扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘楠楠, 李玉林, 孙立伟, 姜晶, 张继红
- LIU Nannan, LI Yulin, SUN Liwei, JIANG Jing, ZHANG Jihong
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(04): 763-767
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(04): 763-767
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160425
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-10-22
2. 吉林大学基础医学院 病理生物学教育部重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 北华大学化学与生物学院生命科学研究中心, 吉林 吉林 132013;
4. 北华大学附属医院病理科, 吉林 吉林 132011
2. Key Laboratory of Pathobiology, Ministry of Education, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Life Science Research Center, School of Chemistry and Biology, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, China;
4. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital, Beihua University, Jilin 132011, China
乳腺癌的发病率已占女性癌症的首位,随着肿瘤分子生物学研究的逐步深入,信号转导通路的研究也越来越受到关注。目前研究[1, 2]表明:转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)信号途径不但在细胞及生物体生长与发育过程中起重要作用,而且与人体肿瘤的发生发展密切相关。细胞信号转导分子Smad2和Smad4是TGF-β信号转导通路中的重要分子。当二者发生异常改变时,可导致信号通路紊乱而使细胞逃脱TGF-β1介导的生长抑制效应而发生肿瘤。有关TGFβ/Smads信号通路中Smad2和Smad4蛋白在乳腺癌发生中的作用机制尚不清楚。本研究应用免疫组织化学法检测Smad2和Smad4蛋白在乳腺癌组织中的表达,分析其表达与乳腺癌临床病理参数间关系,探讨Smad2和Smad4蛋白在乳腺癌发生发展中的分子机制。 吉林大学学报(医学版) 第42卷 第4期 2016年7月 刘楠楠,等. Smad2和Smad4蛋白在乳腺癌组织中的表达及其意义
1 资料与方法 1.1 标本来源选取2010—2014年北华大学附属医院病理科53例乳腺导管癌蜡块存档标本,其中50例有相对应的癌周正常乳腺组织。53例乳腺导管癌患者年龄35 ~73岁,平均年龄(50.21±7.43)岁,均为女性、原发、单侧乳腺导管癌,临床病例资料记录详细。
1.2 主要试剂兔抗人Smad2单克隆抗体和Smad4单克隆抗体均购自英国Abcam公司,通用型免疫组织化学SP试剂盒及DAB试剂盒均购自北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司。
1.3 乳腺癌的病理诊断标准恶性肿瘤国际临床病期(T和N分期)根据2010年美国癌症联合会分期指南(AJCC Cancer Staging Manual)[3]标准确定,见表1。乳腺癌病理诊断参照2003年WHO乳腺病理学分类(WHO分类)中的形态学标准[4]。
| N grade | T grade | Total | |||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | ||
| N0 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 23 |
| N1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| N2 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 16 |
| N3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 9 | 23 | 16 | 5 | 53 |
乳腺组织采用10%甲醛液固定,梯度酒精脱水,透明,浸蜡,包埋,连续切片,厚4μm,HE染色,光镜下观察,确定病理诊断。留取白片待做免疫组织化学染色,检测Smad2和Smad4蛋白表达情况。染色方法按常规操作步骤进行。以正常动物血清代替一抗作阴性对照,用已知阳性片作阳性对照。
