b. School of Life Sciences, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou 510006, China;
c. Department of Natural Resources, Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation (ITC), University of Twente, Drienerlolaan 5, Enschede 7522 NB, the Netherlands
Mountains are defined by their prominence, steep sides, and significant height above the surrounding regions (Fang et al., 2004). They harbor exceptionally high levels of biodiversity and a great number of endemic species worldwide, which are also extremely sensitive to the ongoing global climate change (Zu and Wang, 2022). However, the underlying mechanisms that generate and maintain mountain biodiversity are not well understood (Körner et al., 2016; Rahbek et al., 2019).
Numerous hypotheses have been proposed to explain the large-scale distribution of species diversity (Wang et al., 2009). The contemporary climate hypothesis – e.g., environmental energy (Currie, 1991), water-energy dynamics (O'Brien, 1998; Hawkins et al., 2003) and climate seasonality (Connell and Orias, 1964; Stevens, 1989) – propose that climate (i.e., temperature, moisture, and seasonality) limit the distribution of species by affecting physiological processes. The historical climate change hypothesis posits that a greater number of species survive during periods with stable climates than during period with unstable climates, e.g., the Quaternary period (Liu et al., 2017; Zou et al., 2019). In contrast, the habitat heterogeneity hypothesis states that heterogeneous environments promote species diversity by providing more niches, geographical isolation, and climate refuges (Kerr and Packer, 1997; Stein et al., 2014). Despite extensive theoretical work, it remains unclear whether these hypotheses explain observed diversity in mountain plant species.
An additional theory that may help understand mountain species biodiversity is island biogeography theory (IBT). This theory explains that species diversity on islands is mediated by variation in island area and distance to the mainland (i.e., isolation degree) (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967). Specifically, island area is inversely correlated with extinction rate, whereas isolation degree is inversely correlated with immigration rate (Wu, 1990; Han, 1994). In addition, studies have confirmed that isolation degree is negatively correlated with species similarity (Sklenář et al., 2014; Ménde-Castro et al., 2018). Most studies of IBT focus on ‘true islands’, i.e., ocean islands (Han, 1994; Costanzi and Steifetten, 2019), which can be described as suitable habitats for populations from the mainland, surrounded by unsuitable matrix habitats (e.g., ocean) (Haila, 2002). However, IBT has been extended to various habitat islands on land that may not have a clear boundary with matrix habitats (Han, 1994; Kreft et al., 2008; Matthews, 2021), such as forests (Lovei et al., 2006), grasslands (Lindgren and Cousins, 2017), and mountains (Sklenář et al., 2014). Mountains are surrounded and separated by lowland, just as ‘true islands’ are surrounded by water, and hence they have been referred to as ‘islands on land’ or ‘sky islands’ (Howell, 1947; Heald, 1967; Carlquist, 1974; Han, 1994; Ding and Zheng, 1996; Fang et al., 2004; Quammen, 2004; Sklenář et al., 2014). However, few studies have determined whether the same factors drive and maintain biodiversity on mountains and ‘true islands’ (Costanzi and Steifetten, 2019; Mendez-Castro et al., 2021).
Rhododendrons are an excellent model for examining the underlying factors that regulate mountain biodiversity (Shrestha et al., 2018b). Rhododendron is a large genus of more than 1000 species that occur in every possible habitat in Asia, Europe, North America and Oceania (Fang and Ming, 1995; Gibbs et al., 2011). Rhododendron is also one of the most important genera of mountainous regions (Kumar, 2012; Yu et al., 2017). It is the dominant species in the understory of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests in subalpine coniferous forests, and plays a very important role in maintaining the stability of the structure and function of mountain ecosystems (Gibbs et al., 2011; Kumar, 2012). Previous studies have tried to explain the large-scale patterns of Rhododendron diversity with various environmental hypotheses (Shrestha et al., 2018b; Xia et al., 2022), these studies relied on evolutionary and genetic explanations of patterns of Rhododendron diversity. However, we try to explore the explanatory power of IBT in explaining Rhododendron diversity pattern, and the applicability and extensibility of IBT when regarding mountains as islands.
In this study, we determined which of six hypotheses best explains the formation and maintenance of Rhododendron diversity. These hypotheses included contemporary climate parameters (environmental energy, water availability, climate seasonality), Quaternary climate change, habitat heterogeneity, and IBT. After our analysis indicated that Rhododendron diversity can be largely explained by the IBT, we examined whether the main tenants of this theory are all valid for ‘mountain islands’, including the relationships between diversity and island area, diversity and distance from the mainland, as well the number of shared species and distance from the ‘mainland’.
2. Materials and methods 2.1. Species dataThe global distribution records of Rhododendron species were collected from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF, https://www.gbif.org/). We identified and deleted records with no coordinates, outlier coordinates, zero coordinates, identical latitudes/longitudes, and invalid coordinates based on the R package ‘CoordinateCleaner’ (Zizka et al., 2019). We supplemented these data with distribution records from herbaria and botanical museums at Kunming Institute of Botany (KUN), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); South China Botanical Garden (SCBG), CAS; Wuhan Botanical Garden (WBG), CAS; Sichuan University of Botany (SUB); Sichuan Forest School (SFS); and Lushan Botanical Garden (LBG). The scientific names of Rhododendron were checked by the R package ‘plantlist’ (Zhang et al., 2022), and only the correct records were kept. Ultimately, a total of 262,496 occurrence records, including 898 species of Rhododendron were retained.
To eliminate the influence of area on diversity estimation and statistical analysis, the distribution data were transferred into 1° × 1° grid cells. Grids located at the land boundary or coastal regions with a land area of less than 50% of the grid were removed. When calculating species diversity, the number of Rhododendron species in each grid was taken as the species diversity of the grid.
