扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘换新, 张国祥, 郭琳琅, 唐松山
- LIU Huanxin, ZHANG Guoxiang, GUO Linlang, TAN Songshan
- miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及其临床意义
- Expression of miR-139-5p in small cell lung cancer tissue and its clinical significance
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(05): 942-948
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(05): 942-948
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160520
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-07-30
2. 南方医科大学附属珠江医院病理科, 广东 广州 510282;
3. 广东药学院生化与分子生物学教研室, 广东 广州 510006
2. Department of Pathology, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, China;
3. Deparment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Guangdong College of Pharmacy, Guangzhou 510006, China
小细胞肺癌是肺癌的一种病理学分类,占肺癌的15%~20%,其治疗方案一般为化疗和放疗联合方案,由于其转移快,极易产生化疗耐药,故常导致治疗失败[1-2]。因此,早发现、早诊断和早治疗仍然是包括小细胞肺癌在内的所有肿瘤诊治的关键 [3-4],从分子水平寻找有效的诊断、治疗和预后评估的生物学标志物是目前临床亟待解决的问题。
微小DNA(microRNA,miRNA)是一种内源性的非编码RNA(ncRNA),是由17~25个碱基组成的单链RNA分子,广泛存在于各种生物体中,在转录和转录后水平调控细胞生命活动。近年研究[5] 发现:miRNA在很多肿瘤中异常表达,与肿瘤的形成、侵袭转移、分期预后、治疗反应和疗效预测等有密切关联。目前,在淋巴瘤、前列腺癌、小细胞肺癌和结直肠癌等多种肿瘤组织中检测到与肿瘤相关的miRNA[6-8]。研究[9-11] 发现:miR-139-5p参与调解多种肿瘤的增殖、凋亡及化疗敏感性,然而关于miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌中的作用国内外尚未见相关报道。本研究探讨miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义,阐明miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌发生发展过程中的作用,为寻找小细胞肺癌患者临床预后的靶基因提供依据。
1 资料与方法 1.1 标本收集收集 2011年1月—2014年5月在武警广东总队医院行手术或支气管镜活检的50例临床资料完整的小细胞肺癌患者石蜡包埋组织。所有组织均经病理学确诊为小细胞肺癌,所有病例确诊前均未行放化疗。患者平均年龄(50.0±7.2)岁,随访时间6~72个月。其中男性27例,女性23例;年龄<50岁30例,年龄 ≥ 50岁20例;临床分期:局限期21例,广泛期29例;化疗敏感(化疗5~6个周期后肿瘤完全缓解或部分缓解)21例,化疗耐药(化疗5~6个周期后疾病稳定或进展者)29例。50例患者均接受EP方案化疗。本研究经本院伦理委员会批准,所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 随访 50例患者出院后均获随访,随访方式为电话随访和复查随访,随访内容包括一般情况、临床症状及影像学检查。随访起点为确诊日期,末次随访时间为2014年8月31日,至随访截止日,依然生存22例,死亡28例,无失访病例。
1.3 细胞和主要试剂人小细胞肺癌细胞株H69、H446及人正常肺泡上皮细胞HPAEpiC均来自美国ATCC公司。应用含15%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基做细胞扩增培养基,在37℃、 5% CO2细胞培养箱中培养。RPMI-1640培养基、胎牛血清、 Opti-MEM、LipofectamineTM2000和胰酶(0.02%EDTA)购自美国Gibco生物技术有限公司,CCK8及凋亡检测试剂盒购自上海碧云天公司,Trizol RNA试剂盒、RT试剂盒、Taq酶和PCR试剂盒均购自美国Invitrogen公司,第1链cDNA合成试剂盒购自大连宝生物公司。
1.4 建立稳定表达miR-139-5p的细胞株取对数生长期的细胞转至6孔板中培养,待细胞生长到60%汇合时,加入包含miR-139-5p的前体表达质粒(Ambion),用LipofectamineTM 2000和Opti-MEM分别将上述质粒转入细胞,经G418筛选后,获得稳定表达的miR-135-5p细胞。提取细胞总蛋白和RNA备用。
1.5 实时荧光定量PCR(QRT-PCR)法检测miR-139-5p表达收集小细胞肺癌癌细胞、癌组织及癌旁组织(50~100 mg)在液氮中磨成粉末后,加入1 mL Trizol液研磨(样品总体积不超过所用Trizol体积的10%),分别移入去RNA酶的EP管中,提取总RNA。取上述准备的RNA,逆转录反应参照AMV逆转录试剂盒说明,在20 μL体系中加2 μg总RNA进行cDNA的合成。QRT-PCR采用2 × SYBR Green PCR Master Mix,取适量cDNA作为模板,引物浓度为0.4 μmol·L-1,15 μL体系进行扩增,每个待测样本设置3个平行样。以U6 snRNA作为内参。PCR反应在实时定量PCR反应仪上进行。3次独立实验后得到的数据采用公式RQ = 2-ΔΔCt进行分析。
