近些年来,高精度数值方法的研究成为计算流体力学(Computational Fluid Dynamics, CFD)领域研究中的前沿热点问题之一。我们通常所说的高精度方法是指空间精度为三阶或三阶以上的高精度数值格式,相比于传统的空间二阶精度的有限体积格式,高精度方法具有空间精度高,数值分辨率高,数值耗散小的优点。
目前计算流体力学领域高精度方法主要可以分为三大类:高精度有限差分(Finite Difference, FD)方法[1-3],高精度有限体积(Finite Volume, FV)方法[4-9]和高精度有限元类(Finite Element, FE)方法[10-17]。高精度有限差分法,通常为在结构化网格下一种高效而易于实施的高精度格式,由于其计算量小,且易于达到较高数值精度的特点,常用于简单几何区域的复杂流动直接数值模拟。这一类型的高精度格式一般只能用于结构化的笛卡尔网格,对于处理复杂几何区域则会带来一定的困难,但近年来邓小刚等[18]做了大量的工作将该方法推广到复杂几何网格上;高精度有限体积法是通过选取目标单元及其周围的相邻单元作为模板,构造满足一定条件的重构高阶多项式来达到高阶精度的目的,比较有代表性的高精度有限体积格式有:有限体积型加权本质无振荡格式[4-5]、高精度k-exact有限体积格式[6]和近年来的紧致高阶精度有限体积法[7-9]。这类方法理论上可以处理任意网格和较为复杂的几何区域,能够保证格式的守恒性且具有良好的数值稳定性。然而传统的高精度有限体积法的不足之处在于其模板的非紧致性,即模板不仅包含目标单元及其有公共边的邻居单元,通常还需要包含其邻居单元的相邻单元。因此,该方法在处理边界和三维问题方面则存在一定困难。紧致高阶精度有限体积法克服了这一问题,不过需要采用隐式方法求解重构方程。第三种高精度方法以间断伽辽金方法(Discontinuous Galerkin Method,DGM)为代表,通过提高相应单元上的解函数多项式的次数,增加相应单元上解函数的自由度(Degree of Freedom, DoF)来提高空间精度,这类方法中其他有代表性的方法还包括:谱体积方法(Spectral Volume, SV)[11-12],谱差分方法(Spectral Difference, SD)[13-15],通量重构方法(Flux Reconstruction, FR)[16]和修正过程重构方法(Correction Procedure via Reconstruction, CPR) [17]。间断伽辽金方法具有易于处理任意网格和复杂几何区域的能力,且易于实现高阶精度,格式构造的紧致性导致这类方法更适合做大规模的并行和自适应计算。正因为这些优势,使得间断伽辽金方法得到了计算流体力学、计算电磁学领域等诸多学者的广泛关注,成为高精度格式研究的热点之一。
本文将对间断伽辽金方法的基本思想和理论发展历程做出概述,并重点介绍在可压缩流CFD领域国内外对该方法的发展以及研究现状。本文也将给出部分将该方法应用于CFD领域的实例。最后,对间断伽辽金方法中仍然存在的问题和可能的发展空间做出分析和展望。
1 间断伽辽金方法基本概念高精度间断伽辽金方法是有限元方法的一种,该方法的基本思路,是利用分段连续的多项式空间来近似表达偏微分方程组的解。以一个典型的一阶双曲守恒型方程系统为例:
| $ \frac{{\partial \boldsymbol{U}}}{{\partial t}} + \nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{F}\left( \boldsymbol{U} \right) = 0 $ | (1) |
将计算域划分为互不重叠的单元集合Ωv=∪kΩvk,定义Φh, p是单元Ωvk上直到p阶的多项式函数张成的函数空间,p≥0且为整数,设单元内守恒变量的近似Uh∈Φh, p。在每个单元内,对方程两边同时乘以测试函数φh,在计算域内积分,进行分部积分整理后,得到原方程(1) 的弱解形式为:
| $ \begin{gathered} \int_{{\mathit{\Omega} _v}} {{\varphi _h}\frac{{\partial {\boldsymbol{U}_{^h}}}}{{\partial t}}} {\text{d}}{\mathit{\Omega} _v} + \int_{\partial {\mathit{\Omega} _v}} {{\varphi _h}\boldsymbol{F}\left( {{\boldsymbol{U}_h}} \right)} \cdot \boldsymbol{n}{\text{d}}{\sigma _v} \hfill \\ - \int_{{\mathit{\Omega} _v}} {\nabla {\varphi _h} \cdot \boldsymbol{F}\left( {{\boldsymbol{U}_h}} \right)} {\text{d}}{\mathit{\Omega} _v} = 0,\forall {\varphi _h} \in {\mathit{\Phi} _{h,p}} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} $ | (2) |
式(2) 中,对于边界通量H = F (Uh)· n,与有限体积方法中的处理方法类似,可以采用一个相容的数值通量来代替,而在边界上对守恒变量不做连续性要求。如此便得到了p阶间断伽辽金方法的离散格式。
因此间断伽辽金方法结合了有限元方法和有限体积方法的优点:在单元内部同传统的连续有限元方法一样,使用多项式逼近来获得高阶精度;在单元边界上借鉴有限体积法,通过解决Riemann问题来实现逆风格式。实际上,当p=0时,间断伽辽金方法即退化为传统的有限体积方法。
除高精度外,间断伽辽金方法还有很多其他吸引人的特点:
1) 能够保持单元平均值意义下守恒性,最重要的是具有良好的稳定性和收敛性[19];
2) 通过改变插值多项式的阶数,很容易延拓到高阶(p>2),并且允许不同的单元采用不同的阶数,即p-adaptivity[20];
3) 能够处理复杂的几何外形和物理边界条件,甚至可以直接处理含有悬挂点的网格[21-22],因此极易实现网格自适应,即h-adaptivity[20-23]。另外方法本身适用于各种类型的网格;
4) 利用该方法进行计算时,具有紧致性,单元只与相邻单元有数据交换,很容易实现大规模并行计算且并行效率很高;
因此,高精度间断伽辽金方法在计算流体力学领域得到广泛的尝试。
2 间断伽辽金方法的历史和现状 2.1 国际发展与现状在应用间断伽辽金方法处理双曲型方程的研究理论方面,1973年,Reed和Hill[10]在关于求解中子输运方程(时间无关的线性双曲型方程)问题的论文中首次在间断伽辽金方法中引入了逆风格式。1982年,Chavent和Salzano[24]首先在间断伽辽金方法中引入Godunov数值通量求解了非线性双曲型问题,将间断伽辽金方法从求解线性问题延伸到求解非线性双曲型问题。在20世纪末,Cockburn和Shu等[25-30]对用间断伽辽金方法和显式时间积分方法求解非线性双曲型问题的研究取得了重大突破,成功地建立了著名的龙格-库塔间断伽辽金(RKDG)方法。最初始的RKDG有限元方法采用Shu和Osher[31]提出的显式TVD二阶龙格-库塔格式,随后他们将该方法在时间和空间上都发展到高阶精度。同一时期,Allmaras[32]和Giles[33]采用二阶精度间断伽辽金方法求解了二维欧拉方程,他们将van Leer的moments限制器从一维线性波动方程拓展到二维欧拉方程,在每个单元内部计算单元平均和单元梯度平均值从而对单元变量进行线性重构。
而应用间断伽辽金方法求解椭圆型方程或求解NS方程的粘性项则存在相当的困难,诸多学者对此展开了研究。Arnold[34]和Wheeler[35]于20世纪80年代在间断伽辽金方法中引入了内罚函数(interior penalty),这种方法随后被广泛应用于求解扩散问题。1999年,Oden和Babuska[36]等提出了一种求解扩散问题新格式,其优点是没有引入额外的过渡变量,但理论上该格式必须在2阶以上才稳定。21世纪初,Bassi和Rebay[37-40]提出了经典的混合方法(mixed formulation),将二阶方程写成多个一阶方程的形式,然后采用间断伽辽金方法对一阶系统进行数值离散。Bassi和Rebay提出的第一种混合方法(BR1格式)计算模板较大,不紧致,且采用隐式方法计算时稳定性会受到影响。为了克服这些缺点,他们又在BR1格式基础上进行了修改,得到了稳定紧致的BR2格式。Cockburn和Shu[41-42]则在同一时期对混合方法思想进行了一般化分析,得出了当地间断伽辽金方法(Local Discontinuous Galerkin methods, LDG)。但是在多维度数值计算时,当地间断伽辽金方法同样存在模板大、不紧致的问题,于是之后Persson和Peraire[43]对该方法进行了修改,提出了紧致间断伽辽金方法(Compact Discontinuous Galerkin methods, CDG),在保留当地间断伽辽金方法优点的同时使得该格式紧致。Arnold等[44]也引入了内罚函数和混合方法的统一分析框架,对各种格式进行误差分析。近年来,由Liu和Yue[45-46]提出的一类直接间断伽辽金方法(Direct DG, DDG)逐渐受到了学者的关注,DDG方法的导出过程不需要引入临时变量将原有的二阶偏微分方程分解为一阶偏微分方程组,而是直接基于DG方法的弱形式构造单元界面处的粘性数值通量。
在上述数值格式研究成果的基础上,间断伽辽金方法迅速在气动可压缩流数值模拟方面引发了广泛关注和尝试。如前文所述,在计算流体力学的应用中,间断伽辽金方法结合了传统有限元方法和有限体积方法的优点,因此相比于传统的有限元方法,间断伽辽金方法由于容易实现逆风格式,很容易对对流项主导的流动问题进行离散求解;相比于有限体积方法,高阶间断伽辽金方法达到高精度所需要的计算量大大减少。得益于这些优势,间断伽辽金方法成为了目前计算流体力学领域极具潜力的高精度方法之一。