2.2. Predictors used to test environmental hypothesesTo explore the role of different processes in explaining species diversity, we calculated 17 predictors that represented measurable properties of the hypotheses associated with contemporary climate, Quaternary climate change, habitat heterogeneity and island biogeography theory (see Table 1 for details). The contemporary climate group was divided into three categories: environmental energy, water availability, and climate seasonality. All climate data were obtained from WorldClim (https://www.worldclim.org/) and the CGIAR Consortium for Spatial Information (https://cgiarcsi.community/2019/01/24/global-aridity-index-and-potential-evapotranspiration-climate-database-v3/) with a spatial resolution of 30 arc seconds. The climate data from the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) of the Quaternary were calculated from the average of three commonly used global climate models (GCMs): CCSM4 (Gent and Danabasoglu, 2011), MIROC-ESM (Watanabe et al., 2011), and MPI-ESM-P (Giorgetta et al., 2013) at a spatial resolution of 2.5 arc minutes. Elevation data were downloaded from the GMTED2010 digital elevation model (https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-global-multi-resolution-terrain-elevation) at a spatial resolution of 30 arc seconds. Global mountain polygon data (the ‘Basic’ map unit in the version of Global Mountain Biodiversity Assessment (GMBA) Mountain Inventory v.2_standard) were downloaded on EarthEnv (https://www.earthenv.org/mountains). All environmental predictors were aggregated to the 1° × 1° grid. The mountain area of each grid was estimated as the sum of planimetric area of mountain polygons on each grid, and the mountain area values less than half of the grid cell area were not included in the statistics to reduce error in the results. The distance to the mainland was calculated as the centroid distance between each grid and the ‘mainland’ of Rhododendrons (see section 2.3 for more information about ‘mainland’).
| Hypothesis | Abbreviations | Variables | References | |
| Contemporary climate | Environmental energy | MAT | Mean annual temperature | (Currie, 1991) |
| MTCQ | Mean temperature of the coldest quarter | |||
| WI | Warmth index | |||
| Water availability | MAP | Mean annual precipitation | (O'Brien, 1993; Hawkins et al., 2003) | |
| PDQ | Precipitation of the driest quarter | |||
| AI | Aridity index | |||
| Climate seasonality | ART | Annual range of temperature | (Connell and Orias, 1964; Stevens, 1989) | |
| TSN | Temperature seasonality | |||
| PSN | Precipitation seasonality | |||
| Paleo-climate change | MAT=ano | Anomaly of mean annual temperature | (Svenning and Skov, 2007; Sandel et al., 2011) | |
| MAP=ano | Anomaly of mean annual precipitation | |||
| MAT=vel | Velocity of annual average temperature from the LGM to the present | |||
| Habitat heterogeneity | ELER | Range of elevation | (Kerr and Packer, 1997; Stein et al., 2014) | |
| MATR | Range of mean annual temperature | |||
| MAPR | Range of mean annual precipitation | |||
| Island biogeography theory | MA | Mountain area | (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967) | |
| MD | Distance to mainland |
In classic IBT, the mainland plays important roles as it is the species pool or colonist source of islands, and promotes potential immigration events (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967; Han, 1994). However, it is much more complicated to identify a ‘mainland’ in terrestrial habitat islands than it is for ‘true islands’. Studies have tried to identify the ‘mainland’ as regions with the longest species history (Allen et al., 2009) or with the most numerous species (Sanchez and Parmenter, 2002) or the largest and most continuous habitats in the study areas (Costanzi and Steifetten, 2019; Yan et al., 2023). The Hengduan Mountains to Himalayas region in southwestern China harbor a large and continuous distribution of mountains suitable for Rhododendrons, and it has been recognized as the diversity center of world's Rhododendrons (Yu et al., 2017) for most of extant Rhododendron species originated from evolutionary radiations occurred here in history (Shrestha et al., 2018b; Xia et al., 2022). These conditions make this region a good choice for being the ‘mainland’ of Rhododendrons.
To further test the ‘island area-diversity’ relationship, ‘distance-diversity’ relationship and ‘distance-shared species’ relationship of IBT in mountains, we regarded each mountain as an ‘island’ and the Hengduan Mountains region as the ‘mainland’ (Fig. 1). A total of 6717 mountains were initially included in global mountain polygon data downloaded from GMBA Mountain inventory v.2.
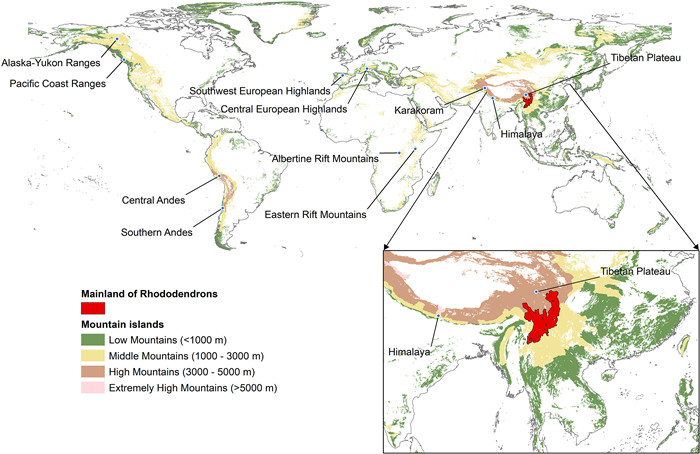
|
| Fig. 1 Global distribution of the ‘mountain islands’ and ‘mainland’ of Rhododendrons. |
We calculated the planimetric area of each mountain as the ‘area of islands’ (i.e., the projected area of the mountains on the horizontal plane). Because mountains are three-dimensional, we also calculated the rough volume of each mountain, which was calculated as: the planimetric area × the highest elevation of the mountain. We then used both the planimetric area and the volume as indicators of the area of ‘mountain islands’, and counted the number of Rhododendron species in each ‘mountain island’. To explore the ‘distance-shared species’ relationship of IBT in ‘mountain islands’, we calculated the centroid distance between each ‘mountain island’ and the ‘mainland’, and then counted the number of same species in each pair of ‘mountain island’ and ‘mainland’.
2.4. Statistical analysisBecause species diversity per grid cell normally fits a Poisson distribution (Wang et al., 2011), we first established generalized linear models (GLMs) with Poisson errors to estimate the relationship between species diversity and 17 explanatory variables. For each predictor, we established a GLM and the explanatory power of the predictor was estimated by the adjusted R2, which was calculated as follows: Radj2(%) = 100–100*(residual deviance/null deviance). To control the influence of spatial autocorrelation in the associations between species diversity and variables (Kissling and Carl, 2007), we further applied simultaneous autoregressive (SAR) models and used the Akaike information criterion (AIC) as an evaluation.
