扩展功能
文章信息
- 宫睿, 谢湘林, 杜冰, 武毅, 刘宏雁
- GONG Rui, XIE Xianglin, DU Bing, WU Yi, LIU Hongyan
- 桦褐孔菌对血管性痴呆模型大鼠的保护作用
- Protective effect of Inonotus obliquus on vascular dementia model rats
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(01): 57-61
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2017, 43(01): 57-61
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20170112
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-07-25
桦褐孔菌(Inonotus obliquus)作为一种可食用的真菌,近年来受到国内外学者广泛关注。大量研究[1-6]显示:桦褐孔菌具有多种药理作用,如抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗炎、抗病毒、抗辐射和免疫调节等作用,以其抗氧化和抗炎作用尤为突出。氧化损伤及炎症反应为血管性痴呆(vascular dementia,VD)主要发病机制。桦褐孔菌对VD是否有保护作用, 国内外文献尚未见相关报道。本研究首次通过反复夹闭大鼠双侧颈总动脉再灌注合并腹腔注射硝普钠降压法制备大鼠VD模型,初步探讨桦褐孔菌对VD大鼠的保护作用,为桦褐孔菌的临床应用提供实验依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、主要试剂和仪器清洁级Wistar大鼠100只,雄性,体质量220~280 g,动物使用许可证号:SCXK-(吉)2013-0001,由吉林大学基础医学院实验动物中心提供。桦褐孔菌(原粉系200目的细粉,由吉林大学药学院药理教研室制备); 硝普钠注射液(开封康诺药业有限公司,批号:1301021);吡拉西坦片(天津金世制药有限公司,批号:H12020667)。XR-XM101型Morris水迷宫装置(成都泰盟科技有限公司),CX31型光学显微镜(日本Olympus公司)。
1.2 实验方法采用双侧颈总动脉反复夹闭再灌注联合腹腔注射硝普钠降压法,建立大鼠VD模型。按参考文献[7]方法,将大鼠用10%的水合氯醛(0.35 mg·100g-1)腹腔注射麻醉后,仰卧固定于手术台上,颈正中切口,分离双侧颈总动脉,穿线备用。在夹闭之前,腹腔注射0.05%硝普钠2.5 mg·kg-1, 随即夹闭双侧颈总动脉8 min,再通10 min,重复3次。术前预留出正常对照组大鼠。术后14d,将存活的大鼠随机分为模型组,阳性药(吡拉西坦,PT, 0.5 g·kg-1)组,低、中、高剂量(0.5、1.0和2.0 g·kg-1)桦褐孔菌组,连续给药8周后进行水迷宫实验,实验期间继续给药直至实验结束。水迷宫实验连续7 d,前6 d将大鼠分别从1、2、3和4象限4个不同的入水点放入水中,记录大鼠游到平台的潜伏期、游程、平均游速和朝向角;实验第7天移走平台,记录大鼠2 min内经过平台的次数、平台区的逗留时间、在平台区的停留距离、经过有效区的次数、有效区的逗留时间、有效区的停留距离、平台停留时间/总时间、平台停留距离/总路程、有效区停留时间/总时间、有效区停留距离/总路程、总游程、平均游速和朝向角的变化情况。水迷宫实验后,处死大鼠,取脑组织甲醛固定,HE染色,制备病理切片,光学显微镜下观察大鼠大脑皮质和海马区组织的病理形态表现。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS13.0统计学软件包进行统计学分析。水迷宫实验数据均以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组大鼠Morris水迷宫实验结果与模型组比较,低剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠在实验第2~6天到达平台的潜伏期、游程、朝向角和游泳速度无明显变化(P>0.05),中和高剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠在实验第2~6天到达平台的潜伏期和游程均明显减少(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),吡拉西坦组大鼠在实验第3~6天游到平台的潜伏期及游程均明显缩短(P < 0.05),各组大鼠朝向角及游泳速度无明显变化(P>0.05)。
在实验第7天,与模型组比较,各剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠在2 min内的总游程、平均游速、平台停留距离和平台停留距离/总路程均无明显变化(P>0.05),中和高剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠穿越平台次数、穿越有效区次数、有效区停留时间、有效区停留距离、有效区停留时间/总时间和有效区停留距离/总路程均明显增加(P < 0.05),高剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠平台停留时间和平台停留时间/总时间明显增加(P < 0.05),吡拉西坦组大鼠经过平台的次数、在平台的停留时间、经过有效区的次数、有效区的停留时间、有效区的停留距离、平台停留时间/总时间、平台停留距离/总路程、有效区停留时间/总时间和有效区停留距离/总路程均明显增加(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);各组大鼠总游程、游泳的平均速度和朝向角均无明显变化(P>0.05)。见表 1~5。
| (x±s, t/s) | |||||||