在相应的网格技术方面,Diosady等于2007年左右对间断多重网格技术及线性预处理方法进行了研究[47-48]。同时Lubon等则对适用于间断伽辽金方法的网格进行了研究,发展了物面弯曲技术并采用间断伽辽金方法进行了RANS及DES数值模拟[49-51]。2007年,Fidkowski在其博士论文中发展了网格切割技术,并采用间断伽辽金方法求解了二维Navier-Stokes方程[52]。随后其又在间断伽辽金方法上发展了网格自适应技术及网格变形方法[53-55]。Oliver研究了二维自适应高阶间断伽辽金方法,结合Spalart-Allmaras一方程湍流模型对湍流流动进行了数值仿真[56-58]。Li Wang在博士论文中对二维间断伽辽金方法的气动优化问题、网格自适应问题及高阶时间积分方法进行了研究[59-62],近年来其采用间断伽辽金方法求解了三维RANS方程及麦克斯韦方程并得到了较好的数值结果,同时其对SUPG方法也在进行研究[63-65]。Burgess采用自适应间断伽辽金方法对二维湍流流动进行了数值模拟,并对湍流方程加速求解技术进行了研究[66-69]。2011到2014年,Bassi等牵头一项欧盟高精度方法工业化应用项目(IDIHOM)[70],吸引了来自欧洲各地的学者,继续推进高阶网格处理技术以及间断伽辽金方法数值求解技术。
在间断伽辽金方法的可压缩流求解技术方面,Bassi和Rebay等于1997年采用间断伽辽金方法求解了Euler方程和Navier-Stokes方程[37-39]之后,又对湍流模型的求解进行了研究,于2005年采用k-ω两方程模型求解了雷诺平均Navier-Stokes (Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes,RANS)方程[40]。随后该团队又将间断伽辽金方法拓展到DES及不可压缩流动领域[71-72]。Landmann在其博士论文中发展了并行高阶间断伽辽金方法并求解了二维Navier-Stokes方程及RANS方程[73-74]。2010年左右,Persson等研究了动网格技术,将间断伽辽金方法应用于两相流及扑翼飞行的数值仿真[75-77]。Wang等研究了CPR-DG有限元方法并求解了二维和三维Navier-Stokes方程,最近又将其拓展到RANS-LES混合方法的求解[78-81]。Hartmann等[82-86]研究了SST两方程湍流模型和激波捕捉技术在间断伽辽金方法上的应用,采用间断伽辽金方法对二维和三维复杂外形的流动进行了数值求解。
值得注意的是,很多学者提出并发展了一类重构型和混合型的间断伽辽金方法。这一类方法的基本思想是在DG方法的框架下,借鉴DG方法的优势,通过重构方式在原有DG解函数自由度的基础上,重构高阶自由度从而达到高阶精度的目的。van Leer等提出并发展了一类重构DG方法(Recovery DG, RDG)[87]。Dumbser等将DG方法和高精度有限体积方法统一到同一PnPm框架下,提出了一类PnPm方法[88]。之后,Luo[89-95]等在成熟的有限体积求解器基础上发展了另一类重构间断伽辽金方法(Reconstructed Discontinuous Galerkin Method),并对隐式LES方法进行了初步探究。
2.2 国内发展与现状国内间断伽辽金方法研究起步相对较晚,但在近十几年得到了越来越多的科研工作者在应用研究方面的关注。目前厦门大学、南京航空航天大学、上海理工大学、北京航空航天大学、西北工业大学、中国空气动力研究与发展中心、北京应用物理与计算数学研究所等学校和研究机构都对间断伽辽金方法开展了相关研究。2005年,蔚喜军和张铁[19]采用RKDG有限元方法求解了二维可压缩Euler方程,并与差分方法的计算结果进行了比较,证明了间断伽辽金法的高精度特性和在处理复杂边界问题上的优势。随后赵国忠等将该方法拓展到拉格朗日坐标系下并求解了二维气动方程组[96-98]。近年来,邱建贤、朱君等将著名的加权本质无振荡(Weighted Essentially Non-Oscillatory, WENO)格式作为限制器应用于间断伽辽金方法,并求解了两相流等流动问题[99-104]。2006年左右,吕宏强等采用间断伽辽金方法求解了面接触弹性流体动力润滑问题,最高阶数达到13阶,并成功应用了hp-adaptivity技术,用极少的计算代价得到了高精度的数值结果[105-106]。近年来,其团队研究了针对高阶间断伽辽金方法的高阶弯曲网格生成方法、网格自适应方法,以及基于间断伽辽金方法和Moro[107]的修正S-A模型的RANS和DES求解方法,并将CFD领域的间断伽辽金方法应用于时域电磁场数值模拟领域[108-113]。2010年左右,陈二云等将间断伽辽金方法应用于弹尾超声速喷流计算问题及气动声学问题中[114-116]。同时,阎超、于剑、姜振华等对间断伽辽金方法中的间断捕捉和Navier-Stokes方程进行了研究,并采用Baldwin-Lomax零方程湍流模型求解了二维流动问题[117-122]。郝海兵、李喜乐等也对高阶间断伽辽金方法的限制器及Baldwin-Lomax零方程湍流模型进行了研究,求解了二维流动问题及三维Euler方程[123-124]。贺立新、张来平[125-130]等发展了DG/FV混合方法,以较少的内存需求得到了与间断伽辽金方法相同的求解精度。程剑和杨小权等[131-132]人成功地实施了一类新型直接间断伽辽金方法用于求解粘性可压缩NS和RANS方程,取得了很好的计算效果。
总的来说,目前国际上对于间断伽辽金方法的理论分析、高效求解方法,以及相应的网格技术(如物面高阶拟合、自适应方法、动网格、变形网格方法等)的研究都很广泛。并且,很多当前的研究工作都已发展到了三维湍流流动模拟阶段,许多正在向RANS-LES混合方法以及一些跨学科方向(如计算电磁学、多学科优化、计算声学)迈进。
3 间断伽辽金方法的研究难点及挑战尽管间断伽辽金方法已经取得了相当的成果,但目前该方法的研究中仍存在着许多难点:
1) 高精度间断伽辽金方法一般应用于较为稀疏的网格,但是稀疏网格对于复杂几何外形的表达精度会对模拟结果的精度产生很大的影响,而在湍流流动模拟中,该方法对网格质量更为敏感,高效通用的高阶物面拟合以及高阶网格处理技术是间断伽辽金方法的研究难点之一;
2) 高阶间断伽辽金方法在处理间断问题时(例如激波)一般需使用限制器抑制数值振荡,然而在实际应用中,特别是定常流动的求解计算过程中,使用限制器会影响残差的收敛性,造成残差收敛困难;
3) 采用高阶间断伽辽金方法数值求解带湍流模型的RANS仍然是一个值得继续深入探索的问题,目前的相关研究显示,湍流模型会导致迭代的稳定性和鲁棒性不强;
4) 高精度间断伽辽金方法中的数值积分策略以及隐式时间格式的采用较同样网格量下的传统方法会产生较大的计算量及内存存储需求且通常需要求解大型的稀疏线性系统。
很多研究者对这些问题做出了努力并且提出了一些较为有效的解决方案,但仍然存在很大的优化和进步空间。
3.1 适用于间断伽辽金方法的网格技术由于间断伽辽金方法的高阶精度特点,在使用该方法进行计算时,如果采用过密的网格,将会带来巨大的计算量和冗余的精度。然而采用稀疏网格进行计算时,传统的分段线性网格无法对弯曲的边界进行精准的表达。Bassi[37]、Krivodonova[133]等在采用间断伽辽金方法进行流场的数值模拟时都发现,物面的表述精度会对模拟结果的精度产生非常大的影响,甚至会引起计算无法收敛的问题。于是利用高阶多项式来精准表达物面几何信息的方法被引入,并且被证明对计算结果的改善十分有效[133]。Lubon等[51]则发展了适用于三维四面体网格单元的壁面弯曲修正方法。
但是弯曲网格的方法并不总是有效,例如存在厚度很小的边界层网格时,弯曲的物面有可能与外层网格交叉,产生负体积。为了解决该问题,Landman[74]博士发展了多层四边形网格弯曲的方法避免网格单元出现负体积。Persson[134]等采用拉格朗日固体平衡方程使边界弯曲信息向外单元传播,通过全局变形达到平衡。Li Wang等则通过CAPRI方法得到三维物体的真实物面信息,然后根据线弹性理论求解各向同性线弹性方程得到全局变形后的网格点坐标[64]。吕宏强等发展了基于求解线性弹性方程的网格高阶弯曲方法[135]。秦望龙等[136]则采用了网格结块的方法,将多个网格单元聚合成高阶有限元单元,利用高阶网格单元来对物面进行拟合,并且不会出现交叉和重叠。
尽管上述方法都被证明十分有效,但这些方法的复杂程度都较高,通用性也有待检验,更通用、更鲁棒、更简单高效的高阶网格处理方法,仍然处在发展之中。
另一方面,诸如传统CFD方法中的动网格、重叠网格、滑移网格及变形网格等网格技术由于前述的物面拟合的难点,这些方法在间断伽辽金方法中的应用存在额外的困难,相关研究也并不多。
3.2 间断问题的处理与激波捕捉由于间断伽辽金方法在单元交界面上对变量不做连续性强制要求,并且采用数值通量来包容间断,所以实际上该方法可以不加处理地解决一些含有弱间断解的问题[20]。但是当变量的强间断落入单元之中时,插值多项式函数无法对其进行准确的高阶表达,进而引发数值振荡甚至发散。为此,在间断伽辽金方法中引入适当的限制器是有必要的。
Shu等采用当地投影的方法抑制数值振荡[26-28]。Luo和Xia[90-92]等采用WENO和HWENO格式结合重构间断伽辽金方法对间断问题进行了数值求解。邱建贤、朱君[99-104]等也将WENO格式作为限制器应用于间断伽辽金方法。
另一类人工黏性的思想也被引入。Persson[138]等采用级数展开思想捕捉间断区域,通过在流动变量间断的单元内添加人工黏性求解了激波问题。在其基础上,Barter[139]等引入了基于偏微分方程(PDE-based)的人工黏性激波捕捉方法,Nguyen[140]等采用速度的散度来表征流场的压缩特性,从而确定单元内部所需添加的人工黏性的数值大小。此外,Bassi和Rebay[141]等在2009年提出了一种新的激波捕捉人工黏性添加方法。该方法通过检测压力梯度添加人工黏性,人工黏性函数则通过考虑单元间无黏数值通量跳跃和单元内无黏数值通量法向分量得出。
然而上述诸多对数值振荡进行抑制的方法,都会或多或少地带来更多的数值耗散和色散,引起数值精度的损失,抑制振荡的效果也不一而足,在实际应用中,特别是定常流动的求解计算过程中,使用限制器还会破坏残差的收敛性,造成残差收敛困难。该方面的研究空间依然很大。
