扩展功能
文章信息
- 任艳芳, 姜永杰, 张秀玲, 姜姗, 王玉红
- REN Yanfang, JIANG Yongjie, ZHANG Xiuling, JIANG Shan, WANG Yuhong
- SHH信号通路对子痫前期患者滋养细胞凋亡和侵袭的影响及其机制
- Effect of SHH signaling pathway on apoptosis and invasion of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia patientsand its mechanism
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(03): 510-515
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(03): 510-515
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180310
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-10-16
子痫前期(preeclampsia,PE)是妊娠期特发的以母体蛋白尿和高血压为特征的多系统综合征,是导致我国孕产妇及围生儿死亡的一个重要因素,目前,该病的发病机制尚未明确,治疗也缺乏有效的手段[1]。滋养细胞向子宫的增殖、侵袭和迁移是人类胎盘形成和胚胎植入的重要环节,胎盘着床的关键时期滋养细胞侵袭能力降低、细胞凋亡增加引起胎盘的浅着床是该病发生的关键环节[2-3]。Sonic Hedgehog(SHH)信号通路属于Hedgehog信号家族中一员,由SHH配体、受体Ptch1和Smo及下游的转录因子Gli蛋白组成,参与胚胎发育的多个过程,在胚胎期的组织发育、细胞分化和器官形成过程中有重要作用,其异常表达会导致一系列的严重疾病[4-5]。目前关于SHH信号通路对PE滋养细胞生物学特性的影响尚未清楚。本研究通过建立滋养细胞缺氧/复氧(H/R)培养模型,观察SHH信号通路激活剂purmorphamine对细胞凋亡和侵袭的影响,旨在为PE的治疗提供新的靶点和理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 胎盘标本来源收集2014年4月—2015年6月新乡医学院第一附属医院行选择性剖宫产术的PE孕妇35例及健康产妇(经检查排除妊娠期综合征)35人,PE孕妇参照《妇产科学》第8版全国统编教材的诊断标准。PE孕妇平均年龄为(28.83±3.22)岁,健康产妇平均年龄为(28.97± 3.02)岁。所有研究对象均为单胎,既往无心脏病、糖尿病、甲状腺功能异常、高血压和肾脏病等病史,无畸胎、复发性自然流产、死胎等不良孕产史,无产期服用药物和吸烟史。所有样本采集均经研究对象和家属知情同意及本院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 细胞、主要试剂和仪器人早孕期绒毛外滋养细胞株(HTR8/SVneo)购自中国科学院细胞库。胎牛血清和RPMI1640培养基购自美国Gibco公司,二喹啉甲酸(bicinchoninic acid,BCA)试剂盒和膜联蛋白Ⅴ-FITC(Annexin Ⅴ-FITC)凋亡试剂盒购自江苏碧云天生物技术研究所,Transwell小室购自美国Millipore公司,SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1、Gli3、基质金属蛋白酶2(matrix metalloproteinase-2,MMP-2)和基质金属蛋白酶9(matrix metalloproteinase-9,MMP-9)抗体购自美国Abcam公司。流式细胞仪购自美国Becton Dickinson公司。
1.3 标本采集分娩后立即剪取大小约为1 cm×1 cm×1 cm的胎盘组织,大量无菌生理盐水漂洗干净,迅速放入灭菌灭酶的冻存管,置于液氮中过夜后转入-80℃冰箱中保存。用于蛋白抽提和Western blotting法检测。
1.4 细胞培养HTR8/SVneo细胞在37℃、5% CO2、95%饱和湿度的恒温培养箱中用含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640细胞培养液培养。
1.5 细胞处理和实验分组将细胞分为正常对照组、H/R处理组和purmorphamine+H/R处理组,purmorphamine+H/R处理细胞按照参考文献[6]进行处理,先缺氧培养8 h,再常规培养16 h,2个循环共48 h,加入1 μmol·L-1purmorphamine孵育2 h后,再进行H/R处理。各组细胞总培养时间均为48 h。
1.6 Western blotting法检测SHH信号通路相关蛋白表达水平提取PE和正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织及上述3组HTR8/SVneo细胞中的总蛋白,BCA试剂盒检测提取蛋白的浓度,每泳道30 μg上样量,经12%十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)分离,转膜、封闭后,分别加入SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1、Gli3、MMP-2、MMP-9(均按照1:500稀释)和GAPDH(1:1 000稀释)一抗,4℃过夜,TBST洗涤(3次×10 min),加入1:5 000稀释的HRP标记的羊抗鼠IgG,室温孵育1 h,ECL化学发光后显影、定影。采用AlphaEaseFC软件分析目的条带相对灰度值,以GAPDH为内参,目的条带相对灰度值=目的条带灰度值/GAPDH灰度值。
1.7 流式细胞术(FCM)检测各组细胞凋亡率各组细胞培养至规定时间后,胰蛋白酶消化细胞,离心后收集细胞,采用AnnexinⅤ-FITC/PI(碘化丙锭)双标记试剂盒处理细胞,采用FCM检测各组细胞凋亡率。