1.5 结果评估评估标准采用盲法阅片方式,随机选取5个高倍视野(×400),以染色强度和阳性细胞率的得分之乘积进行评估。Smad2以细胞质出现明显棕黄色颗粒为阳性细胞;Smad4以细胞质和(或)胞核内出现棕黄色颗粒为阳性细胞。染色结果按每张切片的阳性细胞数比例及着色深浅计分,行半定量分析。阳性细胞数百分率(A)评估:A<10%为0分,10%≤A≤25%为1分,25%<A≤50%为2分,50%<A≤75%为3分,A>75%为4分。染色强度(B)评估:无着色或背景均匀一致的浅黄色为0分,浅棕黄色为1分,棕黄色为2分,棕褐色为3分。根据免疫反应积分(immunoreactive score,IRS)(IRS=A×B)进行最终计分评估,分值越高,蛋白表达水平越高。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。Smad2和Smad4蛋白表达水平以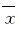 ±s表示,二者在乳腺癌组织与癌周正常组织中表达水平比较采用配对样本Wilcoxon符号秩和检验,Smad2与Smad4蛋白阳性表达率的相关性及其与临床病理参数间的关系采用Spearman等级相关分析。以p<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s表示,二者在乳腺癌组织与癌周正常组织中表达水平比较采用配对样本Wilcoxon符号秩和检验,Smad2与Smad4蛋白阳性表达率的相关性及其与临床病理参数间的关系采用Spearman等级相关分析。以p<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
Smad2蛋白主要呈弥漫性分布于细胞质,Smad2蛋白在乳腺癌组织中呈高表达,其IRS明显高于癌周正常乳腺组织(Z=-2.08,p<0.05)。Smad4蛋白主要存在于细胞质与细胞核中,在乳腺癌组织中Smad4蛋白表达水平明显低于癌周正常乳腺组织,差异有统计学意义(Z=-5.01,P<0.01)。见表2及图1(插页四)。
(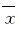 ±s) ±s) | |||
| Group | n | IRS | |
| Smad2 | Smad4 | ||
| Surrounding normal tissue | 53 | 4.29±2.57 | 7.27±0.77 |
| Breast carcinoma tissue | 53 | 5.89±3.05 * | 5.37±1.59** |
| * p<0.05, * * P<0.01 compared with surrounding normal tissue group. | |||
53例乳腺癌组织中有36例Smad2和Smad4蛋白同时呈阳性表达,有13例同时呈阴性表达,有4例为Smad4蛋白呈阴性表达而Smad2蛋白呈阳性表达,但无Smad4呈阳性表达而Smad2呈阴性表达者,Spearman等级相关分析表明:Smad2与Smad4阳性表达呈正相关关系(r= 0.830,P<0.01)。见表3。
| Smad2 | n | Smad4 | r | P | |
| + | - | ||||
| + | 40 | 36 | 4 | ||
| - | 13 | 0 | 13 | 0.830 | 0.001 |
| Total | 53 | 36 | 17 | ||
Smad2和Smad4蛋白阳性表达与患者年龄、肿瘤大小、淋巴结及远处转移及ER、PR表达无相关性(P>0.05),但与HER2的阳性表达呈负相关关系(r=-0.388,P<0.01;r=-0.360,P<0.01),与乳腺癌病理分级呈负相关关系(r=-0.331,p<0.05;r=-0.388,P<0.01)。见表4。
| Clinicopathological parameter | n | Smad2 | r | P | Smad4 | r | P | ||
| - | + | - | + | ||||||
| Age(year) | |||||||||
| <51≥51 | 31 22 | 8 5 | 23 17 | 0.035 | 0.802 | 9 8 | 22 14 | -0.077 | 0.582 |
| Tumor grade | |||||||||
| T1 T2 T3 T4 | 9 23 16 5 | 2 5 5 1 | 7 18 11 4 | 0.128 | 0.360 | 3 8 5 0 | 6 15 11 5 | 0.133 | 0.343 |
| Histological grade | |||||||||
| Ⅰ | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | ||||
| Ⅱ | 30 | 6 | 24 | -0.331 | 0.016 | 8 | 22 | -0.388 | 0.004 |
| Ⅲ | 16 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 7 | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis | |||||||||
| N0 N1 N2 N3 | 23 10 16 4 | 9 3 5 0 | 14 7 11 4 | 0.163 | 0.243 | 7 4 5 1 | 16 6 11 3 | 0.006 | 0.968 |
| Distant metastasis | |||||||||
| M0 M1 | 51 2 | 13 0 | 38 2 | 0.113 | 0.421 | 17 0 | 34 2 | 0.126 | 0.331 |
| ER | |||||||||
| Negative Positive | 14 39 | 4 9 | 10 30 | 0.056 | 0.689 | 5 12 | 9 27 | 0.047 | 0.740 |
| PR | |||||||||
| Negative Positive | 15 38 | 5 8 | 10 30 | 0.129 | 0.359 | 6 11 | 9 27 | 0.107 | 0.447 |
| HER2 | |||||||||
| Negative Positive | 40 13 | 6 7 | 34 6 | -0.388 | -0.004 | 9 8 | 31 5 | -0.360 | 0.008 |
