b. Kunming College of Life Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan, 650201, China
Shibataea is a small genus of the temperate bamboo tribe Arundinarieae (Poaceae: Bambusoideae), members of which are shrubby and usually cultivated as ornamentals in gardens. All members of Shibataea, which comprises seven species and two varieties, are naturally distributed in southeastern China, and one species has been introduced to southwestern Japan (Li et al., 2006). Although Shibataea has been recognized as a distinct genus in its own subtribe, Shibatataeinae, in many traditional classification systems of bamboos (Soderstrom and Ellis, 1987; Dransfield and Widjaja, 1995; Keng and Wang, 1996; Li, 1997; Ohrnberger, 1999), little is known about its phylogenetic position and interspecific relationships.
Molecular analyses of the phylogenetic placement of Shibataea have yielded conflicting results. Studies based on plastid genes have supported the monophyly of Shibataea, and formed clade IV (Shibataea clade) with Gelidocalamus, Ferrocalamus, Sasa, and Indocalamus (Triplett and Clark, 2010; Zeng et al., 2010; Attigala et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2017). However, the sampling of Shibataea in these studies was sparse and several relationships among this genus were poorly resolved. A study that used a single nuclear gene, GBSSI, recovered Shibataea as monophyletic, but clade IV collapsed; furthermore, although poorly supported, this study suggests that Shibataea is closely related to Phyllostachys (Zhang et al., 2012), the most economically important genus of bamboos in China. Recently, the close relationship between Shibataea and Phyllostachys was strongly supported by restriction-site associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) data employed to infer phylogenetic relationships for Fargesia, Yushania and their close relatives in the temperate bamboos (Wang et al., 2017). However, this study only sampled one Shibataea species. To the best of our knowledge, no phylogenomic studies have yet to focus on the genus Shibataea, and the interspecific relationships within Shibataea remain unclear.
One potential approach to improving phylogenetic reconstructions is the use of the double digest restriction-site associated DNA (ddRAD-seq) sequencing protocol. ddRAD-seq samples thousands of genomic regions across the nuclear genome for phylogenetic inference (Baird et al., 2008; Peterson et al., 2012). In addition, genome skimming can be used to characterize complete plastid genomes. These approaches generate high-efficiency data sets that can reveal the underlying reticulate pattern of evolution (Vargas et al., 2017).
The aim of this study is to resolve the phylogenetic placement and interspecific relationships of Shibataea. For this purpose, we performed phylogenetic analysis of all seven species and one variety of Shibataea using ddRAD-seq data and plastid genomes generated from genome skimming. We were also able to compare the genealogies generated from nuclear ddRAD and plastome sequences to explore the reticulate history of this genus.
2. Materials and methods 2.1. Taxon samplingSeven species and one variety of Shibataea were sampled for ddRAD sequencing, in addition to four closely related species (two species from clade IV, Ferrocalamus rimosivaginus and Gelidocalamus tessellatus, and two Phyllostachys species, P. edulis and P. varioauriculata) which were chosen based on the studies of plastid genes in Zhang et al. (2012) and the RAD tree in Wang et al. (2017), respectively. Fargesia nitida was selected as an outgroup based on the studies above. Of the 13 bamboos sampled here, the complete plastid genomes of four bamboos were previously published and downloaded from GenBank database, the remaining nine genomes were newly sequenced for this study (Appendix: Table S1).
2.2. DNA extraction, library preparation and data generationDNA was extracted from ~100 mg dried leave tissue with a modified CTAB method (Doyle, 1987). Our ddRAD sequencing library was prepared using the AvaII and MspI restriction enzymes following the methods of Yang et al. (2016). Paired-end reads of 2 × 150 bp were generated on an Illumina HiSeq X Ten System (San Diego, CA, USA). Total genomic DNA was also fragmented to build short-insert libraries (500 bp) according to the manufacturer's protocol (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) for genome skimming. Paired-end sequencing of 150 bp was conducted on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 at BGI-Shenzhen, generating ~2 Gb data per sample.
