扩展功能
文章信息
- 赵春芳, 李美娟, 于维维, 谢湘林, 冯琳琳, 刘宏雁
- ZHAO Chunfang, LI Meijuan, YU Weiwei, XIE Xianglin, FENG Linlin, LIU Hongyan
- 黄紫堇总生物碱对β-淀粉样蛋白致老年性痴呆大鼠的保护作用
- Protective effect of total alkaloids of Corydalis Ochotensis on rats with Alzheimer's disease induced by β-amyloid protein
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(03): 532-537
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2017, 43(03): 532-537
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20170314
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-11-29
2. 吉林大学口腔医院急诊科, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 吉林大学药学院药理学教研室, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Emergency, School of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
阿尔茨海默症(Alzheimer’s disease, AD)又称老年性痴呆,是以进行性记忆和认知功能损伤为特征的慢性退行性神经系统疾病。AD的临床特点是认知功能障碍、近期记忆缺失、人格改变和思维不清,最后生活不能自理[1-2]。黄紫堇总生物碱(total alkaloids of Corydalis Ochotensis,TAOCO)是从罂粟科植物黄紫堇中提取出来的双重胆碱酯酶抑制剂[3]。在AD的病程发展后期,乙酰胆碱酯酶严重受损,而丁酰胆碱酯酶活性尚存,故丁酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂在AD后期治疗效果较好[4]。TAOCO对AD是否有保护作用国内外未见相关文献报道。本研究采用水迷宫、避暗行为学实验和病理学实验观察TAOCO对AD大鼠的保护作用,为其临床应用提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、主要试剂和仪器清洁级Wistar雄性大鼠100只,体质量300~350 g,由吉林大学实验动物中心提供,动物合格证号:SCXK-(吉)2007-0003。TAOCO(吉林大学药物分析实验室提供,批号:20120510),盐酸多奈哌齐(西安海欣制药有限公司,批号:111212A),β-淀粉样蛋白25-35(amyloid β protein 25-35,Aβ25-35)(美国Sigma公司,批号:20110929)。Morris水迷宫及避暗装置(成都泰盟科技有限公司产品)。
1.2 模型制备随机选取10只大鼠作为正常对照组;其余大鼠海马内注射Aβ25-35,然后按照文献[7]制作大鼠AD模型,大鼠腹腔内注射10%水合氯醛(0.4 mL·100g-1)麻醉后,将大鼠头部固定于立体定位仪上,清洁头顶皮肤做正中竖切口。海马区定位坐标:前囟后3.5 mm,中线外侧2.0 mm,硬脑膜下2.7 mm。5 min内用微量注射器每侧分别注入5 μL(10 μg)聚集肽的Aβ25-35,为避免拔针时药物溢出,注射后留针5 min。正常对照组大鼠的手术方法相同,注射相同体积的盐水。术后牙托粉封固颅骨孔,缝合皮肤并消毒,3 d内每日肌注青霉素G10万U以避免感染。通过模型组与对照组大鼠行为学实验结果证实AD大鼠造模成功。
1.3 动物分组和给药在术后第14天将44只造模成功的大鼠分为模型组(灌胃给予0.5 mL·100 g-1蒸馏水,n=9),阳性对照组(灌胃给予1.75mg·kg-1盐酸多奈哌齐,n=9),低、中和高剂量TAOCO组(分别灌胃给予2.0、4.0和8.0 mg·kg-1 TAOCO,n=8,n=9,n=9)。水迷宫实验和跳台实验于连续给药7 d后进行,实验期间继续给药直至实验结束。
1.4 Morris水迷宫实验测试时间为7 d,前6 d在一、二、三和四象限4个不同的入水点将大鼠放入水中,测定大鼠到达平台的朝向角、潜伏期、游程和平均速度,第7天撤掉平台,记录大鼠在1.5 min内经过平台的次数,在平台的停留时间、在平台区的停留距离、经过有效区次数、有效区的停留时间、有效区的停留距离、平台停留时间/总时间、平台停留距离/总路程、有效区停留时间/总时间、有效区停留距离/总路程、总游程和平均速度。
1.5 避暗实验检测大鼠进入暗箱的错误潜伏期和错误次数水迷宫实验结束后,进行避暗实验,测验记忆保持,即第1天适应,24 h后重新进行测验,记录5 min内大鼠的错误总数和第1次被电击的错误潜伏期。
1.6 大鼠大脑皮层和海马的病理形态表现避暗实验结束后快速取脑组织采用甲醛固定,HE染色,制备病理切片,光学显微镜下(×20) 观察大脑皮层和海马组织的病理形态表现。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS 18.0统计软件进行统计学分析。大鼠前6d到达平台的朝向角、游程、平均速度和潜伏期,第7天大鼠在1.5 min内经过平台的次数、在平台的停留时间、在平台区的停留距离、经过有效区次数、有效区的停留时间、有效区的停留距离、平台停留时间/总时间、平台停留距离/总路程、有效区停留时间/总时间、有效区停留距离/总路程、总游程和平均速度,大鼠进入暗箱的错误次数及潜伏期以x±s表示,组间比较采用t检验。以α=0.05为检验水准。