1.6 CCK8检测细胞增殖能力通过转染 miR-139-5p mimics上调H69和H446中miR-139-5p的表达,QRT-PCR检测miR-139-5p的表达,CCK8法检测细胞增殖能力。取对数生长期稳定表达的miR-139-5p细胞,接种于 96 孔板,每孔2.0 × 103个细胞,每孔体积 200 μL,分别于 0、12、24、36 、48和72 h,每孔加入CCK8溶液20 μL,37℃继续孵育 4 h,用酶联免疫检测仪测定 450 nm 的各孔吸光度(A)值,以时间为横轴,A值为纵轴,绘制细胞生长曲线。每次设 3 个平行孔,至少重复2次。以A值表示细胞的增殖能力。
1.7 流式细胞术检测细胞周期取生长状态良好的稳定表达miR-139-5p细胞及原代细胞 H69AR,用 0.25%胰蛋白酶和 0.02% EDTA 消化细胞,PBS 洗 2 次,75%乙醇冰浴固定 24 h,用含 1% BSA 的 PBS 充分混匀洗涤2 次,PI 染色后进行流式细胞仪测定,并用 Cell Quest 软件分析各组细胞群体在细胞周期各个时相的分布比例。
1.8 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡采用AnnexinⅤ/PI染色法。对数生长期稳定表达的miR-139-5p细胞及原代细胞 H69AR 以每孔4 × 105个细胞接种于6孔板中;培养24 h后加入阿霉素(终浓度为130 mg·L-1),37℃培养 48 h;收集细胞,PBS 洗涤 2 次;细胞重悬于 100 μL含 Annexin Ⅴ-FITC 和 0.5 μg PI 的结合缓冲液 (10 mmol·L-1 HEPES,pH 7.4;0.15 mol·L-1NaCl,5 mmol·L-1 KCl,1 mmol·L-1 MgCl2,1.8 mmol·L-1 CaCl2 )中;避光室温孵育15 min;加入 400 μL结合缓冲液;流式细胞仪分析,按下列公式计算细胞的凋亡指数:细胞凋亡指数 =(早期凋亡细胞数 + 晚期凋亡细胞数)/总细胞数 × 100%。
1.9 统计学分析采用 SPSS 13.0统计学软件进行统计学分析。患者血液及组织标本中miR-139-5p mRNA以x±s表示,2组间样本均数比较采用t检验。miR-139-5p的表达与小细胞肺癌患者不同临床病理参数之间的关系采用Chi-Square检验;应用Cox比例风险模型分析影响小细胞肺癌预后的因素。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果 2.1 miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌患者细胞和组织中的表达水平采用QRT-PCR检测H69、H446及HPAEpiC细胞及50例小细胞肺癌组织和癌旁组织中miR-139-5p的表达,结果显示:在H6和H446细胞中miR-139-5p 表达水平分别为0.370±0.010及0.240±0.003,较正常肺泡上皮细胞HPAEpiC(0.993±0.008)明显降低 (P< 0.01)。miR-139-5p在患者癌组织中的表达水平较癌旁组织明显降低(P< 0.001)。见图 1。
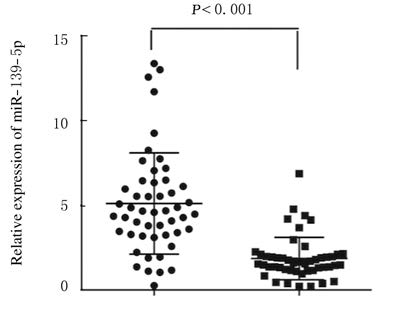
|
| 图 1 miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌患者癌组织和癌旁组织中的表达水平 Figure 1 Expression levels of miR-139-5p in tumor tissue and adjacent normal tissue of patients with small cell lung cancer |
|
|
与对照组比较,转染miR-139-5p mimics后H69和H446细胞中miR-139-5p的表达水平明显上调(P<0.01)(图 2A),同时H69和H446细胞的增殖能力明显降低 (P<0.01)。(图 2B)。
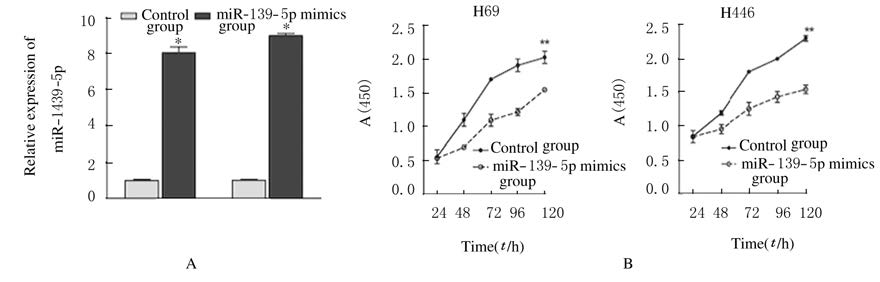
|
| 图 2 CCK8法检测miR-139-5p表达水平(A)和H69细胞及H446细胞增殖能力(B) Figure 2 Expression levels of miR-139-5p (A) and proliferation abilities of H69 and H446 cells(B) detected by CCK8 assay |
|
|
流式细胞术检测:与对照组比较,转染miR-139-5p mimics上调H69和H446细胞中miR-139-5p的表达后,G1期细胞明显增多 (P<0.05)(图 3),提示上调miR-139-5p使细胞周期发生G0/G1期阻滞。
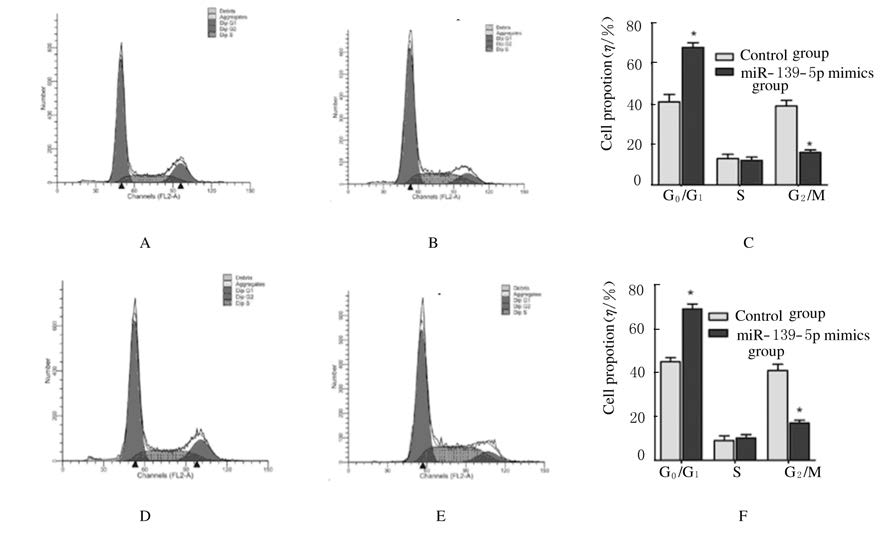
|
| 图 3 流式细胞术检测各组细胞周期 Figure 3 Cell cycles in various groups detected by flow cytometry |
|
|
转染miR-139-5p mimics上调H69和H446细胞中miR-139-5p的表达后,细胞的凋亡率分别较H69及H446对照组明显升高 (P<0.05或P<0.01)。见图 4。

|
| 图 4 流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率 Figure 4 Apoptotic rates in variousgroups measured by flow cytometry |