To explore the relative importance of environmental variable groups represented by six hypotheses in explaining Rhododendron diversity patterns, we performed a hierarchical partitioning analysis that estimated individual contributions of the six groups, and further partitioned their unique contribution, sharing the contribution by variance partitioning analysis. Since each environmental group contained highly correlated variables, this method effectively addresses the collinearity problems between variables (Lai et al., 2022). To maintain the same number of variables for each group, we selected the most explanatory predictor (bold predictors in Table 2) in each hypothesis as their representative.
| Environmental hypotheses | Predictors | GLM | SAR | ||||
| Coeff | Radj2 | Coeff | AIC | ||||
| Contemporary climate | Environmental energy | MAT | 0.0465*** | 14.45 | 0.0362*** | 20,057 | |
| MTCQ | 0.0334*** | 16.07 | 0.0301*** | 20,051 | |||
| WI | 0.0052*** | 8.67 | 0.0025 | 20,068 | |||
| Water availability | MAP | 0.0005*** | 12.52 | 0.0006*** | 20,054 | ||
| PDQ | 0.0017*** | 3.40 | 0.0020* | 20,065 | |||
| AI | 0.0001*** | 4.60 | 0.0001** | 20,061 | |||
| Climate seasonality | ART | −0.0410*** | 16.56 | −0.0453*** | 20,042 | ||
| TSN | −0.0012*** | 17.50 | −0.0013*** | 20,041 | |||
| PSN | 0.0079*** | 2.83 | 0.0050 | 20,069 | |||
| Paleo-climate change | MAT=ano | −0.0781*** | 18.23 | −0.0606*** | 20,046 | ||
| MAP=ano | −0.0018*** | 3.81 | −0.0017** | 20,063 | |||
| MAT=vel | −0.2971*** | 21.08 | −0.2416*** | 20,039 | |||
| Habitat heterogeneity | ELER | 0.0005*** | 29.69 | 0.0022*** | 19,834 | ||
| MATR | 0.0810*** | 27.91 | 0.3875*** | 19,853 | |||
| MAPR | 0.0005*** | 9.50 | 0.0014*** | 20,020 | |||
| Island biogeography theory | MA | 0.0002*** | 35.07 | 0.0004*** | 19,901 | ||
| MD | −0.0001*** | 17.57 | −0.0001*** | 20,044 | |||
Spearman correlation analyses were conducted to assess the relationships between species diversity and the planimetric area and the volume of ‘mountain islands’, species diversity and the number of shared species and the distance from ‘mountain islands’ to the ‘mainland’. We also performed a test of significance by ‘cocor’ package (Diedenhofen and Musch, 2015) for the difference in the correlation coefficients between the species diversity and the planimetric area and the volume of ‘mountain islands’.
All statistical analyses were performed in R 4.1.2 (R Core Team, 2021). Spatial autoregressions were conducted using the R package ‘spatialreg’ (Bivand et al., 2021). The hierarchical partition and variance partition analysis was conducted using the ‘rdacca.hp’ package (Lai et al., 2022).
3. Results 3.1. Geographical patterns of Rhododendron diversityRhododendron hotspots (regions with over 32 species) are mainly distributed in the Hengduan Mountains of southwestern China and the southern regions of the Himalayas (Fig. 2). Regions with species numbers ranging from 5 to 31 are scattered throughout Southeast Asia, including southeastern China, the Japanese archipelago, and the Pacific islands between Asia and Oceania. In contrast, Rhododendron diversity is low (regions with species less than 5) in Northeast Asia, South Asia, Europe, and North America.
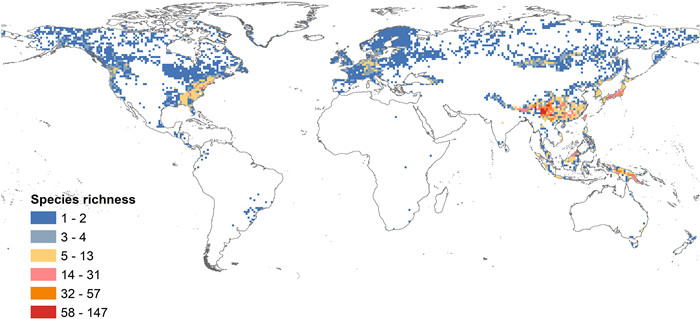
|
| Fig. 2 Global patterns of Rhododendron diversity based on 1° × 1° grid cells. |
The most influential predictor of global patterns of Rhododendron diversity was MA (RGLM2 = 35.07%, P < 0.001; AICSAR = 19,901, P < 0.001), a proxy for the IBT (Table 2 and Fig. 3). Specifically, MA was positively correlated with Rhododendron diversity. The second-best predictors of Rhododendron diversity patterns were proxies for habitat heterogeneity, i.e., ELER (RGLM2 = 29.69%, P < 0.001; AICSAR = 19,834, P < 0.001) and MATR (RGLM2 = 27.91%, P < 0.001; AICSAR = 19,853, P < 0.001). These proxies were also positively correlated with species diversity (Table 2 and Fig. 3). Proxies of the paleo-climate change hypothesis, MAT_vel, explained 21.08% of the total variation in Rhododendron diversity (P < 0.001). Variables with relatively low explanatory power included MD, TSN, ART, MTCQ, MAT, and MAP, with contributions ranging from 12.52% to 17.57% (P < 0.001). The contributions of the remaining predictors were each lower than 10%. The results from GLMs and corresponding SAR models were similar for all predictors.
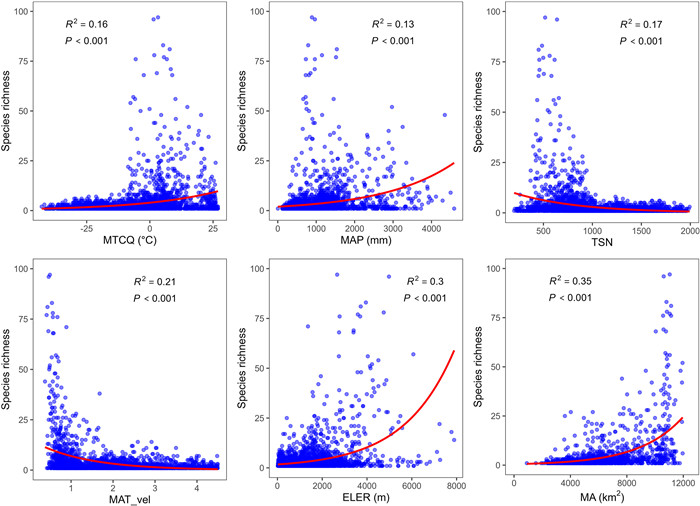
|
| Fig. 3 The relationship between the predictors with the highest explanatory power in each hypothesis and Rhododendron diversity. Trend lines were fitted by GLMs. Abbreviations are defined in Table 1. |
Hierarchical partitioning analysis also revealed that IBT explains the largest variance (10.17%) in Rhododendron diversity patterns (Fig. 4). The individual contribution of habitat heterogeneity explained 7.31% of the total variance. The individual effects of several hypotheses explained similar, low levels of variance, i.e., water availability (4.72%), environmental energy (4.49%), paleo-climate change (3.68%), and climate seasonality (3.35%). All hypotheses combined explained 33.7% of the variance of Rhododendron diversity. The decomposed variance of individual effects in the fractions showed the shared effect between IBT and habitat heterogeneity was the highest, accounting for 6.66%.
