b. Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Orchid Conservation and Utilization, and Key Laboratory of National Forestry and Grassland Administration for Orchid Conservation and Utilization, The National Orchid Conservation Center of China and the Orchid Conservation & Research Center of Shenzhen, Shenzhen, 518114, China;
c. Zhejiang University City College, Hangzhou, 310015, China;
d. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Plant Functional Genomics and Resources, Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden, Shanghai, 201602, China;
e. Jiande Xin'anjiang Forest Farm, Jiande, 311600, China;
f. Institute of Botany, Jiangsu Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nanjing Botanical Garden Mem. Sun Yat-Sen), Nanjing, 210014, China
Cryptic species, which have long puzzled biologists, are often misidentified due to morphological similarity to closely related species (Sáez and Lozano, 2005; Bickford et al., 2007; Winker, 2005; De, 2007). These species can be derived from isolation differentiation (Rieseberg and Willis, 2007), hybridization, and polyploidization (Mallet, 2007; Rieseberg and Willis, 2007). Convergent evolution (Peter et al., 2009; Bravo et al., 2015) is often considered necessary for cryptic speciation in special habitats like arctic, aquatic, desert, rocky, and alpine regions. However, over the last three decades, an increasing number of cryptic species (both animals to plants) have been identified in numerous habitats (from marine to freshwater) (Vrijenhoek et al., 1994; Hebert et al., 2004; Feulner et al., 2006; Grundt et al., 2006; Lombard et al., 2010; Pillon et al., 2010; Li et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Hollingsworth et al., 2016; Hinojosa et al., 2019). More recently, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcoding has been used to identify cryptic species of lycophyte and fern genera, such as Selaginella (Wang et al., 2022), Ceratopteris (Zhang et al., 2020b; Yu et al., 2022), Hymenasplenium (Xu et al., 2019a, 2019b), and Didymochlaena (Shang et al., 2020). As biodiversity conservation based on species diversity has become a hot topic globally, accurate identification of cryptic species is critical for the conservation of biodiversity (Bickford et al., 2007; Nygren, 2014; Fier et al., 2017; Thompson et al., 2020), especially because many cryptic species are at risk of extinction prior to their discovery (Liu et al., 2022). However, the origin of species remains a fascinating scientific problem, and much of the evolution of organisms, as well as the total number of species on earth, still baffles scientists (May, 1988, 1990; Prance et al., 2000; Dirzo and Raven, 2003; Joppa et al., 2011; Pimm et al., 2014). The known number of species may be much smaller than the actual amount because significant morphological changes do not accompany all speciation, and genetic diversity within a species also implicates underappreciated mechanisms of morphologically static species (Bickford et al., 2007).
The stability and homogeneity of aquatic environments have led to morphological similarities between related aquatic organisms (Bickford et al., 2007; Fier et al., 2017). One such group of organisms is the quillworts (Isoëtes spp.), an ancient aquatic group of species. Isoëtes is the only surviving genus of the Isoëtaceae family. These heterosporous lycophytes have fascinated botanists and paleobotanists alike because of their distinctive morphology and long evolutionary history (Gifford and Foster, 1989; Pigg, 2001; Cúneo, 2009; Pereira et al., 2021a). Although the origin of Isoëtes can be dated back to the Devonian (Pigg, 1992), most extant diversity is relatively recent (Wood et al., 2020). Isoëtes are widely distributed from the tropics to subarctic regions and survive in habitats that range from submerged, evergreen aquatic environments of cold, clear water lakes to upland terrestrial ephemerals with seasonally parched soils over bedrock (Smolders et al., 2002; Troia et al., 2016).
Although more than 350 species of Isoëtes have been reported, fewer than 200 have been universally accepted by the scientific community (Troia et al., 2016). Species number varies greatly from country to country; for example, more than 50 species have been reported in the United States (Schafran, 2019), whereas only ten species have been recorded in China (Li et al., 2019; Lu et al., 2021; Shu et al., 2022). These Chinese Isoëtes vary in ploidy level, and include diploid species (e.g., I. hypsophila Hand.-Mazz.; I. shangrilaensis Xiang Li, Yuqian Huang, Xiaokang Dai & Xing; I. yunguiensis Q.F. Wang & W.C. Taylor; and I. taiwanensis De Vol), tetraploid species (e.g., I. sinensis Palmer) (Palmer, 1927; Liu et al., 2002), and hexaploid species (e.g., I. orientalis H. Liu & Q.F. Wang) (Liu et al., 2005). Interestingly, ploidy level appears to be related to geographical distribution. For example, diploids have only been reported in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Southwest Sichuan, and Taiwan (Handel-Mazzetti, 1923; Devol, 1972; Wang et al., 2002; Li et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2002); in contrast, hexaploid species have only been found in Zhejiang Province. Previous studies of Isoëtes in China have ignored geographical variation in ploidy level among known Isoëtes species (Pang et al., 2003; Ye and Li, 2003; Chen et al., 2004; Taylor et al., 2004; Kang et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Xie et al., 2019; Dai et al., 2020). Thus, nearly all the populations from Anhui, Hunan, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang have historically been treated as I. sinensis.
Species identification in Isoëtes is challenging due to morphological convergence between species that has resulted from widespread interspecific hybridization and allopolyploid speciation (Hickey, 1986; Taylor and Hickey, 1992; Hoot and Taylor, 2001). Several features have long been used to distinguish Isoëtes species, including habitat (Pfeiffer, 1922), megaspore and microspore texture (Hickey, 1986; Lellinger and Taylor, 1997; Holmes et al., 2005), and chromosome number (Takamiya et al., 1994; Liu et al., 2002). More recently, molecular barcoding methods using complete chloroplast genome data have been used to distinguish species within this genus (Choi et al., 2018; Schafran et al., 2018; Pereira et al., 2021a, 2021b). However, chloroplast barcoding methods have still failed to distinguish problematic Isoëtes species from species complexes (Romero and Real, 2015; Kim and Choi, 2016; Dai et al., 2020; Suissa et al., 2020). Nevertheless, several new Isoëtes species have been recognized and described around the world (Moraolivo et al., 2016; Pereira et al., 2016, 2017, 2019a; Schafran et al., 2016; Li et al., 2019; Lu et al., 2021; Shu et al., 2022), indicating that Isoëtes species diversity may be grossly underestimated, with many cryptic species unidentified (Schafran, 2019). One approach to identifying additional Isoëtes species is the use of larger data sets such as genomic data.
Genomic-scale data sets have been used to resolve complex evolutionary relationships, including the branching order within rapid radiations (Wei et al., 2017; Wei and Zhang, 2019). Plastid genome (plastome) DNA sequences have been extensively used in recent plant molecular systematics because of their mode of uniparental inheritance and high content of informative loci (Givnish et al., 2010, 2015; Jansen et al., 2011; Ruhfel et al., 2014; Lu et al., 2015; Ross et al., 2016; Schafran et al., 2018). Over the past few years, several studies have demonstrated that the complete plastome has the potential to provide strong support for deep relationships in the plant tree of life, even when dealing with explosions of diversity over short periods of time (Barrett et al., 2016; Welch et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2017; Wei and Zhang, 2019; Foster et al., 2018; Nie et al., 2020; Pereira et al., 2021a; Larsén et al., 2022). Furthermore, plastome sequences provide new opportunities to explore the relationships among lineages with ambiguous or unresolved phylogenies (Wei et al., 2017). Previous studies of Isoëtes species based on plastome data have been reported, and some questions regarding their evolutionary history and phylogeny have been discussed (Karol et al., 2010; Schafran et al., 2018; Santos et al., 2020; Suissa et al., 2020; Pereira et al., 2021a). However, we believe that the species diversity of quillworts might be seriously underestimated, and many cryptic species might be misidentified in China. This belief led us to search for cryptic speciation in Chinese Isoëtes species by re-identifying population ploidy levels, re-observing spores, analyzing haplotypes, and reconstructing phylogenetic trees of almost all Chinese Isoëtes populations.
2. Materials and methods 2.1. Taxon samplingA total of 46 samples of Isoëtes were used in this study: 26 were collected from the field (Table 1), four were cultivated in the greenhouse (Isoëtes sp.8 was in Lushan Botanical Garden, Jiangxi; I. yunguiensis 2 in Harbin Normal University, Heilongjiang; Isoëtes sp.4 in Guangxi Normal University, Guangxi; Isoëtes sp.13 in Zhongshan Botanical Garden, Jiangsu), and three were obtained from herbarium specimens [Isoëtes sp.1 was from South China Botanical Garden Herbarium (IBSC), and I. japonica A. Br. and Isoëtes sp.12 were from China National Herbarium (PE)]. A total of 13 complete plastome sequences from Isoëtes species were downloaded from GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/), including three accessions (I. sinensis, I. yunguiensis 3, and I. taiwanensis) from China and 10 accessions from South America (Table 1).
