扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘相良, 何岍妍, 王以恒, 纪伟, 李理, 李书轩, 王珍, 李幼琼, 李薇, 程凯亮
- LIU Xiangliang, HE Qianyan, WANG YiHeng, JI Wei, LI Li, LI ShuXuan, WANG Zhen, LI Youqiong, LI Wei, CHENG Kailiang
- 薄层CT技术在确定翼腭窝入路手术中圆孔到颈内动脉虹吸段安全距离中的应用
- Application of thin-section computed tomographic images in measurement of safe range from foramen rotundum to siphon of internal carotid artery for operation through pterygopalatine fossa
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(05): 1010-1013
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(05): 1010-1013
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160534
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-12-04
2. 吉林大学基础医学院解剖学系, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 吉林大学中日联谊医院胃肠结直肠肛门外科, 吉林 长春 130033;
4. 吉林大学第二医院妇产科, 吉林 长春 130041;
5. 吉林大学中日联谊医院放射线科, 吉林 长春 130033
2. Department of Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Department of Gastrointestinal Colorectal and Anal Surgery, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130033, China;
4. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Second Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130041, China;
5. Department of Radiology, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130033, China
翼腭窝位于颞下窝前内侧,是一个在翼突与上颌骨之间的骨性狭窄空间[1],由蝶骨体、蝶骨翼突和腭骨垂直板、上颌窦后壁共同围成,大小为(21.4±0.8)mm×(5.2±0.3)mm×(3.2±0.3)mm[2],通过圆孔与颅腔相连[3]。在这个结构内通过很多重要的神经和血管,并且毗邻颅前窝、鼻骨、口部、鼻部、眼部和颊部等其他重要部位。故翼腭窝是发生损伤的主要部位。同时翼腭窝腔隙深而狭长,许多疾病如鼻咽部血管纤维瘤和鼻咽癌等也经常经该处扩散[4]。鼻内镜下经翼腭窝手术入路是目前神经外科最常用的手术通路之一。手术的风险主要是由于颈内动脉的创伤造成患者的致死性出血和神经系统损伤[5],因此详细了解翼腭窝的解剖结构以及测量其与毗邻重要器官的距离有重要意义。文献[6]报道:经翼腭窝的鼻内镜手术只要控制在圆孔下方区域进行,避免过度解剖蝶窦外侧壁以防损伤视神经和颈内动脉虹吸部,手术即可相对安全。但是并无关于颈内动脉虹吸段到圆孔间确切安全距离的相关报道。本研究标注测量了颈内动脉虹吸段底部(A点)与圆孔[6](B点)之间的安全距离,同时测量了经过A和B 2点的直线与3个平面(冠状面、矢状面和水平面)所成的角度,从而能够更加精准地描述其位置。本研究提供了圆孔与颈内动脉虹吸段底部之间有一段手术过程中安全的距离,对外科手术具有指导意义。本研究采用薄层CT技术来取代以往在尸体上进行研究的方法,同时利用三维重建技术更加准确地寻找到相关结构,并进行距离的测量,较以往的方法更为精确。
1 资料与方法 1.1 标本的来源全部CT扫描数据来自121份头颅计算机断层三维重建图像。图像均来自吉林大学中日联谊医院影像数据库。121名志愿者年龄为18~78岁。测量前已确认颈内动脉虹吸段底部、翼腭窝和圆孔等结构CT扫描结果均正常。所有图像均由吉林大学中日联谊医院的西门子64排螺旋断层扫描仪扫描得出。
1.2 参数的测量①使测量平面垂直于两眼球边缘的连线,通过调整图像来消除不同人体位而造成的误差。通过三维重建技术实现了头颅重建的图像。②在颈内动脉虹吸段底部(A点)和圆孔(B点)进行了精确的标注[8-9],并记录其图层图像(图 1)。利用三维重建技术建立一个平行于眼耳平面和鼻中隔平面的坐标系,坐标系以A点作为坐标原点(图 2)。C点是A点在一个平行于眼耳平面的平面上的投影点,且B点经过该平面。D点是C点在一个平行于鼻中隔平面的平面上的投影点,且B点经过该平面。③测量AC与BC的距离,计算A点与B点之间的距离,测量AB所在直线与冠状面、矢状面和水平面3个平面之间的角度[10]。