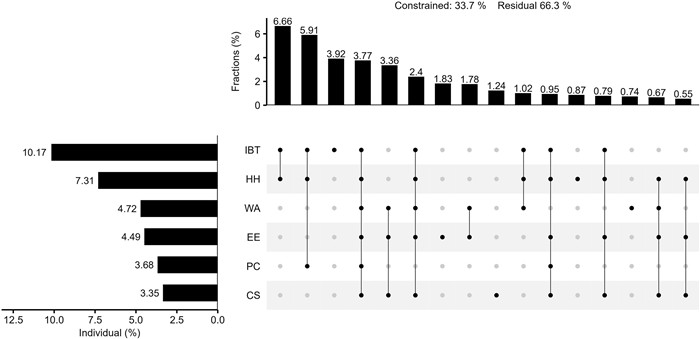
|
| Fig. 4 The relative explanatory power of six environmental hypotheses on Rhododendron diversity patterns. Constrained: total explained variance; Residual: unexplained variance. The column diagram on the left shows the individual effect of each environmental hypothesis (from hierarchical partitioning). In the point-matrix plot on the right, each row corresponds to a hypothesis. For each column, the isolated solid point represents the unique effect explained by each hypothesis. Lines connecting multiple points represent the shared effect among these corresponding hypotheses, and the percentage of variation explained by each component are shown in the top column diagram (from variation partitioning). The individual effect value is equal to its unique effect plus its average value of shared effect with other hypotheses. The individual effects of all hypotheses were significant based on a permutation test of 999 randomizations (P < 0.001). Effects below 0.5% in the fractions were not displayed but they were included in the total variation. IBT: Island biogeography theory; HH: Habitat heterogeneity; WA: Water availability; PC: Paleo-climate change; EE: Environmental energy; CS: Climate seasonality. |
Rhododendron diversity was positively correlated with the planimetric area of mountains (R = 0.39, P < 0.001) (Fig. 5a). This correlation was significantly stronger between species diversity and volume of mountains (R = 0.41, P < 0.001) (Fig. 5b). In addition, Rhododendron diversity of each ‘mountain island’ was negatively correlated with isolation degree, i.e., distance from the ‘mainland’ (R = −0.28, P < 0.001) (Fig. 5c). The number of Rhododendron species shared between ‘mountain islands’ and the ‘mainland’ were also negatively correlated (R = −0.52, P < 0.001) (Fig. 5d).
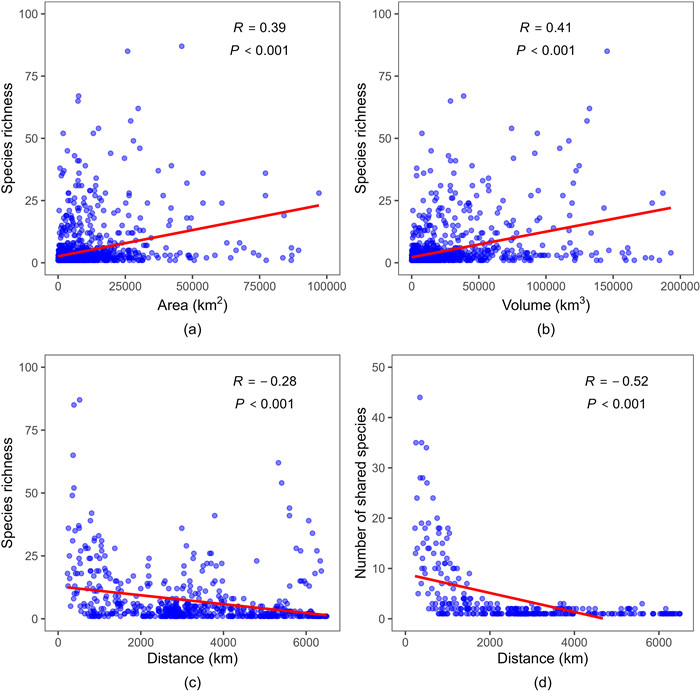
|
| Fig. 5 Correlation between Rhododendron species and the area, volume, and isolation of ‘mountain islands’. (a) The planimetric area of mountains and species diversity. (b) The volume of mountains and species diversity. (c) The ‘mountain islands-to-mainland’ distance and species diversity. (d) The ‘mountain islands-to-mainland’ distance and the number of shared species. |
Our results demonstrate that Rhododendron diversity patterns are best explained by the IBT, then by habitat heterogeneity. Regions that contain large mountain areas tend to have higher species diversity. For example, the Himalayas-Hengduan Mountains (HHM) (Myers et al., 2000) and the Andes Mountains (Hoorn et al., 2013) have both been identified as biodiversity hotspots (Körner and Spehn, 2019). IBT holds that large islands have lower extinction rates and higher species diversity because they provide more available resources, ecological niches, and habitat types (MacArthur and Wilson, 1967; Wu, 1990; Han, 1994). Studies on the growth habits of Rhododendrons seem to confirm that this theory also applies to mountains regions (Gibbs et al., 2011), as mountains with large areas provide sufficient habitats. Furthermore, mountains with smaller areas have lower species diversity (Si et al., 2017), most likely due to increased competition between species. This relationship between island area and species diversity has been shown to exist in other terrestrial habitat islands, such as grassland patches in the agro-pastoral ecotone (Zhang et al., 2021), forest islands (Lovei et al., 2006), alpine plants (Sklenář et al., 2014).
Habitat heterogeneity also helps explain Rhododendron diversity. This finding is consistent with previous studies on Rhododendron evolution and genomics worldwide (Shrestha et al., 2018b; Xia et al., 2022). The main reason that habitat heterogeneity is thought to impact Rhododendron diversity is because environments with complex topography and diverse climates can provide a rich variety of habitats, creating more niches to accommodate more species (López-Pujol et al., 2011; Stein et al., 2014). For example, vegetation zones along elevation gradients in mountain regions provide various habitat conditions for the growth of Rhododendron species (Cox and Cox, 1997; MacKay and Gardiner, 2016). Furthermore, the complex topography of mountains has provided refuges for species under extreme climatic conditions in the past, e.g., during the large temperature changes of the Quaternary glacial and interglacial periods (Fjeldså et al., 2012). These refuges may also reduce extinction rates by minimizing the need to have strong dispersal ability to track climatic fluctuations (Sandel et al., 2011). Finally, complex topography creates geographical isolation, facilitating new species through allopatric speciation and adaption to various environmental conditions (Steinbauer et al., 2016; Xing and Ree, 2017).
