扩展功能
文章信息
- 朱云波, 李佳佳, 马征, 赵亮
- ZHU Yunbo, LI Jiajia, MA Zheng, ZHAO Liang
- 阿替普酶对急性脑梗死大鼠血管内皮细胞中Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达的影响
- Effect of alteplase on expressions of Claudin-1 and Claudin-5 proteins in vascular endothelial cells of rats with acute cerebral infarction
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(06): 1137-1141
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2017, 43(06): 1137-1141
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20170613
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-04-21
脑梗死是人类最常见的严重致死疾病,缺血性脑血管病是致残的最常见临床类型,其中急性缺血性脑梗死占1/3~1/4[1]。因此临床上如何早期积极治疗急性缺血性脑梗死是目前面临的重要问题。溶栓是目前公认的有效治疗急性缺血性脑梗死的方法[2]。研究[3]证明:早期及时的溶栓治疗可以减少梗死面积、改善神经功能缺损,也是是目前治疗急性脑梗死的唯一有效手段。因此利用动物模型来研究脑梗死溶栓机制和溶栓疗效非常重要。
阿替普酶是重组组织型纤溶酶原激活物,为第2代溶栓药物,是基因工程合成产物,其并发症少,溶栓效果好,也是FDA批准的早期溶栓治疗急性缺血性脑梗死的唯一药物[4-5]。研究[6]证明:阿替普酶对急性脑梗死早期临床改善及晚期预后均有积极作用,而且安全、有效,可降低患者病残率、不增加颅内出血死亡的风险。但关于阿替普酶对急性脑梗死大鼠血管内皮细胞蛋白作用的报道较少。本文作者对急性脑梗死大鼠进行溶栓治疗后,研究大鼠血管内皮细胞中相关蛋白闭合蛋白1(Claudin-1)和闭合蛋白5(Claudin-5)的表达水平,为临床治疗脑梗死提供实验数据和理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、药物、主要试剂和仪器54只SPF级SD大鼠,体质量(200±20)g,购自广东省医学实验动物中心,动物合格证号:SCXK(粤)2013-0002。阿替普酶(注射用阿替普酶,50 mg/瓶,德国勃林格殷格翰制药公司)。注射用凝血酶(湖南一格制药有限公司),戊二醛溶液(广州中镜科仪技术有限公司),Western blotting试剂和免疫荧光染色试剂盒(美国Thermo Fisher公司),兔抗大鼠Claudin-1、Claudin-5和β-actin抗体(美国Invitrogen公司),IgG-HRP和IgG-FITC二抗(美国CST公司)。纯水仪(美国Millipore公司),H-7650透射电子显微镜(日本日立公司),TCSNT激光共聚焦显微镜(德国Leica公司),核酸电泳仪和蛋白垂直电泳仪和凝胶成像系统(美国Bio-rad公司),ViiA 7荧光定量PCR仪(美国ABI公司)。
1.2 急性大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠模型的制备参照文献[7-8]方法建立急性大脑中动脉栓塞(MCAO)大鼠模型,大鼠按0.35 mL·100-1体质量腹腔注射10 %水合氯醛麻醉,颈部正中位备皮,消毒,暴露出右侧颈总动脉,分离迷走神经。将含有凝血酶的凝固血液注入静脉留置针管,制成长约1 cm的栓子。将留置针穿刺进入右侧颈总动脉,并向前内侧进入颈内动脉内10 mm,拔出针芯,快速将栓子冲入大鼠颈内动脉,结扎右侧颈总动脉。假手术组操作方法与模型组相同,注入生理盐水代替栓子。
1.3 实验动物分组和药物干预54只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和阿替普酶溶栓组,每组18只。于溶栓后3、6和24 h各组分别取大鼠6只。造模3 h后,阿替普酶溶栓组按大鼠体质量5 mg·kg-1经股静脉注射阿替普酶。假手术组与模型组大鼠分别给予等体积生理盐水。
1.4 透射电子显微镜下观察大鼠内皮细胞超微结构在给药溶栓3、6和24 h后,各组分别取大鼠6只,开颅,以镊子轻分离纹状体边缘, 取出非缺血侧和缺血侧的纹状体组织,立即置于2.5%戊二醛中固定1h,采用PBS漂洗2次,再置于1%锇酸中固定1 h,清洗,用不同浓度丙酮(50%、70%、90%和100%)脱水,包埋,切片,采用醋酸铀和柠檬酸铅染色,透射电子显微镜下观察大鼠中枢神经系统脑毛细血管内皮细胞和内皮细胞之间超微结构的变化,以内皮细胞之间紧密连接、结构完整度及基膜厚薄等作为观察指标。
1.5 荧光免疫组织化学法检测大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平在相应时间点取各组大鼠,处死后取脑组织纹状体组织,冰冻切片,采用免疫荧光染色试剂盒,先加入Claudin-1和Claudin-5一抗各150 μL低温孵育12 h,冲洗后,再加入荧光二抗150 μL,室温孵育1 h,最后加入150 μL Hochest,室温孵育10 min,PBS冲洗,封片,显微观察并分析荧光强度,检测各组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平,以Claudin-1和Claudin-5免疫染色呈绿色作为阳性表达, 采用Image pro plus6.0图像处理软件进行蛋白分析。
1.6 Western blotting法检测大鼠血管内皮细胞中Claudin-l和Claudin-5表达水平[21]取脑组织纹状体组织标本切片称质量,粉碎,加入组织裂解液提取蛋白,采用Western blotting试剂盒进行蛋白定量。每组取10 μg蛋白进行SDS-PAGE电泳,经转印后分别检测血管内皮细胞中Claudin-l和Claudin-5和内参β-actin等蛋白的表达水平,得到的条带用凝胶成像分析仪进行灰度分析。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。大鼠血管内皮细胞中相关蛋白Claudin-1、Claudin-5的表达组间比较采用单因素方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组大鼠内皮细胞超微结构假手术组大鼠脑梗死区域可见清晰的脑毛细血管内皮细胞,内皮细胞之间紧密连接,结构致密、完整,呈连续条带状,内皮细胞无肿胀,基膜厚薄均匀。模型组大鼠缺血区域脑体积明显增大,内皮细胞肿胀,部分皮质与周围脑组织界限明显,基膜厚薄不均匀,紧密连接结构非常松散、出现断裂和消失。阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠脑梗死区域毛细血管内皮细胞肿胀明显减轻,基膜厚薄不均匀改善,脑毛细血管内皮细胞、内皮细胞之间大部分紧密连接结构断裂情况消失。见图 1。
