扩展功能
文章信息
- 高丽君, 何程远, 李盈诺, 巴宏宇, 李梓僮, 夏薇, 李明成, 苑广信, 张丽华, 艾金霞
- GAO Lijun, HE Chengyuan, LI Yingnuo, BA Hongyu, LI Zitong, XIA Wei, LI Mingcheng, YUAN Guanxin, ZHANG Lihua, AI Jinxia
- 基于双重PCR技术的鹿茸及其伪品DNA指纹特征和鉴定
- Characteristics and identification of DNA fingerprint of velvet antler and its counterfeits based on duplex PCR technique
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(04): 839-844
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(04): 839-844
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180428
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-10-30
2. 北华大学药学院药物分析 教研室, 吉林 吉林 132013;
3. 吉林雷宁食品药品检测技术服务有限公司, 吉林 吉林 132013
2. Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, School of Pharmacy, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, China;
3. Jilin Leining Food and Drug Testing Services Co. Ltd, Jilin 132013, China
鹿茸是我国名贵中药,《本草纲目》中记载:鹿茸具有生精补髓、养血益阳和强健筋骨等功效。我国2015年版《中华人民共和国药典》中指出:鹿茸为鹿科动物梅花鹿(Cervus Nippon Temminck)或马鹿(Cervus elaphus Linnaeus)的雄鹿未骨化密生茸毛的幼角,前者习称“花鹿茸”,后者习称“马鹿茸”[1]。目前,鹿茸药材品种繁多、成分复杂,市场上易混品和伪品较多,再加之我国中药现行质量标准中检验方法的局限性,很难对同属的鹿茸真伪做出准确判断。目前,国内外多采用红外线、紫外线、化学和液相色谱等方法鉴别中药,这些方法虽为鹿茸药材的鉴定提供了一定的参考依据,但均存在一定的不足,例如对同科、同属、不同种的易混药材鉴别的专属性差,尤其对化学结构相似物质鉴别的特异性不强,而且操作繁琐、费用高,很难满足对中药材、尤其对中药易混品种的鉴定[2]。
分子遗传学标记技术为中药及其伪品的鉴别提供了一条新的途径[3]。线粒体DNA(mitochrondrial DNA,mtDNA)作为遗传信息的载体,是研究动物起源进化及对群体进行遗传分析的理想对象。鹿科动物mtDNA呈共价闭合环状,是细胞核外具有自主复制、转录和翻译能力的遗传物质,与核DNA比较,因其具有分子结构简单、碱基突变率高、不同区域进化速度存在差异等特点,使mtDNA成为一种有效的遗传标志[4]。线粒体细胞色素b(cytochromeb, Cytb)基因进化速度适中,是分析种内及种间遗传多样性和进化关系的适当的DNA片段,可应用于生物的分类、系统发育和遗传多样性的研究[5-6]。细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ(cytochrome C oxidase subunit 1,COⅠ)是线粒体中约650bp的一段序列,其基因进化速度比Cytb基因更快,因此可以用来区分进化非常紧密的物种[7-8]。
本课题组建立了基于鹿科动物mtDNA的Cytb和COⅠ具有特异性鉴别意义的基因序列[9-10]。在此基础上,利用Cytb及COⅠ的特性,设计了用于鉴定鹿茸的双重特异性引物,即在同一PCR反应体系中同时检测梅花鹿、马鹿、新西兰鹿和驯鹿鹿茸,达到快速、准确鉴定鹿茸真伪的目的,以期为中药真伪的鉴别提供又一新的方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料、主要试剂和仪器本实验所用的鹿茸共11个批次。梅花鹿茸(吉林)由中国食品药品检定研究院提供,马鹿茸和驯鹿茸由吉林省双阳鹿养殖基地提供,新西兰鹿茸和梅花鹿茸(安徽)购自吉林省吉林市汇丰参茸行,市售鹿茸样品P1、P2、P3、P4、P5和P6购自吉林省吉林市参茸市场。样品真伪由吉林省吉林市食品药品检验所鉴定。DNA混合酶购于北京天根生物技术有限责任公司,批号:Lot#Q5328;琼脂糖购于北京康润诚业生物科技有限公司。GeneAmp R PCR System2700 Applied Biosystem(美国Perkin-Elmer公司),UV WHITE2020D凝胶成像分析系统(美国Bio-rad公司)。