The shared contribution of IBT and habitat heterogeneity on Rhododendron diversity patterns explained the largest part of decomposed variance (Fig. 4), suggesting that IBT and habitat heterogeneity are strongly associated. Several studies have confirmed that the impact of island area on species diversity may include the mediating effect of diverse habitats (Han, 1994; Keppel et al., 2016; MacDonald et al., 2018). In addition, mountains have strong climatic and topographic heterogeneity (Perrigo et al., 2019). Hence, large ‘mountain islands’ increase inherently high habitat heterogeneity, further promoting species diversity. The HHM contains a dense array of mountains and an extremely complex environment (Kumar, 2012). This unique environment creates many habitats, ecological niche spaces, and favorable conditions for Rhododendron (Shrestha et al., 2018a; Namgay and Sridith, 2020), which may provide one explanation for why it is global center of Rhododendron diversity (Shrestha et al., 2018b). Rhododendron is an ancient plant that colonized the southeast of the Himalayas around 30–40 Ma (Shrestha et al., 2018b). Previous studies showed that Rhododendron and several other seed plants may have experienced rapid diversification during the Miocene (Wen et al., 2014; Xia et al., 2022), which coincided with the formation of the HHM (Harrison et al., 1992). This further indicates that the emergence of Hengduan and surrounding mountains and the development of environmental heterogeneity have formed rich ecological niches and geographical isolation, which jointly enhanced the diversity of Rhododendron and provided an important ‘cradle’ for plants in East Asia (Xing and Ree, 2017).
Although the relative contributions of the contemporary climate and paleoclimate change hypotheses was not high, together these hypotheses accounted for nearly half of the total explanatory variance (Fig. 4). Rhododendron generally prefer environments with high rainfall, high humidity, and mild climates (Gibbs et al., 2011; Kumar, 2012). The climate fluctuation and glacial movement since the Quaternary may have affected the modern distribution of Rhododendron (Fang and Ming, 1995; Dynesius and Jansson, 2000). Furthermore, several refuges concentrated in the HHM may have ensured the survival of many plants and animals during the glacial period, including Rhododendron species (Zhan et al., 2011; Srinivasan et al., 2014).
4.2. The application of island biogeography theory in mountain islandsThis study confirms that IBT is applicable ‘mountain islands’. This claim is supported by our findings that Rhododendron diversity conform to predictions of IBT. Specifically, we found that Rhododendron diversity is significantly correlated with the ‘area of mountain islands’, the ‘volume of mountain islands’, ‘distance to the mainland’ (isolation degree), and that the number of shared species is correlated with ‘distance to the mainland’. These findings are consistent with previous studies that have found mountains share attributes with ‘true islands’, including limited size, isolation, and dispersal limitation (Ding and Zheng, 1996; Fang et al., 2004; Hughes and Atchison, 2015).
Most studies of classical IBT have used the planimetric area of islands as the measurement of ‘island species-area’ relationships (Lindgren and Cousins, 2017; Zhou et al., 2019). Here, we showed that species diversity is more highly correlated with the volume of ‘mountain islands’ than with their planimetric area. Previous studies have found a similar relationship between species diversity and the volume of islands. For example, tree and beetle species diversity are positively correlated with the volume of some forest vegetation (LaRue et al., 2023); similarly, specialist herbivore species diversity has been positively correlated with the volume of desert shrub islands (Sanchez and Parmenter, 2002). The stronger correlation between species diversity and ‘mountain island’ volume can be explained by the increased niche space and environmental heterogeneity along the elevational plane of mountains (Coverdale and Davies, 2023), especially for Rhododendron, which occupy habitats across vast elevational ranges (Fang and Ming, 1995).
Our findings also confirmed that both species diversity and the number of shared species are influenced by the distance between ‘mountain islands’ and the ‘mainland’. Specifically, Rhododendron diversity is lower in ‘mountain islands’ that are greatly isolated from the ‘mainland’. In addition, fewer species are shared between ‘mountain islands’ and the ‘mainland’ when they are separated by large distances. Rhododendron have small, light, and winged seeds, which enable them to be spread over long distances by wind and animals (Stephenson et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2022). However, long distances between ‘mountain islands’ and the ‘mainland’ increase dispersal resistance and provide fewer opportunities for Rhododendron species to migrate, decreasing the number of island species and creating large differences between populations. Conversely, short distances promote high species diversity and species similarity. The ‘mountain islands’ surrounding the ‘mainland’ may have more similar natural environments than those farther away, which may explain their species similarity (Ménde-Castro et al., 2018).
Although studies on island species diversity have largely focused on the balance between immigration/colonization and extinction, speciation (e.g., isolation and divergence, hybridization and polyploidy in plant) is also thought to play a significant role (Presgraves and Glor, 2010; Flantua et al., 2020), either through adaptive changes after colonization or by acting as another form of colonization (Heaney, 2001; Alzate et al., 2018). Several studies have confirmed that the formation rate of island endemic species through in situ speciation are positively correlated with island area and isolation (Whittaker et al., 2008; Valente et al., 2020). Local speciation may play a key role in present diversity patterns of Rhododendron. Phylogenetic analyses of global Rhododendron (Shrestha et al., 2018b; Xia et al., 2022) revealed that the evolutionary radiations of this genus occurred in the HHM and Malay Archipelago in the Miocene, resulting in higher speciation rate of Rhododendron in Southeast Asia than in other regions of the world (e.g., Europe, North America). However, it remains unclear how speciation, immigration/colonization, and extinction interact to shape regional Rhododendron diversity.
4.3. Diversity patterns and conservation implications for RhododendronUnderstanding the spatial patterns of species diversity plays a critical role in the conservation of species and diversity (Yu et al., 2017; Shrestha and Wang, 2018). Mountains have long been biodiversity hotspots and refuges that, play an important role in biodiversity conservation planning (Körner et al., 2016; Rahbek et al., 2019; Li et al., 2022). Our study confirms that mountain regions are hotspots of Rhododendron, especially in the HHM region. Therefore, strengthening mountain conservation is a priority for protecting Rhododendron diversity. However, several studies have shown that a large proportion of mountain regions with Rhododendron hotspots are not protected by nature reserves (Mao, 2010; Shrestha and Wang, 2018; Zhao et al., 2023). Furthermore, global climate change has been shown to disproportionally affect species with wide elevational distributions (Ma et al., 2014; Elsen et al., 2018; Vincent et al., 2019). We therefore strongly recommend the establishment of protected areas for Rhododendrons that inhabit mountain regions, and strengthen the elevation gradient protection of Rhododendron species.