| Taxon | Collecting site | Voucher No. and Herbarium | Length of plastome sequences (bp) | GC content (%) | GenBank Accession | |||
| Total | LSC | SSC | IR | |||||
| Isoëtes sp.1 | Xiuning City, Anhui Province | Renhua Shan; 2405, NAS |
145, 474 | 91, 848 | 27, 216 | 13, 205 | 38.0 | OP831295 |
| I. fengii | Chuxiong City, Yunnan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08918, PE |
145, 545 | 91, 899 | 27, 232 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831287 |
| I. fengii | Chuxiong City, Yunnan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08917, NOCC |
145, 642 | 91, 888 | 27, 340 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831288 |
| I. hypsophila 1 | Daocheng County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08963, NOCC |
146, 362 | 91, 741 | 27, 239 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | MW405450 |
| Isoëtes sp.2 | Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15155, NOCC |
145, 505 | 91, 866 | 27, 225 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831296 |
| Isoëtes sp.3 | Taining City, Fujian Province | Yufeng Gu; Fern08947, NOCC |
145, 491 | 91, 865 | 27, 213 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831297 |
| Isoëtes sp.4 | Guilin City, Guangxi Province | Yuehong Yan; Fern09577, NOCC |
145, 502 | 91, 867 | 27, 221 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831298 |
| I. yunguiensis 1 | Nayong City, Guizhou Province | Qiang Luo; Fern09070, NOCC |
145, 507 | 91, 880 | 27, 214 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831313 |
| Isoëtes sp.5 | Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15158, NOCC |
145, 481 | 91, 850 | 27, 217 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831299 |
| I. yunguiensis 2 | Harbin Normal University | Baodong Liu; artificial breeding Fern09965, NOCC |
145, 509 | 91, 879 | 27, 216 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831314 |
| I. japonica | Japan | Miyoshi; 57, 289, PE |
145, 517 | 91, 868 | 27, 241 | 13, 204 | 38.0 | MZ596344 |
| Isoëtes sp.6 | Jiande City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu; Fern08745, NOCC |
145, 668 | 91, 864 | 27, 390 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831300 |
| I. hypsophila 2 | Jiulong County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08988, NOCC |
146, 359 | 91, 740 | 27, 237 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | OP831289 |
| I. hypsophila 3 | Jiulong County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08989, NOCC |
146, 363 | 91, 740 | 27, 237 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | OP831290 |
| Isoëtes sp.7 | Tonggu County, Jiangxi Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15062, NOCC |
145, 503 | 91, 865 | 27, 224 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831301 |
| Isoëtes sp.7 | Tonggu County, Jiangxi Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15061, NOCC |
145, 505 | 91, 865 | 27, 226 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831302 |
| Isoëtes sp.7 | Tonggu County, Jiangxi Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15063, NOCC |
145, 503 | 91, 865 | 27, 224 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831303 |
| Isoëtes sp.8 | Lushan Botanical Garden | Yufeng Gu et al.; Artificial breeding YYH15159, NOCC |
145, 492 | 91, 847 | 27, 231 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831304 |
| Isoëtes sp.9 | Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15157, NOCC |
145, 490 | 91, 862 | 27, 214 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831305 |
| I. longpingii | Ningxiang, Hunan Province | Ou, Z.G.; YYH15160, PE |
145, 482 | 91, 849 | 27, 219 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831294 |
| I. orientalis | Songyang County, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu; Fern08748, NOCC |
145, 502 | 91, 862 | 27, 226 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OL467336 |
| Isoëtes sp.10 | Tengchong County, Yunnan Province | Jianyun Wang YYH15162, NOCC |
145, 510 | 91, 874 | 27, 222 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831306 |
| I. xiangfei | Tongdao County, Hunan Province | Yuehong Yan; YYH15161, PE, NOCC |
145, 500 | 91, 858 | 27, 228 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831310 |
| I. xiangfei | Tongdao County, Hunan Province | Yuehong Yan; YYH15161, PE, NOCC |
145, 500 | 91, 858 | 27, 228 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831311 |
| I. xiangfei | Tongdao County, Hunan Province | Juan Yang; Fern09828, PE, NOCC |
145, 500 | 91, 858 | 27, 228 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831312 |
| I. taiwanensis | NCBI | NCBI | 145, 519 | 91, 887 | 27, 218 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | MF149843 |
| Isoëtes sp.11 | Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; YYH15156, NOCC |
145, 489 | 91, 861 | 27, 214 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831307 |
| I. hypsophila 4 | Daocheng County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08960, NOCC |
146, 361 | 91, 744 | 27, 239 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | OP831291 |
| I. hypsophila 5 | Daocheng County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08961, NOCC |
146, 361 | 91, 746 | 27, 239 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | OP831292 |
| I. hypsophila 6 | Daocheng County, Sichuan Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08962, NOCC |
146, 361 | 91, 741 | 27, 239 | 13, 691 | 38.1 | OP831293 |
| I. yunguiensis | NCBI | NCBI | 145, 507 | 91, 879 | 27, 214 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | MF149844 |
| Isoëtes sp.12 | Kunming City, Yunnan Province | Weiming Zhu; 1316 |
145, 520 | 91, 885 | 27, 221 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831308 |
| I. yunguiensis 3 | Nayong City, Guizhou Province | Qiang Luo; Fern09069 |
145, 509 | 91, 879 | 27, 216 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831315 |
| I. sinensis | Fuzhou City, Fujian Province | NCBI | 145, 490 | 91, 863 | 27, 213 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | MN172503 |
| I. baodongii | Zhuji City, Zhejiang Province | Yufeng Gu et al.; Fern08746, PE, NOCC |
145, 495 | 91, 860 | 27, 221 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831286 |
| Isoëtes sp.13 | Zhongshan Botanical Garden | Qimeng Sun; artificial breeding Fern09050 |
145, 498 | 91, 860 | 27, 224 | 13, 207 | 38.0 | OP831309 |
| I. engelmannii | Hiawassee River, Reliance, Tennessee | Schafran P.W.; Schafran 46, ODU |
144, 817 | 91, 674 | 27, 031 | 13, 056 | 38.0 | NC_038080 |
| I. piedmontana | Heggie's Rock, Appling, Georgia | Schafran P.W.; Schafran 18, ODU |
145, 030 | 91, 748 | 27, 198 | 13, 042 | 38.0 | NC_040925 |
| I. graniticola | NCBI | Schafran P.W.; Schafran 14, ODU |
145, 118 | 91, 736 | 27, 194 | 13, 094 | 38.0 | MG_792, 132 |
| I. mattaponica | NCBI | Bray Chick 12 | 145, 065 | 91, 718 | 27, 191 | 13, 078 | 38.0 | NC_039703 |
| I. melanospora | Summit of Stone Mountain, Georgia | Schafran P.W.; Schafran 12, ODU |
145, 045 | 91, 675 | 27, 184 | 13, 093 | 38.0 | NC_038072 |
| I. flaccida | St. Marks River, Newport, Florida | Taylor 6770, US | 145, 303 | 91, 862 | 27, 205 | 13, 118 | 37.9 | GU191333 |
| I. valida | Michaux State Forest, Cumberland Co., Pennsylvania | Schafran P.W.; Schafran 37, ODU |
145, 132 | 91, 760 | 27, 164 | 13, 104 | 38.0 | NC_038074 |
| I. butleri | Ft. Worth Nature Center, Texas | Schafran P.W.; Schafran P.W.; Schafran 47, ODU |
144, 912 | 91, 543 | 27, 171 | 13, 099 | 38.0 | NC_038080 |
| I. malinverniana | NCBI | Mower J.P. et al. | 145, 535 | 91, 715 | 27, 386 | 13, 217 | 38.0 | NC_040924 |
| I. nuttallii | Vernal Fall, Mariposa Co., California | Taylor 6734, US | 144, 680 | 90, 760 | 27, 282 | 13, 319 | 38.2 | NC_038073 |
| Note: LSC is a large single-copy region; SSC is a small single-copy region; IR is an inverted repeat region. | ||||||||
The morphology of spores was examined under a scanning electron microscope (Quanta 250 FEI, USA). Untreated plant spores were collected after maturation and dried under natural conditions. Spores were mounted on a double-sided adhesive tape attached to metal stubs, sputter-coated with gold, and viewed under a Quanta 250 system at an accelerating voltage of 25 kV (kV) for megaspores and 30 kV for microspores. Previous studies were used as references to describe spore ornamentation (Hickey, 1986; Ranker, 1993; Watanabe et al., 1996; Wang and Yu, 2003; Wang and Dai, 2010; Holmes et al., 2005; Liu et al., 2008). To determine the average size of spores, we measured the length of the equatorial axis of 10–30 megaspores and microspores. Photographs are shown in Figs. 1 and 2, and the spore descriptions are presented in Table 2.
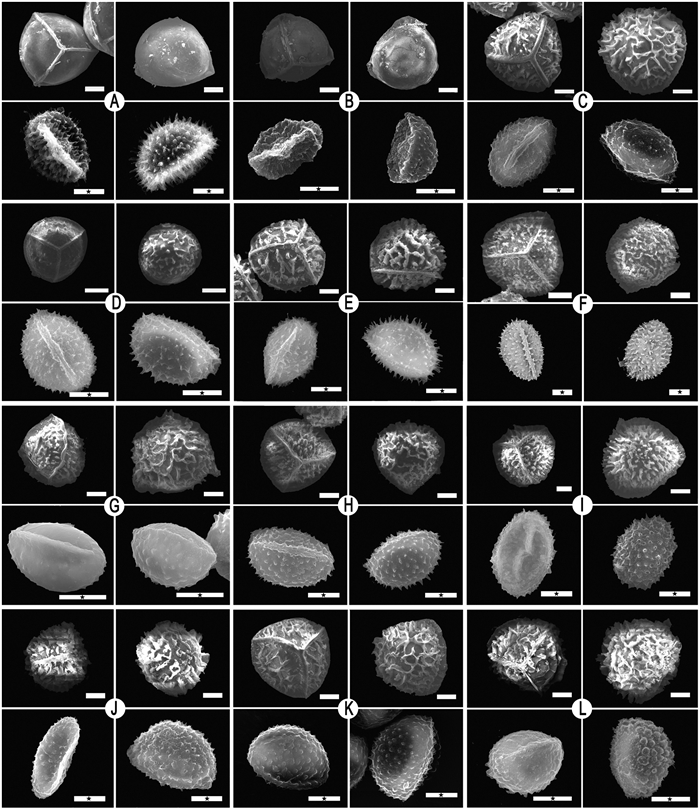
|
| Fig. 1 Megaspores and microspores of samples. (A) & (B) Isoëtes hypsophila (C) Isoëtes sp.10 (D) Isoëtes sp.13 (E) I. baodongii (F) Isoëtes sp.6 (G) Isoëtes sp.5 (H) Isoëtes sp.4 (I) Isoëtes sp.9 (J) Isoëtes sp.11 (K) I. xiangfei (L) Isoëtes sp.7. Scale bar = 100 μm (megaspore) & 10 μm (microspore, with ★). |
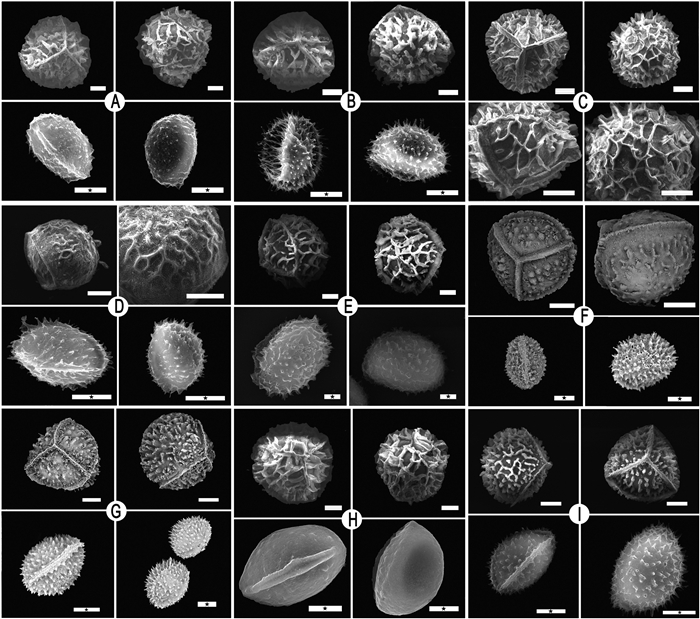
|
| Fig. 2 Megaspores and microspores of samples. (A) Isoëtes sp.3 (B) I. orientalis (C) Isoëtes sp.12 (D) I. taiwanensis (E) I. fengii (F) I. longpingii (G) Isoëtes sp.2 (H) I. japonica (I) Isoëtes sp.8. Scale bar = 100 μm (megaspore) & 10 μm (microspore, with ★). |
| Taxon | Spore morphology | Size (μm) | Chromosome numbers | |||
| Megaspore | Microspore | Megaspore | Microspore | |||
| Isoëtes fengii | reticulate | echinate | 470–500 (mean = 480) | 28–30 (mean = 29) | 66 | |
| I. japonica | reticulate | levigate | 380–500 (mean = 455) | 32–35 (mean = 33) | 66+ | |
| Isoëtes sp.3 | reticulate | levigate-granulate | 450–490 (mean = 470) | 24–27 (mean = 25) | 66 | |
| I. orientalis | cristate-reticulate | echinate | 440–470 (mean = 450) | 24–26 (mean = 25) | 66 | |
| I. xiangfei | cristate-reticulate | tuberculate-echinate | 390–450 (mean = 425) | 25–28 (mean = 27) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.7 | reticulate | tuberculate-echinate | 330–410 (mean = 370) | 18–21 (mean = 20) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.5 | cristate-reticulate | levigate-granulate | 370–430 (mean = 400) | 19–22 (mean = 21) | 44 | |
| I. longpingii | tuberculate-cristate | echinate | 310–350 (mean = 325) | 27–30 (mean = 29) | 44 | |
| I. sinensis | echinate-cristate | echinate | 350–430 (mean = 380) | 27–31 (mean = 29) | 44* | |
| Isoëtes sp.4 | echinate-cristate | echinate | 350–410 (mean = 375) | 25–28 (mean = 27) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.6 | echinate-cristate | echinate | 320–410 (mean = 370) | 30–33 (mean = 32) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.8 | echinate-cristate | echinate | 370–390 (mean = 382) | 24–29 (mean = 26) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.2 | echinate | echinate | 390–420 (mean = 400) | 25–27 (mean = 26) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.9 | echinate | echinate | 400–460 (mean = 435) | 26–29 (mean = 28) | 44 | |
| Isoëtes sp.11 | cristate | echinate | 330–420 (mean = 360) | 24–28 (mean = 27) | 44 | |
| I. hypsophila | levigate | echinate | 350–410 (mean = 385) | 24–26 (mean = 25) | 22* | |
| I. hypsophila | levigate | echinate | 350–430 (mean = 385) | 22–25 (mean = 24) | 22* | |
| I. hypsophila | levigate | echinate# | 370–470 (mean = 430) | 19–25 (mean = 22) | 22* | |
| I. yunguiensis | cristate-reticulate# | levigate-granulate# | 340–430 (mean = 390) | 20–25 (mean = 22) | 22* | |
| Isoëtes sp.10 | cristate-reticulate | levigate-granulate | 360–420 (mean = 390) | 25–28 (mean = 26) | 22 | |
| Isoëtes sp.12 | cristate-reticulate | / | 400–430 (mean = 415) | / | / | |
| Isoëtes sp.13 | tuberculate-cristate | echinate | 280–330 (mean = 300) | 22–23 (mean = 23) | 22 | |
| I. baodongii | cristate-echinate | echinate | 390–510 (mean = 450) | 24–26 (mean = 25) | 22 | |
| I. taiwanensis** | regulate | echinate | 310–390 (mean = 350) ** | 20–24 (mean = 22) ** | 22** | |
| Note: * cited from Liu et al. (2002), # cited from Liu et al. (2008), + cited from Takamiya et al. (1994), ** cited from Devol (1972), / means data lacking. | ||||||
Chromosomes were counted using the methodology of Zhang et al. (2019) but with some procedural modifications (see Table 3). Young root tips of the sporophytes were pretreated in saturated p-dichlorobenzene aqueous solution for 5 h and were then fixed in Carnoy's solution for 1 h at 4 ℃. They were dissociated in a mixture containing a ratio of 3% cellulase: 2.5% pectinase (1:1) for 15 min. The chromosomes from 20 samples were counted, and photographs were taken in the laboratory (Figs. 2 and 3). Three Isoëtes xiangfei Y.H. Yan, Y.F. Gu & J.P. Shu (Shu et al., 2022) samples from the same collection site had equivalent chromosome numbers. The chromosome number was determined using a line drawing on each photograph.
