扩展功能
文章信息
- 周解平, 王鹏, 钱立庭, 吴爱东
- ZHOU Jieping, WANG Peng, QIAN Liting, WU Aidong
- 宫颈癌术后静态调强放疗与单个和2个全弧容积调强弧形治疗的剂量学比较
- Dosimetric comparison between IMRT and a single full arc,two full arc VMAT for postoperative cervical cancer patients
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016, 42(01): 120-124
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2016, 42(01): 120-124
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20160124
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-08-10
2. 安徽省肿瘤医院放疗科, 安徽合肥 230001
2. Department of Radiotherapy, Anhui Provincial Cancer Hospital, Hefei 230001, China
宫颈癌是常见的妇科恶性肿瘤之一,手术是早期宫颈癌的首选治疗方案,而术后放射治疗可有效降低肿瘤局部复发率,延长生存时间[1, 2, 3]。容积调强弧形治疗(volumetric modulated arc therapy,VMAT)是在调强适形放疗(intensity modulated radiotherapy,IMRT)基础上发展的先进放射治疗技术,是在机架旋转照射的同时动态地改变MLC形状、照射剂量率、机架转速甚至准直器的角度,产生高度适形的剂量分布[4, 5, 6]。文献[7, 8]报道:VMAT技术能有效减少鼻咽、前列腺等肿瘤的治疗时间,而且与常规IMRT相比,并不降低最终的剂量分布。Guckenberger等[9]进一步研究发现:复杂靶区单个全弧VMAT难以得到相当于IMRT的剂量分布,对于鼻咽癌应当使用2~3个全弧VMAT进行照射。宫颈癌术后靶区形状多以凹形靶区为主,存在多个危及器官(organs at risk,OAR)且靶区形状较复杂,单个全弧(Arc1)VMAT能否得到相当于IMRT的剂量分布,目前尚无报道。本文作者利用本科室的治疗计划系统对20例宫颈癌术后患者分别设计7F-IMRT、单个全弧 VMAT(Arc1)和2个全弧 VMAT(Arc2)治疗计划,并分别对7F-IMRT与Arc1、7F-IMRT与Arc2的计划质量、治疗效率和执行精度进行比较研究。
1 资料与方法 1.1 病例选择选取2013年1月—2014年2月安徽省肿瘤医院放疗科宫颈癌术后患者20例,年龄45~72岁,中位年龄55岁。采用国际妇产科联盟(FIGO,2009)分类法,其中Ⅰb1期4例,Ⅰb2期4例,Ⅱa1期6例,Ⅱa2期6例。患者术后病理均为中低分化鳞癌,有高危因素如盆腔淋巴结转移、管癌栓或宫颈深层浸润,需要接受术后盆腔放疗。
1.2 CT模拟定位患者仰卧位,真空负压袋固定,定位扫描前1h排空膀胱,并饮水500mL使膀胱充盈。使用Siemens Spirits CT模拟定位机增强扫描,扫描范围从L2椎体下缘到坐骨结节下5cm,层厚5mm,并重建成3mm传至治疗计划系统。
1.3 靶区勾画与定义临床靶体积(clinical target volume,CTV)包括阴道上段1/2及残端,阴道旁软组织和盆腔淋巴引流区域(包括髂总、髂外、髂内、闭孔及髂前淋巴结区)。考虑到器官运动和摆位误差,CTV外放8 mm形成计划靶体积(planning target volume,PTV)。处方剂量统一为95% PTV,50 Gy/25次。OAR包括小肠、直肠、膀胱、双侧股骨头和盆骨,均参照ICRU83号报告[10]定义和勾画。OAR限量如下:小肠V50(接受50Gy剂量照射的体积,以下类推) < 10%,V45 < 195cc(绝对体积195cm3);直肠V50 < 50%;膀胱V50 < 30%;股骨头V50 < 5%;骨盆V20 < 70%,V10 < 95%。
1.4 治疗计划设计采用ADAC Pinnacle 9.2治疗计划系统、Trilogy直线加速器,共60对MLC、6 MV X线对每个患者分别设计7F-IMRT、Arc1、Arc2计划。7F-IMRT 7野共面均分,分别为180°、128°、76°、24°、332°、280°和228°,采用直接子野优化(direct machine parameter optimization,DMPO),最大子野数为70个,最小子野面积和最小剂量机器跳数(monitor unit,MU)分别设置为4cm2和2MU,最大剂量率为600 MU·min-1。Arc1计划机架的旋转角度顺时针从181°到179°,采用SmartArc优化算法,最大叶片运动速度为0.46cm/Deg,最终间隔的弧形角度为4°,最大剂量率为600MU·min-1。Arc2在Arc1基础上,增加一个逆时针从179°到181°方向的弧。为减少系统内偏差,3种治疗计划均采用相同的优化目标函数。