2.3. Data assemblyFor ddRAD-seq data, paired-end raw reads were demultiplexed, trimmed and filtered using the program 'process_radtags' of Stacks v1.41 (Catchen et al., 2013) to 140 bp. Then the sequence quality of filtered reads was assessed using FASTQC v.0.11.5 (Andrews, 2016). Because the results revealed low quality over the restriction overhang regions and a portion of the R2 reads, we excluded R2 reads from subsequent analyses. Data were assembled into loci using de novo assembly method in ipyrad version 0.7.28 (http://ipyrad.readthedocs.io/), a toolbox for assembly and analysis of RAD-seq data sets based on the pyRAD pipeline (Eaton, 2014). Filtered reads were clustered at 90% thresholds for clustering within each sample. Clusters with a minimum depth of coverage less than five were discarded. Error rate and heterozygosity were jointly estimated based on counts of site patterns across clustered reads for each sampled individual and the average parameter values were used for consensus base calling. Consensus loci were then clustered across samples at 90% similarity and aligned. We filtered loci to be shared by at least 4e13 taxa, which hereafter refer to these 10 alignments as min4-min13, and then wrote output files.
We assembled the genome skimming data using the GetOrganelle v1.9.77 (https://github.com/Kinggerm/GetOrganelle) with a range of k-mers of 65, 75, 85, 95 and 105. The published plastome, F. rimosivaginus (NC_015831.1) was used as the reference genome for assembly of all other accessions. Contigs were visualized and extracted using Bandage v0.8.0 (Wick et al., 2015). We filled the gaps produced by non-overlapping contigs using GapCloser as a package for SOAPdenovo2 (https://sourceforge.net/projects/soapdenovo2/files/GapCloser). Chloroplast sequences were checked by aligning the contigs to the reference with pairwise align option and scanned by eye to confirm appropriate mapping using Geneious v.9.1.4 (Kearse et al., 2012). Finally, whole plastome sequences from all 13 species were aligned with MAFFT v.7.222 (Katoh and Standley, 2013) using the default settings. A few poorly aligned regions were manually adjusted in Geneious.
2.4. Phylogenomic analysesFor each assembled RAD data set, all the loci were concatenated and maximum likelihood (ML) trees were inferred in RAxML v8.2.10 (Stamatakis, 2014). Bootstrap supports were estimated from 100 replicates and the best-scoring ML tree was searched for using the GTR + Γ nucleotide substitution model.
To account for incomplete lineage sorting (ILS), we also inferred species trees based on quartet trees inferred from phylogenetic invariants using the program tetrad implemented in ipyrad (https://github.com/dereneaton/ipyrad). To avoid issues with linkage, we opted to use only one SNP per locus for a total of 15, 837 (min6), 2221 (min9) and 155 SNPs (min12). We inferred all 715 possible quartets for the 13 taxa, performed 100 bootstraps replicates and constructed a 50% majority-rule consensus tree.
The plastome dataset was unpartitioned, and subsequent phylogenetic analyses were performed with GTR þ G nucleotide substitution model. The ML trees with bootstrap support were inferred from 1000 bootstrap replicates and the best-scoring ML tree was searched.
2.5. Network analysisWe used network analysis on the 13 taxa of the min9 dataset to visualize the signal in the dataset and to investigate possible phylogenetic signal conflicts. SplitsTree4 (Huson and Bryant, 2006) was used with the Neighbor-Net algorithm and uncorrected Pdistances. The position of S. kumasasa in the ML trees was inconsistent (see Results for more details); to further compare the effect of S. kumasasa on the conflict, we excluded it from network analyses.
3. Results 3.1. Characteristics of the ddRAD-seq and genome skimming data setsAfter quality filtering, we obtained 2, 577, 856 to 21, 573, 017 paired-end reads for 13 samples with an average of 7.6 million (Appendix: Table S2). De novo assembly using ipyrad produced 102 K ± 55.7 K (mean ± SD) consensus loci per sample under clustering (90% similarity). Datasets that were assembled with different minimums for sample coverage had different proportions of missing data: The largest but most incomplete assembled data matrix that includes all loci shared across at least four samples (min4) has 57.55% missing data for 13 individuals across 47, 217 loci, whereas all other matrices have fewer missing data (0.49e50.65%; Appendix: Table S3).