3.3 湍流流动数值模拟尽管湍流流动的机理和理论仍处在研究当中,但是经过研究者的长期摸索,已发展出了一系列被广泛应用的湍流模型,例如一方程Spalart-Allmaras湍流模型、两方程k-ω湍流模型及两方程SST模型。而在实际计算中,湍流方程的计算变量在网格分辨率不够的单元内会出现或短暂出现非连续项。如前文所述,对于间断伽辽金方法,过多的网格将带来巨大的计算量,此时间断伽辽金方法对于网格质量也更加敏感。而由于在单元内通过多项式插值实现高精度格式,间断伽辽金方法又很难对非连续项进行表述。这会导致数值求解的振荡,从而影响计算收敛甚至引发发散。
2005年,Bassi和Rebay[40]对k-ω两方程湍流模型进行了研究并对雷诺平均Navier-Stokes方程进行了数值求解。区别于传统的k-ω湍流模型,其在湍流模型变量中采用
大多数将间断伽辽金方法应用于湍流流动模拟的学者,都对湍流模型方程进行了修正,以使得计算过程能够稳定和鲁棒。但是这些修正的合理性和有效性都需要更深层次的理论与实际检验,新的修正方法或者模型也有待提出。近年来,一大批学者也正在尝试将间断伽辽金方法拓展到分离涡模拟(Detached Eddy Simulation, DES)、大涡模拟(Large Eddy Simulation, LES)及直接数值模拟(Direct Numerical Simulation, DNS)计算当中。
3.4 如何降低存储需求以及计算量尽管高性能计算设备的发展日新月异,但是常规的高性能设备仍然无法满足大规模的间断伽辽金方法的计算量要求。
高精度间断伽辽金方法中通常采用数值积分策略来求解积分项,需要在每个单元内逐个求取积分点上的数值并求和。但是随着近似多项式阶数的提高,积分点的数目迅速增加,高阶间断伽辽金方法的计算量也迅速提高,一些学者为此提出了积分无关方法[145],大大减少了由于积分点数量带来的计算量。
在采用显式方法进行计算时,仅需存储右端残值项,存储量为(Ndegr×Netol)×Nelem,其中Ndegr是单元变量的自由度个数,Netol是方程个数,Nelem是网格单元数。但是在采用高精度方法求解大尺度流动问题时,显式时间积分方法的时间步长比传统显式方法的时间步长还要小,极大影响了收敛速率。因此,我们只能选择稳定性不受时间步长限制的隐式时间格式,很多学者对隐式间断伽辽金方法进行了研究[48, 90, 146-147]。而采用隐式方法计算时,不仅需要保存右端残值项,往往还需对雅可比矩阵进行保存,该矩阵规模为(Ndegr×Netol×Nelem)2。可见雅可比矩阵的存储规模远大于右端残值项。
一些方法被用来解决上述大型雅可比矩阵的存储问题。考虑到该存储矩阵为稀疏矩阵,仅对非零元进行存储可以将存储量降为
另外,计算过程中产生的大型线性方程组系统的求解也非常值得讨论[47-48]。目前常用的有直接求解方法、高斯迭代,高斯赛德尔迭代、LU-SGS方法及Krylov子空间方法等[147, 149-150]。此外,间断伽辽金方法所特有的hp-adaptivity[105-106]和p-multigrid[155]加速收敛方法也是研究的热点之一。
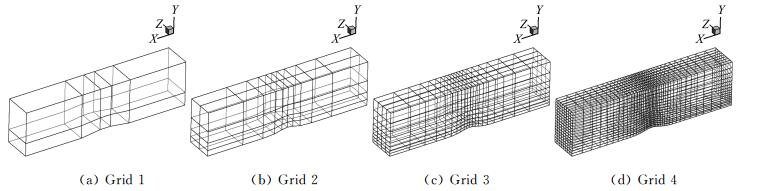
4 间断伽辽金方法的应用举例 4.1 三维带凸起管道流动采用三维带凸起管道流动对三维欧拉方程程序进行精度验证。该问题为内流问题,来流条件为Ma∞=0.5。管道的长、宽和高分别为3、0.5和0.8,管道下表面x=-1.5到x=1.5之间存在凸起,该凸起的函数描述为y=0.0625e-25x2。采用欧拉方程进行计算,管道底面设置为滑移边界条件,两侧设置为对称边界条件,其余面设置为特征边界条件。文中采用四套连续加密的网格进行数值计算,网格点数由疏到密分别为6×3×2、11×5×3、21×9×5和41×17×9(图 1)。网格均采用结块二阶网格进行数值计算。
|
图 1 三维带凸起管道流动计算网格 Figure 1 Mesh for three-dimensional tube with protuberance computation |
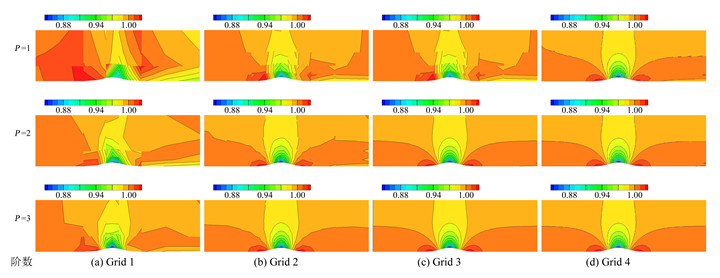
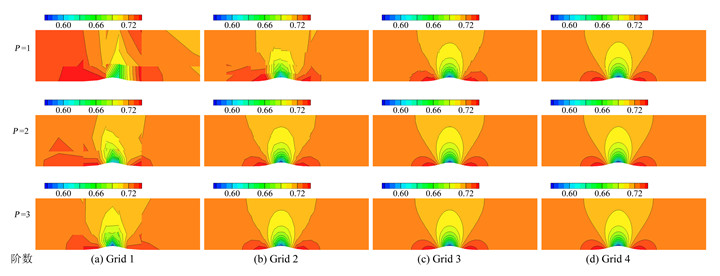
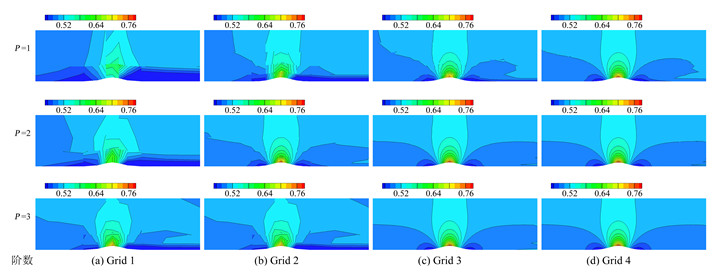
图 2、图 3和图 4分别给出了四套网格上不同阶数情况下计算得到的密度云图,压力云图及马赫数云图结果。横向对比为网格加密,纵向对比为阶数提高。可以发现,计算结果随着网格加密或者计算阶数的提高变得越来越光滑。在相对稀疏的网格上采用高阶方法即可得到较好的数值结果。
|
图 2 四套网格上的计算密度云图 Figure 2 Density contours on four mesh types |
|
图 3 四套网格上的计算压力云图 Figure 3 Pressure contours on four mesh types |
|
图 4 四套网格上的计算马赫数云图 Figure 4 Mach number contours on four mesh types |
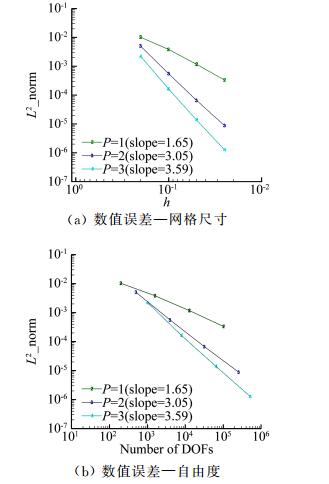
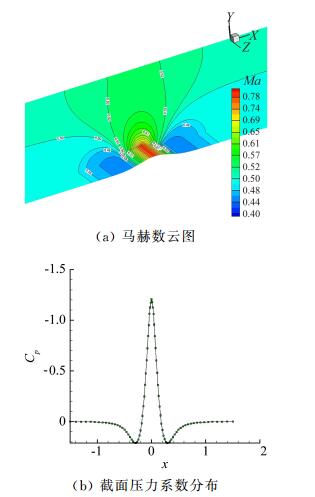
表 1给出了本算例的数值精度计算结果。由于本算例为等熵流动,与二维圆柱绕流算例一样,文中采用熵增的L2误差作为误差计算的标准。从计算结果可以看出,该算例误差为O(hp+1),基本达到了预期的精度。图 5三维带凸起管道流动问题精度测试给出了本算例的数值误差-网格尺寸曲线及数值误差-自由度曲线,可以看出,本文发展的三维DG有限元方法计算程序基本达到了格式的预期计算精度。采用高阶方法进行计算,数值误差下降的速率比低精度更快。在同等自由度情况下对光滑流场进行计算时,采用高阶方法产生的数值误差比低阶方法更小,验证了高阶方法在光滑流场计算中的优势。图 6三维带凸起管道流动流场计算结果为最密的网格上计算得到的马赫数云图及Z=0截面的压力系数Cp的分布。可以看出,流场的计算结果较为光滑,截面得到的压力系数分布较为对称,验证了文中三维DG欧拉方程计算程序的可靠性。
| 表 1 三维带凸起管道流动问题的精度验证 Table 1 Accuracy analysis for three-dimensional tube with a protuberance |
|
|
|
图 5 三维带凸起管道流动问题精度测试 Figure 5 Accuracy analysis for three-dimensional tube with a protuberance |
|
图 6 三维带凸起管道流动流场计算结果 Figure 6 Flowfields and pressure distribution |
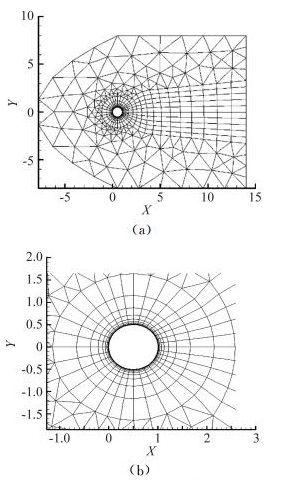
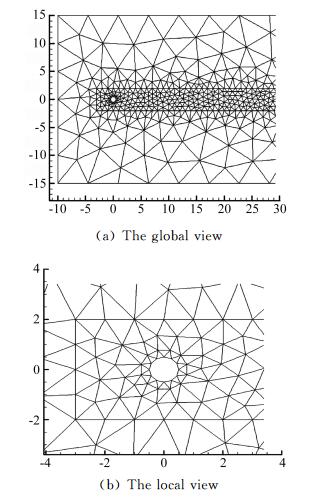
计算来流参数为Ma∞=0.2,Re=3×106,第一层网格高度为8×10-6,y+≈1,物理时间步长无量纲后取值为Δt*=Δt×a/D=0.2。计算区域X方向[-8D, 15D],Y方向[-8D, 8D],物面布点仅有36个,网格数总量为1105,其中结构网格834个单元。在此雷诺数下可以认为圆柱尾部分离流动已经变为湍流分离。图 7为圆柱绕流计算网格。
|
图 7 圆柱绕流计算网格 Figure 7 Mesh for flow past a cylinder |
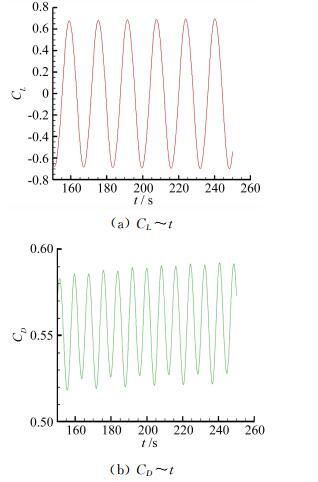
图 8为升力系数、阻力系数随时间的变化,都表现出了良好的周期性。因为二维圆柱没有三维圆柱展向流动,所以非定常流场稳定以后变化幅值为固定值。
|
图 8 CL和CD随时间变化图 Figure 8 Variation of the lift and drag coefficient |
如图 9所示,将五阶精度(DG_p4) 结果取七个周期计算结果平均后的平均压力系数、摩擦系数分布与Achenbach[151]的实验结果进行了对比,两者雷诺数略有差别,但总体趋势吻合程度较好;与Travin[152]基于有限体积法的三维DES结果和Nyugen[153]基于DG的二维DES和二维URANS的结果进行了对比,两者计算的的网格量分别为41万、1.8万。Nyugen虽然也采用了DG方法,但是只达到了P2阶数,也就是三阶空间精度,本文则达到了五阶空间精度。因为雷诺数较高时,圆柱会存在展向间的流动,二维和三维计算结果会有所差异。但是相比Nyugen的结果,本文结果在尾部流动区域结果更趋向合理。摩擦系数和三维DES计算结果也十分接近,尾部流动分离区域模拟结果也更加接近实验值。即使在稀疏网格下,随着阶数提高精度增加,高阶间断有限元法依然可以对分离流动做到极佳的模拟。对比Nyugen的三阶精度计算结果,本文通过提高阶数的方法,相比其提高网格数带来的精度提高效果要更加显著。
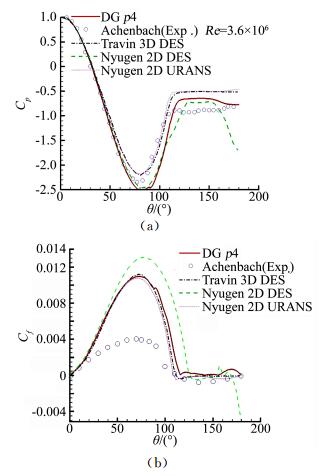
|
图 9 平均压力分布和平均阻力分布结果对比 Figure 9 Averaged pressure and drag distribution |
从图 10中也可以看出,在p1时候,尾迹区没有分离,在进入p2以后, 流场发生了巨大的改变,开始出现明显的周期性的脱落涡。体现了精度提高对流场模拟结果的改善是巨大的。并且随着阶数的继续提高,脱落涡的耗散也被降低,在远场区域也越发明显。
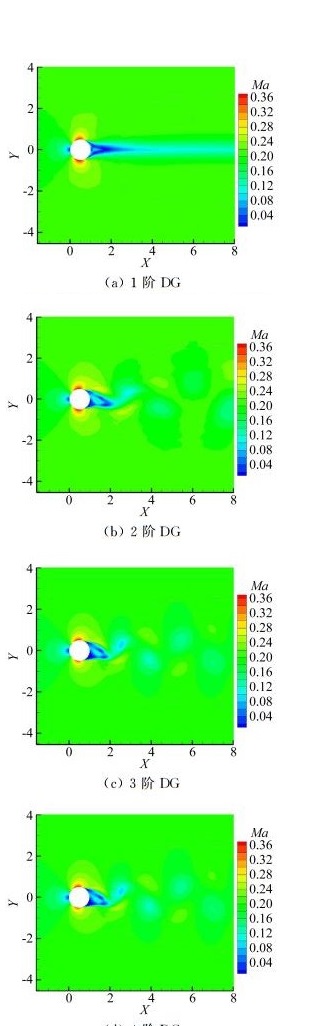
|
图 10 Cl=0时1阶到4阶DG马赫数云图 Figure 10 Mach number contours of different orders while Cl=0 |
图 11为二维URANS计算结果,采用的是SA模型。在采用RANS模型进行计算时,因为湍流模型原因,抑制了尾部的分离流动,未形成周期性的涡街,整体流动转变为定常流动。而在采用二维DES时,可以对圆柱绕流的分离进行准确的捕捉,说明在二维情况下,对长度尺度的修改依然是有效的,有效提高了对分离流动的模拟。
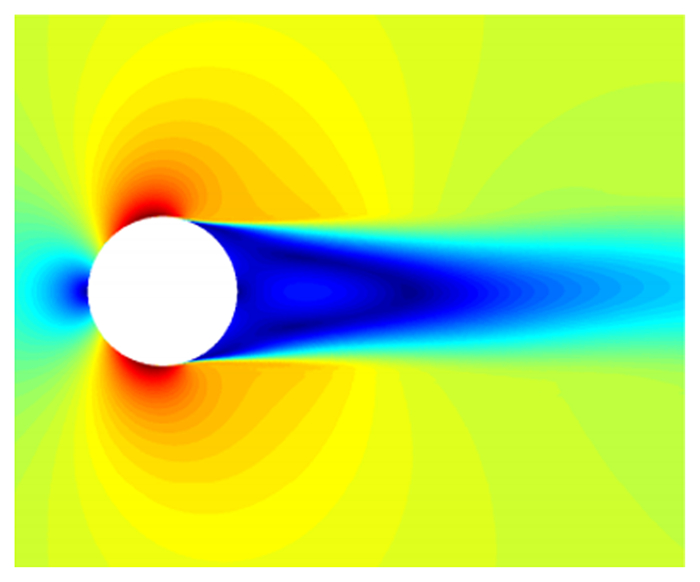