1.2 鹿茸样品基因组DNA的提取采用碱变性方法提取基因组DNA[11]:①取鹿茸样品剪碎至1 mm×1 mm×1 mm左右,称取0.1g样品加入0.01mmol·L-1Tris-HCl 500 μL、10%SDS 30 μL和20 g·L-1 PK15 μL,混匀后置于56℃水浴振荡16~18h;②取出,加入饱和NaAC 500 μL,轻轻振荡10 min,4℃、11000 r·min-1离心10 min,取上清液加入等体积的异丙醇,-20℃放置1h;③ 4℃、11000 r·min-1离心10 min,弃上清液,向沉淀中加入70%乙醇500 μL充分冲洗,4℃、11000r·min-1离心10 min,留沉淀室温干燥(必要时可洗涤2次);④加入80μL双蒸水溶解DNA,即为鹿茸基因组DNA。将所获得的基因组DNA样本经适当稀释,采用紫外分光光度仪测定吸光度(A)值,计算A(260)/A(280)比值。采用0.8%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,采用凝胶成像分析系统观察和分析结果。
1.3 PCR扩增① 引物设计:查找GenBank中鹿茸线粒体Cytb及COⅠ的已知序列,采用Premier 5.0软件进行引物设计,采用Oligo 6.0引物设计软件进行验证。针对Cytb设计了2对引物(Cytb1和Cytb2),COⅠ设计了3对引物(COⅠ1、COⅠ2和COⅠ3)。碱基序列及扩增的片段长度见表 1。②PCR反应体系:以提取的鹿茸基因组DNA为模板,灭菌双蒸水作为阴性对照进行PCR反应。反应体系25 μL,在150 μLPCR反应管中依次加入DNA混合酶12.5 μL,Cytb或COⅠ上、下游引物各1 μL,模板0.5 μL,双蒸水10 μL。③反应程序:单一PCR:94℃预变性5 min,94℃变性30 s,退火温度30s,72℃延伸30s,30个循环后于72℃延伸10 min。PCR产物用2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,90 V、40 min,100~600 bpDNA Marker作参照,凝胶成像分析系统观察和分析结果。④双重PCR扩增:在反应体系中加入Cytb及COⅠ2对引物,上、下游引物各1 μL,双蒸水8 μL,其余条件同单一PCR扩增的反应条件。检测方法与单一PCR扩增的检测方法相同。
| Primer | Sequence(5′-3′) | Expected length(bp) | |
| Cytb1 | Upstream | TTTTCCTCTGTCACCCAT | 395 |
| Downstream | ATAGCGAGTGCTGCGATG | ||
| Cytb 2 | Upstream | ATACATACACGCAAACGG | 342 |
| Downstream | ATAGCGAGTGCTGCGATG | ||
| COⅠ1 | Upstream | ACACCCTAATCAACTGGC | 525 |
| Downstream | AAGAAAGAAGGAGGGAGG | ||
| COⅠ2 | Upstream | TGAGCAGGCATAGTAGGA | 194 |
| Downstream | ATGGGCTCAGGTGATAGA | ||
| COⅠ3 | Upstream | AGACCCTAATCAACTGGC | 257 |
| Downstream | TAGAATGGCTGAGTGAAG |
① PCR反应中特异引物的确定:分别应用Cytb及COⅠ单一引物逐一实验,反应条件及程序同1.3中所述。②PCR反应中最适解链温度的确定:分别设置单独PCR扩增Cytb1及COⅠ1的最适解链温度分别为50℃和56℃;双重PCR扩增解链温度分别为57.5℃、58℃、58.5℃、59℃、60℃和61℃, 其他条件不变。
1.5 市售鹿茸样品的检测按照1.2中的方法提取鹿茸DNA,采用优化的双重PCR反应体系和反应条件对市售鹿茸进行鉴定。
2 结果 2.1 鹿茸样品基因组DNA琼脂糖凝胶电泳特征采用碱变性法从所有鹿茸及其伪品中提取DNA,梅花鹿茸(吉林、安徽)、马鹿茸、驯鹿茸和新西兰鹿茸经琼脂糖凝胶电泳均可见1条片段长度约为23 000bp的单一条带(图 1)。
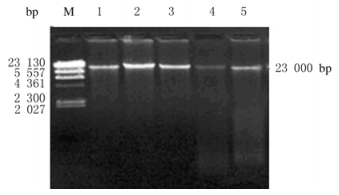
|
| M:546 bp DNA marker; Lane1:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Jilin); Lane 2:Cervus elaphus Linnaeus antler; Lane 3:Rangifer tarandus antler; Lane 4:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Anhui); Lane 5:New Zealand pilose antler. 图 1 鹿茸样品DNA琼脂糖凝胶电泳图 Figure 1 Electrophoregram of agarose gel of genomic DNA extracted from velvet antlers |
|
|
采用碱变性法提取鹿茸基因组DNA,测得样本A(260)/A(280)值为1.80±0.02(表 2),说明此样本无RNA和蛋白质污染。
| Sample | A(260) | A(280) | Purily | [ρB /(μg·L-1)] |
| Cervus Nippon Temminck antler (Jilin) | 0.382 | 0.211 | 1.809 | 1.80 |
| Cervus elaphus Linnaeus antler | 0.368 | 0.210 | 1.750 | 1.81 |
