扩展功能
文章信息
- 孟令俊, 代恩勇, 刁建东, 毕林涛, 卢振霞
- MENG Lingjun, DAI Enyong, DIAO Jiandong, BI Lintao, LU Zhenxia
- Hedgehog通路对乳腺癌细胞增殖和凋亡的作用及其对Cx32和Cx43表达的影响
- Effects of Hedgehog on proliferationand apoptosis of breast cancer cells and its influence in Cx32 and Cx43 expressions
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(02): 236-239
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(02): 236-239
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160209
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-09-09
乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,居女性癌症死因前列[1]。近期研究[2]表明:Hedgehog通路与乳腺癌有密切关联,Hedgehog过表达促进乳腺癌的增殖及转移,是一个独立的不良预后因子,但其具体作用机制仍未完全清楚。环巴胺(cyclopamine) 是20世纪60年代从藜芦属植物内分离得到的一种异甾体类生物碱,为Hedgehog信号通路的阻断剂[5]。本实验通过研究环巴胺对乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7的体外生长抑制效应,以及其对细胞凋亡与间隙连接蛋白32(connexin 32,Cx32)和间隙连接蛋白43(connexin 43,Cx43)胞膜表达的影响,初步探讨Hedgehog通路在乳腺癌细胞增殖和转移中的作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞和主要试剂MCF-7细胞购自中国医学科学院肿瘤医院细胞库。环巴胺购自美国Biomol公司,MEM细胞培养基和胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司,胰蛋白酶、MTS和DMSO购自美国Sigma公司,AnnexiⅤ-FITC/PI试剂盒购自凯基公司,FITC标记CX43及Cx32单抗购自上海信然公司。
1.2 细胞培养MCF-7细胞培养于含10% FBS、100 U·mL-1 青霉素、100 IU · mL-1链霉素MEM培养基中,细胞置于37℃、5% CO2 培养箱中培养。待细胞融合度达80%~90%后,用0.2%含EDTA胰酶消化,1∶3传代培养,每3~4 d传代1次。
1.3 MTT法检测细胞增殖抑制率取对数生长期的MCF-7细胞,调整细胞浓度约为5×104 mL-1,接种于96孔板中,每孔加100μL细胞悬液(约5×103个细胞)。每组设3个复孔,置37℃、5% CO2条件下培养。24 h后,弃各孔内培养基,加入含不同浓度环巴胺培养基,浓度为0(空白对照)、5、10、20、30和40 μmol ·L-1。分别继续培养24、48和72h后,加入MTS (5 g·L-1)溶液,20 μL/孔,37℃继续孵育4 h后,小心吸弃各孔内的培养上清液,加入0.5 g·L-1 DMSO(同时设无细胞DMSO组),100 μL/孔,在水平摇床上振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解。在酶联免疫检测仪492 nm 波长处测定各孔的吸光度(A)值,取平行对照孔均值,计算细胞增殖抑制率。细胞增殖抑制率 =1 -(实验组A值-DMSO组A值)/(空白对照组A值-DMSO组 A值)×100%。
1.4 AnnexinⅤ/PI双染流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率取环巴胺对MCF-7细胞48 h的半数致死量25μmol· L-1为作用浓度,Annexin Ⅴ-FITC、PI双标记染色流式细胞仪检测环巴胺对MCF-7细胞作用48 h的凋亡效应,并计算细胞凋亡率。细胞凋亡率=凋亡细胞数/检测细胞总数×100%。
1.5 流式细胞术检测环巴胺对MCF-7胞膜CX32及CX43表达的影响细胞生长至对数期,0.2%胰酶消化至单细胞悬液,计数细胞,按每孔2 mL(约5 × 105个细胞)将细胞接种于6孔板,培养24 h后,弃去原培养基,加入含不同浓度环巴胺的培养基,浓度分别为0(阴性对照组)和25μmol·L-1,各组设3个复孔。于药物处理48 h后,刮除细胞并收集;0.1 mol·L-1 PBS洗涤细胞2次(1000 r·min-1离心10 min);分别加入100μL 1∶100 FITC-Cx32稀释液;4℃、避光孵育1 h后加入 0.1 mol·L-1 PBS300 μL,混匀,流式细胞仪检测。Cx43检测过程同上。
1.6 统计学分析采用SPSS 11.0统计软件进行数据分析。各组细胞增殖抑制率、细胞凋亡率和胞膜CX32及CX43阳性表达率均以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果 2.1 各组MCF-7细胞增殖抑制率与空白对照组比较,当环巴胺浓度达10 μmol·L-1或以上时,细胞增殖率明显下降(P<0.05)。环巴胺组MCF-7细胞经10、20、30和40 μmol·L-1环巴胺作用24h后,增殖抑制率分别为(14.85±1.77)%、(32.04±3.15)%、(52.87±3.59)%、(71.18±3.00)%;48h后分别为(31.03±6.09)%、(47.11±3.69)%、(62.76±1.93)%、(76.08±3.69)%;72h后分别为(51.68±4.47)%、(66.04±2.85)%、(76.08±3.04)%、(76.08±3.04)%。环巴胺对MCF-7细胞增殖抑制作用随剂量增加和作用时间延长而增强,表明环巴胺对MCF-7细胞增殖的抑制作用具有浓度、时间依赖性。见图 1。
