扩展功能
文章信息
- 朱彤彤, 黄连弟, 李俊玮, 赵本正, 姜梦阳, 李娜, 赵凡
- ZHU Tongtong, HUANG Liandi, LI Junwei, ZHAO Benzheng, JIANG Mengyang, LI Na, ZHAO Fan
- 淫羊藿苷对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松症的保护作用及其机制
- Protective effect of icariin on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats and its mechanism
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(05): 915-919
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(05): 915-919
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160515
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-04-11
2. 吉林大学第二医院眼科, 吉林 长春 130041;
3. 长春中医药大学研发中心, 吉林 长春 130117
2. Department of Ophthalmology, Second Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130041, China;
3. Research and Development Center, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130117, China
骨质疏松症(osteoporosis) 是以骨量减少、骨组织显微结构退化为特征,以致骨脆性升高而导致骨折可能性增加的一种全身性骨病[1]。目前,骨质疏松被视为继高血压、糖尿病、动脉粥样硬化和肿瘤之后的位于第五位的慢性疾病。由于雌激素水平下降和衰老的叠加作用,绝经后妇女成为骨质疏松症的主要受害人群,占总发病人群的70%以上[2]。淫羊藿(Epimedium)又名仙灵脾,为小檗科多年生草本植物,淫羊藿及同属多种植物的干燥地上部分,是常用于治疗骨质疏松症的中药[3-4]。淫羊藿苷是淫羊藿的主要活性成分,研究[5]表明:在切除卵巢的大鼠模型中,淫羊藿苷的抗骨质疏松作用与雌激素相近。在一个长约24个月的随机双盲对照试验研究[6]中发现:淫羊藿衍生的植物雌激素可有效阻止绝经期妇女的骨质流失。研究[7]表明:采用淫羊藿苷对骨质疏松大鼠模型进行6~12周的治疗后,大鼠骨密度(BMD)明显升高并且体内钙离子水平趋于稳定。研究[8] 表明:在体外实验中,淫羊藿苷对于破骨细胞的形成和分化及骨吸收有抑制作用。本研究通过观察淫羊藿苷对雌性大鼠去卵巢所致骨质疏松的影响,阐明其作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、主要试剂和仪器50只6月龄Wistar大鼠,雌性,体质量(250±10)g,购于长春高新医学动物实验研究中心,动物合格证号:SCXK(吉)2013-0001。淫羊藿苷粉(上海源叶生物科技有限公司),尼尔雌醇片(上海医药集团有限公司华联制药厂生产),戊巴比妥钠(上海试剂厂生产)。骨钙素放免试剂盒(原子高科股份有限公司生产),使用意大利PLUS公司生产的双能X射线骨密度仪测定股骨BMD。血清骨钙素(BGP)、血清碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、血清钙(Ca)、血清磷(P)、一氧化氮(NO)和一氧化氮合酶(NOS) 试剂盒购于南京建成生物工程研究所。凋亡相关蛋白caspase-3、Bax和Bcl-2单克隆抗体购于武汉Proteintech公司。
1.2 实验动物分组及动物模型制备50只大鼠分为假手术组、模型组、阳性药组、低和高剂量淫羊藿苷组,每组10只。用戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射麻醉大鼠后并固定,于其最末肋骨下,腋中线至脊柱外侧约1 cm处备皮去毛,以消毒后切开皮肤、肌肉和腹膜,轻轻拉出脂肪团暴露卵巢,结扎卵巢下端输卵管。除假手术组不摘除卵巢,其余4组摘除双侧卵巢,缝合切口,外敷消炎粉。术后正常饲养,切口每日消毒,14 d后开始用药。
1.3 给药处理根据人的临床用量换算,以及前期预实验结果确定给药剂量,阳性药组大鼠每周灌胃给予1 mg·kg-1尼尔雌醇;低和高剂量淫羊藿苷组大鼠每天灌胃给药50和100 mg·kg-1淫羊藿苷;假手术组和模型组大鼠每天给予同等体积的生理盐水,连续给药6 d后停药1 d,共给药12周。
1.4 标本采集给药12周后,活体检测大鼠BMD;腹主动脉取血,分离血清-20℃保存待用,按试剂盒说明书检测大鼠血清生化指标。完整取出大鼠右侧股骨,剔净附着的软组织和软骨,10%甲醛固定。
1.5 骨形态学检测方法以10%甲醛固定的股骨脱钙后石蜡包埋切片,HE染色,光镜下观察。