1.8 Transwell小室法检测各组穿膜细胞数Transwell小室放入24孔板中,上室上层采用50 μL Matrigel胶(用磷酸盐缓冲液按照1:6稀释)包被。上述3组细胞完成处理后,Transwell小室的上室中加入1×105个细胞,下室中加入含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640细胞培养基,37℃、5% CO2培养箱中经过24 h培养,膜清洗,行HE染色,显微镜下拍照,随机取6个不同的视野(×200)观察并记录穿膜细胞数,重复3次,计算每组小室穿膜细胞的平均数。
1.9 统计学分析采用SPSS21.0统计软件进行统计学分析。PE和正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织及各组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1、Gli3、MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平、HTR8/SVneo细胞凋亡率及各组HTR8/SVneo细胞穿膜细胞数均以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用SNK-q检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 PE和正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织中SHH信号通路相关蛋白表达水平正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平分别为0.882±0.06、0.532±0.037、0.492±0.031、0.238±0.024和0.153±0.016,PE胎盘组织中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1、Gli3蛋白表达水平分别为0.187±0.016、0.021±0.007、0.177± 0.018、0.141±0.015和0.025±0.008,PE胎盘组织中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平均明显低于正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织(t=19.386,P=0.000;t=23.504,P=0.000;t=15.220,P=0.000;t=5.936,P=0.004;t=12.394,P=0.000)。见图 1。
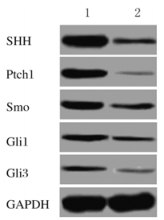
|
| Lane 1: Late trimester of normal pregnancy; Lane 2: PE. 图 1 PE和正常妊娠晚期胎盘组织中SHH信号通路相关蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 1 Electrophoregram of expressions of SHH signal pathway related proteins in placental tissues of PE and late trimester of normal pregnancy |
|
|
正常对照组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平分别为0.711±0.053、0.311±0.022、0.196±0.018、0.191±0.017和0.139±0.015,H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平分别为0.182±0.018、0.131±0.015、0.081±0.012、0.053±0.011和0.024±0.008,purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平分别为0.385±0.034、0.187±0.023、0.129±0.015、0.111±0.010和0.078±0.008;H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1、Gli3蛋白表达水平均明显低于正常对照组(t=16.370,P=0.000;t=11.709,P=0.000;t=9.207,P=0.001;t=11.805,P=0.000;t=11.717,P=0.000);purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平均明显低于正常对照组(t=16.370, P=0.000;t=11.709,P=0.000;t=9.207,P=0.001;t=11.805,P=0.000;t=11.717,P=0.000);purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平均明显高于H/R处理组(t=9.140,P=0.001;t=3.532,P=0.024;t=4.328,P=0.012;t=6.758,P=0.003;t=8.267,P=0.001)。见图 2。
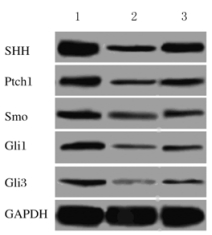
|
| Lane 1: Normal control group; Lane 2:H/R treatment group; Lane 3: Purmorphamine+H/R treatment group. 图 2 各组HTR8/SVneo细胞中SHH信号通路相关蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of SHH signaling pathway related proteins in HTR8/SVneo cells in various groups |
|
|
正常对照组、H/R处理组和purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR/SVneo细胞中MMP-2蛋白表达水平分别为0.655±0.051、0.034±0.008和0.213±0.022,MMP-9蛋白表达水平分别为0.603±0.045、0.046±0.010和0.164±0.015;H/R处理组和purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平低于正常对照组(t=20.836,P=0.000;t=20.928,P=0.000;t=16.709,P=0.000;t=19.210,P=0.000);purmorphamine+H/R处理组HTR8/SVneo细胞中MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平高于H/R处理组(t=13.244,P=0.001;t=11.337,P=0.000)。见图 3。