| Rangifer tarandus antler | 0.351 | 0.203 | 1.732 | 1.78 |
| Cervus Nippon Temminck antler (Anhui) | 0.386 | 0.215 | 1.743 | 1.82 |
| New Zealand pilose antler | 0.374 | 0.212 | 1.763 | 1.82 |
分别应用Cytb和COⅠ单一引物进行多次实验,结果显示:应用单一引物无法鉴定鹿茸正品和伪品。将Cytb 1、Cytb 2和COⅠ1、COⅠ2、COⅠ3分别进行不同的组合,即将Cytb和COⅠ以不同的组合形式同时加入PCR反应体系,最后确定Cytb1和COⅠ1引物组合后特异性强,能区分鹿茸正品及伪品(图 2)。
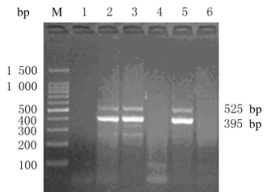
|
| M:100 bp DNA marker; Lane 1:Negative control; Lane 2:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Jilin); Lane 3:Cervus elaphus Linnaeus antler; Lane 4:Rangifer tarandus antler; Lane 5:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Anhui); Lane 6:New Zealand pilose antler. 图 2 特异性引物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图 Figure 2 Electrophoregram of agarose gel of specific primers |
|
|
解链温度是影响PCR扩增的一个重要因素,对于双重PCR尤其如此。由于单独进行PCR扩增时,Cytb1及COⅠ1的最适解链温度分别为50℃和56℃,因此解链温度分别为57.5℃、58℃、58.5℃、59℃、60℃和61℃,其他条件不变,检测双重PCR扩增效果。当解链温度在57.5℃~61.0℃时,均可实现2种目的基因的双重PCR,但以58℃时效果最好。故确定双重PCR的最适解链温度为58℃(图 3)。
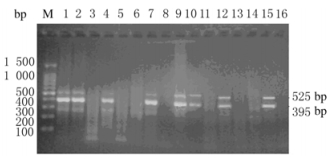
|
| Lane 1-8:57.5℃; Lane 9-16:58.0℃; M:100 bp DNA marker; Lane 1, 9:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Jilin); Lane 2, 10:Cervus elaphus Linnaeus antler; Lane 3, 11:Rangifer tarandus antler; Lane 4, 12:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Anhui); Lane 5, 13:New Zealand pilose antler; Lane 6, 14:Counterfeits of velvet antler; Lane 7, 15: Genuine velvet antler; Lane 8, 16:Negative control. 图 3 选择最适解链温度的琼脂糖凝胶电泳图 Figure 3 Electrophoregram of agarose gel of determination of optimum annealing temperature |
|
|
取待检样品DNA溶液0.5μL、引物(Cytb1及COⅠ1)各1μL,分别置于25μL PCR反应体系中,混匀。PCR反应条件:94℃预变性5min;94℃、30s,58℃、30s,72℃、30s,循环反应30次;72℃延伸10min。
2.6 市售样品的检测结果采用确定的鹿茸DNA的提取方法及最优的PCR反应条件,对市售样品(P1、P2、P3、P4和P5)进行检测,检测结果与实际情况完全一致(图 4)。进一步证明本研究建立的双重PCR技术快速鉴定鹿茸及其伪品的方法可行。
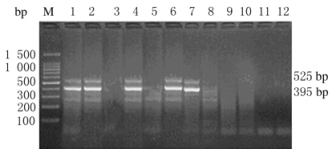
|
| M:100 bp DNA marker; Lane 1:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Jilin); Lane 2:Cervus elaphus Linnaeus antler; Lane 3:Rangifer tarandus antler; Lane 4:Cervus Nippon Temminck antler(Anhui); Lane 5:New Zealand pilose antler; Lane 6-11:Sold velvet antler; Lane 12:Negative control. 图 4 正品和市售鹿茸样品的琼脂糖凝胶电泳图 Figure 4 Electrophoregram of agarose gel of genuine and sold velvet antlers |
|
|
鹿茸作为贵重药材,产源不足但需求量增加,使得不同渠道来源的伪品、混淆品和代用品在国内的药源市场屡见不鲜。伪品鹿茸的价格昂贵却完全失去药用效果,不仅延误患者的救治,而且降低人们对中药的信任,严重影响我国传统药学的发展,更制约着中国传统医药的规范化、标准化和国际化。该情况在其他名贵中草药中也常见,如龟甲、川贝母和貂心等[12-16]。为在世界范围内弘扬我国传统的中医中药学,急需建立一套准确、有效和标准的鹿茸真伪的鉴定方法,确保药材质量,保障临床用药的安全性和准确性。