1.6 Westernblotting法检测大鼠骨组织中凋亡相关蛋白表达水平骨组织以液氮冷冻后钢锤砸碎,加入超声裂解细胞,超声裂解后12 000 r·min-1 离心40 min,取上清蛋白溶液,蛋白定量后,取45μg 蛋白加入5×SDS-PAGE上样缓冲液,100℃煮沸5 min,12% SDS-PAGE电泳分离,100 V转膜1.5 h,用含3% BSA的TBST封闭,TBST洗膜,依次加入一抗、二抗进行免疫结合,AP显色。以β-actin为内参照,计算相对吸光度(A)值。目的蛋白表达水平= (目的蛋白条带A值×平均A值) / (同一样品β-actin 条带A值×平均A值) 。实验重复3次。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行统计学处理。各组大鼠BMD及血清BGP、ALP、钙、磷、NO、NOS和骨组织凋亡相关蛋白表达水平均以x±s表示,多组间样本均数比较采用单因素方差分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果 2.1 各组大鼠BMD和血清钙及磷水平与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠BMD降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,阳性药组和高剂量淫羊藿苷组大鼠BMD明显升高(P<0.01)。 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠血清中钙水平下降(P<0.05),血清磷水平升高(P<0.05);给予淫羊藿苷治疗后,与模型组比较,低和高剂量淫羊灌苷组大鼠血清钙水平升高(P<0.05),血甭磷水平下降(P<0.05)。见表 1。
| (n=10,x±s,η) | |||
| Group | BMD (g·cm-2) | Serum calcium [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | Serum phosphorus [cB/(mmol·L-1)] |
| Sham operation | 0.226±0.059 | 10.26±1.21 | 97.3±13.5 |
| Model | 0.084±0.021** | 6.72±0.84* | 105.7±14.8* |
| Positive drug | 0.135±0.028△△ | 8.13±1.09△ | 71.2±10.8△ |
| Low dose of icariin | 0.095±0.024 | 8.21±1.35△ | 96.3±11.7△ |
| High dose of icariin | 0.143±0.035△△ | 9.04±1.87△ | 73.7±15.6△ |
| *P<0.05 ,** P<0.01 compared with sham operation group;△P<0.05,△△P<0.01 compared with model group. | |||
与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠血清BGP、ALP、NO和NOS水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与模型组比较, 低、高剂量淫羊藿苷组大鼠血清BGP和ALP水平明显升高(P<0.05),NO和NOS水平虽有升高趋势,但组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 2。
| (n=10,x±s,η) | ||||
| Group | BGP [ρB/(mg·L-1)] | ALP [cB/(μmol·L-1)] | NO [cB/(μmol·L-1)] | NOS [cB/(mmol·L-1)] |
| Sham operation | 1.58±0.19 | 164.0±34.8 | 54.2±10.8 | 59.1±7.8 |
| Model | 0.96±0.43** | 115.9±89.5* | 23.5±8.6** | 38.2±4.5** |
| Positive drug | 1.09±0.41 | 148.9±82.4△ | 48.6±11.3 △△ | 39.2±4.9 |
| Low dose of icariin | 1.12±0.34 | 142.5±33.71△ | 26.4±7.2 | 38.5±5.7 |
| High dose of icariin | 1.65±0.43△ | 186.7±41.50 △ | 27.3±8.7 | 39.4±6.1 |
| *P<0.05,** P<0.01 compared with sham operation group;△P<0.05, △△P<0.01 compared with model group. | ||||
HE染色:与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠骨组织皮质变薄,皮/总面积变小,骨小梁宽度变窄,间隙变大;与模型组比较,低和高剂量淫羊藿苷组大鼠骨组织可见骨皮质增厚,骨小梁宽度变宽,皮/总面积变大。见图 1(插页三)。