近年来研究[5]表明:Smads蛋白是将TGF-β家族信号从受体传到胞核的转导分子。TGF-β首先与细胞表面受体(TβRⅡ和TβRⅠ)结合,受到受体活化的刺激,细胞质内Smad2、Smad3蛋白与TβRⅠ激酶瞬时结合,并被磷酸化和活化。磷酸化的Smad2、Smad3与Smad4形成异源复合物,转位到细胞核,与特异DNA序列结合调节基因的转录[6],通常认为Smad2和Smad4主要参与TGF-β1信号转录[7]。
本研究结果显示:在乳腺癌组织中Smad4的表达明显低于癌周正常组织,并与乳腺癌病理级别呈负相关关系,即随乳腺癌级别增高Smad4阳性表达降低,提示Smad4蛋白表达的减少甚至丢失伴随并促进肿瘤的进展,在这部分乳腺癌中Smad4可能发挥抑癌基因的作用。该结果也与先前对乳腺癌穿刺标本和乳腺癌组织芯片标本的研究[8, 9]结果一致,同时得到了其他研究的支持。研究[10]显示:在乳腺导管癌中Smad4mRNA表达水平低于正常乳腺组织。通过对正常乳腺上皮细胞系MCF10A和恶性度不同的乳腺癌细胞系的比较[11]发现:Smad4蛋白在良性MCF10A细胞、癌前病变上皮细胞MCF10At1k.cl2、浸润癌细胞MCF10CA1a中的表达呈递减状态;对这些肿瘤同时进行Smad2蛋白表达检测发现:与Smad4相似,Smad2蛋白表达与乳腺癌的病理学级别也呈负相关关系,即随乳腺癌病理学级别增高其阳性表达降低,并通过相关性检验证实Smad2与Smad4间存在正相关关系,进一步提示Smad2表达降低或丢失同样伴随乳腺癌的进展。尽管Smad2较少被看作抑癌基因,但一些研究[12, 13]证实:Smad2的功能失活 足以抑制TGF-β的生理功能。研究者[14]检测Smad2靶向敲除的鼠角质形成细胞发现:Smad2 -/-鼠不会自然发展成皮肤肿瘤,但在化学致癌实验中能加速肿瘤的形成和恶性转化,Smad2-/-肿瘤分化更差,且显示出促进上皮细胞- 间充质转化(EMT)和血管发生的现象,表明Smad2丢失不是肿瘤的起始事件,但Smad2缺陷的上 皮组织更易形成肿瘤并发生恶性转化。在本研究中,Smad2和Smad4蛋白表达皆为阴性的乳腺癌患者13例,本文作者推测在这部分乳腺癌中,Smad2与Smad4同时失表达可能会起协同作用而促进乳腺癌进展,虽然尚不清楚原因,但有研究[15]显示:Smad2 MH1与MH2区的错义突变和羧基端的截断可能会导致Smad4蛋白的不稳定和遍在蛋白连接酶SCFSKP2催化的蛋白酶体途径的降解。Smad4和Smad2作为TGF-β途径中重要的信号传递分子,其同时表达降低或失表达可能会影响TGF-β对细胞生长抑制作用的调控,而使细胞恶性增殖。
本研究结果显示:Smad2和Smad4蛋白的阳性表达率与患者的年龄、肿瘤的大小、淋巴结转移情况、远处转移及乳腺癌检测指标ER和PR的表达无相关关系,这与有关的研究[11]结果相似。
本研究结果显示:Smad2和Smad4蛋白的阳性表达均与HER2的阳性表达呈负相关关系,即随着Smad4和Smad2阳性表达率降低,HER2阳性表达率升高,意味着在低分化的乳腺癌中呈现出Smad2(-)/Smad4(-)/HER2(+)的表达特点。研究[16]证实:HER2高表达乳腺癌一般分化较差,预后不良,这正与本研究结果吻合。目前Smad2/Smad4与HER2之间直接的相关调节未见报道,但在对TGF-β/Smads信号途径的研究[17]中发现:TGF-β通过Smad传递信号,而Smad信号又受到Ras/Erk/MAPK的调节,HER2/Neu是MAPK途径重要的激活剂。在乳腺癌中HER2/Neu活性的升高将会通过Erk MAPK途径阻碍TGF-β通过磷酸化Smad蛋白而实现的生长抑制功能[18],这或许无法解释在HER高表达的肿瘤中Smad2和Smad4的表达降低或丢失,但可能对理解部分乳腺癌中Smad2(-)/Smad4(-)/HER2(+)的表达特点有重要意义。此外,鉴于HER2和Smads对细胞增殖正负调控作用的不同,本研究也观察到Smads蛋白阳性表达与HER2的阳性表达呈负相关关系,但详细的分子机制及共调解环路的信号途径还有待进一步研究。
综上所述,Smad2和Smad4蛋白至少在部分乳腺癌中发挥抑癌基因的作用,检测Smad2和Smad4蛋白表达既可作为评估乳腺癌进展、恶性程度及预后的重要生物学指标,又有利于了解乳腺癌发病的分子机制,本研究结果为临床诊断和治疗乳腺癌提供了新的途径。
| [1] | Lampropoulos P, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A, Rizos S, et al. TGF-beta signalling in colon carcinogenesis [J]. Cancer Lett, 2012,314 (1):1-7. |
| [2] | Santibanez JF, Pérez-Gómez E, FernandezLA, et al. The TGF-beta co-receptor endoglin modulates the expression and transforming potential of H-Ras [J]. Carcinogenesis, 2010,31(12):2145-2154. |
| [3] | Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual[M].7th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2010:347-376. |
| [4] | Tavassoli FA, Devilee P. WHO classification of tumours. Pathology & genetics tumors of the breast and female genital organs[M].Lyon: IARC Press, 2003:10. |
| [5] | Todorovic -Rakovic N, Milovanovic J, Nikolic-Vukosavljevic D . TGF-β and its coreceptors in cancerogenesis: an overview[J]. Biomark Med, 2011,5(6):855-863. |
