扩展功能
文章信息
- 王映映, 孙利娟, 范紫微, 古虹, 游先梅, 关天昊, 张成义, 陈曦
- WANG Yingying, SUN Lijuan, FAN Ziwei, GU Hong, YOU Xianmei, GUAN Tianhao, ZHANG Chengyi, CHEN Xi
- 黄芩苷对脂多糖诱导的大鼠滑膜RSC-364细胞自噬的抑制作用
- Inhibitory effect of baicalin on autophagy of synovial RSC-364 cells of rats induced by lipopolysaccharide
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(03): 498-503
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 498-503
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200311
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-09-12
2. 北华大学药学院药理教研室, 吉林 吉林 132013;
3. 北华大学医学院医学影像学教研室, 吉林 吉林 132013;
4. 北华大学医学技术学院医学检验技术教研室, 吉林 吉林 132013
2. Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, China;
3. Department of Medical Imageology, College of Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, China;
4. Department of Medical Laboratory Technology, College of Medical Technology, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, China
黄芩苷是一种黄酮类化合物,主要来源于黄芩干根[1-2]。目前的研究[3-4]表明:黄芩苷具有抗氧化、抗炎和抗肿瘤等作用。WANG等[5]已证实:在胶原诱导的关节炎大鼠中,黄芩苷能减少滑膜组织和滑膜成纤维细胞中核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B, NF-κB)蛋白表达,减轻关节炎症。在关节炎小鼠模型中,黄芩苷可明显减轻踝关节肿胀[6]。在类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)发病机制中, 类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞(rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts,RASFs)起重要作用[7]。RASFs能够产生大量炎性细胞因子、趋化因子和基质降解酶,从而促进RA炎症和关节破坏状态[8]。研究[9]显示:RA疾病严重程度与滑膜组织自噬水平呈正相关关系。因此,自噬可能是RA的潜在治疗靶点。目前,黄芩苷对RA滑膜细胞自噬的影响尚未见相关报道。有研究[10]显示:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/雷帕霉素(PI3k/Akt/mTOR)信号传导途径与RA发生发展有关。本研究观察PI3k/Akt/mTOR信号通路对脂多糖(lipopolysaccharides,LPS)诱导的大鼠滑膜RSC-364细胞自噬的影响,探讨黄芩苷抗炎分子机制,为RA的临床治疗提供实验依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞、主要试剂和仪器大鼠滑膜RSC-364细胞购于北京鼎国生物技术有限公司,采用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM完全培养液培养,于37℃、5%CO2培养箱中培养。LPS和ECL底物化学发光液购于北京鼎国生物技术有限公司;DMEM、胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶、二甲基亚砜(DMSO)和噻唑蓝(MTT)购于美国Sigma公司;黄芩苷购于西安瑞芬生物工程有限公司,黄芩苷溶解于完全培养基中配制成40 μmol·L-1储存液;逆转录cDNA试剂盒和高纯度总RNA快捷提取试剂盒购于美国BioTake公司;β-actin多克隆抗体(ab8227)、Beclin1 (ab62557)、微管相关蛋白-轻链3-Ⅱ(microtubule-associated protein-light chain3-Ⅱ, LC3-Ⅱ)(ab48394)和HRP标记二抗(ab205718)均购自英国Abcam公司;Atg5(A0203)、Atg7(A0691)、Atg12(A17045)和P62(A7758)均购自中国武汉AB clonal公司。Bio-Rad 680酶标仪购于美国Bio-Rad公司,E-Gellmager凝胶成像系统购于美国Thermo公司,Eppendorf-PCR仪购于德国Eppendorf公司,JY200C通用型电泳仪购于上海珂淮仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验分组和MTT法检测各组RSC-364细胞存活率采用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM完全培养液培养RSC-364细胞,取处于对数生长期RSC-364细胞,以细胞密度1.0 ×104 mL-1接种于96孔细胞培养板,每组设置6个复孔,每孔接种200 μL,置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养24 h后,分为对照组,模型组,地塞米松(DXMS)组,10、20和40 μmol·L-1黄芩苷组。对照组RSC-364细胞只加入细胞培养基,其他各组RSC-364细胞均给予1 mg·L-1 LPS诱导其炎症反应, 培养12 h后, 黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞分别加入10、20和40 μmol·L-1黄芩苷,DXMS组RSC-364细胞给予终浓度为0.5 μmol·L-1 DXMS,继续孵育24 h后,每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液于培养箱中培养4 h。随后弃去上清液,每孔加入150 μL DMSO,混匀10 min后,在490 nm处检测吸光度(A)值并记录结果,所测A值越小,则存活细胞数就越少。细胞存活率=给药组A值/对照组A值× 100%。
