扩展功能
文章信息
- 贾答淇, 孔雯聪, 苏荣健, 杜晓媛, 贺武斌
- JIA Daqi, KONG Wencong, SU Rongjian, DU Xiaoyuan, HE Wubin
- 巨噬细胞刺激1受体抑制剂BMS777607对肺癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
- Effects of macrophage stimulating 1 receptor inhibitor BMS777607 on proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer cells
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(04): 739-744
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 739-744
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200412
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-09-05
2. 锦州医科大学基础医学院细胞生物学教研室, 辽宁 锦州 121000
2. Department of Cell Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, China
伴随我国肺癌发病率和病死率的递增趋势,肺癌靶向药物的治疗进入新的阶段。超过80%的肺癌为非小细胞肺癌[1],现阶段治疗常用手段仍以手术及化疗为主,但效果差且不良反应明显, 复发率较高[2-3]。因此,寻找临床疗效明显且不良反应少的靶向药物对于治疗非小细胞肺癌具有重要意义。巨噬细胞刺激1受体(macrophage stimulating 1 receptor,MST1R)是C-met原癌基因家族的成员之一[4], 已被证实在多种恶性肿瘤细胞中表达上调,与肿瘤的发生有密切关系[5-6]。MST1R抑制剂BMS777607是一种强效腺苷三磷酸(adenosine triphosphate,ATP)竞争性抑制剂,能有效地阻断C-Met家族激酶的磷酸化,在相关模型中已被证明能抑制肿瘤的生长[7]。然而,MST1R抑制剂对肺癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响尚未明确。本研究采用人类非小细胞肺癌A549细胞为研究对象,观察MST1R抑制剂BMS777607对A549细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,并阐明其作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞、主要试剂和仪器非小细胞肺癌A549细胞系由北京生命科学研究院惠赠,凋亡试剂盒购于南京诺唯赞生物科技有限公司,EdU试剂盒购于广州锐博生物科技有限公司,蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)、磷酸化AKT(p-AKT)、细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinase,ERK)、磷酸化ERK(p-ERK)、聚酰苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶(poly ADP-ribose polymerase,PARP)和含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶9(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase9,Caspase 9)购于德国CST公司,HRP标记的二抗购于中山生物工程有限公司,ECL发光剂购于上海碧云天生物科技有限公司。Facscaliber流式细胞仪(美国BD公司),激光共聚焦显微镜(德国Leica公司),ECL发光成像系统(上海天能科技有限公司),CO2培养箱(美国Thermo公司)。
1.2 细胞培养人肺癌A549细胞置于含有高糖DMEM(10%FBS)、1%青链霉素的培养液中培养,放置于37℃、5% CO2的孵箱中孵育并进行传代培养。
1.3 MTT法检测细胞增殖率取对数生长期的A549细胞,按每孔5×103个细胞的密度接种于96孔板中,置于37℃、5%CO2的孵箱中培养,待贴壁后更换培养液,设置对照组及加药组,加药组的培养液是由BMS777607和培养基配制的工作液,浓度分别为1、5、10、15和20μmol·L-1,每组设置5个复孔,加药完成后继续培养48h,每孔加入20μLMTT,继续孵育4h,终止培养,每孔加入150μLDMSO,低速震荡15min,采用酶联免疫检测仪测定吸光度(A)值,计算细胞增殖率。细胞增殖率=实验组A值/对照组A值×100%。实验重复5次。
A549细胞培养同上,加入5和10μmol·L-1BMS777607分别处理24、48和72h后计算各组细胞增殖率。
1.4 克隆形成实验观察细胞克隆形成情况并检测细胞增殖率将对数生长期的A549细胞接种于6孔板中,每孔1×103个细胞,使细胞均匀分散,置于37℃、5%CO2的孵箱中培养,待细胞贴壁后每孔分别加入含1、5、10、15和20μmol·L-1BMS777607的工作液,同时设对照组,培养14 d后取出,PBS清洗后加入4%多聚甲醛固定,结晶紫染色,观察克隆形成情况。最后将平皿倒置拍照。以二甲亚砜溶解结晶紫并上机检测各组细胞A值,按1.3中方法计算细胞增殖率,实验重复5次。
1.5 EdU掺入法检测EdU阳性细胞率取对数生长期A549细胞接种于3个共聚焦小皿中,每孔(2~3)×104个细胞,37℃培养待贴壁后,分别加入浓度为10和20μmol·L-1BMS777607,同时设对照组,按1:5 000比例将EdU加入每个皿中,37℃培养48h取出,进行清洗及渗透剂打孔和染色,采用共聚焦显微镜观察EdU阳性细胞,计算EdU阳性细胞率。