|
|
miR-139-5p的表达与患者的年龄和性别无关(P>0.05)。miR-139-5p在局限期(LD)患者中的表达水平较广泛期(ED)患者低 (χ2 = 10.546,P = 0.001);miR-139-5p在耐药患者中的表达水平高于化疗敏感患者(χ2 = 7.025,P = 0.008); miR-139-5p在存活患者中的表达水平较死亡患者降低(χ2 = 7.697,P = 0.006)。见表 1。
| Clinicopathological characteristic | Expression of miR-139-5p | χ2 | P | |
| Low | High# | |||
| All cases | 32 | 18 | ||
| Age (year) | ||||
| <50 | 20 | 10 | 0.231 | 0.631 |
| ≥50 | 12 | 8 | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 15 | 12 | 1.817 | 0.178 |
| Female | 17 | 6 | ||
| Disease stage | ||||
| Limited-stage (LD) | 8 | 13 | 10.546 | 0.001* |
| Extensive-stage disease (ED) | 24 | 5 | ||
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Sensitivity | 9 | 12 | 7.025 | 0.008* |
| Resistance | 23 | 6 | ||
| Survival status | ||||
| Survival | 7 | 11 | 7.697 | 0.006* |
| Death | 25 | 7 | ||
| #The median expression level was used as the cutoff. Low expression of miR-139-5p in 32 patients was classified as values of 2-△△ct below 1.0. High miR-139-5p expression in 18 patients was classified as values of 2-△△ct above 1.0.* For analysis of correlation between of miR-139-5p levels and clinical features,Chi-square Test was used. | ||||
Cox回归分析患者的性别、年龄、疾病分期、化疗敏感性及miR-139-5p表达与患者预后的关系,结果显示:疾病分期和miR-139-5p可作为小细胞肺癌独立的预后因子,分期越晚的相对危险度为4.742,95%CI为3.391~21.515,差异有统计学意义(W=13.750,P=0.001);miR-139-5p高表达的相对危险度为0.326,95%CI为0.154~0.935,差异有统计学意义(W=0.224,P= 0.002);化疗敏感者的相对危险度为0.497,95%CI为0.387~0.906,差异有统计学意义(W = 0.137,P = 0.008)。见表 2。
| Variable | B | SE | Wald | P | HR ( 95% CI) |
| Stage | 2.904 | 0.146 | 13.750 | 0.001 | 4.742 (3.391-21.515) |
| MiR-139-5p | -4.453 | -0.581 | 0.224 | 0.002 | 0.326(0.154-0.935) |
| Sensitivity | -9.118 | -2.137 | 0.137 | 0.008 | 0.497(0.387-0.906) |
小细胞肺癌是高侵袭性疾病,在所有肺癌的诊断中占15%~20%,其特点是肿瘤倍增时间快、生长分数高和播散转移早,对一线放化疗高度敏感,但是无论疾病程度如何,绝大多数患者化疗后最终会发生疾病复发或化疗耐受,一直以来这是小细胞肺癌化疗遇到一个很大瓶颈[12-13]。因此,小细胞肺癌的早期诊断和及时有效的治疗是提高其5年生存率的关键,寻找敏感而特异性强的分子标志物、明确治疗的分子靶标以及正确地进行预后评估至 关重要。miRNAs代表了一个新层次的基因表达调控方式,为癌症分子机制的研究提供了新的机遇,其主要通过转录抑制或降解转录产物在转录和转录后水平调节靶基因的表达。约50%得到注解的miRNA在基因组上定位于与肿瘤发生相关的区域和脆性位点,可能发挥着癌基因和抑癌基因的双重作用[14]。
miRNA在多种正常组织与癌组织间的差异表达谱,表明其在影响肿瘤的分类和疗效预测中发挥着重要的作用[15]。2008 年,牛津大学Lawrie等[6]首次报道B 细胞淋巴瘤血清患者中miR-155、miR-210及miR-21 水平升高。近年研究[6]发现:miRNA可作为乳腺癌、肺肿瘤、胶质瘤、胃癌、前列腺癌及肝癌等多种肿瘤诊断的分子标志物。研究[16]发现:miR-184通过靶向作用于E6癌蛋白引起HPV感染的非小细胞肺癌患者对顺铂的耐药。然而关于miRNA在小细胞肺癌中的表达及与化疗敏感性的关系目前国内外研究较少。前期研究发现:miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌中呈低表达。为进一步探讨其生物学功能以及其在小细胞肺癌患者中表达的临床意义,本研究采用细胞生长、凋亡及周期实验检测miR-139-5p的生物学功能,QRT-PCR法检测小细胞肺癌患者癌组织中miR-139-5p的表达,结合临床资料分析其在临床中的作用和意义,结果显示:miR-139-5p在小细胞肺癌组织中的的表达水平低于正常肺组织,其过表达能够抑制细胞的生长,诱导细胞凋亡,细胞周期发生G0/G1期阻滞。