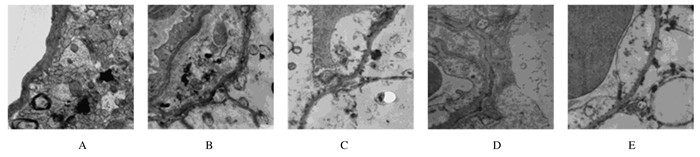
|
| A: Sham operation group; B:Model group; C-E:Alteplase group (3, 6, 24 h). 图 1 各组大鼠脑组织内皮细胞超微结构(×40 000) Figure 1 Ultrastructures of endothelial cells in brain tissue of rats in various groups (×40 000) |
|
|
假手术组大鼠脑毛细血管内皮细胞中绿色荧光蛋白Claudin-1和Claudin-5均沿血管内皮正常表达;与模型组比较,阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-l和Claudin-5的表达水平明显改善;与假手术组比较,阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平明显下调,且随溶栓时间的延长逐渐下降。假手术组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平分别为0.92和0.91;模型组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平分别为0.31、0.33;阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1和Claudin-5的表达水平分别为0.58和0.57。见图 2和3(插页四)。
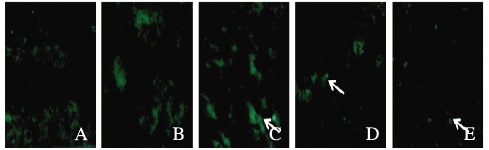
|
| A: Sham operation group; B:Model group; C-E:Alteplase group(3, 6, 24 h). 图 2 荧光免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-1的表达(×100) Figure 2 Expressions of Claudin-1 in cerebral ischemic region of rats in various groups detected by fluorescence immunohistochemical method(×100) |
|
|
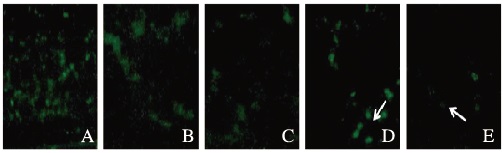
|
| A: Sham operation group; B:Model group; C-E:Alteplase group(3, 6, 24 h). 图 3 荧光免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠脑缺血区Claudin-5的表达(×100) Figure 3 Expressions of Claudin-5 in cerebral ischemic region of rats in various groups detected by fluorescence immunohistochemical method(×100) |
|
|
Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白在目的大小处出现条带,假手术组蛋白表达水平正常,模型组蛋白表达量明显减少,而不同时间点阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠血管内皮细胞中Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达水平均高于模型组。溶栓6和24 h后,与模型组比较,阿替普酶溶栓组大鼠血管内皮细胞中Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达水平均升高,而3 h时两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。各组大鼠血管内皮细胞内参β-actin的蛋白表达水平无明显变化。见图 4。
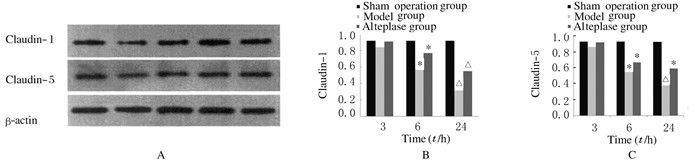
|
| *P < 0.01 vs sham operation group; △P < 0.01 vs model group. 图 4 各组大鼠血管内皮细胞中Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达量电泳图(A)和直条图(B,C) Figure 4 Electrophoregram (A) and histogram(B, C)of expressions of Claudin-1 and Claudin-5 proteins in vascular endothelial cells in various groups |
|
|
脑梗死己经成为全世界范围内危害全人类健康的最主要疾病之一,其具有发病率高、致残率极高和致死率高等特点,75%的脑梗死患者遗留有不同程度残疾[9-11]。在我国人口死因中脑血管病已居第一位,成为神经内科医师防治的重要问题之一。目前基础研究主要通过动物脑梗死模型,采用溶栓模拟人类治疗过程,从而研究脑梗死病理生理机制。本研究在前期研究的基础上,简化建模方法,使模型神经功能缺损症状明显,且大鼠死亡率低;采用急性大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠模型,造模后由于持久的供血中断,模型组大鼠缺血区域脑体积增大,内皮细胞肿胀,形成边界清楚的梗死灶,紧密连接结构非常松散、出现断裂和消失,提示造模成功。
急性脑梗死的发病机制较为复杂,目前的研究水平仍无法阐明原因。紧密连接是血脑屏障的结构和基础,其由跨膜蛋白、细胞骨架蛋白和胞质附着蛋白共同组成。Claudin属于一个多基因家族,Claudin-1和Claudin-5存在于内皮细胞中。研究[12-15]表明:血脑屏障通透性与Claudin-5和Claudin-1表达减少密切相关,其中Claudin-5主要存在于脑毛细血管内皮细胞中,可以选择性地调节紧密连接,可能是脑血管内皮细胞通透性调节的最重要因子[16-19]。故本研究中以脑血管内皮细胞Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达作为检测指标。