2.4 各组大鼠骨组织中凋亡相关蛋白表达水平Western blotting结果显示:与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠骨组织中Bax和caspase-3蛋白表达水平上调(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平下调(P<0.01)。与模型组比较,各给药组大鼠骨组织中Bax和caspase-3蛋白表达水平下调(P<0.05或P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平上调(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 3和图 2。
| (n=10,x±s,η) | ||||
| Group | Bax | Bcl-2 | Caspase-3 | |
| Sham operation | 0.483±0.052 | 1.052±0.097 | 0.432±0.034 | |
| Model | 0.968±0.087* | 0.447±0.036* | 0.836±0.079* | |
| Positive drug | 0.385±0.041△△ | 0.538±0.064△ | 0.424±0.051 △△ | |
| Low dose of icariin | 0.748±0.083△ | 0.633±0.058 | 0.768±0.087 | |
| High dose of icariin | 0.573±0.066△△ | 0.806±0.075 △△ | 0.366±0.044△△ | |
| *P<0.01 compared with sham operation group;△P<0.05,△△P<0.01 compared with model group. | ||||
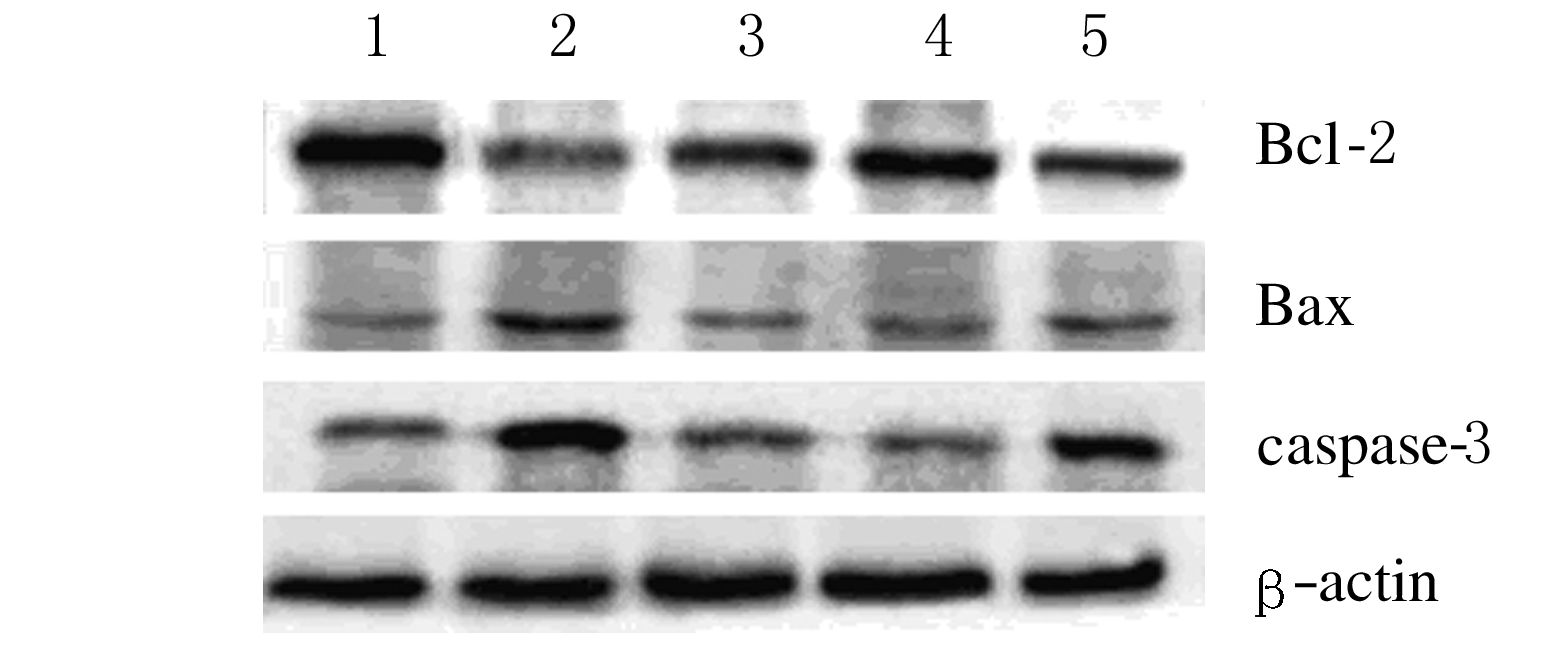
|
| 图 2 各组大鼠骨组织中凋亡相关蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in bone tissue of rats in various groups |
|
|
骨质疏松症的发病在全球呈上升趋势,因其发病率和致残率高却不易被发现而被称为“寂静杀手”[9]。该病常见于绝经期女性,主要病因是雌激素水平下降,导致体内骨代谢平衡紊乱。因此临床上很早便应用雌激素治疗骨质疏松,然而长期使用雌激素可能导致乳腺癌等其他疾病。淫羊藿苷是淫羊藿的活性成分,具有抗肿瘤、延缓衰老和抗骨质疏松[10]等作用,被广泛应用于卵巢切除术后的钙流失和绝经后骨质疏松的预防[11-12]。
切除卵巢大鼠是常用的绝经后骨质疏松症动物模型[13]。本研究利用6月龄雌性大鼠,以切除卵巢法建立骨质疏松模型,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠骨组织中骨小梁稀疏,结构紊乱,间隙增大,出现骨小梁断裂,证明骨质疏松动物模型制备成功。
BMD测定是世界卫生组织定义骨质疏松症的诊断手段[14]。临床上常用双能X线骨密度检测仪检测BMD,这也是诊断骨质疏松症的金标准[15]。本研究中,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠BMD明显降低,而与模型组比较,阳性药组和高剂量淫羊藿苷组大鼠BMD明显升高,阳性药组与高剂量淫羊藿苷组比较差异无统计学意义,提示淫羊藿苷与雌激素提高BMD的效果相近。
在人体中,钙主要存在于骨骼及牙齿,仅1%的钙离子存在于血液、细胞间液及软组织中。磷在体内主要以无机磷的形式存在,血磷下降时可促使机体对骨骼进行吸收,反之则促使骨骼形成。骨钙素(osteocalcin,OC)又名骨谷氨酸蛋白(BGP),由49种氨基酸组成的活性多肽,由成骨细胞、成牙本质细胞和肥大软骨细胞合成,通过调控磷灰石晶体的形成,从而控制生长软骨矿化的速度,因此在一定程度上可以反映骨转化率[16]。血清BGP水平与年龄呈明显负相关关系,进入老年后急剧下降[17]。雌激素水平降低伴随骨转换增加,骨量丢失增加,成骨细胞分泌的ALP增多,使血清中的ALP升高。本研究中淫羊藿苷可导致血清钙、BGP和ALP水平明显升高,血清磷水平降低,提示淫羊藿苷具有降低骨吸收,促进骨形成的作用。
NO由其前体左旋精氨酸在NOS的作用下催生,对骨代谢具有重要影响。NO在成骨细胞和破骨细胞中均有分泌,同时调节2种细胞的功能。Mancini等[18]研究表明:低浓度NO促进骨吸收和成骨细胞的增殖,高浓度NO则抑制骨吸收并诱导成骨细胞凋亡。Leidia等[19]发现:低镁时,NO随着NOS的上调而增高,并抑制成骨细胞的增殖。本研究中,模型组大鼠血清NO和NOS较假手术组明显降低,血钙及血磷有所下降,说明大鼠去卵巢后骨吸收增加。给予阳性药后大鼠血清中NO和NOS水平明显升高,但淫羊藿苷组升高不显著,提示淫羊藿苷与雌激素治疗骨质疏松的机制不同。