Nine complete plastomes were newly determined. All these plastomes were conservative and showed high similarity in genome structure and gene content with published plastomes of bamboos (Burke et al., 2012; Wu and Ge, 2012; Ma et al., 2017). Their genome size ranged narrowly from 139, 467 to 139, 786 bp with an alignment of 140, 851 bp across 13 species, characterized by extremely low sequence divergence with only 775 variable sites (0.55%) and 354 parsimony-informative sites (PICs, 0.25%).
3.2. Well-resolved phylogeny with ddRAD-seq dataThe phylogenies inferred using ML for each of the ten concatenated data sets were highly supported and generally congruent despite variation in the proportion of missing data. The larger and more incomplete data sets yielded similar or identical topologies to the smaller and more complete data sets, although topologies of the latter data sets often had lower bootstrap supports. All phylogenetic analyses recovered strong support for Shibataea as monophyletic (BS = 100%), and Phyllostachys as its sister group, which is consistent with recent phylogenetic results that used RAD-seq data sets (Wang et al., 2017). Within Shibataea, the order of relationships was generally congruent among different data sets except for the position of S. kumasasa. Conflicts among data sets with regard to these relationships are summarized into three alternative topologies. Topologies 1e3 are presented using ML trees inferred from dataset min6, min9 and min12, respectively (Fig. 1a-c). Except for S. kumasasa, all of the concatenated ML topologies resolved S. hispida as the earliest diverged species (BS = 100%, 100%, 100%), followed by S. chinensis (BS = 100%, 100%, 95%), while the remaining species of Shibataea can be further divided into two clades (BS = 100%, 100%, 61%).
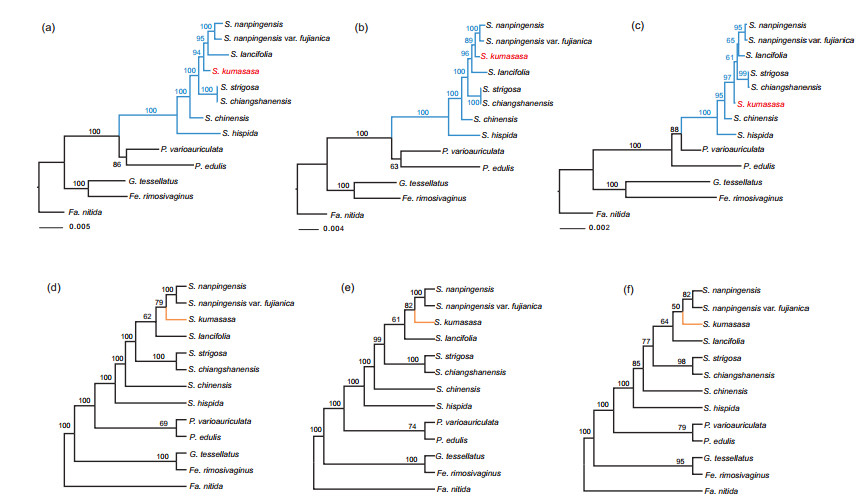
|
| Fig. 1 A summary of three alternative maximum likelihood (ML) topologies and species trees of Shibataea. (a)-(c) represent ML trees reconstructed from min6, min9, and min12 data sets, respectively. (d)-(f) represent consensus species tree inferred from tetrad analysis based on min6, min9, and min12 data sets, respectively. Numbers associated with nodes indicate bootstrap values (BS) |
The tetrad species trees had lower bootstrap support values across some nodes, with three, two, and four nodes receiving less than 80% support in the min6, min9, and min12 data sets (Fig. 1d-f). Interestingly, position of S. kumasasa was resolved differently between the tetrad species tree topologies and the concatenated ML tree topologies from min6 and min12 data sets. However, the topologies of all the tetrad species trees were identical to topology 2. Taking into consideration statistical support, the species trees, and the missing data used in building trees, we focused our remaining analyses on topology 2 (assembled from data set min9).