AcknowledgmentsThis work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 41901060). We are grateful to anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful comments on the manuscript.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Yanwei Guan: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Formal analysis, Data curation. Yongru Wu: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. Zheng Cao: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. Zhifeng Wu: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. Fangyuan Yu: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Conceptualization. Haibin Yu: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. Tiejun Wang: Conceptualization.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Allen, D., Vandermeer, J., Perfecto, I., 2009. When are habitat patches really islands?. For. Ecol. Manage., 258: 2033-2036. DOI:10.1016/j.foreco.2009.07.060 |
Alzate, A., Etienne, R.S., Bonte, D., et al., 2018. Experimental island biogeography demonstrates the importance of island size and dispersal for the adaptation to novel habitats. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 28: 238-247. |
Bivand, R., Millo, G., Piras, G., 2021. A review of software for spatial econometrics in R. Mathematics, 9: 1276. DOI:10.3390/math9111276 |
Carlquist, S., 1974. Island Biology. New York, NY, USA: Columbia University Press.
|
Connell, J.H., Orias, E., 1964. The ecological regulation of species diversity. Am. Nat., 98: 399-414. DOI:10.1086/282335 |
Costanzi, J.M., Steifetten, Ø., 2019. Island biogeography theory explains the genetic diversity of a fragmented rock ptarmigan (Lagopus muta) population. Ecol. Evol., 9: 3837-3849. DOI:10.1002/ece3.5007 |
Coverdale, T.C., Davies, A.B., 2023. Unravelling the relationship between plant diversity and vegetation structural complexity: a review and theoretical framework. J. Ecol., 111: 1378-1395. DOI:10.1111/1365-2745.14068 |
Cox, P.A., Cox, K.N.E., 1997. The Encyclopedia of Rhododendron Species. Perth, Scotland: Glendoick Publishing.
|
Currie, D.J., 1991. Energy and large-scale patterns of animal- and plant-species richness. Am. Nat., 137: 27-49. DOI:10.1086/285144 |
Diedenhofen, B., Musch, J., 2015. Cocor: a comprehensive solution for the statistical comparison of correlations. PLoS One, 10: e0121945. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0121945 |
Ding, X.Z., Zheng, Y.C., 1996. The second discussion on montology. Mt. Res., 14: 83-88. |
Dynesius, M., Jansson, R., 2000. Evolutionary consequences of changes in species' geographical distributions driven by Milankovitch climate oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 97: 9115-9120. DOI:10.1073/pnas.97.16.9115 |
Elsen, P.R., Monahan, W.B., Merenlender, A.M., 2018. Global patterns of protection of elevational gradients in mountain ranges. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 115: 6004-6009. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1720141115 |
Fang, J.Y., Shen, Z.H., Cun, H.T., 2004. Ecological characteristics of mountains and research issues of mountain ecology. Biodivers. Sci., 12: 10-19. DOI:10.17520/biods.2004003 |
Fang, R.Z., Ming, T.L., 1995. The floristic study on the genus Rhododendron. Acta Bot. Yunnanica, 17: 359-379. |
Fjeldså, J., Bowie, R.C.K., Rahbek, C., 2012. The role of mountain ranges in the diversification of birds. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst., 43: 249-265. DOI:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-102710-145113 |
Flantua, S.G.A., Payne, D., Borregaard, M.K., et al., 2020. Snapshot isolation and isolation history challenge the analogy between mountains and islands used to understand endemism. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 29: 1651-1673. DOI:10.1111/geb.13155 |
Gent, P.R., Danabasoglu, G., 2011. Response to increasing southern hemisphere winds in CCSM4. J. Clim., 24: 4992-4998. DOI:10.1175/JCLI-D-10-05011.1 |
Gibbs, D., Chamberlain, D., Argent, G., 2011. The Red List of Rhododendrons. Botanic Gardens Conservation International, Richmond, UK.
|
Giorgetta, M.A., Roeckner, E., Mauritsen, T., et al., 2013. The Atmospheric General Circulation Model ECHAM6 - Model Description.
|
Haila, Y., 2002. A conceptual genealogy of fragmentation research: from island biogeography to landscape ecology. Ecol. Appl., 12: 321-334. |
Han, X.G., 1994. Island biogeography and biodiversity conservation. In: Qian, Y.Q., Ma, K.P. (Eds). Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies. Science and Technology of China.
|
Harrison, T.M., Copeland, P., Kidd, W.S., et al., 1992. Raising tibet. Science, 255: 1663-1670. DOI:10.1126/science.255.5052.1663 |
Hawkins, B.A., Field, R., Cornell, H.V., et al., 2003. Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology, 84: 3105-3117. DOI:10.1890/03-8006 |
Heald, W., 1967. Sky Island. New Jersey: Van Nostrand.
|
Heaney, L.R., 2001. Dynamic disequilibrium: a long-term, large-scale perspective on the equilibrium model of island biogeography. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 9: 59-74. |
Hoorn, C., Mosbrugger, V., Mulch, A., et al., 2013. Biodiversity from mountain building. Nat. Geosci., 6: 154, 154. DOI:10.1038/ngeo1742 |
Howell, J.T., 1947. Mono Mesa, Sierra, Sky Island. Sierra Club, Bulletin.