| Group | n | Latency | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 10 | 62.38±27.80 | 25.40±14.20 | 15.60±7.47 | 12.57±4.32 | 8.32±3.30 | 8.79±2.69 |
| Model | 10 | 73.40±23.15 | 54.82±37.42* | 39.30±34.49* | 26.16±19.35* | 17.77±9.98* | 22.04±16.30* |
| PT | 8 | 59.51±26.66 | 30.73±15.78 | 12.71±4.86△ | 10.46±1.87△ | 8.20±2.25△ | 7.94±2.16△ |
| Inonotus obliquus | |||||||
| Low | 10 | 57.89±21.13 | 32.42±26.00 | 15.76±10.84 | 14.54±7.21 | 11.06±7.57 | 12.22±10.87 |
| Medium | 10 | 67.56±26.00 | 24.60±16.04△ | 13.57±6.88△ | 11.73±5.38△ | 9.63±2.48△ | 9.06±4.55△ |
| High | 9 | 55.87±31.15 | 22.95±25.94△ | 11.98±6.92△ | 9.85±6.77△ | 8.74±3.28△ | 7.77±4.03△ |
| P < 0.05 compared with control group; △P < 0.05 compared with model group. | |||||||
| (x±s, l/cm) | |||||||
| Group | n | Swimming distance | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 10 | 1 374.81±672.73 | 719.64±355.52 | 418.29±141.81 | 396.65±145.04 | 294.55±92.37 | 263.58±62.61 |
| Model | 10 | 1 718.37±828.75 | 1 370.03±872.72 | 729.22±365.09* | 725.45±428.32* | 528.91±204.47** | 599.59±374.94* |
| PT | 8 | 1 411.97±607.33 | 749.91±316.39 | 377.15±87.57△ | 366.88±104.27△ | 305.01±99.50△ | 304.18±118.32△ |
| Inonotus obliquus | |||||||
| Low | 10 | 1 264.76±414.73 | 845.90±473.58 | 452.59±184.76 | 419.25±201.02 | 347.90±169.87 | 346.57±242.96 |
| Medium | 10 | 1 484.52±337.90 | 631.34±354.45△ | 440.08±188.72△ | 379.57±150.48△ | 358.73±84.83△ | 301.47±158.49△ |
| High | 9 | 1 215.83±395.50 | 558.80±515.83△ | 335.18±149.32△ | 280.91±115.72△ | 271.24±59.26△△ | 206.30±85.12△ |
| * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. | |||||||
| (x±s, θ/°) | |||||||
| Group | n | Starting angle | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 10 | 36.36±20.40 | 35.41±13.75 | 34.05±22.41 | 38.04±20.23 | 26.95±17.07 | 40.94±20.85 |
| Model | 10 | 29.12±19.50 | 43.65±14.40 | 37.34±21.10 | 38.25±25.25 | 29.84±19.77 | 34.61±12.33 |
| PT | 8 | 27.29±16.84 | 43.40±17.59 | 27.61±19.69 | 40.80±17.06 | 33.16±16.44 | 27.78±27.18 |
| Inonotus obliquus | |||||||
| Low | 10 | 30.70±15.82 | 47.07±23.90 | 36.84±22.60 | 23.37±11.81 | 30.73±19.47 | 24.49±17.11 |
| Medium | 10 | 49.14±23.26 | 40.12±15.36 | 31.34±16.66 | 41.41±22.06 | 37.22±20.14 | 35.08±16.29 |
| High | 9 | 43.08±21.28 | 53.98±23.43 | 49.98±24.12 | 43.35±20.51 | 34.28±19.72 | 44.49±26.44 |
| [x±s, v/(cm·s-1)] | |||||||
| Group | n | Average velocitice | |||||
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control | 10 | 26.78±6.48 | 32.59±8.57 | 34.67±10.14 | 33.36±9.04 | 41.53±13.73 | 32.19±7.32 |
| Model | 10 | 25.22±6.74 | 26.92±4.61 | 28.71±6.59 | 36.84±9.37 | 35.45±7.86 | 36.26±8.51 |
