)显示,Δ6 去饱和酶在上述所有检测的组织中均有表达,且在三疣梭子蟹的肝胰腺中表达量最高,表达水平显著高于其他组织(P<0.05);其次是肠道和肌肉组织;在心脏、胸神经节、眼柄、鳃和胃组织中微量表达。
|
| 图 5 三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因mRNA 组织表达图谱 不同字母代表与对照组间差异显著(P<0.05) |
去饱和酶基因家族在脂肪酸代谢调节中有着十分广泛而又不可或缺的功能,Δ6 去饱和酶在HUFA合成过程中起着关键限速酶的作用[13]。在所有已知结构的去饱和酶中都有一个典型的特征:3 个典型的组氨酸簇保守域,一个细胞色素b5 结构域和一个血红素结合的HPGG 结构域[21, 22]。本实验所克隆的三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因与上述特征完全相符,初步确定为三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因。分析多序列比对结果,三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸与人的Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸相似性高于Δ5 去饱和酶氨基酸,同时与中华绒螯蟹Δ6 去饱和酶氨基酸的相似性为66%,因此初步确定为三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因。在构建三疣梭子蟹、多种鱼类、小鼠、人和中华绒螯蟹的进化发育树中,三疣梭子蟹和中华绒螯蟹单独聚为一支,表明两者亲缘关系最近,而与其他脊椎动物关系较远。
Δ6 去饱和酶作为脂肪酸合成过程中的关键酶,在组织中广泛表达[15, 16, 23, 24]。本实验荧光定量PCR 表明,三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶mRNA 在胃、心脏、胸神经组织、肌肉、肝胰腺、肠道、眼柄和鳃组织中均有表达。Δ6 去饱和酶在三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺中表达量最高,这与前人研究中Δ6 去饱和酶基因在虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)[23]和中华绒螯(Eriocheirsinensis)[16]等的表达情况均一致。有研究认为[25, 26],Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基因在肝脏中的高表达与肝脏参与调控脂肪酸的新陈代谢有关。可见肝胰腺作为脂类代谢中心在三疣梭子蟹生命过程中极其重要。
实验结果显示Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基因在肠道中表达量相对较高,表明肠道可能是合成HUFA 的重要部位。在大西洋鲑鱼[27]、建鲤[24]Δ6 去饱和酶基因mRNA 组织表达研究中发现,其在肠中表达量均较高;由此可见,肠道在HUFA 合成过程中必定发挥着重要作用。2001 年,Seiliez 等[23]在虹鳟幼鱼Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶mRNA 组织定量表达时发现,该基因在脑、肝脏和鳃等组织中高表达,而在肌肉中的表达量则较低,这与本实验在成蟹肌肉中表达较高的结果有所不同。许友卿[15]、任洪涛[24]等同样在军曹鱼幼鱼、建鲤幼鱼组织表达中发现,Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基因在幼鱼肌肉组织中表达量较低。究其原因,可能与所研究物种的发育阶段有关。有研究表明,水产动物组织中脂肪酸的功能就是为机体提供三磷酸腺苷(ATP)[28],因此肌肉中高表达的Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶预示着成蟹肌肉较幼蟹肌肉功能更完善。
目前研究表明,Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶通常参与C18 多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)转化为C20 的 HUFA的过程。一般认为海水蟹类合成HUFA 的能力较弱,但是缺乏相关的功能验证,故此初步确定的三疣梭子蟹Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基因是否具有合成HUFA的能力及合成能力的大小还有待进一步研究。
4 结论本实验首次成功克隆获得三疣梭子蟹Δ6 去饱和酶基因全长cDNA 序列,该序列全长2 875 bp,ORF 长1 332 bp,编码443 个氨基酸,具有典型的去饱和酶特征。系统进化树符合物种传统分类进化原则,进化结果显示三疣梭子蟹与中华绒螯蟹亲缘关系最近。该基因在肝胰腺中高表达,其次是肠道和肌肉,其他组织少量表达。
| [1] | Rasmussen BM, Vessby B, Uusitupa M, et al. Effects of dietaryaturated, monounsaturated, and n-3 fatty acids on blood pressure inealthy subjects[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2006, 83(2): 221-226. |
| [2] | Rapoport SI, Rao JS, Igarashim M. Brain metabolism of nutritionallyssential polyunsaturated fatty acids depends on both the diet andhe liver[J]. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2007, 775-6): 251-261. |
| [3] | 王景梓, 徐贵发. n-3 多不饱和脂肪酸的药理作用[J]. 食品与品, 2005, 7(7): 64-66. |
| [4] | Kuriki K, Hirose K, Wakai K, et al. Breast cancer risk andrythrocyte compositions of n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids inapanese[J]. Int J Cancer, 2007, 121(2): 377-385. |
| [5] | Cook HW. Fatty acid desaturation and chain elongation inukaryote[M]// In Vance DE, Vance JE. Biochemistry of Lipids,ipoproteins and Membranchs : Netherlands Elisevier, Amsterdam,996. |
| [6] | Sprecher H. Metabolism of highly unsaturated n-3 and n-6 fattycids[J]. Biochi Biochys Acta, 2000, 1486(2-3): 219-231. |
| [7] | González-Rovira A, Mourente G, Zheng XZ, et al. Molecular andunctional characterization and expression analysis of a Δ6 fatty acylesaturase cDNA of European Sea Bass(Dicentrarchus labrax L.)[J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 298(1-2): 90-100. |