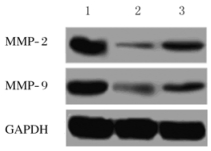
|
| Lane 1: Normal control group; Lane 2:H/R treatment group; Lane 3:Purmorphamine+H/R treatment group. 图 3 各组HTR8/SVneo细胞中MMP-2和MMP-9表达电泳图 Figure 3 Electrophoregram of expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in HTR8/SVneo cells in various groups |
|
|
正常对照组、H/R处理组和purmorphamine+H/R处理组细胞凋亡率分别为(3.23±0.51)%、(13.38±0.72)%和(6.88±0.63)%,H/R处理组细胞凋亡率明显高于正常对照组(t=19.925,P=0.000),purmorphamine+H/R处理组细胞凋亡率明显低于H/R处理组(t=11.768,P=0.000)。见图 4。
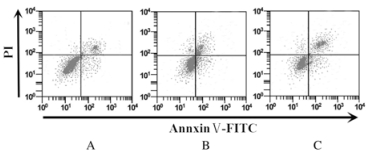
|
| A: Normal control group; B:H/R treatment group; C:Purmorphamine+H/R treatment group. 图 4 FCM检测各组HTR8/SVneo细胞凋亡率 Figure 4 Apoptotic rates of HTR8/SVneo cells in various group detected by FCM |
|
|
正常对照组、H/R处理组和purmorphamine+H/R处理组穿膜细胞数分别为(1.00±0.10)、(0.35±0.08)和(0.76±0.10)个,明显低于正常对照组(t=8.791,P=0.001);purmorphamine+H/R处理组穿膜细胞数明显高于H/R处理组(t=5.545,P=0.005)。见图 5。
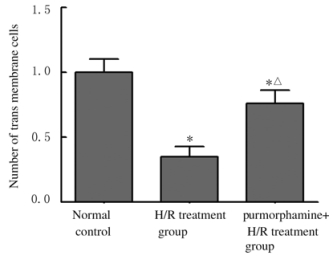
|
| *P < 0.05 vs normal control group; △P < 0.05 vs H/R treatment group. 图 5 各组HTR8/SVneo细胞的穿膜细胞数 Figure 5 Number of transmembrane cells of HTR8/SVneo cells in various groups |
|
|
PE是妊娠期特有的疾病,对母婴健康造成严重的威胁。滋养细胞来自滋养的外胚层,是母-胎界面唯一一个与母体的免疫有直接接触的胎儿细胞,在母-胎免疫耐受和胚胎植入过程中起重要作用[7]。滋养细胞的增殖、凋亡、侵袭、迁移和分化行为是胚胎发生、胎盘形成及妊娠顺利完成的基本部分[8]。滋养细胞异常的侵袭行为可引起胎儿生长受限、不明原因自然流产、PE和子痫等妊娠相关疾病[9-10]。因此,研究滋养细胞的功能对于阐明上述各类疾病的发病机制及治疗效果有重要意义。
近些年对PE的研究[11-12]显示:滋养细胞中一些信号通路和基因的表达异常可能是该病发病的重要原因。如Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在PE表达降低,可促进滋养细胞的氧化应激损伤,而激活该信号通路可对滋养细胞起保护作用[13]。SHH是一种能促进有丝分裂的信号,在Hh家族中表达最广泛,在器官形成、胚胎发育的多个过程中起重要作用,可调控神经干细胞、牙胚发育和干细胞增殖分化等多种生物学行为[14]。研究[15]显示:Hh信号通路主要的受体、配体及转录因子在妊娠中期和囊胚的滋养外胚层的胎盘成熟过程中均有高表达,提示该通路调节囊胚着床和发育及胎盘发育,而SHH作为主要配体影响胎盘发育。研究[16]证实:对于囊胚着床和获能Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是必须的,而Hh信号通路处于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的上游,起调节作用。本研究检测PE胎盘组织中SHH信号通路SHH配体、受体Ptch1和Smo及下游转录因子Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达的结果显示:在PE胎盘组织中SHH、Ptch1、Smo、Gli1和Gli3蛋白表达水平均明显低于正常妊娠晚期。
胎盘的血流动力学异常可使局部组织缺血加重,引起母体血压升高[17];母体血压升高会使胎盘的血流灌注增加,引起缺血再灌注,致使胎盘内的血管形成无法正常完成和血管内皮细胞的氧化应激损伤,最终导致PE症状和体征[18]。本研究采用细胞H/R及SHH信号通路激活剂purmorphamine处理HTR8/SVneo细胞,检测细胞凋亡和侵袭情况的结果显示:H/R可明显增加HTR8/SVneo细胞的凋亡,降低细胞的侵袭能力(穿膜细胞数减少),而加入SHH激活剂purmorphamine可减弱该效应。MMPs是一类锌离子依赖的内肽酶,可使细胞外基质及基膜中的大多数蛋白质降解,在滋养细胞的侵袭过程中,MMPs对细胞外基质的降解是滋养细胞侵袭的限速步骤[19]。有关MMP-2和MMP-9的研究较多,其是参与滋养细胞侵袭的关键酶。研究[20]显示:滋养细胞侵袭能力降低时,MMP-2和MMP-9的表达水平也降低。本研究检测MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平结果显示:H/R可明显降低MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平,而加入SHH激活剂purmorphamine可使MMP-2和MMP-9蛋白表达水平升高。
综上所述,激活SHH信号通路可减少PE HTR8/SVneo细胞凋亡,通过上调MMP-2和MMP-9的表达可提高细胞侵袭能力。
