扩展功能
文章信息
- 李晶, 李媛, 谢金芳, 耿文韬, 高雪彬, 王娜, 张颖丽
- LI Jing, LI Yuan, XIE Jinfang, GENG Wentao, GAO Xuebin, WANG Na, ZHANG Yingli
- 双侧下颌第二磨牙阻生伴牙旁囊肿1例报告并文献复习
- Bilateral mandibular second molar impaction with paradental cyst:A case report and literature review
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(02): 422-424
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2017, 43(02): 422-424
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20170241
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-10-30
2. 吉林大学口腔医院儿童牙病科, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 吉林大学口腔医院综合科, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Department of General Dentistry, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
下颌第二磨牙阻生 (mandibular second molar impaction) 是指第二磨牙被邻近的第一磨牙、第三磨牙或下颌升支阻挡了正常的萌出道,或者牙冠位置正常,但在骨内埋伏未能正常萌出。下颌第二磨牙阻生患病率为0.06%~0.30%[1],调查[2]显示:国内儿童下颌第二磨牙阻生率远高于国外人群,可达到1%。由于其生长位置,萌出顺序及罕见性,第二磨牙阻生的治疗存在困难。
牙旁囊肿 (paradental cyst) 是一种特殊类型的炎症性根侧囊肿 (inflammatory collateral cyst)。据报道[3]:其发生率为3%~5%。牙旁囊肿常发生于阻生下颌第三磨牙的颊侧或远中颊侧,患者常有冠周炎反复发作史,牙齿多为活髓,X线片显示部分阻生的下颌第三磨牙远中有边界清楚的透射区,有时病变可延伸至根尖部[4]。国内外研究[5-7]显示:牙旁囊肿亦可发生于第三磨牙以外的其他牙位,如第二前磨牙、第一恒磨牙和第二恒磨牙,但双侧下颌第二磨牙阻生伴发牙旁囊肿尚无报道。本文作者报道1例双侧下颌第二磨牙阻生伴牙旁囊肿患者的临床资料,讨论其机制,为双侧下颌第二磨牙阻生伴牙旁囊肿的临床诊治提供参考。
1 临床资料 1.1 一般资料患者,女性,15岁,学生,因左下颌间歇性疼痛不适2月余来诊。2个多月前患者左下颌骨出现间歇性疼痛不适,口服头孢类抗生素消炎,疼痛稍好转,后又出现疼痛。为求彻底诊治,来本院就诊,门诊以“左下颌颌骨肿物”收入院。
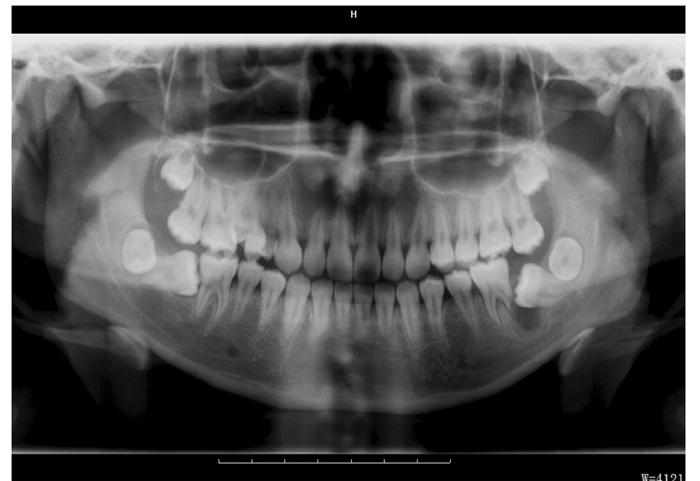
1.2 检查结果专科检查见:双侧第一磨牙及第二磨牙未萌,左下颌第一磨牙及第二磨牙牙髓活力正常,叩诊不适,无松动,大张口时下颌略偏左,余未见明显异常。全口曲面断层片 (图 1) 可见:双侧下颌第二磨牙近中阻生,左下颌第二磨牙冠周可见一类圆形低密度透光区,大小约1.1 cm×0.8 cm,边界清楚,左下颌第一磨牙远中根部分吸收。影像学诊断疑似为左下颌颌骨囊肿,需结合临床。术后病理镜下见:纤维结缔组织囊壁内衬复层增生的无角化上皮,囊壁内可见大量淋巴细胞浸润。病理学诊断考虑为:(下颌骨) 牙旁囊肿。
|
| 图 1 左下颌病变区域的曲面断层片 Figure 1 Panoramic radiograph of mandibular lesion area |
|
|
双侧下颌第二磨牙阻生;牙旁囊肿。
1.4 治疗方案正畸科会诊建议拔除双侧下颌第二磨牙,保留双侧下颌第三磨牙,术后择期正畸治疗;综合正畸科意见与患者病情,主治医师与患者及家长沟通后建议左下颌第一磨牙术前行根管治疗,暂时保留左下颌第一、第三磨牙,右下颌第二、第三磨牙。术中摘除下颌骨囊肿并拔除左下颌第二磨牙,暂时观察左下颌第一磨牙,其余牙暂不做处理。
1.5 手术方案局麻下行颌骨囊肿摘除术+牙拔除术+根切术,术前第一磨牙行根管治疗。局麻下拔除第二磨牙,刮匙刮除病变区残余牙囊、肉芽组织和囊肿壁,球钻打磨创腔及尖锐骨创缘并且磨除第一磨牙部分远中根尖。