凋亡是细胞程序性死亡,成骨细胞凋亡在骨质疏松症的发生发展中具有重要作用[20-21]。Bax和Bcl-2是细胞线粒体凋亡信号通路的关键蛋白,其中Bcl-2主要存在于线粒体外膜,干扰细胞色素C释放;而Bax存在于细胞质,受凋亡信号的刺激促进细胞色素C释放,细胞色素C释放后活化caspase家族蛋白,并引起细胞凋亡。caspase-3是细胞凋亡过程中最主要的终末剪切酶。本研究中,模型组大鼠骨组织中促凋亡蛋白上调而抑凋亡蛋白下调,进一步证明细胞凋亡在去卵巢所致的骨质疏松过程中发挥重要作用。与模型组比较,以淫羊藿苷处理后,大鼠骨组织中促凋亡蛋白表达下调,抑凋亡蛋白表达上调,提示淫羊藿苷可通过抑制细胞凋亡发挥对骨组织的保护作用。
综上所述,淫羊藿苷可对去卵巢大鼠的骨质疏松症具有明显的治疗效果,且其作用与剂量有关,其抗骨质疏松的机制仍需进一步研究。
| [1] | Jabbar S, Drury J, Fordham JN, et al. Osteoprotegerin, RANKL and bone turnover in postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. J Clin Pathol , 2011, 64 (4) : 354–357. DOI:10.1136/jcp.2010.086595 |
| [2] | 陈秋生, 林春燕, 严文健, 等. 甘草酸促进雌二醇分泌拮抗去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的影响研究[J]. 河北医学 , 2016, 22 (3) : 474–477. |
| [3] | Zhang L, Shen C, Chu J. Icariin Decreases the expression of APP and BACE-1 and reduces the β-amyloid burden in an APP transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Biol Sci , 2014, 10 (2) : 181–191. DOI:10.7150/ijbs.6232 |
| [4] | Kapoor S. Icariin and its emerging role in the treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chin Med J , 2013, 126 (2) : 400. |
| [5] | Yang L, Yu Z, Qu H, et al. Comparative effects of hispidulin, genistein, and icariin with estrogen on bone tissue in ovariectomized rats[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys , 2014, 70 (1) : 485–490. DOI:10.1007/s12013-014-9945-0 |
| [6] | Zhang G, Qin L, Shi Y. Epimedium-derived phytoestrogen flavonoids exert beneficial effect on preventing bone loss in late postmenopausal women:a 24-month randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial[J]. J Bone Miner Res , 2007, 22 (7) : 1072–1079. DOI:10.1359/jbmr.070405 |
| [7] | Zhang J, Song J, Shao J. Icariin attenuates glucocorticoid-induced bone deteriorations, hypocalcemia and hypercalciuria in mice[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med , 2015, 8 (5) : 7306–7314. |
| [8] | Hsieh TP, Sheu SY, Sun JS, et al. Icariin inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppression of MAPKs/NF-kappaB regulated HIF-1alpha and PGE(2) synthesis[J]. Phytomedicine , 2011, 18 (2/3) : 176–185. |
| [9] | Ji X, Chen X, Yu X. Micro RNAs in osteoclasto genesis and function:potential therapeutic targets for osteoporosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci , 2016, 17 (3) : 349–365. DOI:10.3390/ijms17030349 |
| [10] | 刘波, 张睿, 徐彭, 等. 淫羊藿对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志 , 2013, 19 (7) : 178–181. |