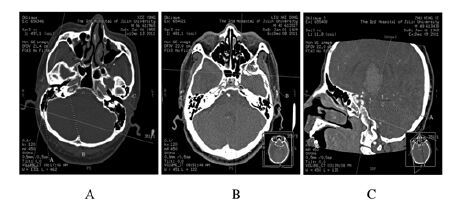
|
| 图 1 采用三维重建技术测量颅骨各解剖标志 Figure 1 Various markers of skull detected by three-dimensional reconstruction technique |
|
|
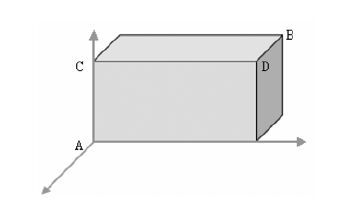
|
| 图 2 采用三维重建技术建立以A点为坐标原点的坐标系示意图 Figure 2 Coordinate system taking point A as coordinate origin established by three-dimensional reconstruction technique |
|
|
采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析。将颈内动脉虹吸段底部(A)、A点在一个圆孔(B)经过的平行于眼耳平面的平面上的投影点(C)以及两者之间的距离AC,AB所在直线与三个平面所成的夹角等统计数据进行统计学分析。因AC的测量结果不符合正态分布,故以中位数(Q)的形式表示。
2 结 果AC长度的测量数据不符合正态分布,所以以中位数和四分位数表示。AC间的长度为 (13.22±3.79) mm(范围为8.33~105.67 mm;95%CI:8.55~21.39 mm)。到矢状面的角度为33.54°±9.23° (范围为5.38°~66.58°;95%CI:30.88°~34.20°)。到冠状面的角度为53.17° ±10.48°(范围为5.60°~75.02°;95%CI:51.29°~55.06°)。到水平面的角度为9.43°±12.91 ° (范围为-28.44°~82.22°;95%CI:7.11°~11.76°)。
3 讨 论鼻内镜下经翼腭窝入路是目前最常见的神经外科手术入路方法。翼腭窝及其周围结构解剖关系复杂,内有颌内动脉及其分支、上颌神经及其分支、翼腭神经节等重要神经血管结构,毗邻眶尖、颈内动脉和视神经等重要结构,是鼻腔进入侧颅底的通道[11],而在手术过程中一旦损伤颈内动脉和神经等重要结构,会造成包括出血和面瘫在内的一系列严重并发症。因此,了解和测量翼腭窝及其与毗邻重要器官的距离显得尤为重要。
颈内动脉虹吸段底部位于蝶窦外侧壁的顶部,而翼腭窝位于蝶窦外侧壁底部[12]。在手术过程中,颈内动脉虹吸段底部以下、翼腭窝以上的位置都相对安全[13]。而圆孔在颅骨内是一个非常重要的结构,位于翼腭窝的外侧,并与颅腔相连接。视神经和颈内动脉虹吸段底部位于圆孔的后上方,因此在圆孔与颈内动脉虹吸段底部之间有一段手术过程中安全的距离。以往国内外的文献并无关于颈内动脉虹吸段到圆孔间准确安全距离的相关报道,因此本研究旨在测量颈内动脉虹吸段到圆孔间准确的安全距离,从而对外科手术给予指导。
本研究的结果有助于在手术中减少和避免并发症,通过对志愿者头部CT扫描数据进行的三维重建[14-15],利用三维重建技术将颈内动脉虹吸段底部、圆孔相应的解剖结构进行定位,投影到各平面上分别进行标注与测量,不仅得出了颈内动脉虹吸段底部到圆孔间的安全距离,还得出多个结构之间的角度数据[16] ,这更有利于提高测量这些重要结构的准确性。本研究结果可以有效指导手术中相关结构的定位,弥补了单纯距离测量的不足[17]。掌握颈内动脉虹吸段底部与圆孔之间的安全距离,能够减少手术中的损伤及并发症,可为外科手术提供指导。
综上所述,与过去的研究比较,本研究提供了准确量化的鼻内镜下翼腭窝手术的安全操作范围,而不再是单纯提出这种安全距离的存在。本研究能够更准确、更安全地确定手术操作的范围,因此,参照本研究所得出的安全范围进行经鼻内镜下翼腭窝入路的手术将更加安全。
| [1] | Cheng Y, Xu H, Chen Y, et al. Location of pterygopalatine fossa and its relationships to the structures in sellar region[J]. Craniofac Surg , 2015, 26 (6) : 1979–1982. DOI:10.1097/SCS.0000000000001899 |
| [2] | Narouze S. Neurostimulation at pterygopalatine fossa for cluster headaches and cerebrovascular disorders[J]. Curr Pain Headache Rep , 2014, 18 (7) : 432. DOI:10.1007/s11916-014-0432-5 |
| [3] | Zheng HN, Wu Yue, Lu YB, et al. Sectional and applied anatomy of pterygopalatine fossa for operative approach[J]. Chin J Clini Anat , 2009, 27 (4) : 379–383. |
| [4] | Zhang QX, Zou J, Qin G, et al. Operation path to pterygopalatine fossa under endoscope[J]. China J Endoscopy , 2007, 13 (8) : 795–797. |