2 结果 2.1 各组大鼠Morris水迷宫实验结果与模型组比较,低剂量TAOCO组大鼠第4~5天到达平台的潜伏期明显缩短(P < 0.05);中剂量TAOCO组和阳性药组大鼠第5~6天到达平台的潜伏期明显缩短(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),第5天达到平台的游程明显缩短(P < 0.05),第3天的朝向角降低(P < 0.05);高剂量TAOCO组大鼠第2和5天到达平台的潜伏期明显缩短(P < 0.05),第6天朝向角明显缩小(P < 0.01)。与模型组比较,各剂量TAOCO组大鼠第7天1.5 min内在平台的停留时间、在平台区的停留距离、平台停留时间/总时间和平台停留距离/总路程均明显增加(P < 0.05);低和高剂量TAOCO组大鼠经过平台的次数和有效区的停留时间明显增加(P < 0.05)。见表 1~5。
| (x±s, t/s) | |||||||
| Group | n | Latency to reach platform | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 9 | 42.26±17.01 | 13.33±4.55 | 11.7±3.15 | 6.93±1.99 | 7.40±1.85 | 7.37±1.99 |
| Model | 9 | 62.53±22.68 | 33.71±14.44** | 34.75±31.94* | 15.97±6.68** | 14.89±5.24** | 11.82±5.77* |
| Positive drug | 9 | 49.16±24.82 | 30.27±22.18 | 18.36±16.21 | 11.59±5.14 | 9.09±4.07△ | 7.10±2.47△ |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 58.11±22.81 | 31.08±24.97 | 17.95±10.34 | 9.22±4.55△ | 7.73±5.40△ | 11.66±5.42 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 48.31±22.54 | 26.65±10.54 | 14.71±4.17 | 12.27±5.38 | 8.54±2.95△△ | 7.23±1.73△ |
| High dose | 9 | 47.47±15.79 | 21.18±6.58△ | 13.08±4.78 | 11.03±2.84 | 8.89±3.68△ | 7.48±2.46 |
| *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. | |||||||
| (x±s, l/cm) | |||||||
| Group | n | Swimming distance to reach platform | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 9 | 1 090.63±462.57 | 406.88±126.37 | 336.27±61.40 | 211.39±75.62 | 236.95±84.59 | 233.62±41.75 |
| Model | 9 | 1 274.50±387.52 | 804.80±301.27** | 688.72±481.93* | 409.63±132.60** | 387.08±119.91** | 398.30±284.01 |
| Positive drug | 9 | 1 007.85±352.08 | 699.00±389.30 | 437.59±258.83 | 309.81±123.14 | 255.66±90.05△ | 216.01±92.59 |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 1 229.77±349.87 | 709.52±350.73 | 457.88±195.98 | 285.64±128.88 | 249.86±144.32 | 313.22±119.11 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 1 039.71±338.20 | 636.18±230.56 | 392.48±119.36 | 392.48±119.36 | 260.18±59.83△ | 211.53±34.20 |
| High dose | 9 | 1 154.37±378.87 | 573.19±133.37 | 353.32±118.55 | 333.91±69.71 | 275.31±111.40 | 267.59±71.00 |
| *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05 compared with model group. | |||||||
| (x±s, θ/°) | |||||||
| Group | n | Starting angle | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 9 | 20.90±9.13 | 37.03±18.68 | 48.24±28.60 | 57.24±23.40 | 42.55±7.22 | 49.22±24.43 |
| Model | 9 | 29.81±19.58 | 38.68±26.49 | 46.86±20.16 | 62.73±22.95 | 58.62±15.73 | 55.09±13.99 |