|
图 11 二维URANS计算结果 Figure 11 Numerical result obtained using two-dimensional URANS |
我们采用非结构自适应网格方法对卡门涡街问题进行了模拟,远场来流Ma=0.1, α=0, Re=150。初始网格如图 12所示,计算域仅包含1114个单元,并且物面仅有12个网格点。
|
图 12 初始网格 Figure 12 The initial mesh |
图 13为p4在初始网格上得到的卡门涡街涡量图,从图中可以看出由于初始网格比较稀疏,得到的涡量云图不是很光滑并且涡的量级都比较小,我们可以认为在稀疏网格条件下,即使采用高阶格式依然得不到高精度的流场数值解,主要原因在于大尺度的网格导致的数值耗散。
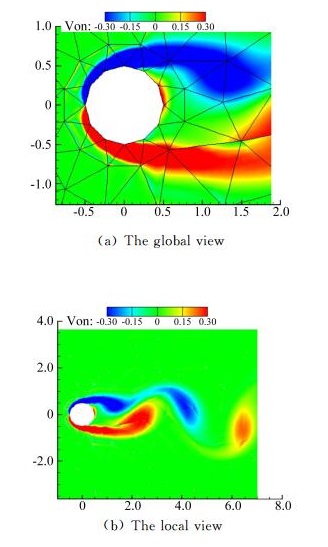
|
图 13 初始网格上的卡门涡街 Figure 13 The Von Karman vortex street on initial mesh |
图 14给出了网格自动加密后的卡门涡街涡量云图。由于在边界层和涡街区域的网格自动加密,数值耗散降低,数值结果变得非常光滑。并且应当注意到,网格自适应过程中生成了包含大量悬挂点、尺度差别悬殊的非结构网格,但是结果并没有对间断伽辽金方法的稳定性和精度产生严重的影响,证明了间断伽辽金方法能够有效地处理具有复杂形状、质量参差不齐的网格。
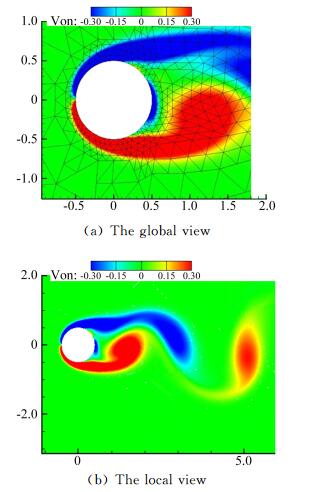
|
图 14 自适应处理后的卡门涡街 Figure 14 The Von Karman vortex street with adaptive method |
图 15为随时间变化卡门涡街脱落,网格自动在涡局部进行加密,在涡量很小的地方放粗的动态结果。对比图 16可以看出,由于卡门涡街是一个准定常问题,流场周期性变化,网格自适应后总量变化不大,验证了自适应方法的可行性。
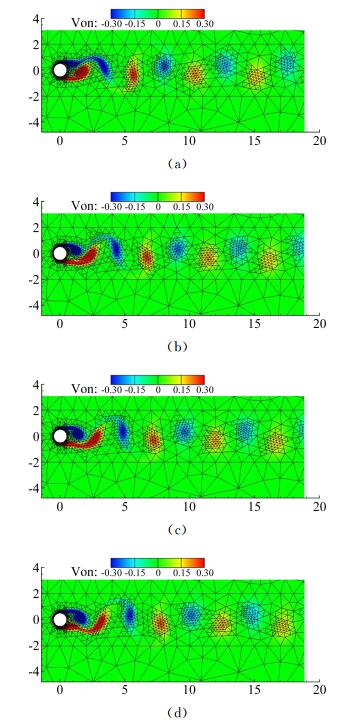
|
图 15 带有网格自适应的卡门涡街 Figure 15 The Von Karman vortex street with mesh adaptivity |
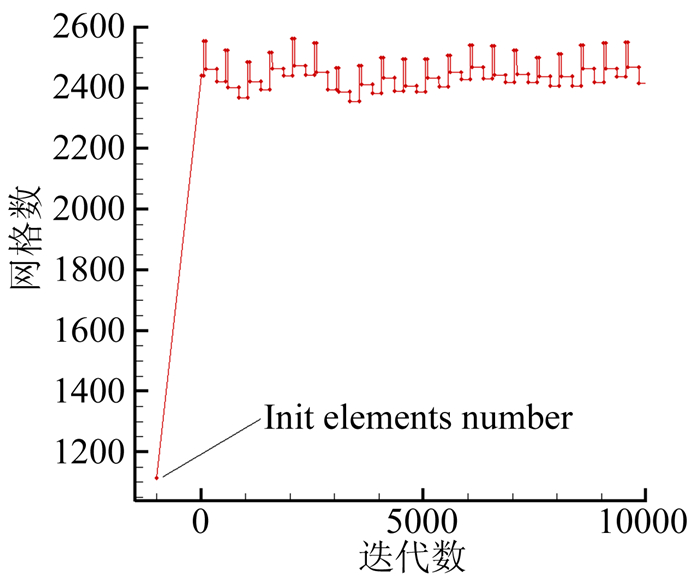
|
图 16 迭代过程中网格数量变化 Figure 16 Number of elements during the iteration |
图 17为物面加密后升力系数和阻力系数随时间的变化,在表 2中与参考文献[154]进行了对比,可以看出加入自适应方法后,即使在很稀疏的初始网格条件下,依然可以得到高精度的数值解结果。
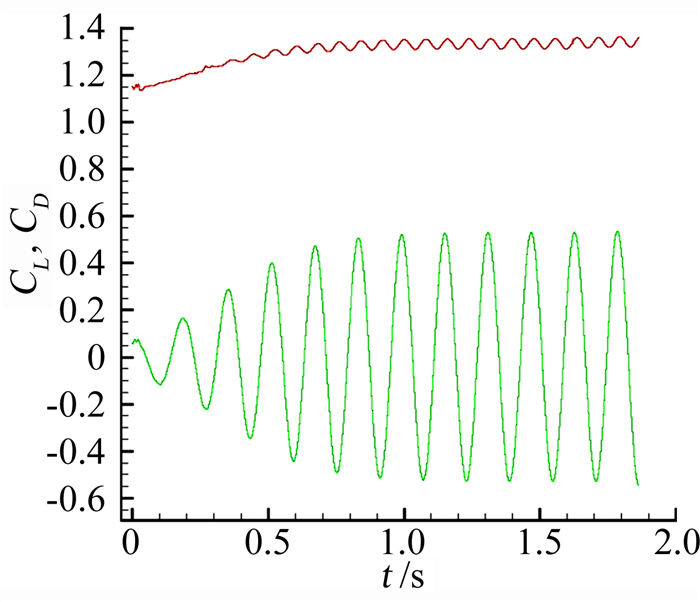
|
图 17 升力与阻力系数波动 Figure 17 Variation of the lift and drag coefficient |
| 表 2 升力与阻力系数对比 Table 2 Comparison between lift and drag coefficient |
|
|
本文总结了自20世纪末期以来间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流数值模拟中的应用研究进展。首先,从间断伽辽金方法的基本概念出发,集中介绍了间断伽辽金方法在可压缩流计算中的国内外研究历史和现状;其次,较为详细地列举分析了间断伽辽金方法在实际应用中面临的挑战和困难;最后,给出了数个典型的算例,展示了间断伽辽金方法在高精度、网格自适应等方面的优势。
经过近二十年的发展,间断伽辽金方法数值求解Euler方程、N-S方程方面有了显著的进步,出现了大量成功的尝试和令人鼓舞的结果,高阶情况下其数值结果表现出来的高精度特性尤其令人印象深刻。然而高阶离散带来的高度非线性也显著增加了迭代求解方面的难度和对弯曲网格精度方面的要求。目前高效、鲁棒的求解复杂流场情况下高阶离散非线性系统是研究的热点问题。相信随着相关技术的进一步发展,高阶间断伽辽金方法会成为复杂流场高精度数值模拟领域的有力工具。
| [1] |
Deng X, Zhang H. Developing high-order weighted compact nonlinear schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 165(1): 22-44. DOI:10.1006/jcph.2000.6594 (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang H, et al. A new class of central compact schemes with spectral-like resolution Ⅰ:Linear schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 248(5): 235-256. (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang H, et al. A new class of central compact schemes with spectral-like resolution Ⅱ:Hybrid weighted nonlinear schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 248(5): 235-256. (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Jiang G S, Shu C W. Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1996, 126(1): 202-228. DOI:10.1006/jcph.1996.0130 (  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Shu C W. Essentially non-oscillatory and weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws[M]. Institute for Computer Applications in Science and Engineering (ICASE), 1997.
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
Timothy J Barth. Recent developments in high order K-exact reconstruction on unstructured meshes[C]//31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, 1993. https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/abs/10.2514/6.1993-668
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
Wang Q, Ren Y X, Li W. Compact high order finite volume method on unstructured Grids Ⅰ:Basic formulations and one-dimensional schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 314: 863-882. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2016.01.036 (  0) 0) |
| [8] |
Wang Q, Ren Y X, Li W. Compact high order finite volume method on unstructured Grids Ⅱ:Extension to two-dimensional Euler equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 314: 883-908. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2016.03.048 (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Wang Q, Ren Y X, Pan J, et al. Compact high order finite volume method on unstructured Grids Ⅲ:Variational reconstruction[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 337: 1-26. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2017.02.031 (  0) 0) |
| [10] |
Reed W H, Hill T R. Triangular mesh methods for the neutron transport equation[R]. Technical Report LA-UR-73-479, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, 1973.
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
