扩展功能
文章信息
- 温剑平, 崔永生, 张雄基
- WEN Jianping, CUI Yongsheng, ZHANG Xiongji
- 转染EGFRL858R的肺腺癌细胞中IL-6和VEGF表达水平及其意义
- Expression levels of IL-6 and VEGF in lung adenocarcinoma cells transfected with EGFRL858R and their significances
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(03): 502-505
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(03): 502-505
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160316
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-01-27
2. 吉林大学第一医院胸外科, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Thoracic Surgery, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
近年来,炎症因子参与肿瘤恶性转移进程的研究受到了人们的重视。有些细胞因子在微环境变得有利于肿瘤细胞生长和迁移时,可成为协助癌细胞扩散和转移的因素[1]。白细胞介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6)是一种与肺癌发生发展有关的细胞因子,其异常分泌与人肺腺癌细胞浸润及恶性胸膜转有密切关联[2]。IL-6的调控异常与非小细胞肺癌的发生发展和胸膜转移亦有密切关联[3, 4]。目前关于IL-6是否参与带有表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)突变型肺腺癌恶性进程尚未见报道。本研究构建带有L858R型突变的EGFR全长基因转染的肺腺癌细胞系,探讨EGFRL858R型突变与肿瘤细胞中IL-6表达及与IL-6相关的血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)之间是否存在关联。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞系、质粒、主要试剂和仪器H1975和H460肺腺癌细胞系及EGFRL858R全长基因表达载体L858R-pCDNA3.1质粒均由吉林大学基础医学院遗传学教研室提供和构建。荧光定量检测试剂盒(杭州博日科技有限公司),SiRNA-IL-6载体(北京合生基因技术有限公司),抗人VEGF抗体(福州迈新生物科技有限公司)。JY600E型电泳仪(北京君意东方电泳设备有限公司),荧光PCR仪FQD48a(杭州博日科技有限公司)。
1.2 稳定转染细胞系的构建和筛选H460是表达野生型EGFR的肺腺癌细胞系,无EGFRL858R突变存在。将含有L858R-pCDNA3.1质粒稳定转染入H460细胞系中,G418压力筛选,获得稳定表达的EGFRL858R突变型细胞,命名为EGFRL858R-H460细胞(EGFRL858R-H460组)。提取细胞基因组DNA,等位基因PCR法筛选鉴定EGFRL858R-H460细胞。将空pCDNA3.1稳定转染的H460细胞系作为阴性对照,命名为Vec-H460细胞(Vec-H460组)。
根据人IL-6基因序列,设计带有互补发卡结构的siRNA片段,克隆入真核表达载体,委托北京合生基因技术有限公司完成。选取多个IL-6片段为靶片段。将上述IL-6 siRNA载体转染的H1975细胞系进行药物筛选,获得多个稳定转染的细胞后,采用qRT-PCR法鉴定细胞中IL-6表达情况,选择IL-6 mRNA表达水平最低的细胞用于下一步实验,该细胞命名为IL-6siH1975(IL-6siH1975组)。以转染空载体的H1975细胞为对照,命名为Vec-H1975细胞(Vec-H1975组)。
1.3 QRT-PCR法检测各组细胞中IL-6和VEGFmRNA表达水平分别提取EGFRL858R-H460、Vec-H460、Vec-H1975和IL-6 siH1975组细胞总RNA,逆转录,以β-actin为内参对照,以人IL-6和VEGF特异性引物行qRT-PCR,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算实验结果。应用公式计算ΔΔCt 值,ΔΔCt=(实验组目的基因Ct-实验组内参基因Ct)-(对照组目的基因Ct- 对照组内参基因Ct),2-ΔΔCt值即实验组相对于对照组ΔΔCt值的倍数。
1.4 Western blotting 法检测IL-6 siH1975和Vec-H1975组细胞中VEGF蛋白表达水平提取IL-6 siH1975和Vec-H1975组细胞的蛋白,以β-actin为内参对照,Western blotting 法检测IL-6 siH1975和Vec-H1975组细胞中VEGF蛋白的表达强度。
1.5 统计学分析采用SPSS 11.5统计软件对数据进行统计学分析。各组细胞中IL-6和VEGF mRNA 表达水平以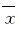 ± s
表示,组间比较采用t检验。以ɑ=0.05为检验水准。
± s
表示,组间比较采用t检验。以ɑ=0.05为检验水准。