2 讨论由于下颌第二磨牙阻生萌出需要第一磨牙的远中根诱导,两者之间过大的间隙导致第一磨牙牙根无法诱导第二磨牙的正常萌出,导致第二磨牙阻生。第二磨牙阻生不仅影响牙弓的稳定性,降低咀嚼效能,伴发颞颌关节疾病,而且容易引起邻牙的邻面龋损,严重可致牙髓疾病。而牙旁囊肿不仅可以伴有牙齿的阻生,还可伴有第三磨牙与多生牙的融合[8]。下颌第二磨牙阻生依据其阻生情况,临床治疗有以下方法:①正畸治疗。该方法创伤小,预后佳,可获得良好的咬合关系,与其他方法相比较较受医生和患者青睐。②外科方式。a.外科直立法:适用于倾斜角度大并且不宜正畸治疗的患者。进行该法直立磨牙的理想牙根长度为牙根发育占总长度的1/3或1/2,这样有助于磨牙在定位后根尖血运的重新建立。当选择通过外科的方法直立磨牙时不要进行颊舌向的倾斜移位,直立第二磨牙的角度不要超过90°。具体方法:局麻下在下颌第二磨牙的颊侧做切口,翻瓣,将阻生齿周围骨进行一定程度的松解后再轻柔地直立近中阻生的下颌第二磨牙。为了防止近中阻生的第二磨牙复发到原来的位置,应在阻生下颌第二磨牙的近中放置分牙簧[9]。b.第三磨牙萌出替代法。拔除严重阻生的第二磨牙,并诱导第三磨牙近中萌出,填补缺牙间隙。由于第三磨牙萌出期间存在诸多不确定因素,该方法的可行性存在质疑[10]。c.自体牙拔出再植法。拔除严重阻生的患牙,立即植入正确的垂直位置。再植后常引起牙根吸收,牙固连等并发症,当无法采用正畸直立时才考虑该方法[11]。③分牙方式。适用于轻度阻生,通过放置分牙簧,松解第一磨牙与第二磨牙过紧接触,使其自行调整倾角,逐渐恢复至正常位置[12]。
牙旁囊肿的发病机制目前仍不清楚。Craig[13]认为:牙旁囊肿是由正在萌出的牙齿表层牙周组织中的慢性炎症刺激牙源性上皮细胞增殖引起,鉴别诊断包括根端囊肿、牙周侧方囊肿、牙囊和含牙囊肿[14]。Maruyama等[15]采用免疫组织化学染色观察牙旁囊肿组织显示:K13、K14、K17、K19、UEA-I结合蛋白和串珠素阳性表达,表明其具有结合上皮的特征,因此可以认为是在牙周袋中产生的一种包涵囊肿。研究[16]显示:牙旁囊肿一般位于下颌骨,第一磨牙的牙旁囊肿一般发生于10岁以下的儿童,牙旁囊肿发生的时间和位置与牙齿萌出有关。下颌双侧第二磨牙阻生伴发牙旁囊肿比较罕见,多科室会诊有利于伴有牙齿阻生、牙根吸收的牙旁囊肿的综合治疗。目前牙旁囊肿仍以手术治疗为主,如有其他并发症应一并处理。术前使用锥体束计算机断层扫描 (cone-beam computed tomography,CBCT) 提供高对比度三维图像,有助于诊断及制定治疗计划。
| [1] | Vedtofte H, Andreasen JO, Kjaer I. Arrested eruption of the permanent lower second molar[J]. Eur J Orthod, 1999, 21(1): 31–40. DOI:10.1093/ejo/21.1.31 |
| [2] | Cho SY, Ki Y, Chu V, et al. Impaction of permanent mandibular second molarsinethnic Chinese school children[J]. J Can Dent Assoc, 2008, 74(6): 521. |
| [3] | Ackermann G, Cohen MA, Altini M. The paradental cyst:a clinicopathologic study of 50 cases[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1987, 64(3): 308–312. DOI:10.1016/0030-4220(87)90010-7 |
| [4] | 于世凤. 口腔病理学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,1979: 330. |
| [5] | 张维儒, 杨会荣, 张春芝. 儿童下颌骨牙旁囊肿1例[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2008, 22(3): 238. |
| [6] | Borgonovo AE, Reo P, Grossi GB, et al. Paradental cyst of the first molar:Report of a rare case with bilateral presentation and review of the literature[J]. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent, 2012, 30(4): 343–348. DOI:10.4103/0970-4388.108940 |
