扩展功能
文章信息
- 谢金芳, 李天博, 耿文韬, 李晶, 李媛, 李雪洋, 高华丽, 张颖丽
- XIE Jinfang, LI Tianbo, GENG Wentao, LI Jing, LI Yuan, LI Xueyang, GAO Huali, ZHANG Yingli
- 双侧上颌第四磨牙1例报告及文献复习
- Bilateral maxillary fourth molars: A case report and literature review
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(02): 401-403
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(02): 401-403
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180236
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-08-31
2. 吉林大学口腔医院儿童牙病科, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
多生牙(supernumerary teeth)也称额外牙,是一种牙齿发育异常现象,指比正常牙列多的牙[1];多生牙可发生于任何生牙区,最常见于切牙区(89.6%),其次是尖牙、前磨牙区(9.0%)及磨牙区(0.5%)[2-5]。多生牙可单个或多个、单侧或双侧发生,形态可同正常牙,也可是畸形牙、过小牙[6]。这种病症通常与系统性疾病如Gardner综合征、Ehlers-Danlos综合征、Cleidocranial发育不良、唇裂和裂腭裂、Tricho-rhino-phalangeal综合征、Ellis-van Creveld综合征和Fabry-Anderson综合征伴发[7]。虽然非综合征型多发病例罕见,但其发生可能引起多种临床症状,如拥挤、肿胀、延迟萌出、囊性病变、错位、旋转及邻牙吸收。因此,适当的临床和影像学评估后,恰当的治疗必不可少[8]。第四磨牙位于第三磨牙远中,也称远中磨牙,在现代人类中非常少见[9]。本文作者报道1例双侧上颌第四磨牙,并结合国内外研究现状对其并发症和治疗方案进行探讨。
1 临床资料 1.1 一般资料患者,女性,32岁,汉族。主诉左上颌后牙间歇性隐痛数月,加重5 d。患者数月前出现左上后牙区间断性隐痛,有食物嵌塞史,冷热刺激痛,无夜间痛及自发痛等,自行服用消炎药(具体药物及剂量不详)后症状略有缓解,近5 d疼痛加重,来本院就诊。既往体健,否认药物过敏史和常规血液检查在内的家族遗传史,口外检查和全身性检查均未发现任何临床综合征。
1.2 检查结果专科检查见:颌面部对称,张口及咬合关系基本正常;口内见牙弓左右对称,18、28、38和48正常萌出,18牙冠深龋露髓,大量腐质及食物残渣,仅近中余留少量牙体组织,探(-),温度测试无反应,叩痛(-),远中牙龈略红肿。28牙冠大面积龋坏达牙本质深层,探(±),温度测试进入龋洞内出现疼痛,刺激去除后症状消失,叩痛(±),Ⅰ°松动,牙龈颜色正常。全口曲面断层片(图 1)可见:双侧上颌区4颗磨牙,即第四磨牙(19、29)位于18、27远中,完全阻生,19、29牙根较短,29牙冠较其他磨牙小且压迫28, 28牙根吸收至根长2/3, 18可见较大龋洞达髓腔。
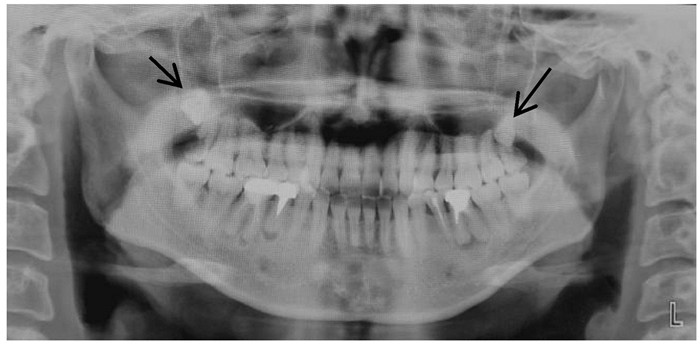
|
| The arrow showed the fourth molars. 图 1 患者双侧上颌区曲面断层X线片 Figure 1 Panoramic radiograph of bilateral maxillary area of patient |
|
|
19低位垂直阻生,29低位近中阻生,18残冠,28深龋。
1.4 治疗计划和治疗结果因18龋损已达龈下且根部牙体组织较薄不宜行修复治疗;28牙根已吸收至根长2/3。建议拔除18、28后观察患者主诉症状有无缓解。局部麻醉下拔除18、28,手术顺利,1周后复诊拔牙创愈合良好,但患者左上颌后牙区隐痛未缓解,怀疑疼痛可能为29压迫27根尖所致,建议拔除29,患者知情同意,手术顺利。术后1周复诊,患者左上颌后牙区疼痛消失。19因完全骨阻生,位置较靠后,且无临床症状,考虑拔除手术难度较大,故建议暂时保留,定期随访。
2 讨论多生牙的发生与多种因素有关,但其病因至今尚未完全清楚。目前比较公认以下几种理论:遗传因素、牙板剩余上皮活性增强或牙胚异常分裂及人类发育过程中出现“返祖现象”[10-11]。多生牙有时与其他一些可阻止牙萌出或导致邻牙的移位、吸收的缺陷有关,如腭裂、锁骨颅骨发育不良等[12]。多生牙大多数位于舌腭侧(82.5%),其次为混合部位及前庭部位。
第四磨牙是位于第三磨牙远中的多生牙,又称远端磨牙,其发生率约为0.33%[13];多为单发,少有多发,其牙冠多较其他磨牙小,牙根短且多为融合根。第四磨牙通常无明显自觉症状,多在影像学检查中被发现。但多生牙存在与一些伴发症状相关,如本病例中患者出现间歇性隐痛。Schmitd等[14]发现因第四磨牙的存在引起含牙囊肿,国内外也有研究[15-16]显示:第四磨牙引起牙列拥挤加重、邻牙的延迟或异位萌出、压迫、拥挤、疼痛、肿胀、牙根吸收、第三磨牙冠周炎、腮腺胀痛和张口受限等。因此,临床上早发现、早诊断、早治疗对阻止及减少第四磨牙引发的不良后果至关重要。
随着人类的进化,颌骨的退化与牙量的退化不一致,导致骨量相对小于牙量,颌骨缺乏足够的空间容纳全部恒牙,以致第四磨牙常阻生在颌骨内。本病例中存在双侧上颌第四磨牙,患者左上颌第四磨牙引起间歇性隐痛的临床症状,已造成第三磨牙牙根吸收至根长2/3,且未能通过其他治疗方法缓解,因此经患者知情同意建议拔除。而右上颌第四磨牙完全骨阻生,位置较靠后,且该牙牙根距上颌窦底较近,无临床症状,考虑拔除手术难度较大,故建议暂时保留,定期随访。对于第四磨牙,临床上主要有以下治疗方案:对于患者不愿意承担手术可能带来的出血、感染和组织损伤等风险,且无临床症状的第四磨牙,考虑拔除的风险及患者的个人意愿可保守观察;对于有价值的正畸建议保留的第四磨牙,应尽量保留并定期拍片检查,必要时拔除;对于已有临床症状或已造成邻牙吸收、冠周炎及颌骨囊肿等伴发症状的第四磨牙应予以拔除;如为保证正畸治疗效果,应正畸需要应予以拔除;因完全骨阻生而被疑为某些原因不明的神经痛病因者应予以拔除。
| [1] | Gürler G, Delilbaş C, Delilbaş E. Investigation of impacted supernumerary teeth:a cone beam computed tomograph (cbct) study[J]. J Istanb Univ Fac Dent, 2017, 51(3): 18–24. |