| [6] | Massagué J. TGFβ signalling in context[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2012,13(10):616-630. |
| [7] | Yang G, Yang X. Smad4-mediated TGF-beta signaling in tumorigenesis [J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2010,6(1):1-8. |
| [8] | Liu N, Yu C, Shi Y, et al.SMAD4 expression in breast ductal carcinoma correlates with prognosis[J].Oncol Lett, 2015,10(3):1709-1715. |
| [9] | Liu NN, Xi Y, Callaghan MU, et al. SMAD4 is a potential prognostic marker in human breast carcinomas[J].Tumour Biol, 2014,35(1):641-650. |
| [10] | Miller DV, Leontovich AA, Lingle WL, et al. Utilizing Nottingham Prognostic Index in microarray gene expression profiling of breast carcinomas [J]. Mod Pathol, 2004, 17(7): 756-764. |
| [11] | Stuelten CH, Buck MB, Dippon J, et al. Smad4-expression is decreased in breast cancer tissues: a retrospective study [J]. BMC Cancer, 2006, 6(1):25-34. |
| [12] | Dumont E, Lallemand F, Prunier C, et al. Evidence for a role of Smad3 and Smad2 in stabilization of the tumor-derived mutant Smad2.Q407R [J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278 (27): 24881-24887. |
| [13] | Xu J, Attisano L. Mutations in the tumor suppressors Smad2 and Smad4 inactivate transforming growth factor beta signaling by targeting Smads to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000, 97 (9): 4820-4825. |
| [14] | Hoot KE, Lighthall J, Han G, et al. Keratinocyte-specific Smad2 ablation results in increased epithelial-mesenchymal transition during skin cancer formation and progression [J]. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118 (8): 2722-2732. |
| [15] | Liang M, Liang YY, Wrighton K, et al. Ubiquitination and proteolysis of cancer-derived Smad4 mutants by SCFSkp2 [J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24 (17): 7524-7537. |
| [16] | Caldarella A, Crocetti E, Bianchi S, et al. Female breast cancer status according to ER, PR and HER2 expression: a population based analysis [J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2011, 17(3):753-758. |
| [17] | Hynes NE, Stern DF. The biology of erbB-2/neu/HER-2 and its role in cancer [J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1994,1198 (2/3): 165-184. |
| [18] | Kretzschmar M. Transforming growth factor-beta and breast cancer: Transforming growth factor-beta/SMAD signaling defects and cancer [J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2000,2(2):107-115. |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