3.3. Network analysisThe neighbor-net network constructed from the min9 data set revealed Shibataea as monophyletic, while also revealing conflicting signals that were evident in phylogenetic analyses. In particular, clusters connected by many parallel short edges indicate character conflicts among S. kumasasa, S. changshanensis, and S. nanpingensis (Fig. 2a). After discarding S. kumasasa, the remaining relationships were more tree-like and fewer conflicts were contained (Fig. 2b).
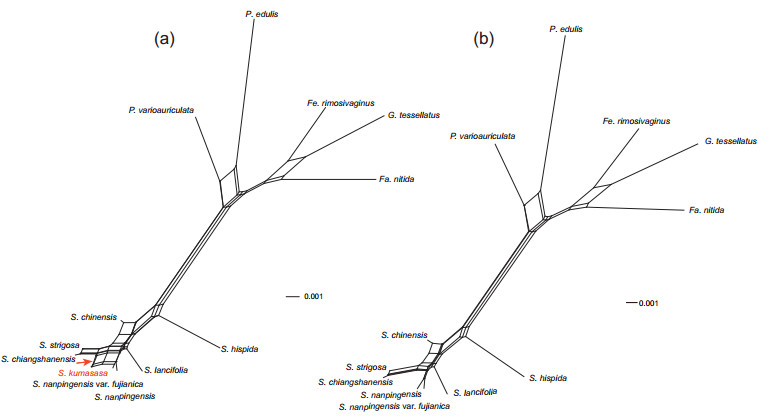
|
| Fig. 2 Split network of Shibataea based on min9 data set. (a) contains all 13 species, while (b) contains 12 species with S. kumasasa discarded |
Phylogenetic analyses of plastid genomes recovered Shibataea as monophyletic, with relationships among them generally strongly supported (Fig. 3). Two species belonging to clade IV, F. rimosivaginus and G. tessellatus, were strongly supported as a sister group of Shibataea, which is congruent with previous studies based on plastid genes (Zeng et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2017). Within Shibataea, two monophyletic clades were strongly supported (BS = 99%, 89%).
3.5. Incongruence among the different genomic data setsThe plastid topologies conflict significantly with the nuclear ddRAD results (Fig. 3). Our plastid tree was consistent with trees from previous studies that were based on chloroplast sequences (Zeng et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2014, 2017). Specifically, all Shibataea species formed clade IV (Shibataea clade) together with Fe. rimosivaginus and G. tessellatus (Fig. 3). In our ddRAD tree, by contrast, genus Shibataea grouped with Phyllostachys, and the remaining clade IV genera formed a new clade. Moreover, the plastid and ddRAD trees were in conflict at the genus level. The plastid tree shows S. hispida and S. chinensis clustered with the clade that contains S. chiangshanensis, S. strigosa and S. kumasasa. The ddRAD tree, however, shows S. hispida and S. chinensis are early diverged species. The relationships between S. nanpingensis, S. nanpingensis var. fujianica and S. lancifolia in the ddRAD tree are generally consistent with those in the plastid tree, except that in the ddRAD tree, S. kumasasa is nested with S. nanpingensis and S. nanpingensis var. fujianica.