| [5] | Solari D, Magro F, Cappabianca P, et al. Anatomical study of the pterygopalatine fossa using an endoscopic endonasal approach:spatial relations and distances between surgical landmarks[J]. J Neurosurg , 2007, 106 (1) : 157–163. DOI:10.3171/jns.2007.106.1.157 |
| [6] | 沈鹏, 孙中武, 李建瑞, 等. 鼻内镜下经鼻径路解剖翼腭窝区临床观察[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报 , 2015, 2 (2) : 58–61. |
| [7] | 金涌, 白志强, 陶宝鸿. 翼管、圆孔和蝶腭孔的CT三维重建解剖学[J]. 解剖学报 , 2014, 45 (3) : 359–363. |
| [8] | Bhatki AM, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, et al. Endonasal surgery of the ventral skull base——endoscopic transcranial surgery[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am , 2010, 22 (1) : 157–168. DOI:10.1016/j.coms.2009.10.005 |
| [9] | Hofstetter CP, Singh A, Anand VK, et al. The endoscopic, endonasal, transmaxillary transpterygoid approach to the pterygopalatine fossa, infratemporal fossa, petrous apex, and the Meckel cave[J]. J Neurosurg , 2010, 113 (5) : 967–974. DOI:10.3171/2009.10.JNS09157 |
| [10] | Sandu K, Monnier P, Pasche P. Anatomical landmarks for transnasal endoscopic skull base surgery[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol , 2012, 269 (1) : 171–178. DOI:10.1007/s00405-011-1698-4 |
| [11] | 敖勇.鼻内镜下鼻腔外侧壁入路翼腭窝解剖学研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2009. |
| [12] | 刘涛, 杜忠良. 鼻内镜下经鼻径路翼腭窝区的临床解剖特点分析及意义[J]. 中外医疗 , 2016, 35 (5) : 81–82. |
| [13] | Sun XJ, Pang RL, Zhao W, et al. The correlation study of the applied anatomy of internal carotid artery with brain DSA[J]. J Intervent Radiol , 2004, 13 (1) : 66–67. |
| [14] | Kodama S, Mabuchi H, Suzuki M. Endoscopic endonasal transturbinate approach to the pterygopalatine fossa in the management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol , 2012, 2012 : 786262. |
| [15] | Fortes FS, Sennes LU, Carrau RL, et al. Endoscopic anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa and the transpterygoid approach:development of a surgical instruction model[J]. Laryngoscope , 2008, 118 (1) : 44–49. DOI:10.1097/MLG.0b013e318155a492 |
| [16] | 王雷, 李俊, 梁健, 等. 三维CT血管造影在脑肿瘤微创切除术的评估作用[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志 , 2011, 16 (7) : 317–318. |
| [17] | Cavallo LM, Messina A, Gardner P, et al. Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa:anatomical study and clinical considerations[J]. Neurosurg Focus , 2005, 19 (1) : E5. |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