DNA分子遗传标记技术在中药材鉴定中被广泛使用,该标记技术具有多态性强和准确性高等优点。利用DNA分子标记技术对鹿茸进行鉴别,直接从遗传物质DNA的核苷酸序列上检测遗传变异,可准确鉴别鹿茸的真伪。
动物线粒体在细胞中有较多的拷贝数,无论哪个生长期、哪种形态线粒体均能较好地保存下来,而且每个部位的DNA序列均完全一致,这种高保真性结构有利于物种种内、种间和进化的研究[17]。Cytb位于线粒体内膜脂质双分子层中,是线粒体本身编码的少数功能蛋白之一,进化速度合理,目前主要被用于动物的种类鉴别[18]。COⅠ比Cytb基因进化迅速,适合鉴别关系紧密的物种,尤其可鉴别动、植物亚种[19]。
本研究利用COⅠ和Cytb分别设计引物,采用双重PCR技术进行真伪鹿茸的鉴别。双重PCR是Chamberian等在1988年提出的,指在同一反应体系中同时加入2对引物,使2个PCR同时完成。双重PCR可同时扩增2个目的基因,具有特异性强、效率高和成本低的优势,已经被广泛应用[20]。双重PCR在同一体系中特异性地扩增2个位点,其技术难度大,需要反复实验、全面分析,才能确定特异的反应体系和反应条件等[21]。
本研究采用碱变性方法提取鹿茸及其伪品的基因组DNA,用引物设计软件分别设计出针对鹿茸的Cytb和COⅠ的特异性引物,并进行双重PCR扩增。经多次实验,确定了特异的PCR反应条件和反应体系。本研究结果显示:如果在395和525bp处同时出现特异性条带即为鹿茸正品,反之为伪品,正品与伪品有明显差别。因此,本研究实现了从分子水平鉴定鹿茸的真伪,该方法简单、快速,结果可靠,易于推广应用。
本研究利用已确定的方法检验市售鹿茸,检验结果与吉林省吉林市食品药品检验所的结果完全一致,进一步证明本研究确定的检验方法可从分子水平鉴别鹿茸的真伪。
| [1] | 国家药典委员会. 中国药典[M]. 一部. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社,2015: 323. |
| [2] | 钱忠直, 林瑞超, 肖培根. 中药鉴定与标准研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(12): 2153–2154. |
| [3] | Wang Y, Xu L, Xu G, et al. Prospects of application of DNA molecular genetic marker to pharmacognostical identification[J]. Clin J Chin Mat Med, 1997, 22(10): 583–586. |
| [4] | 周永娜, 刘华淼, 鞠妍, 等. 牛、羊、马及鹿科动物母系起源和父系起源研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2017, 39(4): 52–57. |
| [5] | Nolan JR, Bergthorsson U, Adema CM. Physella acuta:atypical mitochondrial gene order among panpulmonates (Gastropoda)[J]. J Molluscan Stud, 2014, 80(4): 388–399. DOI:10.1093/mollus/eyu025 |
| [6] | 艾金霞, 李明成, 夏薇, 等. 线粒体DNA在鹿胎鉴定中的应用[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2017, 52(18): 1589–1593. |
| [7] | Lah EF, Ahamad M, Haron MS, et al. Establishment of a molecular tool for blood meal identification in Malaysia[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed, 2012, 2(3): 223–227. DOI:10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60046-X |
| [8] | Joseph S, Poriya P, Kundu R. Probing the phylogenetic relationships of a few newly recorded intertidal zoanthids of Gujarat coast (India) with mtDNA COⅠ sequences[J]. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal, 2016, 27(6): 3858–3864. |
| [9] | Adibah AB, Darlina MN. Is there a cryptic species of the golden snapper (Lutjanus johnii)?[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2014, 13(4): 8094–8104. DOI:10.4238/2014.October.7.4 |