| Haplotype | Taxon | Sample code | Haplotype | Taxon | Sample code |
| Hap1 | Isoëtes xiangfei | TD1, TD2, TD3 | Hap12 | Isoëtes sp.8 | JXLS |
| Hap2 | Isoëtes sp.9 Isoëtes sp.11 |
LWG, WJL | Hap13 | I. yunguiensis | GZYG, YNYG, HSD, MF149844 |
| Hap3 | I. sinensis | FZ | Hap14 | Isoëtes sp.12 | YN1316 |
| Hap4 | I. taiwanensis | TW | Hap15 | Isoëtes sp.10 | TC |
| Hap5 | Isoëtes sp.4 | GX | Hap16 | Isoëtes sp.6 | JD |
| Hap6 | Isoëtes sp.7 | JX1, JX2, JX3 | Hap17 | Isoëtes sp.13 | ZSZWY |
| Hap7 | I. orientalis | SY | Hap18 | I. baodongii | ZJ |
| Hap8 | Isoëtes sp.3 | EMF | Hap19 | Isoëtes sp.2 | DQH |
| Hap9 | Isoëtes sp.1 | AH | Hap20 | I. fengii | CX1, CX2 |
| Hap10 | I. longpingii | NX | Hap21 | I. japonica | JP |
| Hap11 | Isoëtes sp.5 | HDS | Hap22 | I. hypsophila | DC, XYC1, XYC2, XYC3, JL1, JL2 |

|
| Fig. 3 Chromosome squash of mitotic root tip cells and line drawing of 18 samples. (A, a) Isoëtes yunguiensis (B, b) Isoëtes sp.10 (C, c) I. baodongii (D, d) Isoëtes sp.13 (E, e) Isoëtes sp.2 (F, f) Isoëtes sp.4 (G, g) Isoëtes sp.5 (H, h) Isoëtes sp.7 (I, i) Isoëtes sp.6 (J, j) Isoëtes sp.8 (K, k) Isoëtes sp.9 (L, l) I. longpingii (M, m) I. xiangfei (N, n) Isoëtes sp.9 (O, o) I. fengii (P, p) I. fengii (Q, q) Isoëtes sp.3 (R, r) I. orientalis. Scale bar = 10 μm. |
Isoëtes plastome library construction was done at Majorbio Corporation (Shanghai, China). Briefly, DNA was extracted from 33 leaf samples (fresh or silica-dried) and then sequenced for plastome library construction using the TruSeq Nano DNA HT Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA) following the manufacturer's recommendations. Specifically, each DNA sample was indexed with a unique marker for downstream sequence identification. The samples were divided into 350-base-pair (bp) fragments, which were end polished, A-tailed, and ligated with full-length adapters for subsequent Illumina sequencing and PCR amplification. The libraries were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform (Illumina), and 150-bp paired-end reads were generated with insert sizes of approximately 400 bp. After enrichment of each sample, between 2 and 4 Gigabases (Gb) of sequence data were obtained.
To assemble the reads, raw reads were filtered using the default settings (-L: 5 -p: 0.5-N: 0.1) in ng_QC v.2.0 (Majorbio Corporation, Shanghai). Then the scripts and libraries in the GetOrganelle toolkit (Jin et al., 2020) were used to recruit target organelle reads from the sequence data, with Isoëtes yunguiensis used as the reference. The total target-associated reads underwent de novo sequencing assembly into a FASTG file using the St. Petersburg genome assembler (SPAdes v.3.13.0). The slimmed FASTG file was visualized using a Bioinformatics Application for Navigating De novo Assembly Graphs Easily (Bandage) (Wick et al., 2015) to finalize the complete target genome manually. Geneious Prime 2021.0.3 (https://www.geneious.com) was also used for data visualization and sequence correction.
2.5. Phylogenetic analyses for the complete plastid genomePhylogenetic analyses of Isoëtes were conducted by both Maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI). First, we aligned the complete plastome sequences of 46 Isoëtes samples using Mauve Aligner v.2.4.0 implemented in Geneious Prime. We used an advanced algorithm and assumed collinearity, excluding poorly aligned regions from the complete plastome data set, using Gblocks v.0.91b (Gerard and Jose, 2007) implemented in PhyloSuite v.1.2.2 (Zhang et al., 2020a) with DNA as the type of sequence (-t) up to half gap positions enabled (b5: half), and other parameters within the default settings. The resulting alignment was first trimmed for phylogenomic analysis to exclude misaligned regions and positions with > 90% missing data. ML analyses were performed using IQ-TREE v.1.6.12 (Nguyen et al., 2015) with 10, 000 bootstrap replicates. The best fitting model was selected by ModelFinder (Kalyaanamoorthy et al., 2017) and implemented in IQ-TREE. We visualized ML trees and ML bootstrap values (MLBS) using FigTree v.1.4.4 (Andrew, 2018); trees were rooted using Isoëtes nuttallii as the reference sequence in accordance with the methodology of Dai et al. (2020). BI analysis was performed using MrBayes v.3.2.6 (Ronquist et al., 2012) in PhyloSuite (Zhang et al., 2020a) under a GTR + I + G model selected by the Bayesian information criterion in ModelFinder. Analyses were performed using four parallel Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) runs for 20, 000, 000 generations, sampling every 1000 generations with a 25% burn-in. We combined simultaneous, independent runs to obtain majority rule consensus trees and to calculate Bayesian inference posterior probabilities (BIPP).
2.6. Variant calling with sequence dataAll sequences, which we treated as low-depth, were mapped to the Isoëtes xiangfei reference genome (Shu et al., unpublished data) using the Burrows-Wheeler Alignment Tool (BWA v.0.6) with default settings (Li et al., 2009). Picard-tools v.1.92 (https://picard.sourceforge.net) was used to assign read group information that contained the sample library number, lane number, and sample identity. BWA was also used to sort the Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM)-format files, remove reads marked as duplicates, and generate Binary Alignment Map (BAM)-format files. Raw single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were filtered with VCFtools (Danecek et al., 2011) (using the parameters -minMapQ 30 -minQ 20 -max-missing 0.98) to obtain high-quality SNPs. To infer the individual ancestry proportions, we used ADMIXTURE v.1.23 (Alexander and Lange, 2011) with cross-validation for numbers of genetic clusters (K) from 1 to 20. The optimum number of clusters (K) was determined using the cross-validation errors (CV-error).
2.7. Haplotype and networkDNA Sequence Polymorphism (DnaSP v.6) was used to identify the haplotypes in the plastid sequences (Julio et al., 2017), producing an RDF format (.rdf) file. Network 10.2 was employed to analyze the.rdf file and draw the network (Bandelt and Dress, 1992).
2.8. Estimation of divergence timesThe divergence times were estimated using the BEAST v.2.6.6 program (Bouckaert et al., 2019). The GTR + F + I model for the combined data set was applied with a Yule speciation tree and a relaxed clock log normal clock model after. We generated two calibrated notes by inputting the results from Dai et al. (2020) into the TimeTree online platform (http://www.timetree.org/). The age of the root was set to 'normal distribution, ' and the treeModel.rootHeight parameter was set to normal. BEAST trees were run for 200, 000, 000 generations and were sampled every 1000 generations. Tracer v.1.7.1 (http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer) was used to check whether the effective sample size (ESS) parameter values were greater than 200. The final annotation was completed using TreeAnnotator v.1.8.0 after discarding the first 10% of generations.
3. Results 3.1. Spore characteristicsWe examined spores from 24 Isoëtes samples, including megaspores and microspores. The megaspores of Isoëtes samples were globose and trilete, with an equatorial ridge dividing the proximal and distal hemispheres and three radial ridges converging at the pole of the proximal hemisphere, where the surface is laevigate or has various types of ornamentation (Figs. 1 and 2; Table 2). Microspores were ellipsoid, monolete, with a smooth or textured surface, ornamented with spines, granules, or tubercles (Figs. 1 and 2; Table 2).
Megaspores can be divided into eight types based on ornamentation characteristics. Megaspores are (ⅰ) laevigate in Isoëtes hypsophila; (ⅱ) reticulate in I. fengii (Gu et al., unpublished data) and Isoëtes sp.3; (ⅲ) echinate in Isoëtes sp.2 and Isoëtes sp.9; (ⅳ) cristate in Isoëtes sp.11; (ⅴ) echinate-cristate in Isoëtes sp.4, Isoëtes sp.6, Isoëtes sp.8, I. baodongii, and I. sinensis; (ⅵ) cristate-reticulate in Isoëtes sp.5, I. yunguiensis, Isoëtes sp.7, I. orientalis, Isoëtes sp.10, I. xiangfei, and Isoëtes sp.12; (ⅶ) tuberculate-cristate in I. longpingii Y.H. Yan, Y.F. Gu & J.P. Shu (Shu et al., 2022) and Isoëtes sp.13; and (ⅷ) rugulate in I. taiwanensis. Microspores can be divided into five types. Microspores are (ⅰ) echinate in I. fengii, Isoëtes sp.4, Isoëtes sp.6, Isoëtes sp.8, I. hypsophila, Isoëtes sp.9, I. longpingii, I. orientalis, I. taiwanensis, I. baodongii, Isoëtes sp.13, and I. sinensis; (ⅱ) levigate-granulate in Isoëtes sp.3, Isoëtes sp.5, Isoëtes sp.10, and I. yunguiensis; (ⅲ) tuberculate-echinate in Isoëtes sp.7; and (ⅳ) laevigate in I. xiangfei. We assessed other studies for any missing information. The sizes of both megaspores and microspores are shown in Table 2.
3.2. Chromosome countChromosomes from 18 samples were observed, photographed, and counted with line drawings (Fig. 3). Four samples—Isoëtes yunguiensis, Isoëtes sp.10, I. baodongii, and Isoëtes sp.13—have 22 chromosomes; I. fengii, I. orientalis, and Isoëtes sp.3 have 66 chromosomes, and ten samples have 44 chromosomes. For samples in which chromosomes were uncounted in this study, we supplemented our observations with data from previous studies (see Table 2).
3.3. Genomic structure and phylogenetic analysesWe obtained new plastome sequences for 33 samples. Complete plastome lengths for these Isoëtes samples ranged from 145, 474 to 146, 363 bp (Table 1). The GC content of the plastomes was approximately 38.0% (Table 1). All 46 sequences used in this study presented strong collinearity; furthermore, Mauve Aligner identified only one locally collinear block without any rearrangement (Fig. 4).