| PT | 8 | 27.62±5.86 | 30.11±7.92 | 34.68±9.96 | 29.47±7.87 | 38.02±10.10 | 43.02±14.16 |
| Inonotus obliquus | |||||||
| Low | 10 | 23.43±2.84 | 33.46±9.88 | 35.22±7.44 | 39.10±9.63 | 43.82±15.05 | 34.72±10.81 |
| Medium | 10 | 25.39±6.72 | 27.18±8.23 | 35.89±9.87 | 30.93±9.50 | 38.85±9.97 | 33.12±10.27 |
| High | 9 | 28.48±5.13 | 32.79±8.73 | 29.80±5.50 | 35.45±12.76 | 35.99±8.85 | 30.02±12.44 |
| (x±s) | |||||||||||||
| Group | n | Total swimming distance (t/cm) |
Average velocity [v/(cm·s-1)] |
Times of crossing platform |
Time of staying on platform (t/s) |
Distance of staying on platform (l/cm) |
Times of crossing effective area |
Time of staying in effective area (t/s) |
Distance of staying in effective area (l/cm) |
Time of staying on platform/ Total time |
Distance of staying on platform/ Total distance |
Time of staying in effective area/Total time |
Distance of staying in effective area/ Total distance |
| Control | 10 | 2710.37±529.13 | 22.66±4.41 | 5.10±3.21 | 2.55±1.68 | 72.65±43.61 | 8.00±1.76 | 26.76±12.88 | 696.66±306.02 | 0.021±0.014 | 0.026±0.016 | 0.224±0.108 | 0.252±0.080 |
| Model | 10 | 2633.93±549.56 | 22.00±4.58 | 2.30±1.89* | 1.10±1.22* | 33.01±39.21* | 5.10±3.03* | 16.19±8.52* | 420.18±247.27* | 0.009±0.010* | 0.010±0.012* | 0.135±0.071* | 0.162±0.094* |
| PT | 8 | 2705.18±297.87 | 22.59±2.48 | 4.63±2.56△ | 3.09±2.10△ | 70.26±36.19 | 8.38±3.16△ | 31.31±12.43△△ | 699.97±269.77△ | 0.026±0.018△ | 0.027±0.017△ | 0.261±0.104△△ | 0.260±0.998△ |
| Inonotus obliquus | |||||||||||||
| Low | 10 | 2568.91±601.01 | 21.46±5.12 | 4.11±3.18 | 2.01±1.68 | 53.70±48.56 | 5.78±1.39 | 24.84±11.70 | 642.57±255.21 | 0.017±0.014 | 0.021±0.023 | 0.207±0.977 | 0.258±0.105 |
| Medium | 10 | 2696.48±630.29 | 22.50±5.25 | 5.78±4.00△ | 2.72±2.24 | 71.72±57.16 | 8.11±2.26△ | 29.87±12.87△ | 746.56±295.45△ | 0.023±0.019 | 0.027±0.021 | 0.249±0.107△ | 0.272±0.094△ |
| High | 9 | 2799.70±716.71 | 23.39±6.02 | 6.13±5.33△ | 2.99±2.06△ | 85.31±72.64 | 8.00±2.56△ | 32.73±16.67△ | 798.77±399.68△ | 0.025±0.017△ | 0.029±0.024 | 0.273±0.139△ | 0.280±0.107△ |
| * P < 0.05 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. | |||||||||||||
与对照组比较,模型组大鼠的大脑皮质神经细胞变性、坏死细胞较多,核仁不清,胞浆染色深;大鼠海马神经细胞数量减少,层次不清,可见较多的变性、坏死细胞。与模型组比较,吡拉西坦组和低、中剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠大脑皮层、海马无明显改变;高剂量桦褐孔菌组大鼠大脑皮层神经细胞数较多,变性、坏死细胞较少,海马神经细胞数较多,排列较整齐,坏死细胞少。见图 1(插页三)。
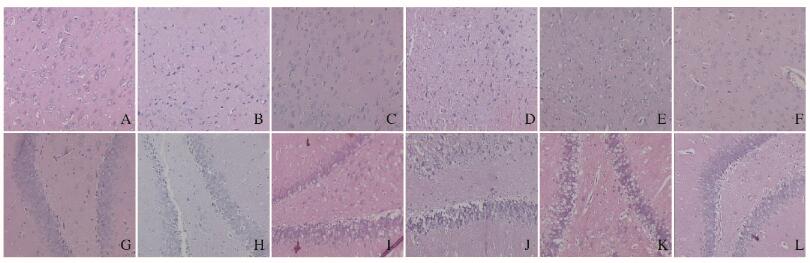
|
| A-F: Cerebral cortex; G-L: Hippocampus; A, G:Control group; B, H: Model group; C, I:PT group; D, J: Low dose of IO group; E, K: Middle dose of IO group; F, L: High dose of IO group. 图 1 各组大鼠脑组织病理形态表现(×20) Figure 1 Pathomorphology of brain tissue of rats in various groups (×20) |