1.3 RT-PCR法检测各组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt、mTOR、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达水平采用RNA提取试剂盒提取各组大鼠滑膜RSC-364细胞总RNA。采用逆转录cDNA试剂盒(BioTake)以总RNA为模板,进行逆转录cDNA;RT-PCR反应体系(25 μL)包括:2 Taq Master Mix 12.5 μL、双蒸水9.5 μL、上游引物1 μL、下游引物1 μL和cDNA1 μL。PCR扩增以逆转录cDNA为模板,在94℃、3 min条件下进行初始变性,经过20个循环,94℃、30 s变性,65℃、30 s退火和72℃、1 min延伸过程,72℃、10 min充分延伸;其次点样,100 V、40 min电泳,采用ImageJ6.0软件分析扩增后的琼脂糖凝胶电泳条带灰度值,进行目的基因mRNA半定量分析,计算各组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt、mTOR、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达水平。目的基因mRNA表达水平=目的基因条带灰度值/内参GAPDH条带灰度值。以上实验至少重复3次。RT-PCR引物序列见表 1。
| Primer | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Fragment length (bp) |
| Atg5 | Forward: TGTGATCCCGGTAGACCCAA Reverse: AAACCACACGTCTCGAAGCA |
170 |
| Atg7 | Forward: GGTGAGGGGACTGGACTTTTA Reverse: GCACCAACTCTGCTGTTCTC |
264 |
| Atg12 | Forward: GCTGAAGGCTGTAGGAGACA Reverse: CATCCCCATGCCTGTGATTTG |
249 |
| PI3k | Forward: GTGGACACCCAAGCTGACTG Reverse: AAGCAAATCCCTTCACCCCAA |
179 |
| Akt | Forward: GGAGTGTGTGGACAGTGAACG Reverse: TCAGGTACAGATGATCCATGCG |
150 |
| mTOR | Forward: CAGAGGTGTGGTTTGACCGA Reverse: CAGCATCAGGTTGGATGGGT |
110 |
| Beclin1 | Forward: AACTCTGGAGGTCTCGCTCT Reverse: CGCCTTAGACCCCTCCATTC |
109 |
| LC3-Ⅱ | Forward: TCCCAAGAAACCTTCGGCTT Reverse: CCAGCACCCAAAAGAGCAAG |
231 |
| GAPDH | Forward: GGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG Reverse: GCCAGTAGACTCCACGACAT |
124 |
细胞裂解缓冲液、PMSF和磷酸酶抑制剂配置工作液,用于滑膜RSC-364细胞总蛋白的提取。采用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒对蛋白质进行定量分析。具体方法:配胶,浓缩胶、分离胶(12%SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶);上样,各组取50 μg样本蛋白;电泳,浓缩胶80V、30 min,分离胶100 V、1.5 h;转模,PVDF膜,100 V、1 h;封闭,5%脱脂奶粉,室温封闭1 h;孵育一抗,4℃过夜。采用TBST稀释兔抗大鼠抗体、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、LC3-Ⅱ、Beclin1、P62和β-actin;回收一抗,TBST进行洗膜3次,每次10 min;孵育二抗:HRP标记山羊抗兔IgG(1:10 000稀释)室温1 h,TBST洗3次,每次10 min;采用增强化学发光底物试剂盒进行免疫检测。以β-actin作为蛋白内参对照,采用ImageJ6.0软件对特异蛋白条带的灰度值进行定量分析, 计算各组RSC-364细胞中Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、LC3-Ⅱ和P62蛋白表达水平。目的蛋白表达水平=目的蛋白条带灰度值/内参β-actin条带灰度值。以上实验至少重复3次。
1.5 统计学分析所有数据均采用Graphpad Prism 5.0软件进行统计学分析。各组RSC-364细胞存活率,RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt、mTOR、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA及Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、LC3-Ⅱ和P62蛋白表达水平均以x ±s表示,多组间样本均数比较采用单因素方差分析,组间样本均数两两比较采用SNK-q检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组RSC-364细胞存活率与对照组比较,模型组RSC-364细胞存活率明显升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,不同浓度黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞存活率明显降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。见图 1。
