扩展功能
文章信息
- 孙兰芳, 及昕, 史册, 韩茹钰, 张宁, 韩明林, 李明贺, 韩成敏
- SUN Lanfang, JI Xin, SHI Ce, HAN Ruyu, ZHANG Ning, HAN Minglin, LI Minghe, HAN Chengmin
- 3种恶性成分的腮腺区多形性腺瘤癌变1例报告及文献复习
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma composed of three malignant components in parotid gland:A case report and literature review
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(06): 1265-1267
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2017, 43(06): 1265-1267
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20170637
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-05-06
2. 吉林大学口腔医院病理科, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 吉林大学口腔医院正畸科, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Pathology, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Department of Orthodontics, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
多形性腺瘤癌变(carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, CXPA)是一种上皮性恶性肿瘤,起源于多形性腺瘤。CXPA约占唾液腺肿瘤的3.6%,占所有唾液腺恶性肿瘤的12%[1]。CXPA中最常见的恶性成分是非特异性腺癌和唾液腺导管癌,其他类型的癌如肌上皮癌少见[2]。既往报道的CXPA中一般只含有1种恶性成分,多种恶性成分混合的CXPA极为罕见。国内外尚无含有3种恶性成分的CXPA完整病例报道。本文作者报道1例罕见的3种恶性成分混合的CXPA病例。
1 临床资料 1.1 一般资料患者,女性,71岁,约30年前发现左侧腮腺区有1个0.5 cm×0.5 cm大小的无痛性肿物,未经过任何治疗,肿物缓慢增大,近1年肿物生长加速,1个月前患者自觉肿物疼痛。门诊以“腮腺区肿物”于2016年12月19日收入本院治疗。口腔专科检查见患者左侧面部膨隆,有1个直径约20 cm×10 cm×9 cm的不规则形肿物(图 1,见封三)。前界至左侧口角垂线,后界至左侧乳突表面后3 cm,上界至耳屏水平,下界至颈部中1/2。可见肿物表面血管扩张,皮温不高,质地中等,扪诊结节状,与周围组织界限尚清楚,活动度欠佳。肿物前部隆起处有1个直径约5 cm类圆形紫红色区域,表面结节状,与皮肤粘连。表面皮肤无破溃,触之囊性感,触压痛明显。双侧颞下颌关节活动正常,关节无压痛、无弹响,张口度轻度受限,开口度“两横指”,开口型右偏。双侧腮腺导管乳头无红肿,左侧分泌液减少,双侧舌下肉阜无红肿,分泌正常。下颌下、颏下及颈部未触及明显肿大淋巴结。

|
| A:Entopicview; B:Lateralview. 图 1 CXPA患者外观 Figure 1 Appearance of CXPA patient |
|
|
影像学检查: 2016年12月19日彩色超声检查可见:左面部肿物处扫查,可见1个杂乱回声肿物,边界清,远场回声增强,内可见血流信号,最大肿物前后径为9.6 cm、上下径为9.6 cm。该肿物位于左颈动静脉浅侧面。左腮腺及颌下腺显示不清。胸片检查排除肺转移。
1.3 治疗方法患者住院后第3天于手术室全麻下行“左侧腮腺肿物切除术”。术中见肿瘤包膜完整,肿瘤质地中等,与周围组织界限清楚,无粘连,直径约15cm。肿瘤下方腮腺组织受压萎缩,左侧颈动脉体受压变细。术中冰冻快速病理检查诊断:多形性腺瘤,细胞生长活跃。
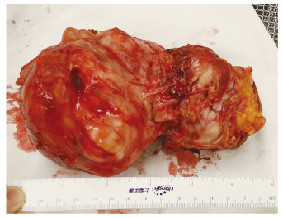
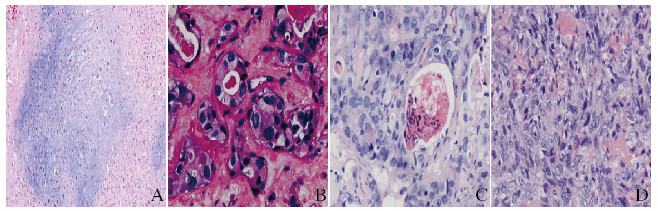
2 结果术后患者恢复良好。术后病理(病理号162311: 1)肉眼所见: 15 cm×10 cm×10 cm大小肿物1个,表面结节状,质地中等,取材12块; 光镜下所见:肿瘤结构多样,可见非特异性腺癌、肌上皮癌和导管癌结构,大部分结构为包膜内恶变,部分区域可见侵犯包膜外脂肪组织。Vimentin(+)、S-100(+)、actin(-)、SMA(-),非特异性腺癌部位CK7(+)、CK5/6(-),肌上皮癌区CK7(-)、CK5/6(-)、p63(-)、AB(-)、PAS(-)、Ki67阳性率大于50%。术后病理诊断符合(左腮腺)CXPA,肿瘤结构多样,可见非特异性腺癌、肌上皮癌和导管癌结构。大部分结构为包膜内恶变,部分区域可见侵犯包膜外脂肪组织。见图 2(封三)和3(封三)。
|
| 图 2 肿物的大体标本 Figure 2 Gross specimen of tumor |
|
|
|
| A:Residual pleomorphic adenoma component (HE, ×100); B:Non-specific adenocarcinoma(HE, ×200); C:Duct carcinoma(HE, ×200);D:Myoepithelial carcinoma(HE, ×200) 图 3 CXPA的3种恶性成分 Figure 3 Three malignant components of CXPA |
|
|