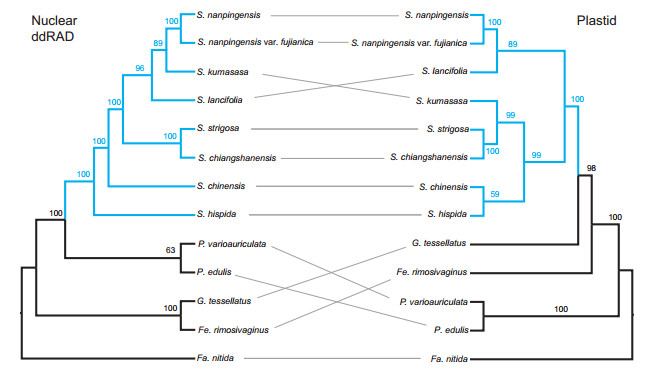
|
| Fig. 3 Tanglegram of the nuclear ddRAD (left) and plastid (right) phylogenies of Shibataea. Gray lines connect taxa between the phylogenies. Maximum likelihood bootstrap support values are shown above branches |
Our phylogenomic analysis based on ddRAD-seq data congruently recovered Shibataea as monophyletic. Trees inferred from ten ddRAD data sets recovered three topologies that all support identical orders of species in Shibataea except for S. kumasasa, as summarized in Fig. 1. Species trees reconstructed from different data sets generated congruent topologies. These results illustrate the great promise of ddRAD-seq data for the resolution of an intractable bamboo genus and other non-model plant groups. As we presented here, the potential power of genomic data is not limited to resolving phylogenetic relationships, but in revealing genealogical discordance that would be otherwise undetected. We propose that incongruence in the placement of S. kumasasa among trees estimated from different ddRAD data sets is likely due to the conflicting signals, as revealed by network analysis (Fig. 2).
4.2. Conflicting signals and overlapped distribution imply past hybridization eventsAs revealed by previous empirical studies in bamboos (Zhang et al., 2012; Wysocki et al., 2015, 2016), incongruence between the topologies obtained from nuclear and plastid genomic datasets is also found in Shibataea. According to Maddison (1997), several factors can contribute to such conflicts, including phylogenetic uncertainty and/or biological factors such as ILS and interspecies gene flow. The conflicting nodes in our trees are well supported (BS > 89%, Fig. 3); therefore, the incongruence observed in these trees is unlikely to be due to errors in phylogenetic reconstruction.
Phylogenetic data sets may show a high degree of gene tree incongruence due to incomplete lineage sorting (ILS) of genes (e.g. Pollard et al., 2006; García et al., 2017). In our study, data sets from concatenating loci shared across different taxa disclose three alternative topologies. Moreover, Zhang et al. (2012) found more than half of the species sampled in their study possessed two alleles of the GBSSI gene, which supports the ancestral polymorphism of these species and demonstrates that ILS may be common in Arundinarieae.
Despite long reproductive cycles — from a few up to 120 years— in temperate bamboos (Janze, 1976; Ma et al., 2017), hybridization is still proposed to have played a significant and recurrent role in bamboo evolution (Triplett, 2008; Triplett and Clark, 2010; Yang et al., 2013; Triplett et al., 2014). In our study, phylogenetic discordances between the ddRAD tree and the plastid tree are focused on S. kumasasa. This species formed a well-supported clade with S. nanpingensis, S. nanpingensis var. fujianica and S. lancifolia in the ddRAD tree, but clustered closely with S. strigosa and S. chiangshanensis in the plastid tree.S. kumasasa is very likely hybridized with either S. strigosa, S. chiangshanensis or their ancestor, and captured their plastome during the introgression. And S. nanpingensis or S. lancifolia may be the paternal donor when they hybridized with S. kumasasa.
Consistent chromosome number among temperate bamboos (2n = 48) (Zhou et al., 2017) provides adequate opportunity for plants to overcome hybridization barriers. One of the most important conditions for hybridization is overlapping geographic distributions. Of the species examined in our study, S. strigosa, S. chiangshanensis and S. nanpingensis are endemic species with narrow distributions. Specifically, S. strigosa is narrowly endemic to Longquan, Zhejiang province in Eastern China; S. chiangshanensis only occurs in Jiangshan, Zhejiang; and S. nanpingensis is endemic to Nanping, Fujian province in Eastern China (Fig. 4). Moreover, S. kumasasa and S. lancifolia are widely distributed in Zhejiang and Fujian provinces, thus, their overlapping distribution with the other three species may largely promote gene exchange. This pattern is quite common in plants, even in the temperate bamboos. In North American Arundinaria, Triplett and Clark, 2010 have identified hybrids among Arundinaria gigantea, A. tecta, and A. appalachiana in regions of geographic range overlap. In addition, in the American live oaks, Eaton et al. (2015) found that species occurring in close geographic proximity show some degree of gene flow, and provide evidence of introgression that is concordant with the present-day geographic distributions of species. Further analyses at the population level should be carried out to provide more evidence of admixture between S. kumasasa and the other four species.