1.5 计划质量评估3种计划质量比较是基于1cGy的分辨率生成剂量体积直方图(DVH),并均归一至95%的PTV接受50Gy剂量。根据ICRU 83号报告[10],D2% (2% PTV体积受照的最大剂量,以下类推)表示近似最大剂量,D98% 表示近似最小剂量,D50%为中位剂量,引入适形性指数(conformity index,CI)和均匀性指数(homogeneity index,HI)来评估3种计划质量。
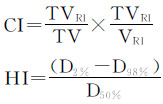
记录3种治疗计划的剂量MU和实际执行时间,比较3种治疗计划的治疗效率。实际执行时间为瓦里安Trilogy直线加速器治疗计划时间,即摆位完成后,第1个照射野开始照射到治疗完毕所用的时间。采用三维剂量验证模体ArcCheck验证3种治疗计划。剂量验证前模体进行本底校准、矩阵校准和绝对剂量校准,运用γ分析法(采用3 mm/3%绝对剂量和DTA标准)评价通过率[11, 12]。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行统计学处理。PTV和OAR剂量、MU、治疗时间等均以x±s表示,不同治疗计划之间比较采用配对t检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
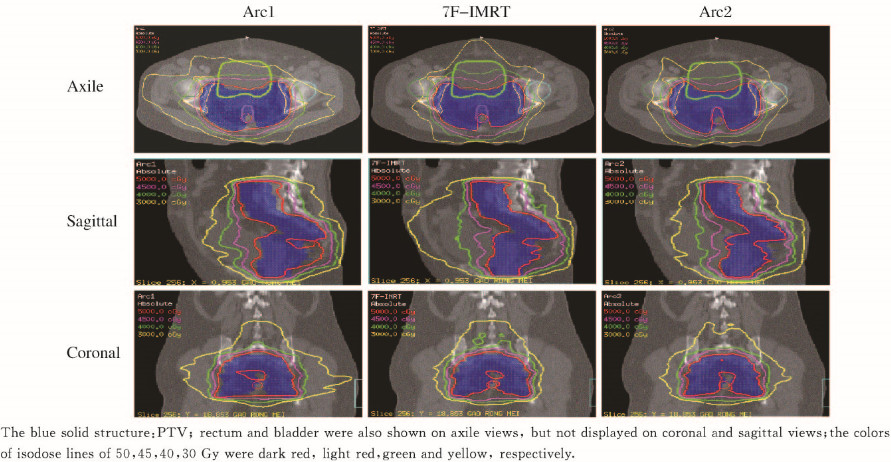
2 结果 2.1 靶区剂量分布与7F-IMRT计划比较,除D50%外,其余靶区剂量学参数比较差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Arc2计划靶区近似最大剂量D2%最低,靶区近似最小剂量D98%更接近处方剂量要求,同时HI最小、CI最大,表明Arc2计划在靶区剂量均匀性和适形度方面均优于其他2种计划(表1)。从Ⅱa1期宫颈癌3种治疗计划横断面、冠状位和矢状位的三维剂量分布可以看出:Arc2计划50Gy的处方剂量线更好地包绕PTV,也同样说明Arc2计划靶区适形度更高(图1,见插页三)。
| (n=20,x±s) | |||||
| Group | D 2% ( D/Gy) | D 98% ( D/Gy) | D 50% ( D/Gy) | HI | CI |
| 7F-IMRT | 53.48±0.56 | 49.35±0.21 | 51.86±0.29 | 0.08±0.01 | 0.86±0.02 |
| Arc1 | 54.12±0.87 * | 49.31±0.29 * | 52.06±0.38 | 0.09±0.02 * | 0.81±0.06 * |
| Arc2 | 53.16±0.51 * | 49.56±0.15 * | 51.71±0.33 | 0.07±0.01 * | 0.90±0.05 * |
| * P < 0.05 compared with 7F-IMRT group. | |||||
|
| 图 1 Arcl计划、7F-IMRT计划和Arc2计划的三维计量分布 Fig.1 Three-dimensional isodose distribution of Arcl plan, 7F-IMRT, and Arc2 plan |
除Arc1计划直肠、膀胱的V50 超过临床限值外,3种治疗计划的其他OAR受量均能满足临床要求。直肠:Arc1计划的近似最大剂量D2cc(2 cm3体积的直肠受照的最大剂量,以下类推)、平均剂量(Dmean)和剂量体积V50均高于7F-IMRT计划(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);而Arc2计划的V50低于7F-IMRT(P < 0.05)。膀胱:Arc1计划的D2cc、Dmean和V50均高于7F-IMRT计划(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);而Arc2计划与7F-IMRT的剂量参数比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。小肠:Arc1计划的D2cc、Dmean、V50和V40均高于7F-IMRT计划(P < 0.05);而Arc2计划的V40和V10均低于7F-IMRT计划(P < 0.05)。股骨头:与 7F-IMRT计划比较,Arc2计划和Arc1计划Dmean均升高(P < 0.05)。Arc1计划对OAR的保护差于7F-IMRT计划,特别是直肠、膀胱的V50难以满足临床要求,可能会导致严重的并发症,而Arc2计划优于或相当于7F-IMRT计划。见表2和图1(插页三)。