| Positive drug | 9 | 26.63±13.53 | 38.80±20.50 | 33.33±18.53 | 50.56±26.84 | 62.19±21.19 | 37.99±18.31* |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 27.95±18.80 | 29.49±19.31 | 38.14±14.17 | 62.95±28.51 | 48.73±29.97 | 47.63±13.57 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 21.28±10.75 | 36.42±23.69 | 30.35±9.86* | 51.24±22.86 | 52.56±18.02 | 48.15±18.32 |
| High dose | 9 | 20.68±10.25 | 23.78±16.85 | 41.30±22.67 | 46.49±17.67 | 43.81±17.69 | 31.60±16.20** |
| *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with model group. | |||||||
| [x±s, v/(cm·s-1)] | |||||||
| Group | n | Average speed | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 9 | 29.82±4.64 | 32.27±4.54 | 31.38±7.72 | 29.57±6.75 | 33.48±7.73 | 35.02±9.67 |
| Model | 9 | 21.83±3.83 | 27.99±4.18 | 27.34±4.82 | 27.36±4.81 | 27.35±6.05 | 28.33±4.97 |
| Positive drug | 9 | 26.49±6.74 | 29.76±7.61 | 27.75±4.31 | 58.62±10.91 | 30.80±4.99 | 34.24±11.28 |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 24.77±6.59 | 30.72±7.19 | 30.02±9.47 | 33.45±13.18 | 62.19±21.19 | 30.33±7.90 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 29.67±7.29 | 26.65±7.55 | 32.11±6.13 | 31.71±7.31 | 34.33±10.12 | 33.32±6.92 |
| High dose | 9 | 27.87±3.59 | 33.29±11.51 | 29.40±7.27 | 35.12±6.61 | 32.92±7.22 | 38.26±11.17 |
| (x±s) | |||||||
| Group | n | Total distance (l/cm) |
Average speed [v/(cm·s-1)] |
Times of passing platform |
Duration of staying on platform(t/s) |
Times of passing effective area |
Distance of staying on platform(l/cm) |
| Control | 9 | 2 314.50±188.16 | 25.86±2.093 | 5.78±1.86 | 2.95±1.34 | 6.80±82.89 | 88.21±37.41 |
| Model | 9 | 2 020.50±290.50* | 22.49±3.23* | 3.33±2.00* | 1.76±0.96* | 4.33±2.12* | 50.25±30.24* |
| Positive drug | 9 | 2 060.76±337.20 | 23.01±3.67 | 5.78±2.91 | 3.88±3.07 | 4.00±2.12 | 84.83±59.31 |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 2 017.76±239.09 | 22.47±2.66 | 5.75±2.19△ | 3.50±2.17△ | 4.50±2.92 | 86.38±36.04△ |
| Middle dose | 9 | 1 940.18±303.94 | 21.63±3.38 | 5.33±2.06 | 3.20±1.57△ | 3.56±2.74 | 84.25±28.24△ |
| High dose | 9 | 2 172.03±318.07 | 24.24±3.64 | 6.38±2.56△ | 3.92±2.18△ | 4.50±1.31 | 96.54±43.45△ |
| Group | n | Duration of staying on effective area(t/s) |
Distance of staying on effective area(l/cm) |
Duration of staying on platform/total time |
Duration of staying in effective area/total time |
Distance of staying on platform/ total distance |
Distance of staying in effective area/ total distance |