|
Hughes, C.E., Atchison, G.W., 2015. The ubiquity of alpine plant radiations: from the Andes to the Hengduan Mountains. New Phytol., 207: 275-282. DOI:10.1111/nph.13230 |
Keppel, G., Gillespie, T.W., Ormerod, P., et al., 2016. Habitat diversity predicts orchid diversity in the tropical south-west Pacific. J. Biogeogr., 43: 2332-2342. DOI:10.1111/jbi.12805 |
Kerr, J.T., Packer, L., 1997. Habitat heterogeneity as a determinant of mammal species richness in high-energy regions. Nature, 385: 252-254. DOI:10.1038/385252a0 |
Kissling, W.D., Carl, G., 2007. Spatial autocorrelation and the selection of simultaneous autoregressive models. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 17: 59-71. |
Körner, C., Jetz, W., Paulsen, J., et al., 2016. A global inventory of mountains for bio-geographical applications. Alpine Bot., 127: 1-15. |
Körner, C., Spehn, E., 2019. A Humboldtian view of mountains. Science, 365: 1061. DOI:10.1126/science.aaz4161 |
Kreft, H., Jetz, W., Mutke, J., et al., 2008. Global diversity of island floras from a macroecological perspective. Ecol. Lett., 11: 116-127. DOI:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01129.x |
Kumar, P., 2012. Assessment of impact of climate change on Rhododendrons in Sikkim Himalayas using Maxent modelling: limitations and challenges. Biodivers. Conserv., 21: 1251-1266. DOI:10.1007/s10531-012-0279-1 |
Lai, J.S., Zou, Y., Zhang, J.L., et al., 2022. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp. R package. Methods Ecol. Evol., 13: 782-788. DOI:10.1111/2041-210x.13800 |
LaRue, E.A., Downing, A.G., Saucedo, S., et al., 2023. Diversity – volume relationships: adding structural arrangement and volume to species – area relationships across forest macrosystems. Ecography, 2023: e06723. DOI:10.1111/ecog.06723 |
Li, B.V., Jenkins, C.N., Xu, W., 2022. Strategic protection of landslide vulnerable mountains for biodiversity conservation under land-cover and climate change impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 119: e2113416118. DOI:10.1073/pnas.2113416118 |
Lindgren, J.P., Cousins, S.A.O., 2017. Island biogeography theory outweighs habitat amount hypothesis in predicting plant species richness in small grassland remnants. Landsc. Ecol., 32: 1895-1906. DOI:10.1007/s10980-017-0544-5 |
Liu, Y.P., Shen, Z.H., Wang, Q.G., et al., 2017. Determinants of richness patterns differ between rare and common species: implications for Gesneriaceae conservation in China. Divers. Distrib., 23: 235-246. DOI:10.1111/ddi.12523 |
López-Pujol, J., Zhang, F.-M., Sun, H.-Q., et al., 2011. Centres of plant endemism in China: places for survival or for speciation?. J. Biogeogr., 38: 1267-1280. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2011.02504.x |
Lovei, G.L., Magura, T., Tothmeresz, B., et al., 2006. The influence of matrix and edges on species richness patterns of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in habitat islands. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 15: 283-289. DOI:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2005.00221.x |
Ma, Y., Mao, X., Wang, J., et al., 2022. Pervasive hybridization during evolutionary radiation of Rhododendron subgenus Hymenanthes in mountains of southwest China. Natl. Sci. Rev., 9: nwac276. DOI:10.1093/nsr/nwac276 |
Ma, Y.P., Nielsen, J., Chamberlain, D.F., et al., 2014. The conservation of Rhododendrons is of greater urgency than has been previously acknowledged in China. Biodivers. Conserv., 23: 3149-3154. DOI:10.1007/s10531-014-0764-9 |
MacArthur, R.H., Wilson, E.O., 1967. The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
|
MacDonald, Z.G., Anderson, I.D., Acorn, J.H., et al., 2018. The theory of island biogeography, the sample-area effect, and the habitat diversity hypothesis: complementarity in a naturally fragmented landscape of lake islands. J. Biogeogr., 45: 2730-2743. DOI:10.1111/jbi.13460 |
MacKay, M., Gardiner, S.E., 2016. A model for determining ex situ conservation priorities in big genera is provided by analysis of the subgenera of Rhododendron (Ericaceae). Biodivers. Conserv., 26: 189-208. DOI:10.1111/insr.12154 |
Mao, A.A., 2010. The genus Rhododendron in north-east India. Bot. Orient. J. Plant Sci., 7: 26-34. DOI:10.1002/polb.21840 |
Matthews, T.J., 2021. On the biogeography of habitat islands: the importance of matrix effects, noncore species, and source-sink dynamics. Q. Rev. Biol., 96: 73-104. DOI:10.1086/714482 |
Ménde-Castro, F.E., Bader, M.Y., Mendieta-Leiva, G., et al., 2018. Islands in the trees: a biogeographic exploration of epiphyte-dwelling spiders. J. Biogeogr., 45: 2262-2271. DOI:10.1111/jbi.13422 |
Mendez-Castro, F.E., Conti, L., Chytrý, M., et al., 2021. What defines insularity for plants in edaphic islands?. Ecography, 44: 1249-1258. DOI:10.1111/ecog.05650 |
Myers, N., Mittermeier, R.A., Mittermeier, C.G., et al., 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403: 853-858. DOI:10.1038/35002501 |
Namgay, S., Sridith, K., 2020. Distribution pattern of the genus Rhododendron in Bhutan Himalayan range. Sci. Asia, 46: 429. DOI:10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2020.057 |
O'Brien, E.M., 1993. Climatic gradients in woody plant species richness: towards an explanation based on an analysis of southern Africa's woody flora. J. Biogeogr., 20: 181-198. DOI:10.2307/2845670 |
O'Brien, E.M., 1998. Water-energy dynamics, climate, and prediction of woody plant species richness: an interim general model. J. Biogeogr., 25: 379-398. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2699.1998.252166.x |
Perrigo, A., Hoorn, C., Antonelli, A., 2019. Why mountains matter for biodiversity. J. Biogeogr., 47: 315-325. |
Presgraves, D.C., Glor, R.E., 2010. Evolutionary biology: speciation on islands. Curr. Biol., 20: R440-R442. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.032 |
Quammen, D., 2004. The Song of the Dodo: Island Biogeography in an Age of Extinctions. New York: Scribner.