Zou等[17]研究发现:miR-139-5p缺失能够活化激活MAPK、NF-κB和κStat3信号通路,促进肠道炎症和大肠癌的发生。miR-139-5p通过靶向作用于c-met基因抑制非小细胞肺癌的增殖转移,促进其凋亡[18]。miR-139-5p 通过靶向作用于Notch1抑制乳腺癌细胞的生物学功能,调节细胞对化疗药物多西他赛的敏感性[19]。此外,本研究还发现:miR-139-5p的表达与患者的性别、年龄无关,与疾病分期、对化疗的敏感性及生存期有密切关联,差异有统计学意义;Cox回归分析发现:疾病分期和miR-139-5p的表达可作为独立的预后因子。miR-139-5p通过抑制细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡和诱导细胞周期阻滞在小细胞肺癌发生发展中发挥着重要的作用,可作为评估小细胞肺癌患者临床预后的潜在靶基因。
| [1] | Bai Y, Sun Y, Peng J, et al. Overexpression of secretagogin inhibits cell apoptosis and induces chemoresistance in small cell lung cancer under the regulation of miR-494[J]. Oncotarget , 2014, 5 (17) : 7760–7775. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget |
| [2] | Fang S, Gao H, Tong Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA-HOTAIR affects chemoresistance by regulating HOXA1 methylation in small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Lab Invest , 2016, 96 (1) : 60–68. DOI:10.1038/labinvest.2015.123 |
| [3] | Fang S, Zeng X, Zhu W, et al. Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2(ZEB2) regulated by miR-200b contributes to multi-drug resistance of small cell lung cancer[J]. Exp Mol Pathol , 2014, 96 (3) : 438–444. DOI:10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.04.008 |
| [4] | Huang C, Huang M, Chen W, et al. N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V modulates radiosensitivity and migration of small cell lung cancer through epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. FEBS J , 2015, 282 (22) : 4295–4306. DOI:10.1111/febs.13419 |
| [5] | Brücher BL, Li Y, Schnabel P, et al. Genomics, microRNA, epigenetics, and proteomics for future diagnosis, treatment and monitoring response in upper GI cancers[J]. Clin Transl Med , 2016, 5 (1) : 13. DOI:10.1186/s40169-016-0093-6 |
| [6] | Sita-Lumsden A, Dart DA, Waxman J, et al. Circulating microRNAs as potential new biomarkers for prostate cancer[J]. Br J Cancer , 2013, 108 (10) : 1925–1930. DOI:10.1038/bjc.2013.192 |
| [7] | Chi Y, Zhou D. MicroRNAs in colorectal carcinoma-from pathogenesis to therapy[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res , 2016, 35 (1) : 43. DOI:10.1186/s13046-016-0320-4 |
| [8] | Pileczki V, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Maralani M, et al. MicroRNAs as regulators of apoptosis mechanisms in cancer[J]. Clujul Med , 2016, 89 (1) : 50–55. DOI:10.15386/cjmed-2016.89.1 |
| [9] | Dai S, Wang X, Li X, et al. MicroRNA-139-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting ELTD1 and regulating cell cycle in glioblastoma multiforme[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun , 2015, 467 (2) : 204–210. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.006 |