| [8] | Li SL, Mai KS, Xu W, et al. Characterization, mRNA expressionnd regulation of Δ6 fatty acyl desaturase(FADS2)by dietary n-3ong chain polyunsaturated fatty acid(LC-PUFA)levels in grouperarvae(Epinephelus coioides)[J]. Aquaculture, 2014, 434(20): 12-219. |
| [9] | De Antueno RJ, Knickle LC, Smith H, et al. Activity of human Delta5nd Delta6 desaturases on multiple n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fattycids[J]. FEBS Lett, 2001, 509(1): 77-80. |
| [10] | D’Andrea S, Guillou H, Jan S, et al. The same rat Delta6-esaturase not only acts on 18- but also on 24-carbon fatty acidsn very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis[J].iochem J, 2002, 364(part 1): 49-55. |
| [11] | Owen JM, Adron JW, Middeton C, et al. Elongation andesaturation of dietary fatty acids in turbot Scophthalmus maximus. and rainbow trout Salmo gairdnerii rich[J]. Lipids, 1975, 109): 528-531. |
| [12] | Hastings N, Agaba M, Tocher DR, et al. A vertebrate fatty acidesaturase with Delta 5 and Delta 6 activities[J]. Proce Nationcad Sci USA, 2001, 98(25): 14304-14309. |
| [13] | Zheng X, Seiliez I, Hasting N, et al. Characterization andomparison of fatty acyl Delta6 desaturase cDNAs from freshwaternd marine teleost fish species[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol Biochem Mol Biol, 2004, 139(2): 269-279. |
| [14] | Zheng XZ, Tocher DR, Dickson CA. Highly unsaturated fattycid synthesis in vertebrates : new innsights with the cloning andharacterization of a △6-desaturase of Atlantic salmon[J].Lipids, 2005, 40(1): 13-24. |
| [15] | 许友卿, 郑一民, 丁兆坤. 军曹鱼△6 脂肪酸去饱和酶的DNA 序列克隆与基因表达[J]. 中国水产科学, 2010, 6(17): 183-1191. |
| [16] | Yang ZG, Guo ZH, Ji LY, et al. Cloning and tissue distribution of fatty acyl △6-desaturase-like geneand effects of dietary lipidevels on its expression in the hepatopancreas of Chinese mittenrab(Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry andhysiology, 2013, 165(Part B): 99-105. |
| [17] | Takeuchi T, Nakamoto Y, Hamasaki K, et al. Requirement of n-3ighly unsaturated fatty acids for larval swimming crab Portunusrituberculatus[J]. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 1999, 65(5): 97-803. |
| [18] | Wu X, Cheng Y, Sui L, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation ofhospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductiveerformance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab,riocheir sinensis(H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock[J].quaculture, 2007, 273(4): 602-613. |
| [19] | 丰浪. 高不饱和脂肪酸(HUFA)对三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育、内泌激素以及组织生化组成的影响[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学,011. |
| [20] | Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression datasing real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T))ethod[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [21] | Hashimoto K, Yoshizawa AC, Okuda S, et al. The repertoire ofesaturases and elongases reveals fatty acid variations in 56ukaryotic genomes[J]. J Lipid Res, 2008, 49(1): 183-191. |
| [22] | Monroig O, Zheng X, Morais S, et al. Multiple genes for functional 6atty acyl desaturases(Fad)in Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar L.): ene and cDNA characterization, functional expression, tissueistribution and nutritional regulation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,010, 1801(9): 1072-1081. |