1.6 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率取对数生长期的A549细胞接种于6个中皿,于37℃、5%CO2的孵箱中培养,次日按实验分组加药,BMS777607浓度分别为1、5、10、15和20μmol·L-1,取对数生长期的A549细胞接种于6个中皿并设置对照组。培养48h后收取细胞,用不含EDTA的胰酶对其消化,1000 r·min-1离心10min,用100μL结合缓冲液轻柔吹打,在避光条件下用10μLAnnexin和5μLPI标记,震荡混匀室温孵育15min后加入400μL结合缓冲液吹打混匀,在1h内流式上机检测各组细胞凋亡率,实验重复3次。
1.7 Western blotting法检测细胞中凋亡相关蛋白表达水平取对数生长期A549细胞接种于6个中皿内,待细胞贴壁后按实验分组分别加入1、5、10、15和20 μmol·L-1BMS777607,同时设对照组,37℃培养48 h取出,提取蛋白裂解制样,经SDS-PAGE电泳后将蛋白转移至硝酸纤维素膜上,用BSA封闭液封闭1 h,加入一抗Caspase9、Cleved-Caspase 9、p-AKT、AKT、p-ERK、ERK、PARP、Cleaved-PARP和β-actin 4℃孵育过夜,次日TBST清洗后用HRP标记的二抗室温孵育1h,ECL显色,采用灰度分析法计算蛋白表达水平。目的蛋白表达水平=目的蛋白条带灰度值/ β-actin条带灰度值。
1.8 统计学分析采用SPSS 23.0统计软件进行统计学分析。各组细胞增殖率、克隆形成实验中细胞增殖率、EdU阳性细胞率、细胞凋亡率和细胞中凋亡相关蛋白表达水平行正态性检验,符合正态分布,以x±s表示,多组间样本均数比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用SNK-q检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 不同浓度BMS777607作用不同时间后各组细胞增殖率BMS777607对A549细胞增殖的抑制作用呈剂量和时间依赖性,随药物浓度的增加和时间的延长细胞增殖率逐渐降低。与对照组比较,1、5、10、15和20μmol·L-1 BMS777607组A549细胞增殖率逐渐降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与0 h比较,作用24、48和72 h,5和10μmol·L-1 BMS777607组A549细胞增殖率逐渐降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 1和表 2。
| (n=5, x±s, η/%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | Proliferation rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Control | 100.00±1.58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BMS777607 (μmol·L-1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 84.46±2.35** | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 69.16±2.95** | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 44.25±1.92* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | 35.36±2.19** | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 20.05±2.19** | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| *P<0.05,* * P<0.01 compared with control group. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (n=5, x±s, η/%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | Proliferation rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (t/h) 0 | 24 | 48 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 μmol·L-1BMS777607 | 100.0±2.98 | 81.10±2.53** | 45.29±1.94* | 32.25±2.15* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 μmol·L-1BMS777607 | 100.0±1.98 | 70.53±2.56** | 22.36±2.15** | 11.62±2.43** | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| *P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with 0 h. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
与对照组比较,10 μmol·L-1BMS777607组肺癌A549细胞的克隆形成明显减少, 20 μmol·L-1BMS777607组肺癌A549细胞几乎无克隆形成(图 1,见插页三)。与对照组比较,随着BMS777607浓度增加,不同浓度BMS777607组肺癌A549细胞增殖率明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见表 3。