| [7] | Borgonovo AE, Grossi GB, Maridati PC, et al. Juvenile paradental cyst:presentation of a rare case involving second molar[J]. Minerva Stomatol, 2013, 62(10): 397–404. |
| [8] | Ozcan G, Sekerci AE, Soylu E, et al. Role of cone-beam computed Tomography in the evaluation of a paradental cyst related to the fusion of a wisdom tooth with a paramolar:A rare case report[J]. Imaging Sci Dent, 2016, 46(1): 57–62. DOI:10.5624/isd.2016.46.1.57 |
| [9] | García-Calderón M, Torres-Lagares D, González-Martín M, et al. Rescue surgery (su-rgical repositioning) of impacted lower second molars[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2005, 10(5): 448–453. |
| [10] | Sawicka M, Racka-Pilszak B, Rosnowska-Mazurkiewicz A. Uprighting partially impacted permanent second molars[J]. Angle Orthodont, 2007, 77(1): 148–154. DOI:10.2319/010206-461R.1 |
| [11] | Grover P, Lorton L. The incidence of unerupted permanent teeth and related clinical cases[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol, 1985, 59(4): 420–425. DOI:10.1016/0030-4220(85)90070-2 |
| [12] | Solow B. The dentoalveolar compensatory mechanism:background and clinical implications[J]. Br J Orthod, 1980, 7(3): 145–161. DOI:10.1179/bjo.7.3.145 |
| [13] | Craig GT. The paradental cyst.A specific inflammatory odontogenic cyst[J]. Br Dent, 1976, 141(1): 9–14. DOI:10.1038/sj.bdj.4803781 |
| [14] | de Sousa SO, Corrêa L, Deboni MC, et al. Clinicopathologic features of 54 cases of paradental cyst[J]. Quintessence Int, 2001, 32(9): 737–741. |
| [15] | Maruyama S, Yamazaki M, Abé T, et al. Paradental cyst is an inclusion cyst of the junctional/sulcular epithelium of the gingiva:histopathologic and immunohistochemical confirmation for its pathogenesis[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2015, 120(2): 227–237. DOI:10.1016/j.oooo.2015.04.001 |
| [16] | Friedrich RE, Scheuer HA, Zustin J. Inflammatory paradental cyst of the first molar (buccal bifurcation cyst) in a 6-year-old boy:case report with respect to immunohistochemical findings[J]. In Vivo, 2014, 28(3): 333–339. |
 2017, Vol. 43
2017, Vol. 43