机体中细胞与细胞间存在着某些连接,在维持生理功能和细胞结构等方面起着重要的作用。紧密连接即是其中之一,其对于维持内皮细胞和表皮的选择渗透性屏障功能是非常关键的[20-23]。本研究通过检测微结构的变化发现:阿替普酶可以有效保护毛细血管的内皮细胞紧密连接的结构,明显减轻大鼠脑梗死区域毛细血管内皮细胞肿胀,改善基膜厚薄不均匀。研究[13-14]显示:Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白断裂可导致蛋白数据密度的下降或消失。本研究结果显示:阿替普酶可以显著改善Claudin-1、Claudin-5的蛋白表达,阿替普酶组表达水平较假手术组下调明显,且随溶栓时间的延长逐渐下降,提示阿替普酶可以减少Claudin-1和Claudin-5的破坏,进而对紧密连接结构及血脑屏障的通透性产生保护作用,Western blotting结果提示:大鼠在接受溶栓后,Claudin-1和Claudin-5表达水平明显下调,溶栓后6和24 h时表达水平下调更加明显,说明阿替普酶能够减少脑缺血性损伤对紧密连接相关蛋白Claudin-1与Claudin-5的破坏。
本研究结果证明:阿替普酶给药对急性脑梗死大鼠的大脑内皮细胞的结构有改善作用,其作用机制可能与阿替普酶能降低血管内皮细胞中Claudin-1和Claudin-5蛋白表达有关。
| [1] | 张秋月. 急性脑梗死治疗的研究进展[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2015, 28(5): 742–744. |
| [2] | 刘静, 吴雅坤, 吕宪民, 等. 急性脑梗死rt-PA溶栓治疗进展[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2016, 37(3): 355–357. |
| [3] | Huang X, Cheripelli BK, Lloyd SM, et al. Alteplase versus tenecteplase for thrombolysis after ischaemic stroke(ATTEST):a phase 2, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint study[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2015, 14(4): 368–376. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70017-7 |
| [4] | Rha JH, Shrivastava VP, Wang Y, et al. Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke with alteplase in an Asian population:results of the multicenter, multinational Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Non-European Union World (SITS-NEW)[J]. Int J Stroke, 2014, 9(Suppl A100): 93–101. |
| [5] | Whiteley WN, Emberson J, Lees KR, et al. Risk of intracerebral haemorrhage with alteplase after acute ischaemic stroke:a secondary analysis of an individual patient data meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2016, 15(9): 925–933. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30076-X |
| [6] | Li M, Wang-Qin RQ, Wang YL, et al. Symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage after intravenous thrombolysis in Chinese patients:comparison of prediction models[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2015, 24(6): 1235–1243. DOI:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.01.026 |
| [7] | Chen S, Yang Q, Chen G, et al. An update on inflammation in the acute phase of intracerebralhemorrhage[J]. Transl Stroke Res, 2015, 6(1): 4–8. DOI:10.1007/s12975-014-0384-4 |
| [8] | Chen Y, Zhu W, Zhang W, et al. A novel mouse model of thromboembolic stroke[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2015, 256: 203–211. DOI:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.09.013 |
| [9] | 房硕, 胡沛霖, 王建民, 等. 急性后循环脑梗死血管内治疗研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(8): 913–918. |
| [10] | 成峰, 吴宗艺. 静脉溶栓联合血管内治疗对急性后循环脑梗死临床疗效分析[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2016, 26(3): 95–97. |