| (n=20,x±s) | ||||||||
| OAR | Group | D 2cc( D/Gy) | D mean( D/Gy) | V 10( η/%) | V 20( η/%) | V 30( η/%) | V 40( η/%) | V 50( η/%) |
| Rectum | 7F-IMRT | 52.5±0.5 | 49.4±1.1 | - | - | - | 99.1±2.2 | 41.1±8.9 |
| Arc1 | 53.1±0.7 * | 50.3±0.6 ** | - | - | - | 99.3±1.6 | 55.9±9.1 ** | |
| Arc2 | 52.2±0.6 | 49.1±0.7 | - | - | - | 99.1±2.3 | 36.0±8.9 * | |
| Bladder | 7F-IMRT | 52.6±0.7 | 46.6±1.6 | - | - | - | 91.0±9.0 | 25.0±4.9 |
| Arc1 | 53.3±0.6 * | 47.5±1.6 * | - | - | - | 92.1±10.3 | 32.6±6.9 ** | |
| Arc2 | 52.8±0.7 | 46.0±2.3 | - | - | - | 84.2±16.4 | 25.4±4.7 | |
| Intestine | 7F-IMRT | 51.7±0.3 | 23.0±7.0 | 79.9±15.8 | 41.0±15.7 | 55.1±13.6 | 17.8±6.5 | 6.4±3.3 |
| Arc1 | 52.2±0.6 * | 23.6±6.8 * | 72.5±16.0 | 42.3±13.8 | 56.8±13.2 | 19.0±6.5 * | 6.8±3.5 * | |
| Arc2 | 51.6±0.7 | 23.0±7.1 | 73.3±17.1 * | 42.1±16.1 | 58.3±16.2 | 14.6±6.6 * | 6.1±3.4 | |
| Femoral | 7F-IMRT | 48.6±1.1 | 34.0±1.0 | 100.0±0.0 | 98.6±1.1 | 62.2±5.9 | 23.1±4.6 | 0.5±0.5 |
| Arc1 | 49.2±0.9 | 37.9±4.0 * | 100.0±0.0 | 97.3±3.8 | 79.8±6.3 | 37.5±11.4 | 1.1±0.8 | |
| Arc2 | 48.2±1.1 | 35.5±1.5 * | 100.0±0.0 | 98.1±3.3 | 70.8±7.8 | 26.8±7.6 | 0.3±0.3 | |
| Pelvic | 7F-IMRT | 52.4±0.6 | 35.2±1.2 | 92.5±0.5 | 71.5±4.5 | 62.7±3.3 | 52.0±0.9 | 18.8±5.5 |
| Arc1 | 53.0±0.7 | 34.9±2.1 | 95.1±0.5 | 70.9±4.9 | 60.4±6.0 | 50.0±5.4 | 20.8±2.9 | |
| Arc2 | 52.9±0.5 | 34.7±0.9 | 94.9±0.6 | 72.3±6.8 | 59.9±5.1 | 47.7±6.0 | 18.0±2.7 | |
| * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with 7F-IMRT group,“-”:No data reached nearly 100%. | ||||||||
与7F-IMRT计划比较,Arc1计划的MU和治疗时间分别减少46%和73%(P < 0.01),而Arc2计划分别减少了24%和54%(P < 0.01)。但从上述的剂量学参数比较可知,Arc1计划难以满足临床要求,可能由于Arc1计划MU太少,难以实现靶区和OAR的强度调制,减少治疗时间无实际意义。3种治疗计划3mm/3%的γ分析通过率均大于95%,说明3种治疗计划都有很好剂量验证准确性,但相互间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
| (n=20,x±s) | |||
| Group | MU | Treatment time( t/s) | 3 mm/3% γ analysis( η/%) |
| 7F-IMRT | 645±57 | 320±20 | 97.5±1.2 |
| Arc1 | 343±53 * | 85±12 * | 98.2±1.5 |