|
|
VD是老年性痴呆常见的一种类型,是由脑血管疾病引发的一种具有痴呆表现的临床综合征,可导致脑智能的损伤,学习记忆和认知功能的障碍,目前是继阿尔兹海默症(Alzheimer’s disease,AD)之后的第2大痴呆性疾病[8]。
20世纪80年代初,英国心理学家Morris[9]发明了Morris水迷宫实验,用于研究大鼠的空间学习记忆能力,由于其设计的合理性和有效性,现已广泛用于学习记忆的研究。目前采用Morris水迷宫实验结果衡量动物的空间定向能力、空间辨别能力及空间记忆能力。本实验结果表明:桦褐孔菌能明显改善VD大鼠在水迷宫实验中的空间定向能力及空间辨别能力,改善VD大鼠的学习记忆功能。
脑皮层及海马结构对于学习能力是至关重要的, VD大鼠脑皮层及海马组织损伤[10-12],因此在光学显微镜下观察VD大鼠脑组织海马区和皮质区组织细胞的病理形态学变化,可以间接地反映出VD大鼠学习记忆功能变化。
本研究中大鼠脑组织病理结果显示:桦褐孔菌(2.0 g·kg-1)可以减轻VD大鼠大脑皮层及海马区组织细胞的病理损伤,提示桦褐孔菌(2.0 g·kg-1)对VD大鼠的脑组织病理损伤具有保护作用。大量实验[13-17]证实:桦褐孔菌中的乙酸乙酯相及乙醇相有较强的抗氧化作用。本研究结果从行为学与脑组织病理学两方面证实了桦褐孔菌原粉对VD大鼠有一定的保护作用,其作用机制有待于进一步深入研究。
| [1] | 曾小龙. 桦褐孔菌的化学成分与药理作用研究[J]. 广东教育学院学报, 2007, 27(3): 76–81. |
| [2] | 钟秀宏, 赵丽微, 赵芬琴, 等. 桦褐孔菌醇诱导人卵巢癌SKOV3细胞株凋亡及其分子机制研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2014, 49(3): 191–194. |
| [3] | 钟秀宏, 赵芬琴, 高宇, 等. 桦褐孔菌醇对人卵巢癌裸鼠移植瘤的抑制作用[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2015, 30(20): 3351–3353. |
| [4] | 孙艳美, 钟秀宏, 吕士杰. 桦褐孔菌多糖对微波辐射致大鼠免疫损伤的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2015, 35(3): 758–759. |
| [5] | 梁丽雅, 张泽生, 孙玮, 等. 桦褐孔菌醇提物的萃取分离及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中北大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 30(2): 153–158. |
| [6] | 梁丽雅, 张泽生, 王玉本, 等. 桦褐孔菌抗氧化提取物体内抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品科技, 2009, 34(7): 146–148. |
| [7] | 高东, 周中和, 王景周. 实验性血管性痴呆的模型制作问题[J]. 国外医学:老年医学分册, 2002, 23(2): 59–61. |
| [8] | 吴林, 麻小梅, 赵海涛, 等. 血管性痴呆动物模型的研究进展[J]. 广西中医药大学学报, 2014, 17(1): 93–96. |
| [9] | Morris RGM. Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues[J]. Learn Motiv, 1981, 12(2): 239–260. DOI:10.1016/0023-9690(81)90020-5 |
| [10] | 方圣博, 谢湘林, 刘蕾, 等. 血栓心脉宁对大鼠血管性痴呆的治疗作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(10): 2762–2764. |
| [11] | 赵小贞, 王玮, 康仲涵, 等. 血管性痴呆大鼠海马超微结构的变化及药物干预[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2005, 28(3): 311–315. |
| [12] | 赵小贞, 王玮, 康仲涵, 等. 血管性痴呆大鼠海马突触结构参数的变化[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2002, 25(1): 30–34. |
| [13] | 梁丽雅, 张泽生, 吕晨, 等. 桦褐孔菌抗氧化活性物质的提取工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2009, 30(4): 32–35. |
| [14] | 杜秀菊, 张扬, 刘莲芬, 等. 桦褐孔菌醇提物抗氧化活性部位的筛选[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2015, 6(10): 4219–4224. |
| [15] | 黄纪国, 余雄涛, 谢意珍, 等. 桦褐孔菌提取物抗氧化活性研究[J]. 广西植物, 2014, 34(4): 515–519. |
| [16] | 严艾, 高进, 陈萍. 丙泊酚对新生大鼠海马BDNFmRNA、proBDNF/mBDNF表达的影响及其与学习记忆功能的关系[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016, 41(5): 389–394. |
| [17] | 马琼, 满其航, 杜丽, 等. 藤黄霖对微波诱发的大鼠学习记忆能力及精子损伤的辐射防护作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016, 41(8): 685–688. |
 2017, Vol. 43
2017, Vol. 43