| [23] | Seiliez I, Panserat S, Kaushik S, et al. Cloning, tissue distributionnd nutritional regulation of a Delta6-desaturase-like enzyme inainbow trout[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol,001, 130(1): 83-93. |
| [24] | 任洪涛, 俞菊华, 徐跑, 等. 建鲤两种Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基克隆与表达[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2012, 287): 677-684. |
| [25] | Zheng X, King Z, Xu Y, et al. Physiological roles of fatty acylesaturases and elongases in marine fish : Characterisation ofNDAs of fatty acyl △6 desaturase and elovl5 elongase of cobiaRachycentron canadum)[J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 290(1-2): 22-131. |
| [26] | Bell MV, Dick JR, Porter AE. Pyloric ceca are significant sitesf newly synthesized 22 : 6n-3 in rainbow trout(Oncorhynchusykiss)[J]. Lipids, 2003, 38(1): 39-44. |
| [27] | Morais S, Monroig O, Zheng XZ, et al. Highly unsaturated fatty acidynthesis in Atlantic salmon : characterization of ELOVL5- andLOVL2-like elongases[J]. Mar Biotechnol, 2009, 11(1): 27-639. |
| [28] | Sargent JR, Henderson RJ, Tocher DR. The lipids[M]// HalverE. Fish nutrition. 2nd ed. London : Academic Press, 1989 : 153-18. |
| [1] | Rasmussen BM, Vessby B, Uusitupa M, et al. Effects of dietaryaturated, monounsaturated, and n-3 fatty acids on blood pressure inealthy subjects[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2006, 83(2): 221-226. |
| [2] | Rapoport SI, Rao JS, Igarashim M. Brain metabolism of nutritionallyssential polyunsaturated fatty acids depends on both the diet andhe liver[J]. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2007, 775-6): 251-261. |
| [3] | 王景梓, 徐贵发. n-3 多不饱和脂肪酸的药理作用[J]. 食 品与品, 2005, 7(7): 64-66. |
| [4] | Kuriki K, Hirose K, Wakai K, et al. Breast cancer risk andrythrocyte compositions of n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids inapanese[J]. Int J Cancer, 2007, 121(2): 377-385. |
| [5] | Cook HW. Fatty acid desaturation and chain elongation inukaryote[M]// In Vance DE, Vance JE. Biochemistry of Lipids,ipoproteins and Membranchs : Netherlands Elisevier, Amsterdam,996. |
| [6] | Sprecher H. Metabolism of highly unsaturated n-3 and n-6 fattycids[J]. Biochi Biochys Acta, 2000, 1486(2-3): 219-231. |
| [7] | González-Rovira A, Mourente G, Zheng XZ, et al. Molecular andunctional characterization and expression analysis of a Δ6 fatty acylesaturase cDNA of European Sea Bass(Dicentrarchus labrax L.)[J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 298(1-2): 90-100. |
| [8] | Li SL, Mai KS, Xu W, et al. Characterization, mRNA expressionnd regulation of Δ6 fatty acyl desaturase(FADS2)by dietary n-3ong chain polyunsaturated fatty acid(LC-PUFA)levels in grouperarvae(Epinephelus coioides)[J]. Aquaculture, 2014, 434(20): 12-219. |
| [9] | De Antueno RJ, Knickle LC, Smith H, et al. Activity of human Delta5nd Delta6 desaturases on multiple n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fattycids[J]. FEBS Lett, 2001, 509(1): 77-80. |
| [10] | D’Andrea S, Guillou H, Jan S, et al. The same rat Delta6-esaturase not only acts on 18- but also on 24-carbon fatty acidsn very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis[J].iochem J, 2002, 364(part 1): 49-55. |
| [11] | Owen JM, Adron JW, Middeton C, et al. Elongation andesaturation of dietary fatty acids in turbot Scophthalmus maximus. and rainbow trout Salmo gairdnerii rich[J]. Lipids, 1975, 109): 528-531. |
| [12] | Hastings N, Agaba M, Tocher DR, et al. A vertebrate fatty acidesaturase with Delta 5 and Delta 6 activities[J]. Proce Nationcad Sci USA, 2001, 98(25): 14304-14309. |