|
| Fig. 4 (A) Phylogenetic reconstruction based on 46 Isoëtes plastomes; (B) Structural alignment of 46 Isoëtes plastomes; (C) Comparison of boundaries of large single-copy, small single-copy, and inverted repeat regions of Isoëtes plastomes. |
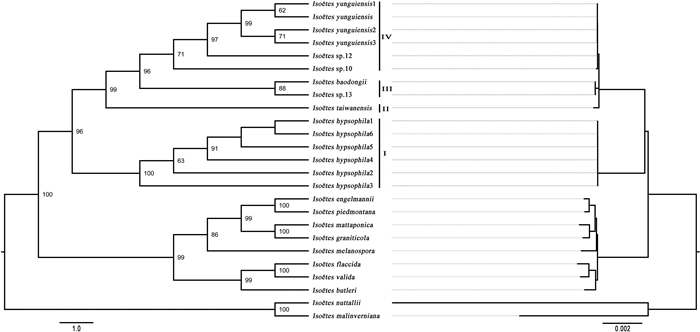
Phylogenetic trees based on complete plastome sequences of 46 Isoëtes samples were reconstructed by ML (Fig. 5a) and BI (Fig. 5b). ML and BI phylogenetic trees were highly consistent except for some variation in the positions of four samples. The ML and BI analyses provided a well-supported phylogenetic structure, with most branches supported by > 90% MLBS values and 1.0 BIPP values (Fig. 5). All 35 samples from China and one from Japan clustered into a large monophyletic branch, in which I. hypsophila formed a monophyletic clade. Isoëtes fengii, together with I. japonica, also formed a monophyletic clade. The tetraploids did not form a monophyletic clade, as I. taiwanensis and I. orientalis were embedded in the branch formed by 14 tetraploid samples. Isoëtes baodongii and Isoëtes sp.13 were clustered with two other tetraploid samples (Isoëtes sp.2 and Isoëtes sp.6).

|
| Fig. 5 ML (a) and BI (b) phylograms of 46 Isoëtes samples. – is a ML bootstrap value lower than 50% or a Bayesian inference posterior probability lower than 0.5. Color of sample names indicates different ploidy; orange is tetraploid, green is diploid, and blue is hexaploid. |
A total of 36, 378 SNPs was obtained and employed to estimate the optimal clustering number. The minimum CV-error was found when K was 19 (Fig. 6A). Almost every sample presented a single structure when the genetic structure was calculated with SNPs (Fig. 6B). Introgression occurred only in Isoëtes longpingii and two I. hypsophila samples. I. xiangfei and Isoëtes sp.4 clustered into the same structure, and Isoëtes sp.2 presented the same structure with Isoëtes sp.9 but not with Isoëtes sp.11, which clustered with I. baodongii. The genetic structure differed between I. yunguiensis distributed in Yunnan Province and I. yunguiensis distributed in Guizhou Province. Similarly, the two samples collected in Yunnan (Isoëtes sp.10 and Isoëtes sp.12) had different genetic structures. Samples with different ploidy on the phylogenetic tree were well separated (Fig. 6C). I. hypsophila formed a monophyletic clade; I. japonica is the sole member of one clade; hexaploid species I. fengii formed a monophyletic clade together with I. yunguiensis and another two Yunnan samples (Isoëtes sp.10 and Isoëtes sp.12); another two hexaploidy species were clustered at a different location in a large clade that also contains two diploid samples (I. baodongii and Isoëtes sp.13) and all tetraploid samples.

|
| Fig. 6 Genetic structure and phylogenetic tree based on SNP data. (A) The ADMIXTURE cross-validation error corresponding to different K values. (B) Individual cluster values (K) of 33 Isoëtes samples with structural analysis. (C) Phylogenetic tree of 33 samples based on 36, 378 SNPs. Green represents diploids, red represents tetraploids, and blue represents hexaploids. |
Six Isoëtes hypsophila samples shared one haplotype (Hap22); two I. fengii samples shared one haplotype (Hap20); three I. xiangfei samples shared one haplotype (Hap1); three Isoëtes sp.7 samples shared one haplotype (Hap6); four I. yunguiensis samples shared one haplotype (Hap13); two Isoëtes sp.9 shared haplotype 2 (Hap2); each of the other samples possessed one haplotype.
When we used these shared haplotypes in network analysis, we found no net structures (Fig. 7). However, a total of 10 median vectors (mv) were produced. Isoëtes hypsophila and I. fengii connected to mva; Isoëtes sp.10, Isoëtes sp.11, and I. yunguiensis connected to mvb; Isoëtes sp.6, Isoëtes sp.12, Isoëtes sp.2, and I. baodongii shared mvc then connected to mvb; Isoëtes sp.1, Isoëtes sp.5, and I. longpingii shared mvf then connected to mve (which only Isoëtes sp.8 connected); no haplotype connected to mvd directly; Isoëtes sp.3, Isoëtes sp.7, I. xiangfei, and I. orientalis shared mvg; Isoëtes sp.4 and Isoëtes sp.9 shared mvh which connected to mvg; I. sinensis connected to mvi; I. taiwanensis and I. japonica shared mvj. A long line segment between Isoëtes hypsophila and the median vector was identified, and I. fengii, Isoëtes sp.1, and I. japonica also showed a long line segment to the median vector they connected with.
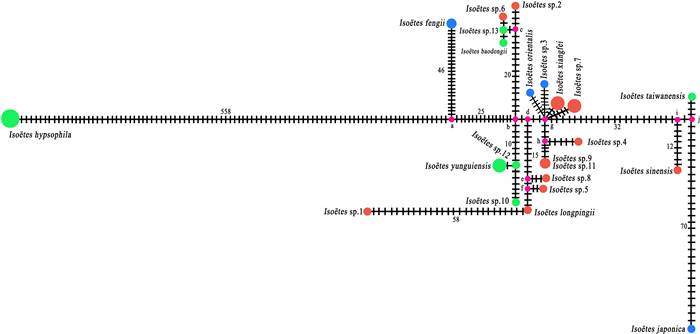
|
| Fig. 7 Network analysis used 22 haplotypes of 36 Isoëtes samples; the number next to the line segment between the circles represents the number of variances. |
High gene arrangement synteny was observed in 35 Isoëtes plastomes from China and Japan (Fig. 4C). Differences in plastome size of Isoëtes can be primarily attributed to the extent of the IR (inverted repeat) region for each individual species (Fig. 4C). All Isoëtes plastomes within this study contained the SSC (small single copy region)/IRB boundary within the ycf2 gene and the SSC/IRA boundary between ycf2 and ycf1 genes. Two types of plastomes were characterized by IR length variation. The type I plastome was identified in I. hypsophila samples, which were characterized by an expanded IR region (reaching a length of 13, 691 bp), and the other 30 samples were identified as a type Ⅱ plastome (ranging from 13, 195 to 13, 207 bp).
3.7. Molecular datingDivergence time for each sample was estimated using the BEAST v.2.6.6 program based on plastome data (Fig. 8). The divergence of Isoëtes distributed in South America and the samples from this current study likely occurred in the Middle Paleocene (~57.79 Ma; 95% HPD = 43.21–71.76 Ma). The first branch to diverge was Isoëtes hypsophila, at about 48.05 Ma (95% HPD = 30.78–66.31 Ma), in the early Eocene. The divergence times for the remaining 30 samples were estimated to occur between 3 and 20 Ma.
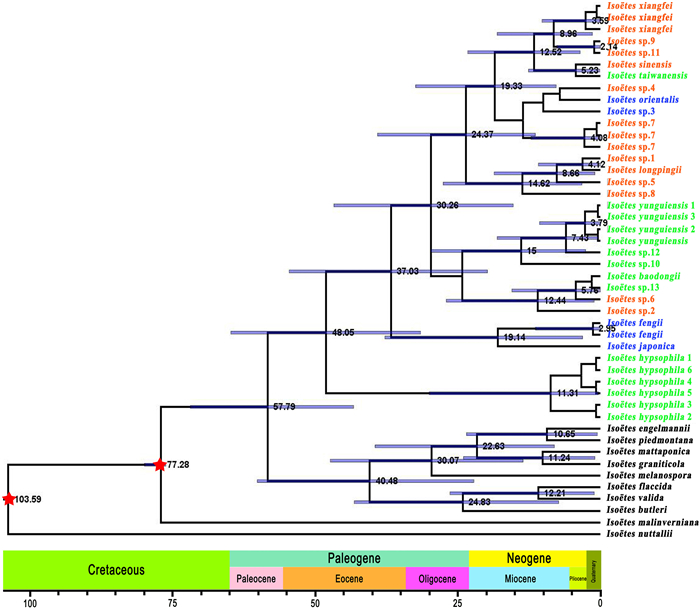
|
| Fig. 8 Chronogram showing divergence times estimated in BEAST based on plastome data. Blue bars represent 95% highest posterior density for the estimated mean dates. Nodes marked with red stars are calibration points. Colors represent ploidy level; green samples are diploid, orange samples are tetraploid, and blue samples are hexaploid. |
Our phylogenetic analysis results showed that the Chinese samples (not including I. japonica) formed a clade, largely consistent with the results of Choi et al. (2018). All the Isoëtes distributing in East Asia clustered a monophyletic clade together with samples from New Guinea and East Australia. Several clades received low support values and some taxa are resolved differently in the ML and BI analyses, but most clades are well supported especially at the first lineage of the two phylogenetic trees. These findings further indicate that our inferred phylogeny can serve as a reliable framework for exploration in the classification of the Chinese Isoëtes diploid–polyploid complex. The species diversity is much higher than we know and cryptic species in this genus are common in China. In our sampling we treated all samples (except for the type species from the original locality) as unknown species, thus, we can avoid preconceived identification of species. Samples used in this study have the widest coverage of Isoëtes and they can represent the taxa in China. The phylogenetic framework can be used to assess the species taxonomy and to reevaluate the delimitation of this family.
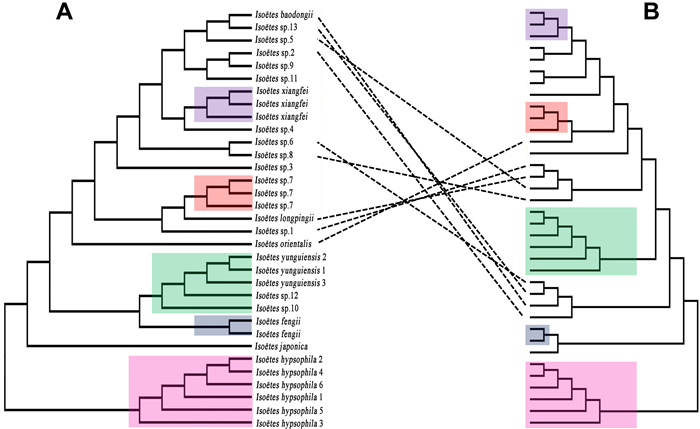
Historical events known as ancient hybridization (Peters et al., 2007) and paleopolyploidization (Barker et al., 2008) may have occurred before the existence of presently known Isoëtes species. This may be the reason why we got the chaotic phylogenetic tree, samples with different chromosome number are clustered together. When diploid samples were separated out to reconstructed phylogeny relationship (Fig. 9), we aquired almost the same topology as the original phylogeny tree employed with all the samples and mainly four clades were well supported of Chinese samples. As ancestor group, these diploids played important roles in the speciation of polyploid species in China. Of course, hybridization between diploids cannot be ignored either. Isoëtes sinensis had been known as formed by I. taiwanensis and I. yunguiensis (Liu et al., 2004; Taylor et al., 2004; Dai et al., 2020) but been queried by Kim et al. (2010), with new tetraploid (Shu et al., 2022) and diploid species (Lu et al., 2021) were discovered, our phylogenetic tree indicates that the speciation of this tetraploid should be reconsidered, I. baodongii may also be involved in the formation of tetraploid species including I. sinensis. Besides allopolyploid, there should be autopolyploids in this genus, the unique genetic structure of each sample in the genetic structure analysis may suggest this possibility. Hybridization, migration and isolation between diploids have led to their present genetic diversity and species diversity, all known and unknown diploids formed other polyploids by hybridization and polyploidization, so that all these samples present an intricate phylogenetic structure.
|
| Fig. 9 Phylogenetic trees based on diploid samples. |
Despite the advent and acceleration of the genomics area, defining what makes a species genetically and morphologically distinct remains a problem in many fields of study. Canonically, a speciation event is defined as when an individual organism (ⅰ) forms a monophyletic branch when reconstructing the phylogenetic tree (Maddison, 1997; Maddison and Lacey, 2006; Liu and Pearl, 2007), (ⅱ) presents a different ploidy (Troia et al., 2016) causing reproductive isolation from other species (Fontaneto et al., 2015; Fier et al., 2017), and (ⅲ) possesses a morphological feature markedly different from other species.