与Vec-H460组(1.00±0.00)比较,EGFRL858R-H460组细胞中IL-6 mRNA表达水平(2.80 ± 0.33)升高(P < 0.01±0.00); 与Vec-H460组(1.00±0.00)比较,EGFRL858R-H460组细胞中VEGF mRNA表达水平(2.54 ± 0.41)升高(P < 0.01)。与Vec-H1975组(1.00±0.01)比较,IL-6 siH1975组细胞中IL-6 mRNA表达水平(0.22 ± 0.04)降低(P < 0.01); 与Vec-H1975组(1.00±0.01)比较,IL-6 siH1975组细胞中VEGF mRNA表达水平(0.20 ± 0.03)降低(P < 0.01)。
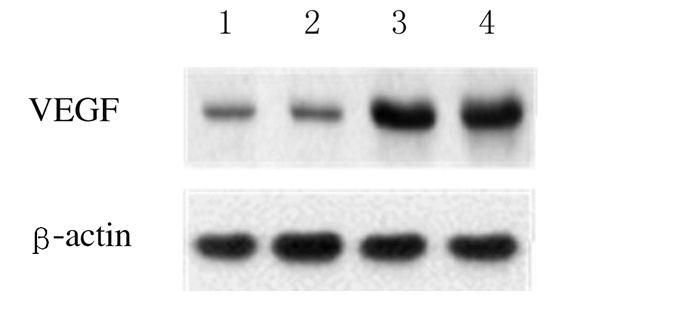
2.2 Vec-H1975和IL-6 siH1975组细胞中VEGF蛋白的表达水平与Vec-H1975组比较,IL-6 siH1975组细胞中VEGF蛋白表达强度明显下降。见图 1。
|
| 图 1 Western blotting 法检测IL-6 siH1975和Vec-H1975组细胞中VEGF蛋白表达电泳图 Fig.1 Electrophoregram of expressions of VEGF protein in cells in IL-6 siH1975 and Vec-H1975 groups detected by Western blotting method Lane 1,2: IL-6 siH1975 group;Lane 3,4: Vec-H1975 group. |
肺腺癌的发生和转移与EGFR基因突变有密切关联,在亚洲人群中,25% ~ 50%肺腺癌细胞中可以检测到EGFR突变[5]。突变后的EGFR发生了不依赖配体表皮生长因子(EGF)的激酶区持续激活,通过信号转导参与肿瘤生长、侵袭、转移和新生血管生成[6]。EGFR突变是否还通过其他途径参与上述肿瘤进程尚未见报道。
研究[7]显示:除免疫细胞外,多种肿瘤细胞也可以自分泌IL-6,IL-6介导的信号通路参与调控肿瘤的发生发展。IL-6自分泌增加的机制及其下游信号通路活化后对于肺腺癌胸膜转移的调节机制尚不清楚。研究[8, 9]显示:IL-6介导的信号转导及转录激活因子3(STAT3)持续激活与其他癌基因的突变或持续激活相互作用,共同促进肿瘤的发生发展。
肺腺癌细胞的浸润和恶性胸膜转移与IL-6的异常分泌有关联,提示作为肺腺癌发生发展的重要因素,癌基因EGFR的突变可能与IL-6的异常分泌有内在关联。
EGFR 21号外显子点突变EGFRL858R型突变是肺癌常见的EGFR突变类型之一。本研究选取该类型突变作为研究对象。本研究结果表明:在体外转染的肺腺癌细胞系中,EGFRL858R型突变可提高IL-6自分泌水平和VEGF水平。因此推测:在肺腺癌恶性转移进程中,EGFRL858R型突变可能是带有该型突变的肺腺癌患者IL-6和VEGF表达水平升高的原因之一。
在体外实验中,EGFR突变引起IL-6和VEGF表达水平升高的信号途径尚不清楚。为探讨IL-6表达水平升高与VEGF表达水平两者之间的关系,本研究构建了IL-6 siRNA转染细胞,观察该细胞中VEGF水平是否有变化。本研究结果表明:转染IL-6 siRNA载体使IL-6低表达的肺腺癌细胞中VEGF表达水平亦降低,说明与EGFRL858R型突变因素比较,IL-6自分泌水平升高是VEGF表达水平升高更为直接的因素。有关肿瘤细胞中IL-6和VEGF表达的关系问题,有研究者[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]在对其他多种肿瘤的研究中得到了相似的结论。
综上所述,在肿瘤发生发展和转移过程中,细胞中的癌基因持续激活且其是否与炎性细胞因子协调作用共同促进肿瘤的发生发展是一个值得深入探讨的问题[15, 16, 17]。
| [1] | Bauer AK,Fostel J,Degraff LM, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of pathways regulated by toll-like receptor 4 in a murine model of chronic pulmonary inflammation and carcinogenesis [J]. Mol Cancer, 2009, 8:107. |
| [2] | Dehai C, Bo P, Qiang T, et al. Enhanced invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells after co-culture with THP-1-derived macrophages via the induction of EMT by IL-6 [J]. Immunol Lett, 2014, 160(1):1-10. |
| [3] | Malanga D, De Marco C, Guerriero I, et al. The Akt1/IL-6/STAT3 pathway regulates growth of lung tumor initiating cells [J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(40):42667-42686. |
| [4] | Bromberg J, Wang TC. Inflammation and cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link [J]. Cancer Cell, 2009, 15(6):79-80. |
| [5] | Heinemann V, Stintzing S, Kirchner T, et al. Clinical relevance of EGFR- and KRAS-status in colorectal cancer patients treated with monoclonal antibodies directed against the EGFR [J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2009, 35(3):262-271. |