|
| A: Control group; B—F: l, 5, 10, 15, and 20 μmol·L-1 BMS77607 groups. 图 1 各组A549细胞克隆形成情况 Fig. 1 Colony formation of A549 cells in various groups |
|
|
| Group | Proliferation rate |
| Control | 100.00±1.18 |
| BMS777607(μmol·L-1) | |
| 1 | 90.16±2.05* |
| 5 | 71.16±3.35** |
| 10 | 49.15±1.02* |
| 15 | 32.03±2.99** |
| 20 | 22.05±3.12* |
| *P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with control group. | |
共聚焦显微镜下观察显示:与对照组比较,不同浓度BMS777607组细胞在绿光激发下细胞核数量明显减少,且随药物浓度增加而递减。见图 2(插页三)。与对照组(100.00%±0.00%)比较,10和20 μmol·L-1BMS777607组A549细胞中EdU阳性细胞率[(48.16±1.22)%和(19.02±2.42)%]明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
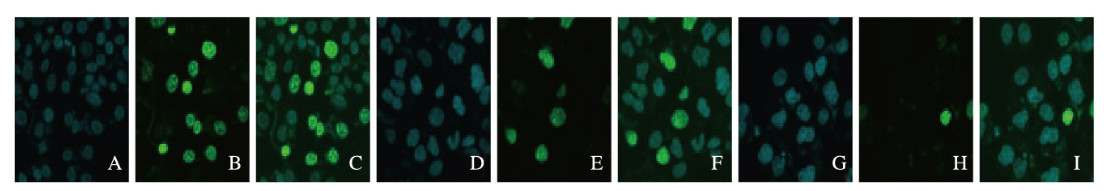
|
| A-C: Control group; D-F: 10 μmol·L-1 BMS77607 group; G-I:20 μmol·L-1 BMS77607 group; A, D, G:DAPl; B, E, H:EdU; C, F, I:Merge. 图 2 各组A549细胞EdU惨入法检测结果(×400) Fig. 2 Results of EdU incorporation method of A549 cells in various groups(×400) |
|
|
不同浓度BMS777607作用A549细胞48h后,各组细胞凋亡率明显升高,5、10、15和20μmol·L-1BMS777607组与对照组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01)。见图 3和图 4。
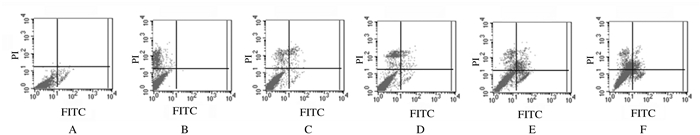
|
| A: Control group; B: 1 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; C: 5 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; D: 10 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; E: 15 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; F: 20 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group. 图 3 流式细胞术检测各组A549细胞凋亡率 Fig. 3 Apoptotic rates of A549 cells in various groups detected by flow cytometry |
|
|
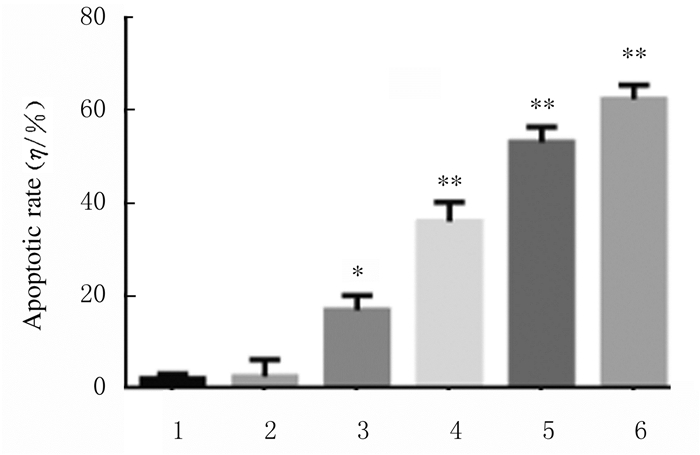
|
| *P < 0.05, * *P < 0.01 vs control group. 1:Control group; 2-6:1, 5, 10, 15, and 20 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 groups. 图 4 各组A549细胞凋亡率 Fig. 4 Apoptosis rates of A549 cells in various groups |
|
|
与对照组比较,10、15和20μmol·L-1 BMS777607组细胞中p-AKT蛋白表达水平及5、10、15和20μmol·L-1 BMS777607组细胞中p-ERK蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),5、10、15和20μmol·L-1 BMS777607组细胞中Cleaved-PARP蛋白表达水平及10、15和20μmol·L-1 BMS777607细胞中Cleaved-Caspase9蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01);不同浓度BMS777607组细胞中AKT、ERK、PARP和Caspase9蛋白表达水平与对照组比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 5。
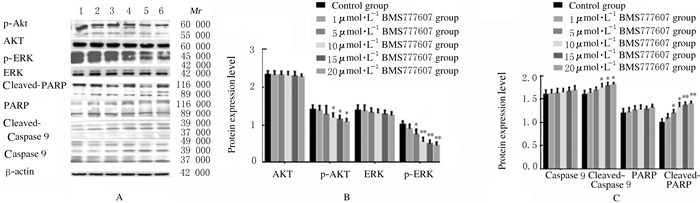
|
| Lane 1: Control group; Lane 2: 1 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; Lane 3: 5 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; Lane 4: 10 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; Lane 5: 15 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group; Lane 6: 20 μmol·L-1 BMS777607 group. 图 5 各组A549细胞中凋亡相关蛋白表达电泳图(A)和直条图(B, C) Fig. 5 Electrophoregram(A) and histogram(B, C) of expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in A549 cells in various groups |