| [1] | Rolnik DL, Wright D, Poon LC, et al. Aspirin versus placebo in pregnancies at high risk for preterm preeclampsia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(7): 613–622. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1704559 |
| [2] | Rosario FJ, Dimasuay KG, Kanai Y, et al. Regulation of amino acid transporter trafficking by mTORC1 in primary human trophoblast cells is mediated by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2[J]. Clin Sci, 2016, 130(7): 499–512. DOI:10.1042/CS20150554 |
| [3] | Li P, Guo W, Du L, et al. microRNA-29b contributes to pre-eclampsia through its effects on apoptosis, invasion and angiogenesis of trophoblast cells[J]. Clin Sci, 2013, 124(1): 27–40. DOI:10.1042/CS20120121 |
| [4] | Nishi Y, Zhang X, Jeong J, et al. A direct fate exclusion mechanism by Sonic hedgehog-regulated transcriptional repressors[J]. Development, 2015, 142(19): 3286–3293. DOI:10.1242/dev.124636 |
| [5] | Tyson JA, Goldberg EM, Maroof AM, et al. Duration of culture and sonic hedgehog signaling differentially specify PV versus SST cortical interneuron fates from embryonic stem cells[J]. Development, 2015, 142(7): 1267–1278. DOI:10.1242/dev.111526 |
| [6] | Li J, Luo X, Xiao X, et al. Decreased expression of Wiskott-Aldrichsyndrome protein family verprolin -homologous protein 2 may be involved in the development of pre-eclampsia[J]. Reprod Biomed Online, 2014, 28(1): 70–79. DOI:10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.07.015 |
| [7] | Inagaki T, Kusunoki S, Tabu K, et al. Up-regulation of lymphocyte antigen 6 complex expression in side-population cells derived from a human trophoblast cell line HTR-8/SVneo[J]. Hum Cell, 2016, 29(1): 10–21. DOI:10.1007/s13577-015-0121-7 |
| [8] | Du MR, Guo PF, Piao HL, et al. Embryonic trophoblasts induce decidual regulatory T cell differentiation and maternal-fetal tolerance through thymic stromal lymphopoietin instructing dendritic cells[J]. J Immunol, 2014, 192(4): 1502–1511. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.1203425 |
| [9] | Song X, Rui C, Meng L, et al. Long non-coding RNA RPAIN regulates the invasion and apoptosis of trophoblast cell lines via complement protein C1q[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(5): 7637–7646. |
| [10] | Lan X, Fu LJ, Hu ZY, et al. Methylated oligonucleotide (MON)-induced promoter hypermethylation is associated with repression of CDH1 expression and contributes to the migration and invasion of human trophoblast cell lines[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2017, 29(8): 1509–1520. DOI:10.1071/RD16031 |
| [11] | Szabo S, Mody M, Romero R, et al. Activation of villous trophoblastic p38 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in preterm preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2015, 21(3): 659–668. DOI:10.1007/s12253-014-9872-9 |