| [6] | Kazandjian D, Blumenthal GM, Yuan W, et al. FDA approval of gefitinib for the treatment of patients with metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2016, 22(6):1307-1312. |
| [7] | Engels EA. Inflammation in the development of lung cancer: Epidemiological evidence[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2008, 8(4):605-615. |
| [8] | Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhou YH, et al. IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway is activated in plasma cell mastitis [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015.doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4643-0. |
| [9] | Jiang Q, Li Q, Chen H, et al. Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits growth and induces apoptosis by suppressing IL-6-inducible STAT3 pathway activation in human colorectal cancer cells [J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 10(4):1602-1608. |
| [10] | Zhao G, Zhu G, Huang Y, et al. IL-6 mediates the signal pathway of JAK-STAT3-VEGF-C promoting growth, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in gastric cancer [J]. Oncol Rep,2016, 35(3):1787-1795. |
| [11] | Sahin E, Baycu C, Koparal AT, et al. Resveratrol reduces IL-6 and VEGF secretion from co-cultured A549 lung cancer cells and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J].Tumor Biol, 2015,32(12):9979-9985. |
| [12] | Cavalla F, Osorio C, Paredes R, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases regulate extracellular levels of SDF-1/CXCL12, IL-6 and VEGF in hydrogen peroxide-stimulated human periodontal ligament fibroblasts [J].Cytokine, 2015, 73(1):114-121. |
| [13] | Li L, Cheng FW, Wang F, et al. The activation of TLR7 regulates the expression of VEGF, TIMP1, MMP2, IL-6, and IL-15 in Hela cells [J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014, 389(1/2):43-49. |
| [14] | Weiss TW, Simak R, Kaun C, et al. Oncostatin M and IL-6 induce u-PA and VEGF in prostate cancer cells and correlate in vivo [J]. Anticancer Res, 2011, 31(10):3273-3278. |
| [15] | Acquavella N, Clever D, Yu Z, et al. Type Ⅰ cytokines synergize with oncogene inhibition to induce tumor growth arrest [J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2015, 3(1):37-47. |
| [16] | 李 琦.肺功能检查在肺癌的应用[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2014,34(增1):22-23. |
| [17] | 曹 晖,叶雪石,张 瑾.伴血小板增多症的慢性髓系白血病合并肺腺癌1例报告[J].中国实用内科杂志,2014,34(5):522-523. |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