| Arc2 | 488±74 * | 147±15 * | 98.5±1.4 |
| * P < 0.01 compared with 7F-IMRT group. | |||
Bortfeld等[13]用Brahme模型理论分析发现:鼻咽癌等复杂靶区,Arc1 VMAT计划可能不能提供满足临床需求的调强剂量分布。张丹丹等[14]研究显示:在鼻咽癌放疗中,与IMRT比较,Arc1 VMAT计划的靶区覆盖率、CI和HI均较差,而且除脑干外其他OAR剂量增加。也有研究[15, 16]表明:Arc1 VMAT计划不足以应用于头颈部的复杂靶区肿瘤。宫颈癌术后靶区形状多以凹形靶区为主,存在多个OAR且靶区形状较复杂,Arc1 VMAT计划能否得到相当于IMRT的剂量分布,目前尚无相关研究。
本文作者对宫颈癌术后患者分别设计了7F-IMRT、Arc1 和Arc2 VMAT 3种治疗计划,结果显示:Arc1计划靶区的CI和HI均较差,而且直肠和膀胱的V50难以满足临床剂量要求,分析可能是由于宫颈癌术后靶区形状较复杂且OAR较多,Arc1 VMAT入射角度较小,剂量强度调制不够。Cozzi等[17]报道:Arc1 VMAT在子宫颈癌中,相对于常规的IMRT,不仅提高了靶区的CI和HI,而且一定程度上降低了小肠、直肠和膀胱等OAR的平均剂量,可能是由于计划系统的优化算法以及机器参数设置不同。
许多文献均报道:相对于常规的IMRT,VMAT都可以减少治疗时间,提高治疗效率。本研究中,Arc2计划相对于7F-IMRT,治疗剂量MU和治疗时间分别减少了24%和54%,治疗时间的减少不仅可以提高本科室内加速器的利用效率,还可以减少患者分次内移动,提高治疗精度。
总之,对于宫颈癌术后患者采用VMAT治疗时,Arc1会造成部分OAR超过了临床限值,可能会导致严重的并发症,宜至少采用Arc2 VMAT计划,且相对于IMRT,不仅缩短了治疗时间,而且提高了靶区的适行度和靶区剂量均匀性,降低了部分OAR的剂量。
| [1] | Mundt AJ,Lujan AE,Rotmensch J,et al.Intensity-modulated whole pelvic radiotherapy in women with gynecologic malignancies[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2002,52(5): 1330-1337. |
| [2] | Portelance L,Chao KS,Grisby PW,et al.Intensity-modulated radiation therapy(IMRT)reduces small bowel,rectum, and bladder doses in patients with cervical cancer receiving pelvic and para-aortic irradiation[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2001,51(1): 261-266. |
| [3] | Yao L,Zhu L,Wang J,et al.Positioning accuracy during VMAT of gynecologic malignancies and the resulting dosimetric impact by a 6-degree-of-freedom couch in combination with daily kilovoltage cone beam computed tomography[J].Radiat Oncol,2015,10:104. |
| [4] | Yu CX,Tang G.Intensity-modulated arc therapy: principles,technologies and clinical implementation[J].Phys Med Boil,2011,56(5):R31-R54. |
| [5] | Otto K.Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc[J].Med Phys,2008,35(1): 310-317. |