| [11] | Li GW, Xu Z, Chang SX, et al. Icariin prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss and lowers marrow adipogenesis[J]. Menopause , 2014, 21 (9) : 1007–1016. DOI:10.1097/GME.0000000000000201 |
| [12] | Liu M, Zhong C, He RX, et al. Icariin associated with exercise therapy is an effective treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chin Med J , 2012, 125 (10) : 1784–1789. |
| [13] | Wei QS, Huang L, Chen XH, et al. Effect of whole body vibration therapy on circulating serotonin levels in an ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci , 2014, 17 (1) : 62–68. |
| [14] | 何渝煦, 魏庆中, 熊启良, 等. 骨质疏松性骨折与骨密度关系的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志 , 2014, 20 (2) : 219–224. |
| [15] | Grzegorzewska AE, Mlot-Michalska M. Bone mineral density,its predictors,and outcomes in peritoneal dialysis patients[J]. Adv Perit Dial , 2011, 27 : 140–145. |
| [16] | Mlakar SJ, Prezeljb J, Marca J. Testing.GSTP1 genotypes and haplotypes interactions in Slovenian post-/pre-menopausal women:novel involvement of glutathione Stransferases in bone remodeling process[J]. Maturitas , 2012, 71 (2) : 180–187. DOI:10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.11.023 |
| [17] | Zhang MM, Zhang YH, Mao WX, et al. Correlation between BMD and TRACP,CTX-1,BALP,BGP,calcium and phosphorus metabolism indicator in 1084 female[J]. Chin J Osteoporos , 2013, 19 (9) : 902–906. |
| [18] | Mancini, Moradi-Bidhendi N, Becherini L, et al. The biphasic effects of nitric oxide in primary rat osteoblasts are cGMP dependent[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun , 2000, 274 (2) : 477–481. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3164 |
| [19] | Leidi M, Dellera F, Mariotti M, et al. Nitric oxide mediates low magnesium inhibition of osteoblast-like cell proliferation[J]. J Nutr Biochem , 2012, 23 (10) : 1224–1229. DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.06.016 |
| [20] | 陈基敏, 陈咸川, 谢吟灵. 阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后女性骨质疏松患者动脉粥样硬化影响的研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学 , 2016, 20 (4) : 544–547. |
| [21] | 高雷, 高华增, 任艳. 绝经后骨质疏松症相关骨代谢指标、细胞因子IFG-1的临床观察[J]. 中国实验诊断学 , 2014, 18 (6) : 919–921. |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