| Control | 9 | 25.19±7.30 | 684.92±153.36 | 0.03±0.02 | 0.28±0.08 | 0.04±0.02 | 0.29±0.05 |
| Model | 9 | 6.45±6.83* | 446.59±240.27* | 0.02±0.01* | 0.20±0.10 | 0.03±0.01 | 0.23±0.10 |
| Positive drug | 9 | 25.77±7.30△ | 604.20±125.06 | 0.04±0.03 | 0.29±0.08 | 0.04±0.03 | 0.30±0.07 |
| TAOCO | |||||||
| Low dose | 8 | 24.83±8.86△ | 589.27±214.22 | 0.04±0.02△ | 0.28±0.10 | 0.04±0.02△ | 0.29±0.08 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 19.72±7.95 | 511.13±190.70 | 0.04±0.02△ | 0.22±0.09 | 0.04±0.01△ | 0.26±0.07 |
| High dose | 9 | 24.53±7.56△ | 583.52±134.08 | 0.04±0.02△ | 0.27±0.08 | 0.05±0.02△ | 0.28±0.07 |
| * P < 0.05 compared with control group; △P < 0.05 compared with model group. | |||||||
与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠在第2天进入暗箱的错误潜伏期明显缩短(P < 0.05),错误次数明显增加(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,阳性药组和各剂量TAOCO组大鼠第2天时的错误潜伏期和错误次数差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表 6。
| (x±s) | |||
| Group | n | Error latency(t/s) | Error time |
| Control | 9 | 272.55±32.98 | 0.55±0.53 |
| Model | 9 | 173.67±120.31* | 2.44±2.45* |
| Positive drug | 9 | 211.78±114.40 | 1.11±1.05 |
| TAOCO | |||
| Low dose | 8 | 203.13±92.57 | 1.75±1.58 |
| Middle dose | 9 | 226.55±105.18 | 1.00±1.50 |
| High dose | 9 | 220.63±100.76 | 1.25±1.48 |
| * P < 0.05 compared with control group. | |||
与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠大脑皮层神经细胞变性、坏死细胞较多;海马神经细胞数量少,层次不清楚,排列松散,神经细胞核浆分界不清。与模型组比较,阳性药组、低和中剂量TAOCO组大鼠大脑皮层和海马组织病理形态表现无明显差异;与模型组比较,高剂量TAOCO组大鼠大脑皮层神经细胞变性、坏死现象减少;海马神经细胞结构清晰,排列较紧密,细胞数无明显减少,坏死细胞减少。见图 1(插页二)。
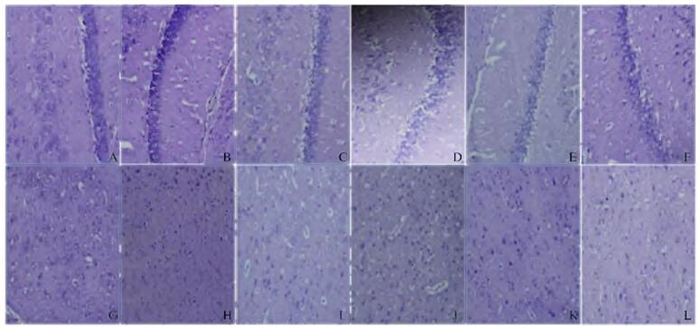
|
| A—F: Hippocampus; G—L: Cerebral cortex; A, G: Control group; B, H: Model group; C, I: Positive drug group; D, J: Low dose of TAOCO group; E, K:Middle dose of TAOCO group; F, L: High dose of TAOCO group. 图 1 各组大鼠大脑海马和皮层组织病理形态表现(×400) Figure 1 Pathomorphology of cerebral hippocampus and cortex tissues of rats in various grou ps(×400) |
|
|
AD的发病机制十分复杂,与多种因素有关,如β-淀粉样蛋白、tau蛋白、载脂蛋白E和氧化应激等,而且各种因素相互关联,从而推动了AD的形成[5-7]。随着人口老龄化的进程,AD发病率逐年升高,严重影响人类生存质量。TAOCO为双重胆碱酯酶抑制剂,在AD的病程发展后期,乙酰胆碱酯酶严重受损,因此本研究探索TAOCO对AD是否有保护作用。
由于大鼠学习记忆能力的行为学指标易受多种因素的干扰,如环境、声音、气味和温度等,因此本研究同时采用Morris水迷宫和避暗实验2种方法观察TAOCO对大鼠学习记忆功能的改善作用。Morris水迷宫可以衡量大鼠的空间学习记忆能力,其原理是对收集与空间定位有关的视觉信息进行整理、记忆、加固和提取,从而使大鼠找到水下隐藏的平台从水中逃脱[8-10]。避暗实验是利用啮齿类动物趋暗避明的生理习性设计的,可反映动物被动回避能力。因其实验周期短、方法简单和指标便于观察等优点而被广泛地应用于动物学习和记忆能力的测试,常被用于药物的筛选[11-13]。本研究结果表明:TAOCO能明显改善AD大鼠空间学习记忆能力,但对AD大鼠的被动回避能力无明显改善作用。