|
|
临床确诊的非小细胞肺癌患者5年生存率为8%~15%,而晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的生存率仅为1%[8],目前化疗是主要治疗手段,但临床治疗效果欠佳。
MST1R又称受体酪氨酸激酶,可促进肿瘤转移,具有调节细胞扩散、转移和微管形成功能[8-9]。目前已有研究[10-13]证明:MST1R在胰腺癌和前列腺癌等细胞中高表达,与肿瘤形成有关,尤其与上皮性肿瘤的发生有密切关联。BMS777607是一种有效的Met激酶抑制剂,可抑制多种激酶的活性,通过对信号通路中的靶蛋白MST1R的抑制进而破坏级联反应中的关键步骤,已证实其可抑制肿瘤的生长,促进肿瘤细胞凋亡[14]。
在肿瘤进展中存在多种信号通路的共同作用[15],AKT在磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase,PI3K)/AKT/雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路中发挥促癌作用,是关键的信号转导因子,经磷酸化后形成p-AKT,可使下游效应分子促进正常细胞向肿瘤细胞转化,促进细胞侵袭和增殖[16-17]。MST1R可在多种癌症中发挥作用,通过激活下游大鼠肉瘤蛋白(rat sarcoma,RAS)/ERK和PI3K/AKT等信号通路对细胞的增殖分化进行调节。本研究结果显示:随着BMS777607浓度增加,p-AKT和p-ERK表达水平逐渐降低。其机制可能是通过抑制表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)/有丝分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK)信号通路的某个级联反应而实现的[16-17]。BMS777607通过抑制p-ERK和p-AKT表达,进而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。
研究[18-19]表明:在许多肿瘤细胞的凋亡中存在Caspase的活化,可采用与Caspase有关的诱导凋亡的方法来治疗肿瘤。本实验结果显示:随着BMS777607浓度增加,各组细胞中Cleaved-Caspase9和Cleaved-PARP表达水平升高。其调控过程可能是:BMS777607刺激细胞线粒体外膜使其释放多种凋亡相关分子,如细胞色素C(CytC),与胞浆结合蛋白结合而募集Caspase9,启动Caspase9活化,使下游Caspase3激活,Caspase9的底物PARP表达增强,细胞最终发生凋亡。因此表明BMS777607可通过内源性线粒体激活途径使A549细胞凋亡。
综上所述,MST1R抑制剂BMS777607能较强地抑制肺癌细胞A549的增殖,其机制可能通过抑制信号通路的凋亡相关蛋白来抑制细胞的增殖,同时利用线粒体为核心成分的途径促使细胞凋亡。本研究结果为非小细胞肺癌的临床治疗提供了参考,其作用机制有待进一步研究。
| [1] |
KAYAWAKE H, OKUMURA N, YAMANASHI K, et al. Non-small cell lungcancer with pathological complete response:predictive factors and surgical outcomes[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2019, 67(9): 773-781. |
| [2] |
林安琪, 陈雨晴, 张小利, 等. 非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗"超进展"[J]. 肿瘤, 2019, 39(8): 680-690. |
| [3] |
BESSE B, MAZIÈRES J, RIBASSIN-MAJED L, et al. Pazopanib or placebo in completely resected stage Ⅰ NSCLC patients:results of the phase Ⅱ IFCT-0703 trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(5): 1078-1083. |
| [4] |
ANNE-MARIE B, DAVID E, MONIKA J, et al. When RON, MET, TAM in mesothelioma:all druggable for one, and one drug for all?[J]. J Thoracic Oncol, 2017, 12(1): S1356-S1357. |
| [5] |
LI C, MORVARIDI S, LAM G, et al. MSP-RON signaling is activated in the transition from pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)[J]. Front Physiol, 2019, 10(4): 147. |
| [6] |
CHEN J F, YU B X, MA L, et al. RON is overexpressed in bladder cancer and contributes to tumorigenic phenotypes in 5637 cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(5): 6547-6554. |
| [7] |