| [11] | 牛国忠. 急性脑梗死血管内治疗新进展[J]. 浙江省科学技术协会会议论文集, 2015, 5(1): 15–17. |
| [12] | Zobel K, Hansen U, Galla HJ. Blood-brain barrier properties in vitro depend on composition and assembly of endogenous extracellular matrices[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2016, 365(2): 233–245. DOI:10.1007/s00441-016-2397-7 |
| [13] | Schossleitner K, Rauscher S, Gröger M, et al. Evidence that cingulin regulates endothelialm barrier function in vitro and in vivo[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2016, 36(4): 647–654. DOI:10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.307032 |
| [14] | Chao AC, Lee TC, Juo SH, et al. Hyperglycemia increases the production of amyloid beta-peptide leading to decreased endothelial tight junction[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2016, 22(4): 291–297. DOI:10.1111/cns.12503 |
| [15] | Cai H, Liu W, Xue Y, et al. Roundabout 4 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability through the modulation of ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-5 expression[J]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2015, 74(1): 25–37. DOI:10.1097/NEN.0000000000000146 |
| [16] | Peng S, Wang SB, Singh D, et al. Claudin-3 and claudin-19 partially restore native phenotype to ARPE-19 cells via effects on tight junctions and gene expression[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2016, 151: 179–189. DOI:10.1016/j.exer.2016.08.021 |
| [17] | Ji C, Wang L, Dai R, et al. Hyperthermia exacerbates the effects of cathepsin L on claudin-1 in a blood-brain barrier model in vitro[J]. Brain Res, 2016, 1631: 72–79. DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.043 |
| [18] | Wang J, Chen J, Tang Z, et al. The effects of copper on brain microvascular endothelial cells and claudin via apoptosis and oxidative stress[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2016, 174(1): 132–141. DOI:10.1007/s12011-016-0685-4 |
| [19] | Li B, Li Y, Liu K, et al. High glucose decreases claudins-5 and -11 in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells:Antagonistic effects of tongxinluo[J]. Endocr Res, 2017, 42(1): 15–21. DOI:10.3109/07435800.2016.1163723 |
| [20] | Abadier M, Haghayegh Jahromi N, Cardoso Alves L, et al. Cell surface levels of endothelial ICAM-1 influence the transcellular or paracellular T-cell diapedesis across the blood-brain barrier[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2015, 45(4): 1043–1058. DOI:10.1002/eji.201445125 |
| [21] | 周晓俊, 边莹, 李莉, 等. 菖葛益智方对血管性认知功能障碍大鼠脑组织微血管内皮细胞occludin和claudin-5表达的影响[J]. 陕西中医, 2016, 37(11): 1550–1552. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2016.11.051 |
| [22] | 曹解华, 刘德荣, 刘尚章, 等. 颈动脉斑块与脑梗死相关性分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(1): 40–41. |
| [23] | 郑鲲, 谭娟, 冯辉斌. 醒脑静联合依达拉奉治疗急性脑梗死昏迷疗效观察[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(1): 46–47. |
 2017, Vol. 43
2017, Vol. 43