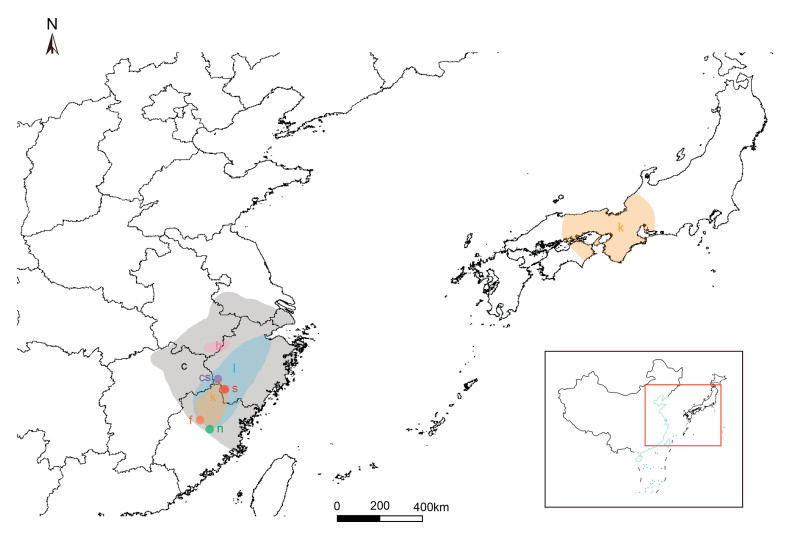
|
| Fig. 4 Geographic distribution of species of Shibataea (after Hu et al., 1989). c, cs, f, h, k, l, n, s represents S. chinensis, S. chiangshanensis, S. nanpingensis var. fujianica, S. hispida, S. kumasasa, S. lancifolia, S. nanpingensis, S. strigosa, respectively |
In this study, we reconstructed the first highly supported phylogenies of Shibataea using genome-wide markers both from ddRAD-seq sequences and plastid genomes. We compared these genealogies and revealed conflicting relationships. Together with the result of network analysis, S. kumasasa was identified as the most admixed species. We then elucidated the potential biological mechanism which may have contributed to the incongruence observed here.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.
AcknowledgmentsThis work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31470322 and 31430011). We thank Dr. Xia-Ying Ye for providing ddRAD-seq data of Fargesia nitida. We are grateful to Prof. Jun-Bo Yang, Dr. Guo-Qian Yang, Ms. Jing Yang and Mr. Ji-Xiong Yang at CAS Kunming Institute of Botany's Germplasm Bank of Wild Species, for providing experimental supports. We also thank the support from the UCAS Joint PhD Training Program.
Appendix A. Supplementary dataSupplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2019.05.003.
Andrews, S., 2016. FastQC: a Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
|
Attigala L., Wysocki W.P., Duvall M.R., Clark L.G., 2016. Phylogenetic estimation and morphological evolution of Arundinarieae (Bambusoideae:Poaceae) based on plastome phylogenomic analysis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol, 101: 111-121. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2016.05.008 |
Baird, N.A., Etter, P.D., Atwood, T.S., Currey, M.C., Shiver, A.L., Lewis, Z.A., Selker, E.U., Cresko, W.A., Johnson, E.A., 2008. Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS One 3, e3376.
|
Burke S.V., Grennan C.P., Duvall M.R., 2012. Plastome sequences of two New World bamboos-Arundinaria gigantea and Cryptochloa strictiflora (Poaceae)-extend phylogenomic understanding of Bambusoideae. Am. J. Bot, 99: 1951-1961. DOI:10.3732/ajb.1200365 |
Catchen J., Hohenlohe P.A., Bassham S., Amores A., Cresko W.A., 2013. Stacks:an analysis tool set for population genomics. Mol. Ecol, 22: 3124-3140. DOI:10.1111/mec.12354 |
Doyle J., 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull, 19: 11-15. |
Dransfield, S., Widjaja, E.A., 1995. Plant Resources of South-East Asia. No. 7: Bamboos. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden.