| [12] | Zhang M, Muralimanoharan S, Wortman AC, et al. Primate-specific miR-515 family members inhibit key genes in human trophoblast differentiation and are upregulated in preeclampsia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113(45): E7069–E7076. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1607849113 |
| [13] | Wu Q, Wu G, Li JX. Effect of hypoxia on expression of placental trophoblast cells SATB1 and β-catenin and its correlation with the pathogenesis of preeclampsia[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2016, 9(6): 567–571. DOI:10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.04.004 |
| [14] | Kong JH, Yang L, Dessaud E, et al. Notch activity modulates the responsiveness of neural progenitors to sonic hedgehog signaling[J]. Dev Cell, 2015, 33(4): 373–387. DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2015.03.005 |
| [15] | Tang C, Mei L, Pan L, et al. Hedgehog signaling through GLI1 and GLI2 is required for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human trophoblasts[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2015, 1850(7): 1438–1448. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.04.005 |
| [16] | Ma Y, Sun N, Sheng F, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 inhibits the growth and invasion of trophoblasts by inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling via downregulation of DDX3X[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2017, 10(6): 6560–6567. |
| [17] | Rahman A, Zhou YQ, Yee Y, et al. Ultrasound detection of altered placental vascular morphology based on hemodynamic pulse wave reflection[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2017, 312(5): H1021–H1029. DOI:10.1152/ajpheart.00791.2016 |
| [18] | Zhong T, Chen J, Ling Y, et al. Down-regulation of neuropathy target esterase in preeclampsia placenta inhibits human trophoblast cell invasion via modulating MMP-9 levels[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(3): 1013–1022. DOI:10.1159/000487296 |
| [19] | Hu Y, Blair JD, Yuen RK, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation identifies trophoblast invasion-related genes:Claudin-4 and fucosyltransferase Ⅳ control mobility via altering matrix metalloproteinase activity[J]. Mol Hum Reprod, 2015, 21(5): 452–465. DOI:10.1093/molehr/gav007 |
| [20] | Zong L, Wei X, Gou W, et al. Zinc improves learning and memory abilities of fetal growth restriction rats and promotes trophoblast cell invasion and migration via enhancing STAT3-MMP-2/9 axis activity[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(70): 115190–115201. |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