Wang Z J, Liu Y. Spectral (finite) volume method for conservation laws on unstructured grids[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2004, 194(2): 716-741. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2003.09.012 (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
Wang Z J, Liu Y. Extension of the spectral volume method to high-order boundary representation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2006, 211(1): 154-178. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.05.022 (  0) 0) |
| [13] |
Liu Y, Vinokur M, Wang Z J. Spectral difference method for unstructured grids Ⅰ:Basicformulation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2006, 216(2): 780-801. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2006.01.024 (  0) 0) |
| [14] |
Sun Y, Wang Z J, Liu Y. High-order multidomain spectral difference method for the Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2013, 2(2): 310-333. (  0) 0) |
| [15] |
Wang Z J, Liu Y, May G, et al. Spectral difference method for unstructured grids Ⅱ:extension to the Euler equations[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2007, 32(1): 45-71. DOI:10.1007/s10915-006-9113-9 (  0) 0) |
| [16] |
Allaneau Y, Jameson A. Connections between the filtered discontinuous Galerkin method and the flux reconstruction approach to high order discretizations[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 200(49): 3628-3636. (  0) 0) |
| [17] |
Gao H, Wang Z J. A conservative correction procedure via reconstruction formulation with the Chain-Rule divergence evaluation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 232(1): 7-13. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2012.08.030 (  0) 0) |
| [18] |
Deng X, Mao M, Tu G, et al. Extending weighted compact nonlinear schemes to complex grids with characteristic-based interface conditions[J]. Aiaa Journal, 2012, 48(12): 2840-2851. (  0) 0) |
| [19] |
Yu X J, Zhou T. Discontinuous finite element methods for solving hydrodynamic equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2005, 22(1): 108-116. (in Chinese) 蔚喜军, 周铁. 流体力学方程的间断有限元法[J]. 计算物理, 2005, 22(2): 108-116. (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
Lu H Q. High-order finite element solution of elastohydrodynamic lubrication problems[D]. PhD thesis. Leeds:University of Leeds, 2006. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.216.8401
(  0) 0) |
| [21] |
Cheng J, Shu C W. High order schemes for CFD:A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2009, 26(5): 633-655. (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
Sun Q, Lu H Q. A straightforward hp-adaptivity strategy for shock-capturing with high-order discontinuous Galerkin methods[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics & Mechanics, 2014, 6(1): 135-144. (  0) 0) |
| [23] |
Sun Q, Lu H Q, Wu Y Z. An h-adaptive discontinuous Galerkin method for laminar compressible Navier-Stokes equations on curved mesh[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 33(5): 566-575. (  0) 0) |
| [24] |
Chavent G, Salzano G. A finite element method for the 1D water flooding problem with gravity[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1982, 42: 307-344. (  0) 0) |
| [25] |
Cockburn B, Shu C W. The Runge-Kutta local projection p1-discontinuous Galerkin method for scalar conservation laws[J]. ESAIM:Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis, 1991, 25(3): 337-361. DOI:10.1051/m2an/1991250303371 (  0) 0) |
| [26] |
Cockburn B, Shu C W. TVB Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for scalar conservation laws Ⅱ:General framework[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1989, 52: 411-435. (  0) 0) |
| [27] |
Cockburn B, Lin S Y, Shu C W. TVB Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws Ⅲ:One dimensional systems[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1989, 84: 90-113. DOI:10.1016/0021-9991(89)90183-6 (  0) 0) |
| [28] |
Cockburn B, Hou S, Shu C W. Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws Ⅳ:The multidimensional case[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1990, 54: 545-581. (  0) 0) |
| [29] |
Cockburn B, Shu C W. The Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws Ⅴ:Multidimensional systems[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1998, 141: 199-224. DOI:10.1006/jcph.1998.5892 (  0) 0) |
| [30] |
Cockburn B, Karniadakis G E, Shu C W. The development of discontinuous Galerkin methods[M]//Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2000:3-50.