| [6] | Palma D,Vollans E,James K,et al.Volumetric modulated arc therapy for delivery of prostate radiotherapy: comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2008,72(4): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Lee TF,Chao PJ,Ting HM,et al.Comparative analysis of SmartArc-based dual arc volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT)versus intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT)for nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].J Appl Clin Med Phys,2011,12(4): 3587. |
| [8] | Zhang P,Happersett L,Hunt M,et al.Volumetric modulated arc therapy: planning and evaluation for prostate cancer cases[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2010,76(5),1456-1462. |
| [9] | Guckenberger M,Richter A,Krieger T,et al.Is a single arc sufficient in volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT)for complex-shaped target volumes[J].Radiother Oncol,2009,93(2):259-265. |
| [10] | Hodapp N.The ICRU 83: prescribing,recording and reporting photon-beam intensity-modulated radiation therapy(IMRT)[J].Strahlenther Onkol,2012,188(1):97-99. |
| [11] | Tachibana H,Takahashi R.Quantitative analysis of geometric information from an end-to-end examination of IMRT and VMAT using the optimal selection method[J].Med Phys,2013,40(6):060709. |
| [12] | McEenzie EM,Balter PA,Stingo FC,et al.Toward optimizing patient-specific IMRT QA techniques in the accurate detection of dosimetrically acceptable and unacceptable patient plans[J].MedPhys,2014,41(12):121702. |
| [13] | Bortfeld T,Webb S.Single-arc IMRT?[J].Phys Med Biol,2009,54(1): 9-20. |
| [14] | 张丹丹,黄劭敏,邓小武,等.初治鼻咽癌VMAT与IMRT的比较评估[J].中华放射肿瘤学,2012,21(4):364-368. |
| [15] | Bertelsen A,Hansen CR,Johansen J,et al.Single arc volumetric modulated arc therapy of head and neck cancer[J].Radiother Oncol,2010,95(2):142-148. |
| [16] | Wopken K,Bijl HP,van der Schaaf A,et al.Development of a multivariable normal tissue complication probability (NTCP)model for tube feeding dependence after curative radiotherapy/chemo-radiotherapy in head and neck cancer[J].Radiother Oncol,2014,113(1):95-101. |
| [17] | Cozzi L,Dinshaw KA,Shrivastava SK,et al.A treatment planning study comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy[J].Radiother Oncol,2008,89(2): 180-191. |