| [10] | Gao L, Xia W, Ai J, et al. Development of multiplex PCR assay for authentication of Cornu Cervi Pantotrichum in traditional Chinese medicine based on cytochrome b and C oxidase subunit 1 genes[J]. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal, 2016, 27(4): 2989–2992. |
| [11] | Kocher TD, Thomas WK, Meyer A, et al. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals:amplification and sequencing with conserved primers[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989, 86(16): 6196–6200. DOI:10.1073/pnas.86.16.6196 |
| [12] | 周亭亭, 李明成. 基于DNA指纹鉴定技术的市售川贝母质量考察分析[J]. 北华大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 18(6): 743–746. |
| [13] | 张丽华, 李明成, 王冰梅, 等. 中草药川贝母DNA指纹鉴定[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2008, 34(5): 790–793. |
| [14] | 苑广信, 李梓僮, 张丽华, 等. 基于毛细管电泳的鹿鞭DNA指纹鉴定方法[J]. 中成药, 2016, 38(3): 620–624. |
| [15] | Li M, Xia W, Wang M. Application of molecular genetics method for differentiating Martes zibellina L.heart from its adulterants in traditional Chinese medicine based on mitochondrial cytochrome b gene[J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 2014, 25(1): 78–82. DOI:10.3109/19401736.2013.815167 |
| [16] | 王淼, 李萧晗, 周雨晴, 等. 中药材龟甲基因组DNA提取及PCR鉴定特征[J]. 北华大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 17(6): 777–780. |
| [17] | 涂剑锋, 司方方, 邢秀梅, 等. 鹿科动物线粒体DNA研究进展[J]. 草食家畜, 2008, 9(3): 1–4. |
| [18] | Yang L, Xia B, Yang X, et al. Mitochondrial DNA hypomethylation in chrome plating workers[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2016, 243: 1–6. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.11.031 |
| [19] | Zinger L, Philippe H. Coalescing molecular evolution and DNA barcoding[J]. Mol Ecol, 2016, 25(9): 1908–1910. DOI:10.1111/mec.13639 |
| [20] | Persson S, Al-Shuweli S, Yapici S, et al. Identification of clinical aeromonas species by rpoB and gyrB sequencing and development of a multiplex PCR method for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila, A.caviae, A.veronii and A.media[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2014, 53(2): 341–341. |
| [21] | Qiu P, Sheng XB, Luo JY. Overview on the studies of DNA finger printing and sequencing techniques in qualitative determination of Chinese crude drugs[J]. Guiding J TCM, 2006, 12(11): 77. |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