海马是记忆储存的关键结构,大脑皮层和海马结构损伤可影响学习记忆功能,因此在光学显微镜下观察AD大鼠脑组织海马区和皮质区组织细胞的病理形态学变化可间接反映药物对AD大鼠的保护作用[14-18]。本研究结果显示:与模型组比较,高剂量TAOCO组大鼠大脑皮层神经细胞变性、坏死现象减少;海马神经细胞结构清晰,排列较紧密,细胞数无明显减少,坏死细胞少。
综上所述,本研究从行为学和脑组织病理学方面证实了TAOCO可明显改善β-淀粉样蛋白AD大鼠的学习记忆功能,明显减轻AD大鼠大脑皮层及海马组织的病理形态变化,但其具体作用机制尚需进一步探讨。
| [1] | 李昕, 陈泽涛, 谢佳利, 等. 阿尔茨海默症早期评估研究综述[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2015, 32(5): 1146–1149. DOI:10.7507/1001-5515.20150203 |
| [2] | 孙凌, 邱霞. 中西医治疗老年痴呆症的研究进展[J]. 中国疗养医学, 2015, 24(3): 232–234. |
| [3] | 於佳佳, 丛登立, 姜颖, 等. 黄紫堇生物碱化学成分及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 中药材, 2014, 37(10): 1795–1798. |
| [4] | Naik RS, Hartmann J, Kiewert C, et al. Effects of rivastigmine and donepezil on brain acetylcholine levels in acetylcholinesterase-deficient mice[J]. Pharm Pharm Sci, 2009, 12(1): 79–85. DOI:10.18433/J3MK59 |
| [5] | 葛润. 阿尔茨海默症的研究进展[J]. 中外医学研究, 2014, 12(9): 155–157. |
| [6] | 董贤慧, 柴锡庆. 阿尔茨海默病发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(20): 5906–5912. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.20.145 |
| [7] | 付剑亮, 邵福源. 阿尔茨海默病发病机制研究进展[J]. 世界临床药物, 2010, 31(7): 390–394. |
| [8] | 方松, 余化霖. Morris水迷宫实验中海马相关空间学习记忆的研究进展[J]. 国际病理科学与临床杂志, 2010, 30(4): 321–326. |
| [9] | 罗小泉, 骆利平, 陈海芳, 等. Morris水迷宫检测大鼠记忆力方法的探讨[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2010, 21(10): 2667–2669. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2010.10.114 |
| [10] | 闫盼盼, 闫国立, 詹向红, 等. Morris水迷宫实验设计的统计学方法探析[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2013, 31(2): 264–266. |
| [11] | 王莹, 杨文微, 罗菊花. 避暗实验测定小鼠学习记忆功能方法的研究[J]. 大理学院学报, 2011, 10(6): 25–27. |
| [12] | 薛丹, 陈善广, 徐淑萍, 等. 构建自动、智能及敏感度高的避暗实验检测系统[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(15): 2778–2782. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2010.15.028 |
| [13] | 李宁, 刘聪, 李佳鸿, 等. 五味子淫羊藿混合提取物对东莨菪碱致小鼠学习记忆障碍的改善作用[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2017, 43(1): 42–46. |
| [14] | 白晶, 杨弋, 杨薇, 等. 神经保护肽重组慢病毒对老年痴呆大鼠行为学及海马结构内NF-kBmRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2008, 12(7): 829–831. |
| [15] | 孙岩, 崔书克, 刘锐, 等. 健脾益肾方对老年性痴呆模型大鼠记忆能力及海马CA1区JNK蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中医学报, 2017, 32(1): 89–92. |
| [16] | 张会平, 刘宇, 高睿, 等. 桑椹首乌补脑颗粒对老年性痴呆模型大鼠血清SOD、MDA含量及脑组织β淀粉样蛋白表达的影响[J]. 世界中医药, 2016, 11(2): 288–290. |
| [17] | 李娜, 康建华, 杨立顺. 阿尔茨海默病(AD)患者外周血Aβ42及Aβ40的变化研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2016, 20(10): 1664–1666. |
| [18] | 胡文兰, 赵兴山, 张虹, 等. 以心力衰竭为主要表现的原发性淀粉样变性1例报告[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(1): 77–78. |
 2017, Vol. 43
2017, Vol. 43