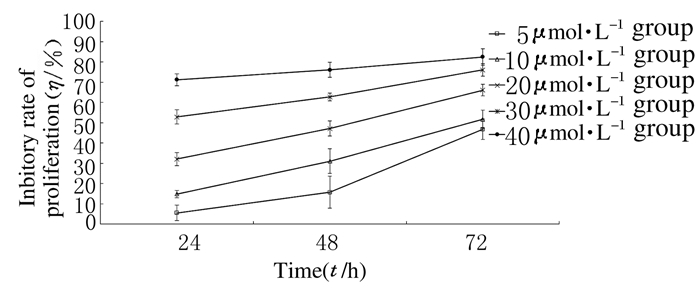
|
| 图1 环巴胺作用不同时间各组MCF-7细胞增殖抑制率 Fig.1 Inhibitory rates of proliferation of MCF-7 cells at different time after treated with cyclopamine in various groups |
经25μmol·L-1环巴胺作用于MCF-7细胞48 h后,细胞凋亡率为(13.88±2.56)%,明显高于空白对照组(3.44%±0.23%)(P<0.05),表明环巴胺抑制细胞增殖可能是通过促进MCF-7细胞发生凋亡所致。
2.3 各组MCF-7细胞胞膜CX32及CX43的表达环巴胺可使MCF-7细胞Cx32及Cx43胞膜表达增加。25 μmol·L-1环巴胺组MCF-7细胞经作用48 h后,胞膜Cx32和Cx43阳性表达率均明显高于阴性对照组(P<0.05)。见表 1。
| (x±s,η/%) | ||
| Group | Membranous expression levels | |
| Cx32 | Cx43 | |
| *P<0.05 compared with negative control group. | ||
| Negative control | 57.66±5.93 | 48.47±6.13 |
| 25μmol·L-1 cyclopamine | 87.90±2.38* | 88.16±2.84* |
Hedgehog通路最初发现于果蝇,并在脊椎动物中高度保守,是胚胎发育过程中的一个重要调节因子[6]。该通路在无配体存在时,跨膜信号受体Ptch抑制SMOH的活性,导致GLI磷酸化后被蛋白酶体降解而无法发挥生物学效应;当Hh配体存在时,通过其与Ptch结合,解除对SMOH活性抑制,GLI从SMOH蛋白复合体中释放,并转移至核内,导致Hedgehog通路下游相关基因的转录激活。近期研究[2]表明:Hedgehog通路与乳腺癌关系密切,是乳腺癌干细胞的重要通路;其激活后可促进乳腺癌的表皮间质转化及转移[7];而且雌激素还可通过激活Gli1增强雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌的干细胞特性及侵袭性[3]。Hedgehog通路过度激活与乳腺癌生存期短有关[4]。
本研究以乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7作为研究对象,应用环巴胺阻断Hedgehog信号通路,观察其对细胞增殖的影响。本研究结果显示:环巴胺可抑制MCF-7细胞的增殖、促进其细胞凋亡,提示 Hedgehog通路影响MCF-7细胞增殖与抑制凋亡有关。
间隙连接蛋白(connexins,Cx)是缝隙连接的基本组成单位。Cx可通过缝隙连接介导的细胞间通讯(gap junctional intercellular communication,GJIC)、半通道介导的细胞间通讯或与胞内蛋白交互联系等方式发挥作用[8]。其中,GJIC是相邻细胞间信号传导的重要途径,对维持组织中细胞群的代谢和生长的均衡性和协调性至关重要,肿瘤组织中Cx胞膜表达往往减少,GJIC功能减弱,从而影响肿瘤的生物学行为。
Cx与乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移有密切关联,体外实验及动物模型研究[9, 10, 11, 12]均显示:Cx可抑制乳腺癌细胞的迁移及侵袭,从而减少乳腺癌肺转移。乳腺癌原发灶Cx的表达还与HER-2状态及Ki-67指数呈负相关关系,新辅助化疗前Cx高表达的乳腺癌患者总生存期更长,是乳腺癌的一种重要的预后指标[13]。但一旦发生转移,循环肿瘤细胞的Cx可能会促进转移细胞在转移灶的黏附与定植,如淋巴结转移[14]、肺转移[15]及脑转移[16],提示Cx在乳腺癌原发灶与转移灶作用的异质性。
以往研究[8]证实:Cx及Hedgehog通路之间存在关联,二者在胚胎发育过程中具有协同作用。为进一步探索Hedgehog通路对乳腺癌细胞的作用机制,本研究应用流式细胞术检测了Hedgehog通路阻断前后MCF-7细胞胞膜Cx32和Cx43的变化。本研究结果显示:阻断Hedgehog通路可增加Cx43及Cx32胞膜表达,表明Hedgehog通路可通过调节乳腺癌细胞Cx43及Cx32的胞膜表达影响 GIJC功能,改变细胞间制约作用,Hedgehog促进乳腺癌转移可能与Cx32和Cx34过表达有关。
综上所述,Hedgehog通路可抑制乳腺癌细胞凋亡,并调节Cx43及Cx32的胞膜表达。
| [1] | Torre LA,Bray F,Siegel RL,et al. Global cancer statistics,2012[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2015,65(2):87-108. |
| [2] | Flemban A,Qualtrough D.The potential role of Hedgehog signaling in the Luminal/Basal phenotype of breast epithelia and in breast cancer invasion and metastasis[J].Cancers,2015,16,7(3):1863-1884. |