| [13] | Zheng X, Seiliez I, Hasting N, et al. Characterization andomparison of fatty acyl Delta6 desaturase cDNAs from freshwaternd marine teleost fish species[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol Biochem Mol Biol, 2004, 139(2): 269-279. |
| [14] | Zheng XZ, Tocher DR, Dickson CA. Highly unsaturated fattycid synthesis in vertebrates : new innsights with the cloning andharacterization of a △6-desaturase of Atlantic salmon[J].Lipids, 2005, 40(1): 13-24. |
| [15] | 许友卿, 郑一民, 丁兆坤. 军曹鱼△6 脂肪酸去饱和酶的DNA 序列克隆与基因表达[J]. 中 国水产科学, 2010, 6(17): 183-1191. |
| [16] | Yang ZG, Guo ZH, Ji LY, et al. Cloning and tissue distribution of fatty acyl △ 6-desaturase-like geneand effects of dietary lipidevels on its expression in the hepatopancreas of Chinese mittenrab(Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry andhysiology, 2013, 165(Part B): 99-105. |
| [17] | Takeuchi T, Nakamoto Y, Hamasaki K, et al. Requirement of n-3ighly unsaturated fatty acids for larval swimming crab Portunusrituberculatus[J]. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 1999, 65(5): 97-803. |
| [18] | Wu X, Cheng Y, Sui L, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation ofhospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductiveerformance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab,riocheir sinensis(H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock[J].quaculture, 2007, 273(4): 602-613. |
| [19] | 丰浪. 高不饱和脂肪酸(HUFA)对三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育、内泌激素以及组织生化组成的影响[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学,011. |
| [20] | Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression datasing real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T))ethod[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [21] | Hashimoto K, Yoshizawa AC, Okuda S, et al. The repertoire ofesaturases and elongases reveals fatty acid variations in 56ukaryotic genomes[J]. J Lipid Res, 2008, 49(1): 183-191. |
| [22] | Monroig O, Zheng X, Morais S, et al. Multiple genes for functional 6atty acyl desaturases(Fad)in Atlantic salmon(Salmo salar L.): ene and cDNA characterization, functional expression, tissueistribution and nutritional regulation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,010, 1801(9): 1072-1081. |
| [23] | Seiliez I, Panserat S, Kaushik S, et al. Cloning, tissue distributionnd nutritional regulation of a Delta6-desaturase-like enzyme inainbow trout[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol,001, 130(1): 83-93. |
| [24] | 任洪涛, 俞菊华, 徐跑, 等. 建鲤两种Δ6 脂肪酸去饱和酶基克隆与表达[J]. 中 国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2012, 287): 677-684. |
| [25] | Zheng X, King Z, Xu Y, et al. Physiological roles of fatty acylesaturases and elongases in marine fish : Characterisation ofNDAs of fatty acyl △6 desaturase and elovl5 elongase of cobiaRachycentron canadum)[J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 290(1-2): 22-131. |
| [26] | Bell MV, Dick JR, Porter AE. Pyloric ceca are significant sitesf newly synthesized 22 : 6n-3 in rainbow trout(Oncorhynchusykiss)[J]. Lipids, 2003, 38(1): 39-44. |
| [27] | Morais S, Monroig O, Zheng XZ, et al. Highly unsaturated fatty acidynthesis in Atlantic salmon : characterization of ELOVL5- andLOVL2-like elongases[J]. Mar Biotechnol, 2009, 11(1): 27-639. |
| [28] | Sargent JR, Henderson RJ, Tocher DR. The lipids[M]// HalverE. Fish nutrition. 2nd ed. London : Academic Press, 1989 : 153-18. |