(  0) 0) |
| [31] |
Shu C W, Osher S. Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shockc apturing schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1988, 77: 439-471. DOI:10.1016/0021-9991(88)90177-5 (  0) 0) |
| [32] |
Allmaras S R. A coupled Euler/Navier-Stokes algorithm for 2-D unsteady transonic shock/boundary-layer interaction[D]. PhD thesis. Massachusetts:Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1989. http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/14457
(  0) 0) |
| [33] |
Allmaras S R, Giles M B. A second-order flux split scheme for the unsteady 2-D Euler equations on arbitrary meshes[R]. AIAA 1987-1119, 1987.
(  0) 0) |
| [34] |
Arnold D N. An interior penalty finite element method with discontinuous elements[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 1982, 19: 742-760. DOI:10.1137/0719052 (  0) 0) |
| [35] |
Wheeler M. An elliptic collocation-finite element method with interior penalties[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 1978, 15: 152-161. DOI:10.1137/0715010 (  0) 0) |
| [36] |
Oden J T, Babuska, et al. A discontinuous hp finite element method for diffusion problems[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1998, 146(2): 491-519. DOI:10.1006/jcph.1998.6032 (  0) 0) |
| [37] |
Bassi F, Rebay S. High-order accurate discontinuous finite element solution of the 2D Euler equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 138: 251-285. DOI:10.1006/jcph.1997.5454 (  0) 0) |
| [38] |
Bassi F, Rebay S. A high-order discontinuous finite element method for the numerical solution of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 131: 267-279. DOI:10.1006/jcph.1996.5572 (  0) 0) |
| [39] |
Bassi F, Rebay S. GMRES discontinuous Galerkin solution of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[M]. Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2000, 197-208.
(  0) 0) |
| [40] |
Bassi F, Rebay S. Discontinuous Galerkin solution of the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes and k-ω turbulence model equations[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2005, 34(4-5): 507-540. (  0) 0) |
| [41] |
Cockburn B, Shu C W. The local discontinuous Galerkin method for time dependent convection-diffusion systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 1998, 35(6): 2440-2463. DOI:10.1137/S0036142997316712 (  0) 0) |
| [42] |
Cockburn B, Shu C W. Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods for convection-dominated problems[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2001, 16(3): 173-261. DOI:10.1023/A:1012873910884 (  0) 0) |
| [43] |
Peraire J, Persson P O. The compact discontinuous Galerkin (CDG) method for elliptic problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2008, 30: 1806-1824. DOI:10.1137/070685518 (  0) 0) |
| [44] |
Arnold D N, Brezzi F, Cockburn B, et al. Unified analysis of discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptical problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2002, 39(5): 1749-1779. DOI:10.1137/S0036142901384162 (  0) 0) |
| [45] |
Liu H L, Yue J. The direct discontinuous Galerkin (DDG) methods for diffusion problems[J]. SIAM J. Numer. Anal, 2009, 47: 675-698. DOI:10.1137/080720255 (  0) 0) |
| [46] |
Liu H L, Yue J. The direct discontinuous Galerkin (DDG) method for diffusion with interface corrections[J]. Commun. Comput. Phys., 2010, 8: 541-564. (  0) 0) |
| [47] |
Diosady L. A linear multigrid preconditioner for the solution of the Navier-Stokes equations using a discontinuous Galerkin discretization[D]. Massachusetts:Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [48] |
Diosady L, Darmofal D. Discontinuous Galerkin solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations using linear multigrid preconditioning[R]. AIAA 2007-3942, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [49] |
Lübon C, Kessler M, Wagner S, et al. High-order boundary discretization for discontinuous Galerkin codes[R]. AIAA 2006-2822, 2006.
(  0) 0) |
| [50] |
Christian Lübon, Manuel Kessler, Siegfried Wagner. Turbulence modeling and detached eddy simulation with a high-order unstructured discontinuous Galerk code[A]. Andreas Dillmann, Gerd Heller, Michael Klaas, et al, New Results in Numerical and Experimental Fluid Mechanics Ⅶ[M], Berlin:Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010:143-150.
(  0) 0) |
| [51] |
Lubon C, Keβler M, Wagner S. A parallel CFD solver using the discontinuous Galerkin approach[A]. Siegfried Wagner, Matthias Steinmetz, Arndt Bode, et al. High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering[M], Berlin:Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009:197-205.
(  0) 0) |
| [52] |
Krzysztof J Fidkowski. A simplex cut-cell adaptive method for high-order discretizations of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[D]. PhD thesis. Massachusetts:Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [53] |
Krzysztof J Fidkowski, David L Darmofal. An adaptive simplex cut-cell method for discontinuous Galerkin discretizations of the Navier-Stokes equations[R]. AIAA 2007-3941, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [54] |
Steven M Kast, Krzysztof J Fidkowski. Output-based mesh adaptation for high order Navier-Stokes simulations on deformable domains[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 252(1): 468-494. (  0) 0) |
| [55] |
Ceze M A, Fidkowski K J. Drag prediction using adaptive discontinuous finite elements[J]. AIAA Journal of Aircraft, 2014, 51(4): 1284-1294. DOI:10.2514/1.C032622 (  0) 0) |
| [56] |
Oliver T, Darmofal D. An unsteady adaptation algorithm for discontinuous Galerkin discretizations of the RANS equations[R]. AIAA 2007-3940:2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [57] |
Oliver T A, Fidkowski K J, Darmofal D L. MultiGrid solution for high-order discontinuous Galerkin discretizations of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[M]. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006.
(  0) 0) |
| [58] |
Oliver T A. A high-order, adaptive, discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations[D]. PhD thesis. Massachusetts:Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2008.
(  0) 0) |
| [59] |
Wang Li. Techniques for high-order adaptive discontinuous Galerkin discretizations in fluid dynamics[D]. PhD thesis. Wyoming:University of Wyoming, 2009.
(  0) 0) |
| [60] |
Wang L, Dimitri J Mavriplis. Implicit solution of the unsteady euler equations for high-order accurate discontinuous Galerkin discretizations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2007, 225(2): 1994-2015. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2007.03.002 (  0) 0) |
| [61] |
Wang L, Mavriplis D J. Adjoint-based h-p adaptive discontinuous Galerkin methods for the compressible Euler equations[R]. AIAA 2009-0952, 2009.
(  0) 0) |
| [62] |
Wang L, Mavriplis D J, Kyle Anderson W. Adjoint sensitivity formulation for discontinuous Galerkin discretizations in unsteady inviscid flow problems[J]. AIAA Journal, 2010, 48(12): 2867-2883. DOI:10.2514/1.J050444 (  0) 0) |
| [63] |
Wang L, Kyle Anderson W. Adjoint based shape optimization for electromagnetic problems using discontinuous Galerkin methods[J]. AIAA Journal, 2011, 49(6): 1302-1305. DOI:10.2514/1.J050594 (  0) 0) |
| [64] |
Wang L, Anderson W K, Erwin J T, et al. Solutions of high-order methods for three-dimensional compressible viscous flows[R]. AIAA 2012-2836, 2012.
(  0) 0) |
| [65] |
Wang L, Anderson W K, Taylor Erwin, et al. High-order methods for solutions of three-dimensional turbulent flows[R]. AIAA 2013-0856, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [66] |
Burgess N K. An adaptive discontinuous Galerkin solver for aerodynamic flows[D]. PhD thesis. Wyoming:University of Wyoming, 2011.
(  0) 0) |
| [67] |
Burgess N K, Mavriplis D J. Robust computation of turbulent flows using a discontinuous Galerkin method[R]. AIAA 2012-0457, 2012.
(  0) 0) |
| [68] |
Mavriplis D, Nastase C, Burgess N. Efficient solution techniques for discontinuous Galerkin discretizations of the Navier-Stokes equations on hybrid anisotropic meshes[R]. AIAA 2010-1448, 2010.
(  0) 0) |
| [69] |
Burgess N K, Mavriplis D J. High-order discontinuous Galerkin methods for turbulent high-lift flows[C]//ICCFD7-4202, 2012.
(  0) 0) |
| [70] |
IDIHOM:Industrialization of high-order methods-a top-down approach:results of a collaborative research project funded by the European union, 2010-2014[M]. Springer, 2015.
(  0) 0) |
| [71] |
Bassi F, De Bartolo C, Hartmann R. A discontinuous Galerkin method for inviscid low Mach number flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2009, 228(11): 3996-4011. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2009.02.021 (  0) 0) |
| [72] |
Crivellini A, D'Alessandro V, Bassi F. A Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model implementation in a discontinuous Galerkin solver for incompressible flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 241: 388-415. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2012.12.038 (  0) 0) |
| [73] |
Landmann B, Kessler M, Wagner S. A parallel, high-order discontinuous Galerkin code for laminar and turbulent flows[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2008, 37(4): 427-438. (  0) 0) |
| [74] |
Landmann B. A parallel discontinuous Galerkin code for the Navier-Stokes and Reynolds -averaged Navier-Stokes equations[D]. PhD thesis. Stuttgart:University of Stuttgart, 2008.