Previous studies of Isoëtes in China more or less ignored the ploidy of the samples collected from different places (Pang et al., 2003; Ye and Li, 2003; Chen et al., 2004; Taylor et al., 2004; Kang et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2008; Xie et al., 2019; Dai et al., 2020). Thus, nearly all the populations from Anhui, Hunan, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang have historically been treated as I. sinensis. The total number of chromosomes has been found to vary among species (Hickey, 1984; Bhu and Goswami, 1990; Liu et al., 2002), and the physical appearances of the mature megaspores were first emphasized by Edward (1922) and are still considered an important taxonomic feature (Schafran, 2019).
The hexaploid species was reported later but is by no means a simple group. Besides Isoëtes orientalis, a hexaploid species, two other hexaploid samples were collected from Taining County (Isoëtes sp.3) and Chuxiong City (I. fengii). Although Isoëtes sp.3 is a sister clade to I. orientalis in the plastome tree, its position is different in the phylogenetic tree based on SNPs (Figs. 6C and 10), and the megaspore morphological features presented dissimilarly to its sister clade, revealing that Isoëtes sp.3 should be considered a new species. Isoëtes fengii formed a solely distinct clade both in the phylogenetic tree based on plastome data and SNP data, confirming that it is a new species. The tetraploid I. sinensis is a historically complex species in China since its megaspore ornamentation can be divided into six types rather than just one (Table 2). The spore sizes of tetraploids often vary, the megaspore size of Isoëtes sp.9 is 400–460 μm (mean = 435) and is the largest, the megaspore size of I. longpingii is 310–350 μm (mean = 325) and is the smallest of the tetraploids. Moreover, all tetraploids appear in nine clades on the phylogenetic tree instead of forming one monophyletic clade (Figs. 4 and 5). By integrating spore morphology and molecular phylogenetic evidence, all tetraploids could be identified as at least six species. The SNP data supported this result; even though some samples' positions changed, they were still separated into five clades.
|
| Fig. 10 Phylogenetic tree based on SNPs (A) and plastome data (B) showed that some samples changed their position. Samples covered by the same color on both sides are identical. |
Our analysis found that diploids did not necessarily cluster into one clade. Some were embedded in different branches of the phylogenetic tree, whereas others clustered with other tetraploid or hexaploidy samples. Four diploids of Isoëtes yunguiensis, I. taiwanensis, I. hypsophila, and I. baodongii have been previously reported in China (Handel-Mazzetti, 1923; Devol, 1972; Wang et al., 2002; Li et al., 2019; Lu et al., 2021); however, here we identified a new diploid sample of Isoëtes sp.13. Morphologically, megaspores of Isoëtes sp.13 were smaller than those of other diploids and had different surface ornamentation (Table 2; Fig. 1). However, Isoëtes sp.13 had the same genetic structure and clustered with I. baodongii. Therefore, we treated Isoëtes sp.13 as I. baodongii. Although four I. yunguiensis samples from Guizhou clustered into one clade, they did not form a monophyletic clade unless together with two Yunnan samples (Isoëtes sp.10 and Isoëtes sp.12). Even more notably, the two Yunnan samples (Isoëtes sp.10 and Isoëtes sp.12) possessed different genetic structures. According to these results, it may be inaccurate to identify the quillworts distributed in Yunnan Province all as I. yunguiensis.
There was some conflict between the phylogenetic tree based on plastome data and the phylogenetic tree based on SNP data (Figs. 8 and 9), which supposed to conflicts between the phylogenies of plastome and nuclear data. These conflicts between different data sets may have been caused by incomplete lineage sorting and hybridization/introgression (Funk and Omland, 2003; Yi et al., 2015; Wei and Zhang, 2022). The network result does not present any net structure, which may be caused by the single parent (maternal) genes. The structure of the network is almost consistent with phylogenetic tree reconstructed based on plastome sequences, besides Isoëtes japonica connected the same mv with I. taiwanensis with so long genetic distance between them. Even though all the samples have short branch lengths on the phylogenetic tree, their haplotypes showed different genetic distances. This result suggests a high genetic diversity in these samples.
As more and more new distribution sites are found in China, we suspect that Isoëtes distribution in China should be universal. Just as Troia et al. (2016) reported, several regions in Asia appear to be without Isoëtes, mostly because of insufficient exploration rather than an unsuitable climate for growth. This region has a potentially high level of species diversity because cryptic species in these unexplored regions were easily ignored, especially for morphologically simple and similar plants inhabiting comparable environments. Few species within this region have been reported and identified because of insufficient field studies and a lack of appropriate research.
4.3. Cryptic speciation of quillworts in ChinaHistorically, we have defined and considered three main pathways for speciation—allopatric speciation, neighborhood speciation, and sympatric speciation. Congruently, isolation, differentiation, and genetic variation have been the main mechanisms we have identified that catalyze the formation of new species (Abbott et al., 2013). Recent studies have found that natural hybridization and polyploidy are the main mechanisms of speciation (Mallet, 2007; Rieseberg and Willis, 2007; Abbott et al., 2013). As Darwin stated in On the Origin of Species (Darwin, 1951), all species living in different places have a common ancestor, who migrated to different places and adapted to new geographical conditions, went through natural selection, accumulated mutations, and evolved into new species. Simpson (1961) challenged this viewpoint and postulated that almost any taxon can appear to be a center of origin if it steadily spreads in all directions until encountering impenetrable barriers and gradually begins to contract (often splitting into small disjunctive areas), creating new species. Geographical isolation can prevent gene exchange between populations, and long-term geographical isolation leads to genetic isolation among individual populations (Rieseberg and Willis, 2007).
Isoëtaceae are likely to have evolved from Annalepis (Pigg, 1992; Meng, 1998), with the family becoming widespread during the Triassic period because global sea-level movements enabled them to travel long distances with ocean currents. With the Tethys Sea flooding from west to east through Yunnan and Sichuan, Isoëtes expanded their range to the entire Yangtze River basin (Meng et al., 2000). Finally, their distribution range has gradually shrunk from east to west because of the periodic regression from east to west in the Yangtze region (Meng et al., 2000). Previous studies have identified. The Asian quillwort is thought to have originated from Annalepis in the Yangtze River Valley before the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, which occurred about 50 Ma (Eocene) (Harrison et al., 1992; An et al., 2001). This study estimates the node age showed that the Chinese samples and I. japonica were divided from the South American samples around 57.79 Ma (Paleocene) before I. hypsophila occurred. This period may be when the Isoëtes species originated in East Asia. The uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau resulted in western China being higher than eastern China, and the Yangtze River flowed from higher regions to lower regions; thus, the spread of Isoëtes species appeared to flow along with water to low elevation regions. Plants inhabiting high-elevation areas are subjected to low temperatures and high-intensity ultraviolet rays, which create species variants. For example, the expanded IR region of I. hypsophila resulted in a longer chloroplast genome with longer non-coding regions than other related species.
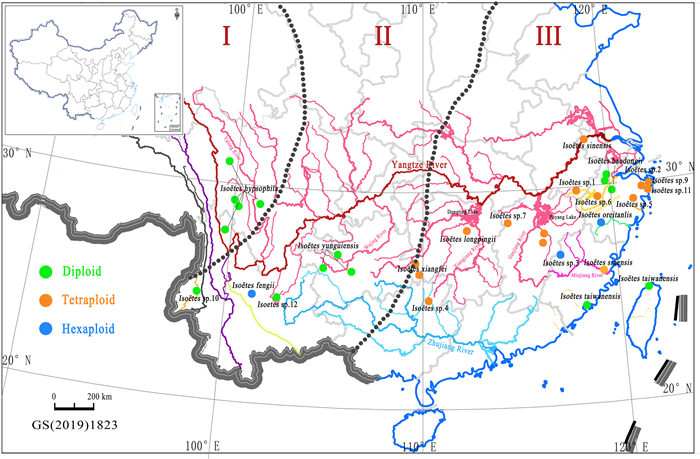
4.4. River system isolation promoted quillworts speciationWith the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, a change in topography could split a continuous water system into isolated systems, which limited gene flow among populations (Liu et al., 2004). When mapping the sites of Isoëtes distribution in China to the water system, each species sample corresponded to a independent water system mainly concentrated in the Yangtze River basin (Fig. 11). Water flow is the primary mode of plant dispersal for Isoëtes (Gentili et al., 2010; Troia et al., 2016) because their sporophylls can be carried by flowing water. This means the species dispersal occurs from higher to lower elevations in a single direction unless other media help to spread the sporophylls. Liu et al. (2004) reported that when isolated spores from populations located in high elevation regions or the headstreams of mountains came together in low elevation regions via the downstream movement of water, there would be a greater opportunity for speciation in low elevation regions. On the upon points, we think that when a new species occurs in a low elevation area or lower reaches of the river, it will be difficult found in a high elevation area or upper reaches of the river. Consequently, polyploid species occurring in Hunan, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Zhejiang, Anhui, and Jiangsu cannot be found in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Almost all the samples in this study grown in the upper reaches of a river or near the end of tributaries, but it's difficult to find them in the downstream. We observed that these quillworts inhabited locations with gently flowing water so they could not be washed away, and these locations with slow-moving water also facilitated reproduction.
|
| Fig. 11 Three types of terrain in China and river systems along and to the south of the Yangtze River. I–III represents the three terrain steps. |
The distribution of species with different ploidy is affected by the geographical environment. For Isoëtes, diploids might have a greater tolerance for environmental extremes than polyploids (Liu et al., 2004); therefore, we can find diploids in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, where they have stronger ultraviolet rays and a lower temperature. However, polyploids could be more competitive within their geographical range (Liu et al., 2004), which may be why we find polyploid species in almost all areas of low elevation along the Yangtze River. It appears that with the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, sporophylls of diploids were swept away by floods from high elevation areas, aggregating in low elevation areas. However, it is difficult to explain the occurrence of hexaploid I. fengii found in Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and diploid I. baodongii inhabiting low elevation areas. Isoëtes fengii and I. japonica formed a monophyletic clade, which was before I. yunguiensis and I. taiwanensis, suggesting that I. yunguiensis was not involved in the formation of I. fengii, and that I. hypsophila should be its mother. As I. fengii is a hexaploid species, an unknown tetraploid species should be involved in its speciation. At low elevation area, Zhejiang Province may be a central area for the speciation of quillworts living in the third terrain step geographically, where the speciation of tetraploids and hexaploids is related to the diploids, such as I. taiwanensis and I. baodongii. With this in mind, future studies are needed to explore these notable knowledge gaps.
4.5. Disappearing cryptic species calls for a new biodiversity conservation strategyCryptic species are at great risk of extinction, with several cryptic species reported extinct each year. Cryptic species, whose prevalence impairs biodiversity estimations, often challenge taxonomists tasked with their identification. Cryptic species seems common in fern taxa, in the last two decades, many cryptic species have been reported, such as Aspleniaceae (Jiang et al., 2011; Xu et al., 2019a, 2019b, 2022), Hypodematiaceae (Li et al., 2018), and Dicranopteris (Wei et al., 2021). Especially some endangered groups of quillworts (Pereira et al., 2019b; Schafran, 2019; Lu et al., 2021; Shu et al., 2022), Ceratopteris (Zhang et al., 2020b; Yu et al., 2022), Ottelia spp. (Ito et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). However, cryptic species substantially add to our overall understanding of biodiversity, and, thus, require increased conservation efforts (Krug et al., 2013; Nygren, 2014; Pante et al., 2015; Struck et al., 2018). Because dispersal and reproduction in Isoëtes plants depend on water (Gentili et al., 2010; Troia et al., 2016), human activities that lead to poor water quality, habitat loss, and invasion by exotic species have increased the number of Isoëtes species listed as threatened worldwide (Chen et al., 2005, 2008; Kang et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2008; Gentili et al., 2010). Furthermore, human activities have decreased the distribution ranges and sizes of Isoëtes populations in China, and have led to the disappearance of some Isoëtes species from their known habitat locations (e.g., I. sinensis, I. yunguiensis, I. longpingii, and unnamed species Isoëtes sp. 1 and 12). Recent research has also predicted that human activities will continue to decrease potential suitable habitat for Isoëtes plant species (Yang et al., 2022).