|
R Core Team, 2021. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
|
Rahbek, C., Borregaard, M.K., Colwell, R.K., et al., 2019. Humboldt's enigma: what causes global patterns of mountain biodiversity?. Science, 365: 1108-1113. DOI:10.1126/science.aax0149 |
Sanchez, B.C., Parmenter, R.R., 2002. Patterns of shrub-dwelling arthropod diversity across a desert shrubland–grassland ecotone: a test of island biogeographic theory. J. Arid Environ., 50: 247-265. DOI:10.1006/jare.2001.0920 |
Sandel, B., Arge, L., Dalsgaard, B., et al., 2011. The influence of Late Quaternary climate-change velocity on species endemism. Science, 334: 660-664. DOI:10.1126/science.1210173 |
Shrestha, N., Su, X.Y., Xu, X.T., et al., 2018a. The drivers of high Rhododendron diversity in south-west China: does seasonality matter?. J. Biogeogr., 45: 438-447. DOI:10.1111/jbi.13136 |
Shrestha, N., Wang, Z.H., 2018. Selecting priority areas for systematic conservation of Chinese Rhododendron: hotspot versus complementarity approaches. Biodivers. Conserv., 27: 3759-3775. DOI:10.1007/s10531-018-1625-8 |
Shrestha, N., Wang, Z.H., Su, X.Y., et al., 2018b. Global patterns of Rhododendron diversity: the role of evolutionary time and diversification rates. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 27: 913-924. DOI:10.1111/geb.12750 |
Si, X., Cadotte, M.W., Zeng, D., et al., 2017. Functional and phylogenetic structure of island bird communities. J. Anim. Ecol., 86: 532-542. DOI:10.1111/1365-2656.12650 |
Sklenář, P., Hedberg, I., Cleef, A.M., et al., 2014. Island biogeography of tropical alpine floras. J. Biogeogr., 41: 287-297. DOI:10.1111/jbi.12212 |
Srinivasan, U., Tamma, K., Ramakrishnan, U., 2014. Past climate and species ecology drive nested species richness patterns along an east-west axis in the Himalaya. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 23: 52-60. DOI:10.1111/geb.12082 |
Stein, A., Gerstner, K., Kreft, H., 2014. Environmental heterogeneity as a universal driver of species richness across taxa, biomes and spatial scales. Ecol. Lett., 17: 866-880. DOI:10.1111/ele.12277 |
Steinbauer, M.J., Field, R., Grytnes, J.-A., et al., 2016. Topography-driven isolation, speciation and a global increase of endemism with elevation. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 25: 1097-1107. DOI:10.1111/geb.12469 |
Stephenson, C.M., Kohn, D.D., Park, K.J., et al., 2007. Testing mechanistic models of seed dispersal for the invasive Rhododendron ponticum (L.). Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Systemat., 9: 15-28. DOI:10.1016/j.ppees.2007.07.004 |
Stevens, G.C., 1989. The latitudinal gradient in geographical range: how so many species coexist in the tropics. Am. Nat., 133: 240-256. DOI:10.1086/284913 |
Svenning, J.-C., Skov, F., 2007. Ice age legacies in the geographical distribution of tree species richness in Europe. Global Ecol. Biogeogr., 16: 234-245. DOI:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2006.00280.x |
Valente, L., Phillimore, A.B., Melo, M., et al., 2020. A simple dynamic model explains the diversity of island birds worldwide. Nature, 579: 92-96. DOI:10.1038/s41586-020-2022-5 |
Vincent, C., Fernandes, R.F., Cardoso, A.R., et al., 2019. Climate and land-use changes reshuffle politically-weighted priority areas of mountain biodiversity. Glob. Ecol. Conserv., 17: e00589. |
Wang, Y.J., Wang, J.J., Lai, L.M., et al., 2014. Geographic variation in seed traits within and among forty-two species of Rhododendron (Ericaceae) on the Tibetan plateau: relationships with altitude, habitat, plant height, and phylogeny. Ecol. Evol., 4: 1913-1923. DOI:10.1002/ece3.1067 |
Wang, Z., Fang, J., Tang, Z., et al., 2011. Patterns, determinants and models of woody plant diversity in China. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci., 278: 2122-2132. DOI:10.1098/rspb.2010.1897 |
Wang, Z.H., Tang, Z.Y., Fang, J.Y., 2009. The species-energy hypothesis as a mechanism for species richness patterns. Biodivers. Sci., 17: 613-624. DOI:10.1007/978-3-642-10467-1_54 |
Watanabe, S., Hajima, T., Sudo, K., et al., 2011. MIROC-ESM 2010: model description and basic results of CMIP5-20c3m experiments. Geosci. Model Dev. (GMD), 4: 845-872. DOI:10.5194/gmd-4-845-2011 |
Wen, J., Zhang, J.Q., Nie, Z.L., et al., 2014. Evolutionary diversifications of plants on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Front. Genet., 5: 4. |
Whittaker, R.J., Triantis, K.A., Ladle, R.J., 2008. A general dynamic theory of oceanic island biogeography. J. Biogeogr., 35: 977-994. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2008.01892.x |
Wu, J.G., 1990. Nature conservation theory and Macarthur-Wilson model. Acta Ecol. Sin., 10: 187-191. |
Xia, X.M., Yang, M.Q., Li, C.L., et al., 2022. Spatiotemporal evolution of the global species diversity of Rhododendron. Mol. Biol. Evol., 39: msab314. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msab314 |
Xing, Y.W., Ree, R.H., 2017. Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 114: E3444-E3451. |
Yan, Y.Z., Jarvie, S., Zhang, Q., et al., 2023. Habitat heterogeneity determines species richness on small habitat islands in a fragmented landscape. J. Biogeogr., 50: 976-986. DOI:10.1111/jbi.14594 |
Yu, F.Y., Skidmore, A.K., Wang, T.J., et al., 2017. Rhododendron diversity patterns and priority conservation areas in China. Divers. Distrib., 23: 1143-1156. DOI:10.1111/ddi.12607 |
Zhan, X., Zheng, Y., Wei, F., et al., 2011. Molecular evidence for Pleistocene refugia at the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Ecol., 20: 3014-3026. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05144.x |
Zhang, J.L., Liu, B., Liu, S., et al., 2022. Plantlist: looking up the status of plant scientific names based on the plant list database. R package version 0.8.0. https://github.com/helixcn/plantlist/.
|
Zhang, S., Zhang, Q., Yan, Y., et al., 2021. Island biogeography theory predicts plant species richness of remnant grassland patches in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Basic Appl. Ecol., 54: 14-22. DOI:10.1016/j.baae.2021.04.010 |
Zhao, Z.X., Feng, X.L., Zhang, Y.B., et al., 2023. Species richness, endemism, and conservation of wild Rhododendron in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv., 41: e02375. |
Zhou, H.N., Zhao, Y.H., Zeng, D., et al., 2019. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of ground ant species diversity on the land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake, China. Biodivers. Sci., 27: 1101-1111. |
Zizka, A., Silvestro, D., Andermann, T., et al., 2019. CoordinateCleaner: standardized cleaning of occurrence records from biological collection databases. Methods Ecol. Evol., 10: 744-751. DOI:10.1111/2041-210x.13152 |
Zou, D.T., Wang, Q.G., Luo, A., et al., 2019. Species richness patterns and resource plant conservation assessments of Rosaceae in China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 43: 1-15. DOI:10.17521/cjpe.2018.0091 |
Zu, K.L., Wang, Z.H., 2022. Research progress on the elevational distribution of mountain species in response to climate change. Biodivers. Sci., 30: 123-137. |