(  0) 0) |
| [75] |
Persson P, Bonet J, Peraire J. Discontinuous Galerkin solution of the Navier-Stokes equations on deformable domains[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 198(17): 1585-1595. (  0) 0) |
| [76] |
Peraire J, Drela M, Persson P. Implicit large eddy simulation of transition to turbulence at low Reynolds numbers using a discontinuous Galerkin method[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2011, 87: 232-261. DOI:10.1002/nme.v87.1/5 (  0) 0) |
| [77] |
Willis D, Persson P. Multiple-fidelity computational framework for the design of efficient flapping wings[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(12): 2840-2854. DOI:10.2514/1.J052997 (  0) 0) |
| [78] |
Gao H, Wang Z J, Huynh H T. Differential formulation of discontinuous Galerkin and related methods for the Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2013, 13(4): 1013-1044. DOI:10.4208/cicp.020611.090312a (  0) 0) |
| [79] |
Zhou C, Wang Z J. An evaluation of implicit time integration schemes for discontinuous high order methods[R]. AIAA 2013-2688, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [80] |
Yu Z, Wang J. Homotopy continuation for correction procedure via reconstruction-discontinuous Galerkin (CPR-DG) methods[R]. AIAA 2015-0570, 2015.
(  0) 0) |
| [81] |
Zhu H, Fu S, Shi L, et al. A hybrid RANS-implicit LES approach for the high-order FR/CPR method[R]. AIAA 2016-1599, 2016.
(  0) 0) |
| [82] |
Hartmann R. Adaptive discontinuous Galerkin methods with shock-capturing for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, 2006, 51(9-10): 1131-1156. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0363 (  0) 0) |
| [83] |
Hartmann R, Held J, Leicht T, et al. Discontinuous Galerkin methods for computational aerodynamics-3D adaptive flow simulation with the DLR PADGE code[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2010, 14: 512-519. DOI:10.1016/j.ast.2010.04.002 (  0) 0) |
| [84] |
Nigro A, Renda S, C.De Bartolo, et al. A high-order accurate discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for laminar low Mach number flows[J]. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, 2013, 72(1): 43-68. DOI:10.1002/fld.3732 (  0) 0) |
| [85] |
Schoenawa S, Hartmann R. Discontinuous Galerkin discretization of the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations with the shear-stress transport model[J]. J. Comput. Phys, 2014, 262: 194-216. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2013.12.062 (  0) 0) |
| [86] |
Renda S, Hartmann R, C.De Bartolo, et al. A high-order discontinuous Galerkin method for all-speed flows[J]. Int. J. Num. Meth. Fluids, 2015, 77(4): 224-247. DOI:10.1002/fld.v77.4 (  0) 0) |
| [87] |
van Leer B, Lo M, van Raalte M. A discontinuous Galerkin method for diffusion based on recovery[C]//18th AIAA computational fluid dynamics conference. 2007:4083.
(  0) 0) |
| [88] |
Dumbser M, Valsara D S, Toro E F, et al. A unified framework for the construction of one-step finite volume and discontinuous Galerkin schemes on unstructured meshes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2008, 227: 8209-8253. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2008.05.025 (  0) 0) |
| [89] |
Luo H, Luo L, Nourgaliev R, et al. A reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations on arbitrary grids[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2010, 229: 6961-6978. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2010.05.033 (  0) 0) |
| [90] |
Luo H, Ali A, Nourgaliev R, et al. A parallel, reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method for the compressible flows on arbitrary grids[J]. Communication in Computational Physics, 2011, 9(2): 363-389. DOI:10.4208/cicp.070210.020610a (  0) 0) |
| [91] |
Luo H, Xia Y, Li S, et al. A Hermite WENO reconstruction-based discontinuous Galerkin method for the Euler equations on tetrahedral grids[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2012, 231: 5489-5503. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2012.05.011 (  0) 0) |
| [92] |
Xia Yidong. A parallel implicit reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible flows on hybrid grids[D]. PhD thesis. North Carolina State:North Carolina State University, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [93] |
Xia Y, Frisbey M, Luo H, et al. A WENO Reconstruction-based discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible flows on hybrid grids[R}. AIAA 2013-0516, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [94] |
Xia Y, Luo H, Nourgaliev R. An implicit reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method based on automatic di_erentiation for the Navier-Stokes equations on tetrahedron grids[R]. AIAA 2013-0687, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [95] |
Xia Y, Luo H, Frisbey M, et al. A set of parallel, implicit methods for a reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible flows on 3D hybrid grids[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2014, 98: 134-151. (  0) 0) |
| [96] |
Wu Di, Yu Xijun. Adaptive discontinuous Galerkin method for Euler equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2010, 27(4): 492-500. (in Chinese) 吴迪, 蔚喜军. 自适应间断有限元方法求解三维欧拉方程[J]. 计算物理, 2010, 27(4): 492-500. (  0) 0) |
| [97] |
Li Zhenzhen, Yu Xijun, Zhao Guozhong, et al. A RKDG finite element method for Lagrangian Euler equations in one dimension[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2014, 31(1): 1-10. (in Chinese) 李珍珍, 蔚喜军, 赵国忠, 等. RKDG有限元法求解一维拉格朗日形式的Euler方程[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(1): 1-10. (  0) 0) |
| [98] |
Li Zhenzhen, Yu Xijun, Jia Zupeng, et al. A new second-order bound-preserving conservative remapping algorithm in the ALE method[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2015, 33(6): 765-786. (in Chinese) 李珍珍, 蔚喜军, 贾祖朋, 等. ALE方法中一种新的二阶保界守恒重映算法[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2015, 33(6): 765-786. (  0) 0) |
| [99] |
Qiu J, Shu C W. Hermite WENO schemes and their application as limiters for Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method Ⅱ:Two dimensional case[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2005, 34: 642-663. (  0) 0) |
| [100] |
Qiu J, Khoo B C, Shu C W. A numerical study for the performance of the Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method based on different numerical fluxes[J]. J. Comput. Phys., 2006, 212: 540-565. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.07.011 (  0) 0) |
| [101] |
Lu C, Qiu J, Wang R. A numerical study for the performance of the WENO schemes based on different numerical fluxes for the shallow water equations[J]. J. Comp. Math., 2010, 28: 807-825. (  0) 0) |
| [102] |
Zhu J, Zhong X, Shu C W, et al. Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method using a new type of WENO limiters on unstructured mesh[J]. J. Comput. Phys., 2013, 248: 200-220. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2013.04.012 (  0) 0) |
| [103] |
Zhu J, Qiu J. Adaptive Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods with the modified ghost fluid method for solving the compressible two-medium flow[J]. J. Math. Study, 2014, 47: 250-273. (  0) 0) |
| [104] |
Zhu J, Zhong X, Shu C W, et al. Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method with a simple and compact Hermite WENO limiter[J]. Commun. Comput. Phys., 2016, 19: 944-969. DOI:10.4208/cicp.070215.200715a (  0) 0) |
| [105] |
Lu H, Berzins M, Goodyer C E, et al. Adaptive high-order discontinuous Galerkin solution of elastohydrodynamic lubrication point contact problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2012, 45(1): 313-324. DOI:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.10.006 (  0) 0) |
| [106] |
Lu H Q, Berzins M, Goodyer C E, et al. High order discontinuous Galerkin method for elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact problems[J]. Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 21(11): 643-650. DOI:10.1002/cnm.781 (  0) 0) |
| [107] |
Moro D, Nguyen N C, Peraire J. Navier-stokes solution using hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods[R]. AIAA 2011-3407, 2011.
(  0) 0) |
| [108] |
Lu Hongqiang, Wu Yizhao, Zhou Chunhua, et al. High resolution of subsonic flows on coarse Grids[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(2): 200-204. (in Chinese) 吕宏强, 伍贻兆, 周春华, 等. 稀疏非结构网格上的亚声速流高精度数值模拟[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(2): 200-204. (  0) 0) |
| [109] |
Xia Yidong, Wu Yizhao, Lu Hongqiang, et al. Parallel computation of a high-order discontinuous Galerkin method on unstructured grids[J]. Acta Aerodynanamica Sinica, 2011, 29(5): 537-541. (in Chinese) 夏轶栋, 伍贻兆, 吕宏强, 等. 高阶间断有限元法的并行计算研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2011, 29(5): 537-541. (  0) 0) |
| [110] |
Qin Wanglong, Lu Hongqiang, Wu Yizhao. High-order discontinuous Galerkin solution of N-S equations on hybrid mesh[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2013, 45(6): 987-991. (in Chinese) 秦望龙, 吕宏强, 伍贻兆. 基于混合网格的高阶间断有限元黏流数值解法[J]. 力学学报, 2013, 45(6): 987-991. DOI:10.6052/0459-1879-13-151 (  0) 0) |
| [111] |
Qin Wanglong, Lu Hongqiang, Wu Yizhao. Discontinuous Galerkin solution of RANS equatioins on curved mesh[J]. Acta Aerodynanamica Sinica, 2014, 32(5): 581-586. (in Chinese) 秦望龙, 吕宏强, 伍贻兆. 弯曲网格上的间断有限元湍流数值解法研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2014, 32(5): 581-586. DOI:10.7638/kqdlxxb-2014.0058 (  0) 0) |
| [112] |
Sun Qiang, Lu Hongqiang, Wu Yizhao. Adaptive discontinuous Galerkin method to solve Euler equations based on high-order approximative boundary[J]. Acta Aerodynanamica Sinica, 2015, 33(5): 446-453. (in Chinese) 孙强, 吕宏强, 伍贻兆. 基于高阶物面近似的自适应间断有限元法欧拉方程数值模拟[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2015, 33(4): 446-453. (  0) 0) |
| [113] |
Lu Hongqiang, Xu Yida, Gao Yukun, et al. A CFD-based high-order discontinuous Galerkin solver for three dimensional electromagnetic scattering problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2015, 83: 1-10. DOI:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.001 (  0) 0) |
| [114] |