CXPA是来自多形性腺瘤上皮性成分的恶变。根据世界卫生组织2005组织学分类[1],恶性多形性腺瘤被分为3种不同的临床组织学类型:①CXPA(存在于已有的多形性腺瘤中的癌);②癌肉瘤(真正的恶性肿瘤);③转移性多形性腺瘤(原发灶、转移灶均为良性多形性腺瘤组织病理学特点)。根据癌细胞浸润周围组织的程度不同,CXPA可分为非侵袭性癌、微侵袭性癌(侵入包膜外≤1.5 mm)、侵袭性癌(侵入包膜外>1.5 mm)[2]。
CXPA中的恶性成分可以是任何类型的癌,最常见的恶性成分是非特异性腺癌和唾液腺导管癌,少见肌上皮癌、上皮-肌上皮癌、未分化癌、腺样囊性癌、肉瘤样癌和腺鳞癌等[2]。CXPA一般只含有1种恶性成分,多种恶性成分混合的病例很少见。使用PubMed在英文文献中检索到5例[3-7]完整报道的由2种恶性成分组成的CXPA病例。其中2例发生在腮腺区,Magaki等[6]报道了1例腮腺区含有导管癌和鳞状细胞癌2种恶性成分的CXPA; Enokida等[7]报道了1例腮腺区含有导管癌和鳞状细胞癌2种恶性成分的CXPA。到目前为止,尚无3种恶性成分共存的CXPA的完整病例报道。
CXPA好发年龄为60~70岁,较多形性腺瘤好发年龄晚约10年, 男性多于女性[8]。CXPA最常见的临床表现是实质性肿块存在超过3年, 在就诊前几个月里出现快速生长[7]。如果浸润神经和周围组织,可伴有面瘫、皮肤浸润、疼痛和张口受限等。临床和放射学研究结果显示:大多数肿瘤表现为T1或T2期[9]。因此超过半数的原发性腮腺癌不存在任何症状和体征可表明是恶性肿瘤。CXPA的术前确诊有赖于更高精度的细针穿刺细胞病理学检查。但是该患者肿瘤体积巨大,恶性成分多,残余多形性腺瘤成分比例少,给细胞穿刺诊断带来很大困难。病理诊断是CXPA最主要的诊断依据。CXPA表现为多形性腺瘤,组织学结构中含有数量不等的恶性成分。恶性成分有时过度生长,导致良性多形性腺瘤成分很难发现或者被忽略,以至于被误诊[9]。本例CXPA在光镜下寻找残余的多形性腺瘤成分很困难,未发现典型的含有多种结构的多形性腺瘤区域,只发现了多形性腺瘤中的黏液样组织。目前,外科治疗腮腺恶性肿瘤的方法为腮腺完整切除术与该侧颈部淋巴清扫结合。对于位于腮腺浅叶的非侵袭性和微侵袭性癌,可以行腮腺浅叶及肿瘤切除术[10]。
CXPA预后与肿瘤的大小、组织学分级、侵犯的程度、细胞增殖活性、恶性成分的比例和癌变类型有关。Spiro等[11]报道肿瘤直径大于6 cm患者生存率低。高分化肿瘤比低分化的更易有不良临床结果,如转移和低生存率[12]。侵犯的程度超过良性多形性腺瘤的范围,被认为是影响预后的最重要的因素,也决定了淋巴清扫和辅助放化疗的应用。一般来说侵袭性癌预后较差[12]。肿瘤恶性成分的比例超过50%时,可明显影响CXPA患者的生存率[8]。Katabi等[13]在对43例CXPA的组织学成分研究中发现:肌上皮癌成分会增加CXPA复发的风险, 即使是非侵袭性CXPA也是如此。Ki67可以标记细胞增殖指数,Ki67百分比越高说明癌细胞增殖越快,也提示该肿瘤恶性程度也越高。本例报道中患者肿瘤巨大,部分区域侵犯包膜外组织,恶性成分中含有肌上皮成分, 肌上皮区域Ki67阳性率大于50%,这些都是影响预后的不利因素。
CXPA一般通过淋巴结转移(通常是颈部淋巴结), 很少发生血行转移。发现远处转移时, 主要转移部位为肺、骨和肝[2]。CXPA患者的生存率有所不同。Lewis等[2]对73例CXPA患者的研究结果显示:CXPA患者的5年疾病特异生存率为37%。Nouraei等[14]对28例CXPA患者的研究结果显示CXPA患者的5年疾病特异生存率为44%。总之,CXPA患者的预后比大多数腮腺恶性肿瘤差。
| [1] | Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, et al. World health organization classification of tumours:pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours[J]. Lyon:IARC Press, 2005: 242–244. |
| [2] | Lewis JE, Olsen KD, Sebo TJ. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma:pathologic analysis of 73 cases[J]. Hum Pathol, 2001, 32(6): 596–604. DOI:10.1053/hupa.2001.25000 |
| [3] | Freeman SR, Sloan P, de Carpentier J. Carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum with adenoid cystic and squamous carcinomatous differentiation[J]. Hum Rhinol, 2003, 41(2): 118–121. |
| [4] | Nakamori K, Ohuchi T, Hasegawa T, et al. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the buccal region is composed of salivary duct carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma components[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 38(10): 1116–1118. DOI:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.04.016 |