Extinction is inevitable, but present extinction rates are exceptionally high because of anthropogenic activities (Pimm et al., 2014). It has been posited that approximately 1 million out of 8.7 million species are thought to be under threat of extinction (Tollefson, 2019). This number is still considered an underestimation because it is based on extinction risk estimates for all known species and does not consider whether undiscovered species may have higher extinction risks than species that have already been described (Liu et al., 2022). Among the anthropogenic changes on earth, habitat conversion represents the leading cause of species extinction, and agricultural activities are the drivers of the destruction of natural environments (Gonalves-Souza et al., 2020). According to the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, 1 in 9 species are threatened by extinction (Tollefson, 2019). Additionally, the global warming crisis has led to increasing biodiversity concerns, and some studies suggest that 12% of species face extinction (Malcolm et al., 2010). Other studies estimate that 7–24% of plant species face extinction-level events (Vuuren et al., 2006).
How do we reduce biodiversity loss and conserve wildlife? These are significant challenges humanity faces that require global participation. Current conservation efforts often focus on species discovered centuries ago or species identified as having significant economic value, excluding newly described and cryptic species. Many unknown, cryptic species become extinct before they are even discovered (Scheffers et al., 2012; Lees and Pimm, 2015). The Chinese government is exploring a set of feasible plans for the protection of cryptic species (40 individual taxa), including Huperzia, Ceratopteris, Cyatheaceae, Angiopteris, Cycas, Podocarpus, Amentotaxus, and Taxus, in which all species, known or unknown, have been listed in the checklist of nationally protected plants. Although the number of protected plants falls short of recommendations of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)—at least 10% of species in each ecological area will be protected (Coates, 2016), contributing to global biodiversity conservation. It is easier and more effective to protect a taxonomic group than just one species, particularly for taxa that include cryptic species. Wildlife conservation should be a long-term and continuous process, requiring the participation of all countries to reduce the global extinction rate and increase biodiversity conservation efforts.
AcknowledgmentsWe want to thank Jian-Ying Xiang (Southwest Forestry University), Jian-Yun Wang (Baoshan University), Xue-Liang Hou (Xiamen University), and Shi-Wei Yao (Zhongshan Botanical Garden) for providing Isoëtes materials. We would also like to thank Wen Shao (Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden) and Guo-Hua Zhao (Fairy Lake Botanical Garden) for their help scanning spores. We also would like to thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com) for linguistic assistance during manuscript preparation. This study was supported by the Key Laboratory of National Forestry and Grassland Administration for Orchid Conservation and Utilization (grant number OC202103), the Harbin Normal University Postgraduate Innovation Project (grant number HSDBSCX2021-01), the National Natural Science Foundation of China General Projects (grant number 32170216), and the Hangzhou Science and Technology Development Project (grant number 20201203B113).
Authors contributions
Yu-Feng Gu: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Wrote the original manuscript draft. Jiang-Ping Shu: Methodology, Formal analysis, Wrote the original manuscript draft. Yi-Jun Lu and Hui Shen: Investigation, Funding acquisition. Wen Shao: Scanning spores. Yan Zhou and Qi-Meng Sun: Investigation, Resources. Jian-Bing Chen, Bao-Dong Liu, and Yue-Hong Yan: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Data curation.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbott, R., Albach, D., Ansell, S., et al., 2013. Hybridization and speciation. J. Evol. Biol., 26: 229-246. DOI:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2012.02599.x |
Alexander, D.H., Lange, K., 2011. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinformatics, 12: 1-6. DOI:10.1186/1471-2105-12-1 |
An, Z.S., Kutzbach, J.E., Prell, W.L., et al., 2001. Evolution of Asian monsoon and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature, 411: 62-66. DOI:10.4319/lo.2001.46.1.0062 |
Andrew, R., 2018. FigTree version 1.4.2: tree figure drawing tool. Available from http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree.
|
Bandelt, H.J., Dress, A.W., 1992. Split decomposition: a new and useful approach to phylogenetic analysis of distance data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 1: 242-252. DOI:10.1016/1055-7903(92)90021-8 |
Barker, M.S., Kane, N.C., Matvienko, M., et al., 2008. Multiple paleopolyploidizations during the evolution of the Compositae reveal parallel patterns of duplicate gene retention after millions of years. Mol. Biol. Evol., 25: 2445-2455. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msn187 |
Barrett, C.F., Baker, W.J., Comer, J.R., et al., 2016. Plastid genomes reveal support for deep phylogenetic relationships and extensive rate variation among palms and other commelinid monocots. New Phytol., 209: 855-870. DOI:10.1111/nph.13617 |
Bhu, I., Goswami, H.K., 1990. A new line of chromosomal evolution in Isoëtes. Bionature, 10: 45-53. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288427866_A_new_line_of_chromosomal_evolution_in_Isoetes. |
Bickford, D., Lohman, D.J., Sodhi, N.S., et al., 2007. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol., 22: 148-155. DOI:10.1016/j.tree.2006.11.004 |
Bouckaert, R., Vaughan, T.G., Barido-Sottani, J., et al., 2019. Beast 2.5: an advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol., 8: e1006650. DOI:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006650 |
Bravo, G.A., Remsen, J.V., Brumfield, R.T., 2015. Adaptive processes drive ecomorphological convergent evolution in antwrens (Thamnophilidae). Evolution, 68: 2757-2774. |
Chen, J.M., Liu, F., Gituru, W.R., et al., 2008. Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the Chinese endemic alpine quillwort Isoëtes hypsophila Hand.-Mazz. (Isoëtaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci., 169: 792-798. DOI:10.1086/588065 |
Chen, J.M., Liu, X., Wang, Q.F., 2005. Genetic diversity in Isoëtes yunguiensis, a rare and endangered endemic fern in China. J. Wuhan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.), 51: 767-770. DOI:10.1038/sj.leu.2403688 |
Chen, J.M., Wang, J.Y., Liu, X., et al., 2004. RAPD analysis for genetic diversity of Isoëtes sinensis. Biodivers. Sci., 12: 348-353. DOI:10.17520/biods.2004042 |
Choi, H.K., Jung, J., Na, H.R., et al., 2018. Molecular phylogeny and the biogeographic origin of East Asian Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae). Korean J. Plant Taxon., 48: 249-259. DOI:10.11110/kjpt.2018.48.4.249 |
Coates, D., 2016. Strategic Plan for Biodiversity (2011-2020) and the Aichi Biodiversity Targets: the Wetland Book I: Structure and Function, management, and methods, pp. 1-7.
|
Cúneo, R., 2009. Paleobotany: the biology and evolution of fossil plants. Ameghiniana, 46. |
Dai, X.K., Li, X., Huang, Y.Q., et al., 2020. The speciation and adaptation of the polyploids: a case study of the Chinese Isoëtes L. diploid-polyploid complex. BMC Evol. Biol., 20: 1-13. DOI:10.1155/2020/2387823 |
Danecek, P., Auton, A., Abecasis, G., et al., 2011. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics, 27: 2156-2158. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330 |
Darwin, C., 1951. On the Origin of Species, sixth ed.
|
De, Q.K., 2007. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol., 56: 879-886. DOI:10.1080/10635150701701083 |
Devol, C.E., 1972. Isoëtes found on taiwan. Taiwania, 17: 1-7. |
Dirzo, R., Raven, P.H., 2003. Global state of biodiversity and loss. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour., 28: 137-167. DOI:10.1146/annurev.energy.28.050302.105532 |
Feulner, P.G.D., Kirschbaum, F., Schugardt, C., et al., 2006. Electrophysiological and molecular genetic evidence for sympatrically occurring cryptic species in African weakly electric fishes (Teleostei: Mormyridae: Campylomormyrus). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 39: 198-208. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.09.008 |
Fier, C., Robinson, C.T., Malard, F., 2017. Cryptic species as a window into the paradigm shift of the species concept. Mol. Ecol., 27: 613-635. |
Fontaneto, D., Flot, J.F.O., Tang, C.Q., 2015. Guidelines for DNA taxonomy, with a focus on the meiofauna. Mar. Biodivers., 45: 433-451. DOI:10.1007/s12526-015-0319-7 |
Foster, C.S.P., Henwood, M.J., Simon, H.Y.W., 2018. Plastome sequences and exploration of tree-space help to resolve the phylogeny of riceflowers (Thymelaeaceae: Pimelea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 127: 156-167. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2018.05.018 |
Funk, D.J., Omland, K.E., 2003. Species-Level paraphyly and polyphyly: frequency, causes, and consequences, with insights from animal mitochondrial DNA. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol., 34: 397-423. DOI:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132421 |
Gentili, R., Abeli, T., Rossi, G., et al., 2010. Population structure and genetic diversity of the threatened quillwort Isoëtes malinverniana and implication for conservation. Aquat. Bot., 93: 147-152. DOI:10.1016/j.aquabot.2010.05.003 |
Gerard, T., Jose, C., 2007. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol., 56: 564-577. DOI:10.1080/10635150701472164 |
Gifford, E.M., Foster, A.S., 1989. Morphology and Evolution of Vascular Plants, third ed. W. H. Freman & Company, New York.