Chen Eryun, Ma Dawei, Le Guigao, et al. Discontinuous finite element method for supersonic flow of a missile propulsive jet[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2008, 25(6): 705-710. (in Chinese) 陈二云, 马大为, 乐贵高, 等. 间断有限元法在弹尾超声速喷流计算中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(6): 705-710. (  0) 0) |
| [115] |
Chen Eryun, Zhao Gaiping, Yang Ailing, et al. Higher-order nodal discontinuous Galerkin method in computational aeroacoustics[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(3): 168-171. (in Chinese) 陈二云, 赵改平, 杨爱玲, 等. 计算气动声学中的高阶Nodal-DG方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(3): 168-171. (  0) 0) |
| [116] |
Chen eryun, Li Zhi, Ma Zunling, et al. Nodal discontinuous Galerkin method for aeroacoustics and comparison with finite difference schemes[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 31(3): 293-302. (  0) 0) |
| [117] |
Yan Chao, Yu Jian, Xu Jinglei, et al. On the achievements and prospects for the methods of computational fluid dynamics[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2011, 41(5): 562-589. (in Chinese) 阎超, 于剑, 徐晶磊, 等. CFD模拟方法的发展成就与展望[J]. 力学进展, 2011, 41(5): 562-589. DOI:10.6052/1000-0992-2011-5-lxjzJ2010-082 (  0) 0) |
| [118] |
Yu jian, Yan Chao. Study on discontinuous Galerkin method for Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(5): 962-969. (in Chinese) 于剑, 阎超. Navier-Stokes方程间断Galerkin有限元方法研究[J]. 力学学报, 2010, 42(5): 962-969. (  0) 0) |
| [119] |
Jiang Z, Yan C, Yu J. High-order discontinuous Galerkin solver on hybrid anisotropic meshes for laminar and turbulent simulations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2014, 35(7): 799-812. DOI:10.1007/s10483-014-1834-9 (  0) 0) |
| [120] |
Jiang Z, Yan C, Yu J. Hermite WENO-based limiters for high order discontinuous Galerkin method on unstructured grids[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2012, 28(2): 241-252. DOI:10.1007/s10409-012-0062-2 (  0) 0) |
| [121] |
Jiang Z, Yan C, Yu J. High-order implicit discontinuous Galerkin schemes for unsteady compressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2014, 27(6): 1384-1389. DOI:10.1016/j.cja.2014.10.004 (  0) 0) |
| [122] |
Yu J, Yan C, Jiang Z. On the use of the discontinuous Galerkin method for numerical simulation of two-dimensional compressible turbulence with shocks[J]. Science China-physics Mechanics & Astronomy, 2014, 57(9): 1758-1770. (  0) 0) |
| [123] |
Hao Haibing, Yang Yong, Zuo Suihan. Effectively applying high-order discontinuous Galerkin method(DGM) to solving 3-D Euler equations on unstructured grids[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2011, 29(1): 128-132. (in Chinese) 郝海兵, 杨永, 左岁寒. 高阶间断Galerkin方法求解三维欧拉方程的研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2011, 29(1): 128-132. (  0) 0) |
| [124] |
Li Xile, Yang Yong, Hao Haibing, et al. Exploring high-order accurate discontinuous Galerkin method for numerical solution of compressible reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes(RANS) equations[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2012, 30(3): 407-411. (in Chinese) 李喜乐, 杨永, 郝海兵, 等. 求解RANS方程的高阶间断Galerkin方法研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2012, 30(3): 407-411. (  0) 0) |
| [125] |
He Lixing, Zhang Laiping, Zhang Hanxin, et al. Discontinuous Galerkin finite element method on 3D arbitrary elements[J]. Acta Aerodynamics Sinica, 2007, 25(2): 157-162. (in Chinese) 贺立新, 张来平, 张涵信, 等. 任意单元间断Galerkin有限元计算方法研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2007, 25(2): 157-162. (  0) 0) |
| [126] |
He Lixin, Zhang Laiping, Zhang Hanxin, et al. A finite element/finite volume mixed solver on hybrid Grids[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2007, 39(1): 15-22. (in Chinese) 贺立新, 张来平, 张涵信, 等. 间断Galerkin有限元和有限体积混合计算方法研究[J]. 力学学报, 2007, 39(1): 15-22. (  0) 0) |
| [127] |
Liu Wei, Zhang Laiping, He Xin, et al. An implicit algorithm for discontinuous Galerkin method based on Newton/Gauss-Seidel iterations[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2012, 44(4): 792-796. (in Chinese) 刘伟, 张来平, 赫新, 等. 基于Newton/Gauss-Seidel迭代的DGM隐式方法[J]. 力学学报, 2012, 44(4): 792-796. (  0) 0) |
| [128] |
Zhang Laiping, Liu Wei, He Lixin, et al. High-order hybrid DG/FV schemes based on "static re-construction" and "dynamic re-construction" for two-dimensional conservation law[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2011, 28(2): 309-319. (in Chinese) 张来平, 刘伟, 贺立新, 等. 基于静动态重构的高阶DG/FV混合格式在二维非结构网格中的推广[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(2): 309-319. (  0) 0) |
| [129] |
Zhang Laiping, Liu Wei, He Lixin, et al. A class of discontinuous Galerkin/finite volume hybrid schemes based on the "static re-construction" and "dynamic re-construction"[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(6): 1013-1022. (in Chinese) 张来平, 刘伟, 贺立新, 等. 基于静动态混合重构的DG/FV混合格式[J]. 力学学报, 2010, 42(6): 1013-1022. (  0) 0) |
| [130] |
Zhang Laiping, Li Ming, Liu Wei, et al. Recent development of high order DG/FV hybrid methods[J]. Acta Aerodynamics Sinica, 2014, 32(6): 717-726. (in Chinese) 张来平, 李明, 刘伟, 等. 基于非结构/混合网格的高阶精度DG/FV混合方法研究进展[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2014, 32(6): 717-726. (  0) 0) |
| [131] |
Cheng J, Yang X Q, Liu T G, et al. A direct discontinuous Galerkin method for 2D compressible Navier-Stokes equations on arbitrary grid[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 327: 484-502. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2016.09.049 (  0) 0) |
| [132] |
Yang X Q, Cheng J, Wang C J, et al. A fast, implicit discontinuous Galerkin method based on analytical Jacobians for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[R]. AIAA 2016-1326, 2016.
(  0) 0) |
| [133] |
Krivodonova L, Berger M. High-order accurate implementation of solid wall boundary conditions in curved geometries[J]. J comput Phys, 2006, 211(2): 492-512. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.05.029 (  0) 0) |
| [134] |
Persson P O, Peraire J. Curved mesh generation and mesh refinement using Lagrangian solid mechanics[R]. AIAA 2009-949, 2009.
(  0) 0) |
| [135] |
Lu Hongqiang, Cao Kai, Bian Lechao, et al. High-order mesh generation for discontinuous Galerkin methods based on elastic deformation[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016, 8(4): 693-702. DOI:10.4208/aamm.2014.m618 (  0) 0) |
| [136] |
Qin Wanglong. Numerical simulation of compressible flows using discontinuous Galerkin method[D]. PhD thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016.(in Chinese) 秦望龙. 基于间断Galerkin有限元方法的可压缩流数值模拟[D]. PhD thesis. 南京航空航天大学, 2016. (  0) 0) |
| [137] |
Chen Jianwei. Simulation of unsteady flow based on high-order discontinuous Galerkin method[D]. Master thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016.(in Chinese) 陈建伟. 基于高阶间断有限元法的非定常流场数值模拟[D]. Master thesis. 南京航空航天大学, 2017. (  0) 0) |
| [138] |
Persson P O, Peraire J. Sub-cell shock capturing for discontinuous Galerkin methods[R]. AIAA 2006-112, 2006.
(  0) 0) |
| [139] |
Barter G E, Darmofal D L. Shock capturing with PDE-based artificial viscosity for DGFEM:Part Ⅰ. Formulation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2010, 229(5): 1810-1827. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2009.11.010 (  0) 0) |
| [140] |
Nguyen N C, Peraire J. An adaptive shock-capturing HDG method for compressible flows[R]. AIAA 2011-3060, 2011.
(  0) 0) |
| [141] |
Bassi F, Crivellini A, Ghidoni A, et al. High-order discontinuous Galerkin discretization of transonic turbulent flows[R]. AIAA 2009-180, 2009.
(  0) 0) |
| [142] |
Hartmann R, Held J, Leicht T, et al. Discontinuous Galerkin methods for computational aerodynamics-3D adaptive flow simulation with the DLR PADGE code[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2010, 14: 512-519. DOI:10.1016/j.ast.2010.04.002 (  0) 0) |
| [143] |
Nguyen N C, Persson P O, Peraire J. RANS solutions using high order discontinuous Galerkin methods[R]. AIAA 2007-0914, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [144] |
Allmaras S R, Johnson F T, Spalart P R. Modifications and clarifications for the implementation of the Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model[C]//ICCFD7-1902, 2012.
(  0) 0) |
| [145] |
Atkins H, Shu C W. Quadrature-free implementation of the discontinuous Galerkin method for hyperbolic equations[J]. AIAA Journal, 2013, 36(5): 775-782. (  0) 0) |
| [146] |
Zhou C, Wang Z J. An evaluation of implicit time integration schemes for discontinuous high order methods[R]. AIAA 2013-2688, 2013.
(  0) 0) |
| [147] |
Schoenawa S, Hartmann R. Discontinuous Galerkin discretization of the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations with the shear-stress transport model[J]. J. Comput. Phys,, 20147, 262: 194-216. (  0) 0) |
| [148] |
Butcher J C. Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2016.
(  0) 0) |
| [149] |
Saad Y, Schultz M H. GMRES:A generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 1986, 7(3): 856-869. DOI:10.1137/0907058 (  0) 0) |
| [150] |
Saad Y. Iterative methods for sparse linear systems[M]. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2003.
(  0) 0) |
| [151] |
E A. Distribution of local pressure and skin friction around a circular cylinder in cross-flow up to Re=5×106[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1968, 34(34): 625-639. (  0) 0) |
| [152] |
Travin A, Shur M, Strelets M, et al. Detached-eddy simulationspast a circular cylinder[J]. Flow Turbulence & Combustion, 2000, 63(1-4): 293-313. (  0) 0) |
| [153] |
AIAA. RANS solutions using high order discontinuous Galerkin methods[C]//AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit Reno for Discontinuous Galerkin, 2007.
(  0) 0) |
| [154] |
Inoue O, Hatakeyama N. Sound generation by a two-dimensional circular cylinder in a uniform flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2002, 471: 285-314. (  0) 0) |
| [155] |
Fidkowski K J, Oliver T A, Lu J, et al. p-multigrid solution of high-order discontinuous Galerkin discretizations of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2005, 207(1): 92-113. DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.01.005 (  0) 0) |
 2017, Vol. 35
2017, Vol. 35