| [5] | Sedassari BT, da Silva Lascane NA, Tobouti PL, et al. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the palate composed of invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma components:an unusual case with immunohistochemical approach[J]. Medicine, 2014, 93(27): e146. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000000146 |
| [6] | Magaki SD, Bhuta S, Abemayor E, et al. Carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland consisting of high-grade salivary duct carcinoma and keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2015, 120(3): e169–e173. DOI:10.1016/j.oooo.2015.01.014 |
| [7] | Enokida T, Fujii S, Kuno H, et al. Combined salivary duct carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma suspected of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma[J]. Pathol Int, 2016, 66(8): 460–465. DOI:10.1111/pin.2016.66.issue-8 |
| [8] | Olsen KD, Lewis JE. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma:a clinicopathologic review[J]. Head Neck, 2001, 23(9): 705–712. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0347 |
| [9] | Zbären P, Zbären S, Caversaccio MD, et al. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma:diagnostic difficulty and outcome[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 138(5): 601–605. DOI:10.1016/j.otohns.2008.01.013 |
| [10] | Antony J, Gopalan V, Smith RA, et al. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma:a comprehensive review of clinical, pathological and molecular data[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2012, 6(1): 1–9. DOI:10.1007/s12105-011-0281-z |
| [11] | Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Strong EW. Malignant mixed tumor of salivary origin. A clinicopathologic study of 146 cases[J]. Cancer, 1977, 39(2): 388–396. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0142 |
| [12] | Zhao J, Wang J, Yu C, et al. Prognostic factors affecting the clinical outcome of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma in the major salivary gland[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2013, 11(1): 180. DOI:10.1186/1477-7819-11-180 |
| [13] | Katabi N, Gomez D, Klimstra DS, et al. Prognostic factors of recurrence in salivary carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, with emphasis on the carcinoma histologic subtype:a clinicopathologic study of 43 cases[J]. Hum Pathol, 2010, 41(7): 927–934. DOI:10.1016/j.humpath.2009.12.011 |
| [14] | Nouraei SAR, Hope KL, Kelly CG, et al. Carcinoma ex benign pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland[J]. Plast Reconstruct Surg, 2005, 116(5): 1206–1213. DOI:10.1097/01.prs.0000181654.68120.0f |
 2017, Vol. 43
2017, Vol. 43