| [3] | Sun Y,Wang Y,Fan C,et al.Estrogen promotes stemness and invasiveness of ER-positive breast cancer cells through Gli1 activation[J].Mol Cancer,2014,13(1):137. |
| [4] | O'Toole SA,Machalek DA,Shearer RF,et al.Hedgehog overexpression is associated with stromal interactions and predicts for poor outcome in breast cancer[J].Cancer Res,2011,71(11):4002-4014. |
| [5] | Heretsch P,Tzagkaroulaki L,Giannis A.Cyclopamine and hedgehog signaling:chemistry,biology,medical perspectives[J].Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,2010,49(20):3418-3427. |
| [6] | Infante P,Alfonsi R,Botta B,et al.Targeting GLI factors to inhibit the Hedgehog pathway[J].Trends Pharmacol Sci,2015,36(8):547-558. |
| [7] | Hui M,Cazet A,Nair R,et al.The Hedgehog signalling pathway in breast development,carcinogenesis and cancer therapy[J].Breast Cancer Res,2013,15(2):203. |
| [8] | Goodenough DA,Paul DL.Gap junctions[J].Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol,2009,1(1):a002576. |
| [9] | Fu Y,Jiang BQ,Wu Y,et al.Hsa-miR-206 inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer by targeting Cx43[J].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2013,93(36):2890-2894. |
| [10] | Li Z,Zhou Z,Welch DR,et al.Expressing connexin 43 in breast cancer cells reduces their metastasis to lungs[J].Clin Exp Metastasis,2008,25(8):893-901. |
| [11] | Plante I,Stewart MK,Barr K,et al.Cx43 suppresses mammary tumor metastasis to the lung in a Cx43 mutant mouse model of human disease[J]. Oncogene,2011,30(14):1681-1692. |
| [12] | 李徐奇,雷建军,徐勤鸿,等.Gli-1在缺氧诱导乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞上皮-间质转分化中的重要作用[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2014,35(6):800-804,819. |
| [13] | Teleki I,Krenacs T,Szasz MA,et al.The potential prognostic value of connexin 26 and 46 expression in neoadjuvant-treated breast cancer[J].BMC Cancer,2013,13:50. |
| [14] | Kanczuga-Koda L,Sulkowska M,Koda M,et al.Increased expression of gap junction protein——connexin 32 in lymph node metastases of human ductal breast cancer[J].Folia Histochem Cytobiol,2007,45(Suppl 1):S175-180. |
| [15] | Elzarrad MK,Haroon A,Willecke K,et al.Connexin-43 upregulation in micrometastases and tumor vasculature and its role in tumor cell attachment to pulmonary endothelium[J].BMC Med,2008,6:20. |
| [16] | Stoletov K,Strnadel J,Zardouzian E,et al.Role of connexins in metastatic breast cancer and melanoma brain colonization[J].J Cell Sci,2013,126:904-913. |
 2016, Vol. 42
2016, Vol. 42