BAUMANN C, ULLRICH A, TORKA R. GAS6 expressing and self-sustaining cancer cells in 3D spheroids activate the PDK-RSK-mTOR pathway for survival and drug resistance[J]. Mol Oncol, 2017, 11(10): 1430-1447. |
| [8] |
O'DEA D, LYNG F M, NICHOLSON S, et al. Recent advances in the vibrational spectroscopic diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Vib Spectrosc, 2019, 10(4): 104-107. |
| [9] |
杜卫东, 何超, 王达, 等. 巨噬细胞刺激蛋白受体过表达对癌细胞侵袭能力的初步研究[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2006, 26(5): 304-307. |
| [10] |
BABICKY M L, HARPER M M, CHAKEDT J, et al. MST1R kinase accelerates pancreatic cancer progression via effects on both epithelial cells and macrophages[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(28): 5599-5611. |
| [11] |
CULLY M. Bone diseases:MST1R inhibitor prevents bone osteolysis[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16(3): 164-165. |
| [12] |
BENIGHT N M, WAGH P K, ZINSER G M, et al. HGFL supports mammary tumorigenesis by enhancing tumor cell intrinsic survival and influencing macrophage and T-cell responses[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(19): 17445-17461. |
| [13] |
KOH X Y, KOH X H, HWANG L A, et al. Therapeutic anti-cancer activity of antibodies targeting sulfhydryl bond constrained epitopes on unglycosylated RON receptor tyrosine kinase[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38(48): 7342-7356. |
| [14] |
LIANG S Z, YU B, QIAN D M, et al. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 affects the migration of glioblastoma by mediating the different splicing patterns of RON through hnRNP A2B1[J]. Neuroreport, 2019, 30(12): 805-811. |
| [15] |
玄香兰, 安昌善. c-MET抑制剂联合EGFR-TKI对耐药肺癌细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其机制[J]. 山东医药, 2017, 57(39): 15-18. |
| [16] |
林珊, 孟玲楠, 珊丹, 等. EGFR靶向抑制剂ZD1839联合放疗对非小细胞肺癌细胞凋亡的影响及其机制研究[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2019, 31(3): 34-38. |
| [17] |
ZHOU Z W, LI X X, HE Z X, et al. Induction of apoptosis and autophagy via sirtuin1- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways by plumbagin in human prostate cancer cells[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2015, 9(1): 1511-1554. |
| [18] |
REN M, XU W J, XU T. Salidroside represses proliferation, migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells through AKT and MEK/ERK signal pathway[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2019, 47(1): 1014-1021. |
| [19] |
LIU L, BAI X Q, GAO Y, et al. PCSK9 promotes oxLDL-induced PC12 cell apoptosis through the bcl-2/bax-caspase 9/3 signaling pathway[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017, 57(3): 723-734. |
 2020, Vol. 46
2020, Vol. 46