| [2] | Asrani MK, Tarsariya VM, Pathan JM. Bilateral maxillary fourth and fifth molars:An unusual radiographic appearance[J]. Indian J Dent Res, 2016, 27(1): 103–105. DOI:10.4103/0970-9290.179840 |
| [3] | Ceperuelo D, Lozano M, Duran-Sindreu F. Supernumerary fourth molar and dental pathologiesin a Chalcolithic individual from the E1 Mirador Cave site(Sierrade Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain)[J]. Homo, 2015, 66(1): 15–26. DOI:10.1016/j.jchb.2014.05.007 |
| [4] | Pushparaja S, Amith A, Somya A, et al. The prevalence of hypodontia and supernumerary teeth in 2469 school children of the Indian population:An epidemiological study[J]. Indian J Stomatol, 2012, 3(3): 150–152. |
| [5] | Ozden MC, Taysi M, Cankaya AB, et al. Bilateral molariform supernumerary teeth in the anterior maxilla:a report of two cases[J]. J Istanb Univ Fac Dent, 2017, 51(1): 57–60. |
| [6] | Wang X, Pan X. Bilateral mandibular fourth molars:a case report[J]. West China J Stomatol, 2013, 31(5): 536–537. |
| [7] | Singhal P, Sah VK, Kumar A, et al. Unilateral fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh molar in a nonsyndromic patient:A rare and unusual case report[J]. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent, 2017, 35(4): 374–377. DOI:10.4103/JISPPD.JISPPD_186_16 |
| [8] | Bashir A, Khan SA, Kashif M, et al. Supernumerary molars:A rare finding[J]. BJMMR, 2017, 12(6): 1–5. |
| [9] | 李峰, 谢小燕. 右侧下颌第四磨牙1例[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2016, 43(1): 36–37. DOI:10.7518/gjkq.2016.01.010 |
| [10] | 盖云, 曾参, 周静艳. 双侧上颌第四磨牙异位1例报告[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2014, 7(11): 703–704. DOI:10.7504/kq.2014.11.018 |
| [11] | Asahara M. The origin of the lower fourth molar in canids, inferred by individual variation[J]. Peer J, 2016, 4: e2689. DOI:10.7717/peerj.2689 |
| [12] | 于世凤. 口腔组织病理学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2012: 139. |
| [13] | Cassetta M, Altieri F, Giansanti M, et al. Morphological and topographical characteristics of posterior supernumerary molar teeth:An epidemiological study on 25, 186 subjects[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2014, 19(6): e545–e549. |
| [14] | Schmitd LB, Assao A, Ramalho-Ferreira G, et al. An uncommon occurrence of three-fourth molars concomitant to hypodontia in a nonsyndromic patient[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28(2): 482–483. DOI:10.1097/SCS.0000000000003322 |
| [15] | Ata-Ali F, Ata-Ali J, Pearrocha-Oltra D, et al. Prevalence, etiology, diagnosis, treatment and complications of supernumerary teeth[J]. J Clin Exp Dent, 2014, 6: 414–418. |
| [16] | Banavar SR, Chippagiri P. Mandibular bilateral fourth molars:a rare and interesting occurrence[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2014, 8(5): ZJ01. |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