|
Eaton, D.A., 2014. PyRAD: assembly of de novo RADseq loci for phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 30, 1844-1849.
|
Eaton, D.A., Hipp, A.L., Gonzalez-Rodríguez, A., Cavender-Bares, J., 2015. Historical introgression among the American live oaks and the comparative nature of tests for introgression. Evolution 69(10), 2587-2601.
|
García N., Folk R.A., Meerow A.W., Chamala S., Gitzendanner M.A., de Oliveira R.S., Soltis D.E., Soltis P.S., 2017. Deep reticulation and incomplete lineage sorting obscure the diploid phylogeny of rain-lilies and allies (Amaryllidaceae tribe Hippeastreae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol, 111: 231-247. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2017.04.003 |
Hu C.H., Gao Z.S., Dai T., An S.Q., Qin J.W., 1989. Studies on the geographic distribution of the genus Shibataea Makino. J. Wuhan Bot. Res, 7(2): 155-161. |
Huson D.H., Bryant D., 2006. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol, 23: 254-267. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msj030 |
Janze D., 1976. Why bamboos wait so long to flower. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst, 7: 347-391. DOI:10.1146/annurev.es.07.110176.002023 |
Katoh K., Standley D.M., 2013. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7:improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol, 30: 772-780. DOI:10.1093/molbev/mst010 |
Kearse, M., Moir, R., Wilson, A., Stones-Havas, S., Cheung, M., Sturrock, S., Buxton, S., Cooper, A., Markowitz, S., Duran, C., Thierer, T., Ashton, B., Meintjes, P., Drummond, A., 2012. Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28, 1647-1649.
|
Keng, P.C., Wang, C.P., 1996. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Tomus 9. Science Press, Beijing.
|
Li, D.Z., 1997. The Flora of China Bambusoideae Project-Problems and Current Understanding of Bamboo Taxonomy in China. Academic Press, London.
|
Li, D.Z., Wang, Z.P., Zhu, Z.D., Xia, N.H., Jia, L.Z., Guo, Z.H., Yang, G.Y., Stapleton, C.M.A., 2006. Bambuseae (Poaceae). In: Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y. (Eds.), Flora of China, vol. 22. Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis.
|
Ma P.F., Zhang Y.X., Zeng C.X., Guo Z.H., Li D.Z., 2014. Chloroplast phylogenomic analyses resolve deep-level relationships of an intractable bamboo tribe Arundinarieae (Poaceae). Syst. Biol, 63: 933-950. DOI:10.1093/sysbio/syu054 |
Ma P.F., Vorontsova M.S., Nanjarisoa O.P., Razanatsoa J., Guo Z.H., Haevermans T., Li D.Z., 2017. Negative correlation between rates of molecular evolution and flowering cycles in temperate woody bamboos revealed by plastid phylogenomics. BMC Plant Biol, 17: 260. DOI:10.1186/s12870-017-1199-8 |
Maddison W.P., 1997. Gene trees in species trees. Syst. Biol, 46: 523-536. DOI:10.1093/sysbio/46.3.523 |
Ohrnberger, D., 1999. The Bamboos of the World: Annotated Nomenclature and Literature of the Species and the Higher and Lower Taxa. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam and New York, pp. 126-128.
|
Peterson, B.K., Weber, J.N., Kay, E.H., Fisher, H.S., Hoekstra, H.E., 2012. Double digest RADseq: an inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species. PLoS One 7, e37135.
|
Pollard D.A., Iyer V.N., Moses A.M., Eisen M.B., 2006. Widespread discordance of gene trees with species tree in Drosophila:evidence for incomplete lineage sorting. PLoS Genet, 2(10): e173. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020173 |
Soderstrom, T.R., Ellis, R.P., 1987. The position of bamboo genera and allies in a system of grass classification. In: Soderstrom, T.R., Hiu, K.W., Campbell, C.S., Barkworth, M.F. (Eds.), Grass Systematics and Evolution. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC.