|
Givnish, T.J., Ames, M., McNeal, J.R., et al., 2010. Assembling the tree of the monocotyledons: plastome sequence phylogeny and evolution of Poales. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 97: 584-616. DOI:10.3417/2010023 |
Givnish, T.J., Spalink, D., Ames, M., et al., 2015. Orchid phylogenomics and multiple drivers of their extraordinary diversification. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci., 282: 20151553. DOI:10.1098/rspb.2015.1553 |
Gonalves-Souza, D., Verburg, P.H., Dobrovolski, R., 2020. Habitat loss, extinction predictability and conservation efforts in the terrestrial ecoregions. Biol. Conserv., 246: 108579. DOI:10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108579 |
Grundt, H.H., Kjolner, S., Borgen, L., et al., 2006. High biological species diversity in the arctic flora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 103: 972-975. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0510270103 |
Handel-Mazzetti, H., 1923. Isoëtes hypsophila Hand.-Mazz. Akad. Wiss. Wien, 13: 95. |
Harrison, T.M., Copeland, P., Kidd, W., et al., 1992. Raising tibet. Science, 255: 1663-1670. DOI:10.1126/science.255.5052.1663 |
Hebert, P.D.N., Penton, E.H., Burns, J.M., et al., 2004. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 101: 14812-14817. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0406166101 |
Hickey, R.J., 1984. Chromosome numbers of neotropical Isoëtes. Am. Fern J., 74: 9-13. DOI:10.2307/1547103 |
Hickey, R.J., 1986. Isoëtes megaspore surface morphology: nomenclature, variation, and systematic importance. Am. Fern J., 76: 1-16. DOI:10.2307/1547394 |
Hinojosa, J.C., Koubínová, D., Szenteczki, M.A., et al., 2019. A mirage of cryptic species: genomics uncover striking mitonuclear discordance in the butterfly Thymelicus sylvestris. Mol. Ecol., 28: 3857-3868. DOI:10.1111/mec.15153 |
Hollingsworth, P.M., Li, D.Z., Michelle, v.d.B., et al., 2016. Telling plant species apart with DNA: from barcodes to genomes. Philos. T. R. Soc. B, 371: 20150338. DOI:10.1098/rstb.2015.0338 |
Holmes, W.C., Rushing, A.E., Singhurst, J.R., 2005. Taxonomy and identification of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) in Texas based on megaspore features. Lundenllia, 8: 1-6. DOI:10.25224/1097-993x-8.1.1 |
Hoot, S.B., Taylor, W.C., 2001. The utility of nuclear ITS, a LEAFY homolog intron, and chloroplast atpB-rbcL spacer region data in phylogenetic analyses and species delimitation in Isoëtes. Am. Fern J., 91: 166-177. DOI:10.1640/0002-8444(2001)091[0166:TUONIA]2.0.CO;2 |
Ito, Y., Tanaka, N., Barfod, A.S., et al., 2019. Molecular phylogenetic species delimitation in the aquatic genus Ottelia (Hydrocharitaceae) reveals cryptic diversity within a widespread species. J. Plant Res., 132: 335-344. DOI:10.1007/s10265-019-01109-7 |
Jansen, R.K., Saski, C., Lee, S.B., et al., 2011. Complete plastid genome sequences of three Rosids (Castanea, Prunus, Theobroma): evidence for at least two independent transfers of rpl22 to the nucleus. Mol. Biol. Evol., 28: 835-847. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msq261 |
Jiang, R.H., Zhang, X.C., Liu, Y., 2011. Asplenium cornutissimum (Aspleniaceae), a new species from karst caves in Guangxi, China. Brittonia, 63: 83-86. DOI:10.1007/s12228-010-9139-z |
Jin, J.J., Yu, W.B., Yang, J., et al., 2020. GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol., 21: 1-31. DOI:10.1117/1.oe.59.1.016110 |
Joppa, L.N., Roberts, D.L., Pimm, S.L., 2011. How many species of flowering plants are there?. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci., 278: 554-559. DOI:10.1098/rspb.2010.1004 |
Julio, R., Albert, F.M., Carlos, S.-D.J., et al., 2017. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol., 34: 3299-3302. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msx248 |
Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B.Q., Wong, T.K.F., et al., 2017. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods, 14: 587-589. DOI:10.1038/nmeth.4285 |
Kang, M., Ye, Q.G., Huang, H.W., 2005. Genetic consequence of restricted habitat and population decline in endangered Isoëtes sinensis (Isoëtaceae). Ann. Bot., 96: 1265-1274. DOI:10.1093/aob/mci277 |
Karol, K.G., Arumuganathan, K., Boore, J.L., et al., 2010. Complete plastome sequences of Equisetum arvense and Isoëtes flaccida: implications for phylogeny and plastid genome evolution of early land plant lineages. BMC Evol. Biol., 10: 321. DOI:10.1186/1471-2148-10-321 |
Kim, C., Shin, H., Chang, Y.T., et al., 2010. Speciation pathway of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) in East Asia inferred from molecular phylogenetic relationships. Am. J. Bot., 97: 958-969. DOI:10.3732/ajb.0900162 |
Kim, C., Na, H.R., Choi, H.K., 2008. Genetic diversity and population structure of endangered Isoëtes coreana in South Korea based on RAPD analysis. Aquat. Bot., 89: 43-49. DOI:10.1016/j.aquabot.2008.02.004 |
Kim, C.K., Choi, H.K., 2016. Biogeography of North Pacific Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequence data. J. Plant Biol., 59: 386-396. DOI:10.1007/s12374-016-0123-3 |
Krug, P.J., Vendetti, J.E., Rodriguez, A.K., et al., 2013. Integrative species delimitation in photosynthetic sea slugs reveals twenty candidate species in three nominal taxa studied for drug discovery, plastid symbiosis or biological control. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 69: 1101-1119. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2013.07.009 |
Larsén, E., Wikström, N., Khodabandeh, A., et al., 2022. Phylogeny of Merlin's grass (Isoëtaceae): revealing an "Amborella syndrome" and the importance of geographic distribution for understanding current and historical diversity. BMC Ecol. Evol., 22: 1-17. DOI:10.1155/2022/9332922 |
Lees, A.C., Pimm, S.L., 2015. Species, extinct before we know them?. Curr. Biol., 25: R177-R180. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2014.12.017 |
Lellinger, D.B., Taylor, W.C., 1997. A classification of spore ornamentation in the pteridophyta. In: John, R.J. (Ed.), Holttum Memorial. Kew: Royal Botanical Garden, Volume London.
|
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., et al., 2009. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics, 25: 2078-2079. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352 |
Li, X., Huang, Y.Q., Dai, X.K., et al., 2019. Isoëtes shangrilaensis, a new species of Isoëtes from Hengduan mountain region of Shangri-la, Yunnan. Phytotaxa, 397: 65-73. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.397.1.6 |
Li, X.J., Li, J.X., Meng, F.Y., 2018. A new species of Hypodematium (Hypodematiaceae) from China. PhytoKeys, 92: 37-44. DOI:10.3897/phytokeys.92.21815 |
Li, X.W., Yang, F., Henry, R.J., et al., 2015. Plant DNA barcoding: from gene to genome. Biol. Rev., 90: 157-166. DOI:10.1111/brv.12104 |
Li, Z.Z., Ngarega, B.K., Lehtonen, S., et al., 2020. Cryptic diversity within the African aquatic plant Ottelia ulvifolia (Hydrocharitaceae) revealed by population genetic and phylogenetic analyses. J. Plant Res., 133: 1-9. DOI:10.1007/s10265-019-01155-1 |
Liu, H., Wang, Q.F., Taylor, W.C., 2005. Isoëtes orientalis (Isoëtaceae), a new hexaploid quillwort from China. Novon, 15: 164-167. |
Liu, J., Möller, M., Gao, L.M., et al., 2015. DNA barcoding for the discrimination of Eurasian yews (Taxus L., Taxaceae) and the discovery of cryptic species. Mol. Ecol. Resour., 11: 89-100. |
Liu, J.J., Slik, F., Zheng, S.L., et al., 2022. Undescribed species have higher extinction risk than known species. Conserv. Lett., 15: 1-8. |
Liu, L., Pearl, D.K., 2007. Species trees from gene trees: reconstructing Bayesian posterior distributions of a species phylogeny using estimated gene tree distributions. Syst. Biol., 56: 504-514. DOI:10.1080/10635150701429982 |
Liu, X., Gituru, W.R., Wang, Q.F., 2004. Distribution of basic diploid and polyploid species of Isoëtes in East Asia. J. Biogeogr., 31: 1239-1250. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2004.01115.x |
Liu, X., Liu, H., Wang, Q.F., 2008. Spore morphology of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) from China. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin., 46: 479-489. |
Liu, X., Wang, Y., Wang, Q.F., et al., 2002. Chromosome numbers of the Chinese Isoëtes and their taxonomical significance. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin., 40: 351-356. |
Lombard, L., Crous, P.W., Wingfield, B.D., et al., 2010. Multigene phylogeny and mating tests reveal three cryptic species related to Calonectria pauciramosa. Stud. Mycol., 66: 15-30. DOI:10.3114/sim.2010.66.02 |
Lu, J.M., Zhang, N., Du, X.Y., et al., 2015. Chloroplast phylogenomics resolves key relationships in ferns. J. Syst. Evol., 53: 448-457. DOI:10.1111/jse.12180 |
Lu, Y.J., Gu, Y.F., Yan, Y.H., 2021. Isoëtes baodongii (Isoëtaceae), a new basic diploid species of quillwort from China. Novon, 29: 206-210. DOI:10.3417/2021680 |
Maddison, W.P., 1997. Gene trees in species trees. Syst. Biol., 3: 523-536. |
Maddison, W.P., Lacey, K.L., 2006. Inferring phylogeny despite incomplete lineage sorting. Syst. Biol., 55: 21-30. DOI:10.1080/10635150500354928 |
Malcolm, J.R., Liu, C., Neilson, R.P., et al., 2010. Global warming and extinctions of endemic species from biodiversity hotspots. Conserv. Biol., 20: 538-548. |
Mallet, J., 2007. Hybrid speciation. Nature, 446: 279-283. DOI:10.1038/nature05706 |
May, R.M., 1988. How many species are there on earth?. Science, 241: 1441-1449. DOI:10.1126/science.241.4872.1441 |
May, R.M., 1990. How many species?. Philos. T. R. Soc. B, 330: 293-303. DOI:10.1098/rstb.1990.0200 |
Meng, F.S., 1998. Studies on Annalepis from middle triassic along the YangZi river and ITS bearing on the origin of Isoëtes. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 8: 89-95. |
Meng, F.S., Zhang, Z.L., Niu, Z.J., et al., 2000. Primitive Lycopsid Flora in the Yangtze Valley of China and Systematics and Evolution of Isoëtales. Hunan: Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha.
|
Moraolivo, A., Mendozaruiz, A., Martínezávalos, J.G., 2016. Isoëtes tamaulipana (Isoëtaceae), a new species from Mexico. Phytotaxa, 267: 113-120. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.267.2.3 |
Nguyen, L.T., Schmidt, H.A., Arndt, V.H., et al., 2015. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol., 32: 268-274. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msu300 |
Nie, Y., Foster, C.S., Zhu, T., et al., 2020. Accounting for uncertainty in the evolutionary timescale of green plants through clock-partitioning and fossil calibration strategies. Syst. Biol., 69: 1-16. DOI:10.1093/sysbio/syz032 |
Nygren, A., 2014. Cryptic polychaete diversity: a review. Zool. Scripta, 43: 172-183. DOI:10.1111/zsc.12044 |
Palmer, T.C., 1927. A Chinese Isoëtes-I. sinensis. Am. Fern J., 7: 111-113. DOI:10.2307/1544551 |
Pang, X.A., Wang, Q.F., Robert, G.W., et al., 2003. A preliminary study of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) in the endangered aquatic quillwort Isoëtes sinensis Palmer in China. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci., 8: 455-458. DOI:10.1007/BF02907231 |
Pante, E., Puillandre, N., Viricel, A., et al., 2015. Species are hypotheses: avoid connectivity assessments based on pillars of sand. Mol. Ecol., 24: 525-544. DOI:10.1111/mec.13048 |
Pereira, J.B.D.S., Salino, A., Arrdua, A., et al., 2016. Two new species of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) from northern Brazil. Phytotaxa, 272: 141-148. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.272.2.5 |
Pereira, J.B.S., Giulietti, A.M., Pires, E.S., et al., 2021a. Chloroplast genomes of key species shed light on the evolution of the ancient genus Isoëtes. J. Syst. Evol., 59: 421-441. |
Pereira, J.B.S., Giulietti, A.M., Prado, J., et al., 2021b. Plastome-based phylogenomics elucidate relationships in rare Isoëtes species groups from the Neotropics. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 161: 107177. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2021.107177 |
Pereira, J.B.S., Guimaraes, J.T.F., Watanabe, M.T.C., 2019a. Isoëtes dubsii and Isoëtes santacruzensis, two new species from lowland areas in South America. PhytoKeys, 131: 57-67. DOI:10.3897/phytokeys.131.36983 |
Pereira, J.B.S., Labiak, P.H., Thomas, S., et al., 2019b. Nuclear multi-locus phylogenetic inferences of polyploid Isoëtes species (Isoëtaceae) suggest several unknown diploid progenitors and a new polyploid species from South America. Bot. J. Linn. Soc., 189: 6-22. DOI:10.1093/botlinnean/boy068 |
Pereira, J.B.S., Stützel, T., Schulz, C., 2017. Isoëtes nana, a new species from the coastal mountains of southeastern Brazil. PhytoKeys, 89: 91-105. DOI:10.3897/phytokeys.89.20171 |
Peter, T., Douady, C.J., Cene, F., et al., 2009. A molecular test for cryptic diversity in ground water: how large are the ranges of macro-stygobionts?. Freshw. Biol., 54: 727-744. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01877.x |
Peters, J.L., Zhuravlev, Y., Fefelov, I., et al., 2007. Nuclear loci and coalescent methods suppot ancient hybridization as cause of mitochondrial paraphyly between gadwall and falcated duck (Anas spp.). Evolution, 61: 1992-2006. DOI:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00149.x |
Pfeiffer, N.E., 1922. Monograph on the Isoëtaceae. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 9: 79-233. DOI:10.2307/2990000 |
Pigg, K.B., 1992. Evolution of isoetalean lycopsids. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 79: 589-612. DOI:10.2307/2399754 |
Pigg, K.B., 2001. Isoetalean lycopsid evolution: from the Devonian to the present. Am. Fern J., 91: 99-114. DOI:10.1640/0002-8444(2001)091[0099:ILEFTD]2.0.CO;2 |
Pillon, Y., Hopkins, H., Munzinger, J., et al., 2010. Cryptic species, gene recombination and hybridization in the genus Spiraeanthemum (Cunoniaceae) from New Caledonia. Bot. J. Linn. Soc., 161: 137-152. |
Pimm, S.L., Jenkins, C.N., Abell, R., et al., 2014. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344: 1246752. DOI:10.1126/science.1246752 |
Prance, G.T., Beentje, H., Dransfield, J., et al., 2000. The Tropical flora remains under collected. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 87: 67-71. DOI:10.2307/2666209 |
Ranker, T.A., 1993. Spores of the Pteridophyta: surface, wall structure, and diversity based on electron microscope studies. Syst. Bot., 18: 377. DOI:10.2307/2419410 |
Rieseberg, L.H., Willis, J.H., 2007. Plant speciation. Science, 317: 910-914. DOI:10.1126/science.1137729 |
Romero, M.I., Real, C., 2015. A morphometric study of three closely related taxa in the European Isoëtes velata complex. Bot. J. Linn. Soc., 148: 459-464. |
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., et al., 2012. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol., 61: 539-542. DOI:10.1093/sysbio/sys029 |
Ross, T.G., Barrett, C.F., Gomez, M.S., et al., 2016. Plastid phylogenomics and molecular evolution of Alismatales. Cladistics, 32: 160-178. DOI:10.1111/cla.12133 |
Ruhfel, B.R., Gitzendanner, M.A., Soltis, P.S., et al., 2014. From algae to angiosperms–inferring the phylogeny of green plants (Viridiplantae) from 360 plastid genomes. BMC Evol. Biol., 14: 23. DOI:10.1186/1471-2148-14-23 |
Sáez, A.G., Lozano, E., 2005. Body doubles. Nature, 433: 111. DOI:10.1038/433111a |
Santos, M.P., Araujo, J.V.S.R., Lopes, A.V.S.A., et al., 2020. The genetic diversity and population structure of two endemic Amazonian quillwort (Isoëtes L.) species. PeerJ, 8: e10274. DOI:10.7717/peerj.10274 |
Schafran, P.W., 2019. Molecular systematics of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) in Eastern North America. Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Dissertation, Biological Sciences. Old Dominion University.