| [10] | Emmrich S, Engeland F, El-Khatib M, et al. miR-139-5p controls translation in myeloid leukemia through EIF4G2[J]. Oncogene , 2016, 35 (14) : 1822–1831. DOI:10.1038/onc.2015.247 |
| [11] | Watanabe K, Amano Y, Ishikawa R, et al. Histone methylation-mediated silencing of miR-139 enhances invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Med , 2015, 4 (10) : 1573–1582. DOI:10.1002/cam4.2015.4.issue-10 |
| [12] | Li X, Zhu W, Chen Z, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 regulates cell growth and multidrug resistance of small-cell lung cancer through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway[J]. Anticancer Drugs , 2014, 25 (10) : 1152–1164. DOI:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000153 |
| [13] | Liu H, Wu X, Huang J, et al. miR-7 modulates chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer by repressing MRP1/ABCC1[J]. Int J Exp Pathol , 2015, 96 (4) : 240–247. DOI:10.1111/iep.12131 |
| [14] | Huang J, Peng J, Guo L. Non-coding RNA:a new tool for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol , 2015, 10 (1) : 28–37. DOI:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000394 |
| [15] | Adams BD, Kasinski AL, Slack FJ. Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer[J]. Curr Biol , 2014, 24 (16) : R762–R776. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.043 |
| [16] | Tung MC, Lin PL, Cheng YW, et al. Reduction of microRNA-184 by E6 oncoprotein confers cisplatin resistance in lung cancer via increasing Bcl-2[J]. Oncotarget , 2016 . DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.8708.[Epubaheadofprint] |
| [17] | Zou F, Mao R, Yang L, et al. Targeted deletion of miR-139-5p activates MAPK, NF-κB and STAT3 signaling and promotes intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer[J]. FEBS J , 2016, 283 (8) : 1438–1452. DOI:10.1111/febs.2016.283.issue-8 |
| [18] | Sun C, Sang M, Li S, et al. Hsa-miR-139-5p inhibits proliferation and causes apoptosis associated with down-regulation of c-Met[J]. Oncotarget , 2015, 6 (37) : 39756–39792. |
| [19] | Zhang HD, Sun DW, Mao L, et al. MiR-139-5p inhibits the biological function of breast cancer cells by targeting Notch1 and mediates chemosensitivity to docetaxel[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun , 2015, 465 (4) : 702–713. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.053 |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