|
Stamatakis, A., 2014. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and postanalysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312-1313.
|
Triplett, J.K., Clark, L.G., 2010. Phylogeny of the temperate bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae: Bambuseae) with an emphasis on Arundinaria and allies. Syst. Bot. 35(1), 102-120.
|
Triplett, J.K., 2008. Phylogenetic relationships among the temperate bamboos(Poaceae: Bambusoideae) with an emphasis on Arundinaria and allies[D]. Iowa State University, Iowa, United States.
|
Triplett J.K., Clark L.G., Fisher A.E., Wen J., 2014. Independent allopolyploidization events preceded speciation in the temperate and tropical woody bamboos. New Phytol, 204(1): 66-73. DOI:10.1111/nph.12988 |
Vargas O.M., Ortiz E.M., Simpson B.B., 2017. Conflicting phylogenomic signals reveal a pattern of reticulate evolution in a recent high-Andean diversification(Asteraceae:Astereae:Diplostephium). New Phytol, 214: 1736-1750. DOI:10.1111/nph.14530 |
Wang, X.Q., Ye, X.Y., Zhao, L., Li, D.Z., Guo, Z.H., Zhuang, H.F., 2017. Genome-wide RAD sequencing data provide unprecedented resolution of the phylogeny of temperate bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Sci. Rep. 7, 11546.
|
Wick, R.R., Schultz, M.B., Zobel, J., Holt, K.E., 2015. Bandage: interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 31, 3350-3352.
|
Wu Z.Q., Ge S., 2012. The phylogeny of the BEP clade in grasses revisited:evidence from the whole-genome sequences of chloroplasts. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol, 62: 573-578. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2011.10.019 |
Wysocki, W.P., Clark, L.G., Attigala, L., Ruiz-Sanchez, E., Duvall, M.R., 2015. Evolution of the bamboos (Bambusoideae; Poaceae): a full plastome phylogenomic analysis. BMC Evol. Biol. 15, 50.
|
Wysocki, W.P., Ruiz-Sanchez, E., Yin, Y., Duvall, M.R., 2016. The floral transcriptomes of four bamboo species (Bambusoideae; Poaceae): support for common ancestry among woody bamboos. BMC Genom. 17, 384.
|
Yang, G.Q., Chen, Y.M., Wang, J.P., Guo, C., Zhao, L., Wang, X.Y., Guo, Y., Li, L., Li, D.Z., Guo, Z.H., 2016. Development of a universal and simplified ddRAD library preparation approach for SNP discovery and genotyping in angiosperm plants.Plant Meth. 12, 39.
|
Yang H.M., Zhang Y.X., Yang J.B., Li D.Z., 2013. The monophyly of Chimonocalamus and conflicting gene trees in Arundinarieae (Poaceae:Bambusoideae) inferred from four plastid and two nuclear markers. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol, 68: 340-356. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2013.04.002 |
Zeng C.X., Zhang Y.X., Triplett J.K., Yang J.B., Li D.Z., 2010. Large multi-locus plastid phylogeny of the tribe Arundinarieae (Poaceae:Bambusoideae) reveals ten major lineages and low rate of molecular divergence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol, 56: 821-839. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.03.041 |
Zhang, X.Z., Zeng, C.X., Ma, P.F., Haevermans, T., Zhang, Y.X., Zhang, L.N., Guo, Z.H., Li, D.Z., 2016. Multi-locus plastid phylogenetic biogeography supports the Asian hypothesis of the temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Mol.Phylogenet. Evol. 96, 118-129.
|
Zhang Y.X., Zeng C.X., Li D.Z., 2012. Complex evolution in Arundinarieae (Poaceae:Bambusoideae):incongruence between plastid and nuclear GBSSI gene phylogenies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol, 63: 777-797. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2012.02.023 |
Zhou, M.B., Xu, C.M., Shen, L.F., Xiang, W.B., Tang, D.Q., 2017. Evolution of genome sizes in Chinese Bambusoideae (Poaceae) in relation to karyotype. Trees 31(1), 41-48.
|