|
Schafran, P.W., Leonard, S.W., Bray, R.D., et al., 2016. Isoëtes mississippiensis: a new quillwort from Mississippi, USA. PhytoKeys, 74: 97-106. DOI:10.3897/phytokeys.74.10380 |
Schafran, P.W., Zimmer, E.A., Taylor, W.C., et al., 2018. A whole chloroplast genome phylogeny of diploid species of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae, Lycopodiophyta) in the Southeastern United States. Castanea, 83: 224-235. DOI:10.2179/17-132 |
Scheffers, B.R., Joppa, L.N., Pimm, S.L., et al., 2012. What we know and don't know about earth's missing biodiversity. Trends Ecol. Evol., 27: 501-510. DOI:10.1016/j.tree.2012.05.008 |
Shang, H., Xue, Z.Q., Gu, Y.F., et al., 2020. Revision of the fern genus Didymochlaena (didymochlaenaceae) from Madagascar. Phytotaxa, 459: 252-264. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.459.4.1 |
Shu, J.P., Gu, Y.F., Ou, Z.G., et al., 2022. Two new tetraploid quillwort species, Isoëtes longpingii and I. xiangfei from China. Guihaia, 42: 1623-1631. |
Simpson, G.G., 1961. Principles of Animal Taxonomy. New York: Columbia University Press.
|
Smolders, A.J.P., Lucassen, E.C.H.R.T., Roelofs, J.G.M., 2002. The isoetid environment: biogeochemistry and threats. Aquat. Bot., 73: 325-350. DOI:10.1016/S0304-3770(02)00029-3 |
Struck, T.H., Feder, J.L., Bendiksby, M., et al., 2018. Finding evolutionary processes hidden in cryptic species. Trends Ecol. Evol., 33: 153. DOI:10.1016/j.tree.2017.11.007 |
Suissa, J.S., Kinosian, S.P., Schafran, P.W., et al., 2020. Revealing the evolutionary history of a reticulate polyploid complex in the genus Isoëtes. bioRxiv. DOI:10.1101/2022.11.11.516104 |
Takamiya, M., Watanabe, M., Ono, K., 1994. Biosystematic studies on the genus Isoëtes in Japan I. Variations of the somatic chromosome numbers. J. Plant Res., 107: 289-297. DOI:10.1007/BF02344257 |
Taylor, W.C., Hickey, R.J., 1992. Habitat, evolution, and speciation in Isoëtes. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 79: 613-622. DOI:10.2307/2399755 |
Taylor, W.C., Lekschas, A.R., Wang, Q.F., et al., 2004. Phylogenetic relationships of Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) in China as revealed by nucleotide sequences of the nuclear ribosomal ITS region and the second Intron of a LEAFY Homolog. Am. Fern J., 94: 196-205. DOI:10.1640/0002-8444(2004)094[0196:PROIII]2.0.CO;2 |
Thompson, M.S.A., Couce, E., Webb, T.J., et al., 2020. What's hot and what's not: making sense of biodiversity 'hotspots. Global Change Biol., 27: 521-535. |
Tollefson, J., 2019. Humans are driving one million species to extinction. Nature, 569: 171-172. DOI:10.1038/d41586-019-01448-4 |
Troia, A., Pereira, J.B., Kim, C., et al., 2016. The genus Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae): a provisional checklist of the accepted and unresolved taxa. Phytotaxa, 277: 101-145. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.277.2.1 |
Vrijenhoek, R.C., Schutz, S.J., Gustafson, R.G., et al., 1994. Cryptic species of deep-sea clams (Mollusca: Bivalvia: vesicomyidae) from hydrothermal vent and cold-water seep environments. Deep-Sea Res. Pt. I, 41: 1171-1189. DOI:10.1016/0967-0637(94)90039-6 |
Vuuren, D.P.v., Sala, O.E., Pereira, H.M., 2006. The future of vascular plant diversity under four global scenarios. Ecol. Soc., 11: 3213-3217. |
Wang, H., Dai, J., Chen, Z., et al., 2022. Selaginella orientali-chinensis, a new resurrection spikemoss species from southeastern China based on morphological and molecular evidences. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni, 61: 57-64. DOI:10.1596/978-1-4648-1853-0_bm |
Wang, J.Y., Gituru, R.W., Wang, Q.F., 2006. Ecology and conservation of the endangered quillwort Isoëtes sinensis in China. Egypt. J. Nat. Hist., 39: 4069-4079. DOI:10.1080/00222930500505052 |
Wang, Q.F., Liu, X., Taylor, W.C., et al., 2002. Isoëtes yunguiensis (Isoëtaceae), a new basic diploid quillwort from China. Novon, 12: 587-591. DOI:10.2307/3393143 |
Wang, Q.X., Dai, X.L., 2010. Spores of Polypodiales (Filicales) from China. Beijing: Science Press.
|
Wang, Q.X., Yu, J., 2003. Classification of spore ornamentation in Filicales under SEM. Acta Bot. Yunnan., 25: 313-320. |
Watanabe, M., Takamiya, M., Matsusaka, T., et al., 1996. Biosystematic studies on the genus Isoëtes (Isoëtaceae) in Japan. Ⅲ. Variability within qualitative and quantitative morphology of spores. J. Plant Res., 109: 281-296. DOI:10.1007/BF02344475 |
Wei, R., Yan, Y.H., Harris, A.J., et al., 2017. Plastid phylogenomics resolve deep relationships among eupolypod Ⅱ ferns with rapid radiation and rate heterogeneity. Genome Biol. Evol., 9: 1646-1657. DOI:10.1093/gbe/evx107 |
Wei, R., Zhang, X.C., 2019. Phylogeny of Diplazium (Athyriaceae) revisited: resolving the backbone relationships based on plastid genomes and phylogenetic tree space analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 143: 106699. |
Wei, R., Zhang, X.C., 2022. A revised subfamilial classification of Polypodiaceae based on plastome, nuclear ribosomal, and morphological evidence. Taxon, 71: 288-306. DOI:10.1002/tax.12658 |
Wei, Z.Y., Xia, Z.Q., Shu, J.P., et al., 2021. Phylogeny and taxonomy on cryptic species of forked ferns of Asia. Front. Plant Sci., 12: 748562. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2021.748562 |
Welch, A.J., Collins, K., Ratan, A., et al., 2016. The quest to resolve recent radiations: plastid phylogenomics of extinct and endangered Hawaiian endemic mints (Lamiaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 99: 16-33. |
Wick, R.R., Schultz, M.B., Justin, Z., et al., 2015. Bandage: interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 31: 3350-3352. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv383 |
Winker, K., 2005. Sibling species were first recognized by William Derham (1718). Auk, 122: 706-707. |
Wood, D., Besnard, G., Beerling, D.J., et al., 2020. Phylogenomics indicates the "living fossil" Isoëtes diversified in the Cenozoic. PLoS One, 15: e0227525. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0227525 |
Xie, Y.C., Cheng, H.S., Chen, Y., et al., 2019. Complete chloroplast genome of Isoëtes sinensis, an endemic fern in China. Mitochondrial DNA B, 4: 3276-3277. DOI:10.1080/23802359.2019.1666687 |
Xu, K.W., Lin, C.X., Guo, J.Q., et al., 2022. Asplenium danxiaense sp. nov. (Aspleniaceae, Aspleniineae), a new tetraploid fern species from Guangdong, China, based on morphological and molecular data. Eur. J. Taxon., 798: 162-173. DOI:10.5852/ejt.2022.798.1679 |
Xu, K.W., Lorence, D., Wood, K.R., et al., 2019a. A revision of the Hymenasplenium unilaterale subclade (Aspleniaceae; Pteridophyta) with the description of nine new species. Phytotaxa, 419: 1-27. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.419.1.1 |
Xu, K.W., Chen, C.W., Kamau, P., et al., 2019b. Four new species of the fern genus Hymenasplenium (Aspleniaceae) from africa and Asia. Phytotaxa, 416: 34-42. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.416.1.4 |
Yang, J., Huang, Y., Jiang, X., et al., 2022. Potential geographical distribution of the endangered plant Isoëtes under human activities using MaxEnt and GARP. Global Ecol. Conser., 38: e02186. |
Ye, Q.G., Li, J.Q., 2003. Distribution status and causation of endangerment of Isoëtes sinensis palmer in Zhejiang Province. J. Wuhan Bot. Res., 21: 216-220. |
Yi, T.S., Jin, G.H., Wen, J., 2015. Chloroplast capture and intra- and inter-continental biogeographic diversification in the Asian - new World disjunct plant genus Osmorhiza (Apiaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 85: 10-21. |
Yu, J.H., Zhang, R., Liu, Q.L., et al., 2022. Ceratopteris chunii and Ceratopteris chingii (Pteridaceae), two new diploid species from China, based on morphological, cytological, and molecular data. Plant Divers., 44: 300-307. |
Zhang, D., Gao, F., Jakovli, I., et al., 2020a. PhyloSuite: an integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour., 20: 348-355. DOI:10.1111/1755-0998.13096 |
Zhang, R., Wang, F.G., Zhang, J., et al., 2019. Dating whole genome duplication in Ceratopteris thalictroides and potential adaptive values of retained gene duplicates. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20: 1926. DOI:10.3390/ijms20081926 |
Zhang, R., Yu, J.H., Shao, W., et al., 2020b. Ceratopteris shingii, a new species of Ceratopteris with creeping rhizomes from Hainan, China. Phytotaxa, 449: 23-30. DOI:10.11646/phytotaxa.449.1.3 |