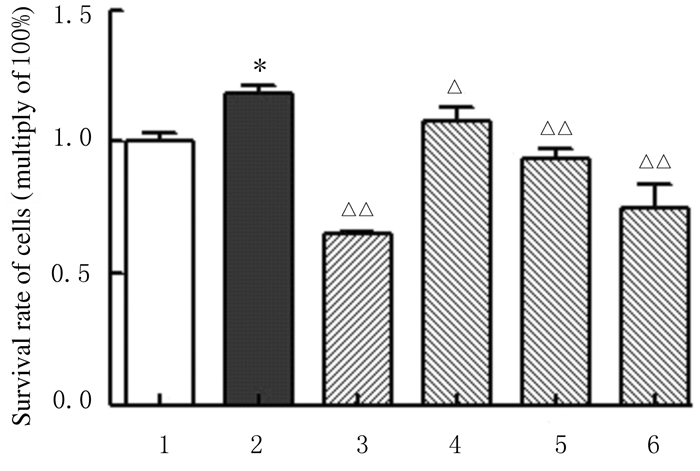
|
| 1:Control group; 2:Model group; 3:DXMS group; 4:10 μmol·L-1 baicalin group; 5:20 μmol·L-1 baicalin group; 6:40 μmol·L-1 baicalin group; *P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. 图 1 MTT法检测各组RSC-364细胞存活率MTT法检测各组RSC-364细胞存活率 Fig. 1 Survival rates of RSC-364 cells in various groups detected by MTT assay |
|
|
与对照组比较,模型组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达水平升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);与模型组比较,不同浓度黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12及LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);不同浓度黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞中上述指标比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 2和图 3。
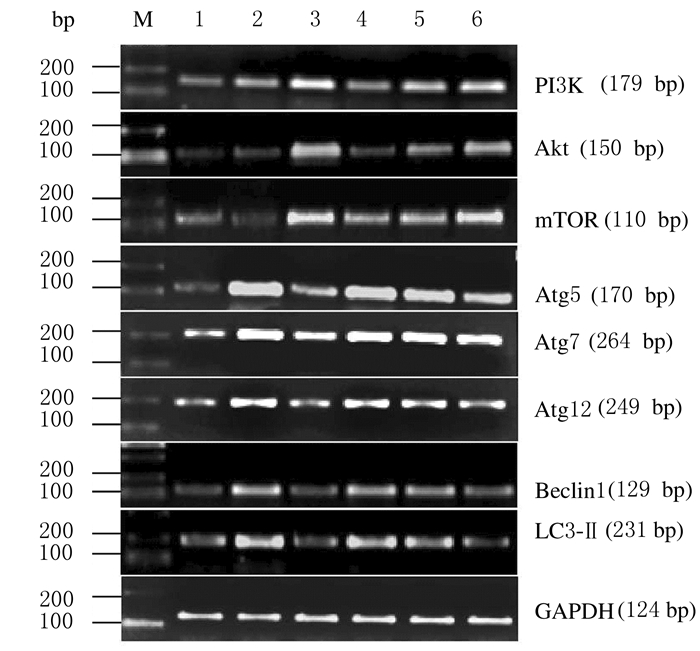
|
| Lane1: Control group; Lane 2: Model group; Lane 3: DXMS group; Lane 4-6:10, 20, and 40 μmol·L-1 baicalin groups. 图 2 各组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt、mTOR、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、Beclin1和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达电泳图 Fig. 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of PI3k, Akt, mTOR, Atg5, Atg7, Atg12, Beclin1, and LC3-Ⅱ mRNA in RSC-364 cells in various groups |
|
|

|
| A:Expression levels of PI3K, mTOR, and Atg5 mRNA; B:Expression levels of Atg7, Atg12, Beclin1, and LC3-Ⅱ mRNA; 1:Control group; 2:Model group; 3:DXMS group; 4-6:10, 20, and 40 μmol·L-1 baicalin groups.*P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. 图 3 各组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt、mTOR、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7、Atg12和LC3-Ⅱ mRNA表达水平 Fig. 3 Expression levels of PI3k, Akt, mTOR, Atg5, Atg7, Atg12, Beclin1, and LC3-Ⅱ mRNA in RSC-364 cells in various groups |
|
|
与对照组比较,模型组RSC-364细胞中LC3-Ⅱ、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7和Atg12蛋白表达水平明显升高(P < 0.01),P62蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,不同浓度黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞LC3-Ⅱ、Beclin1、Atg5、Atg7和Atg12蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),P62蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);不同浓度黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞中上述指标比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 4和图 5。
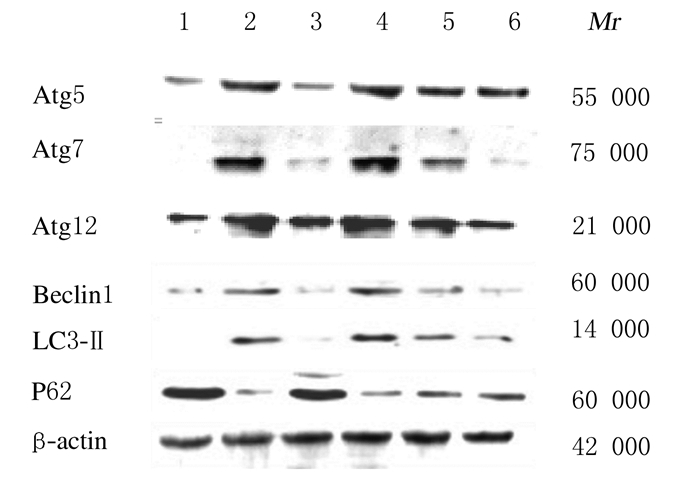
|
| Lane 1: Control group; Lane 2: Model group; Lane 3: DXMS group; Lane 4-6:10, 20, and 40 μmol L-1 baicalin groups. 图 4 Western blotting法检测各组RSC-364细胞中Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、Beclin1、LC3-Ⅱ和P62蛋白表达电泳图 Fig. 4 Electrophoregram of expressions of Atg5, Atg7, Atg12, Beclin1, LC3-Ⅱ, and P62 proteins in RSC-364 cells in various groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|

|
| A:Expression levels of Atg5, Atg7, and Atg12 proteins; B:Expression levels of Beclin1, LC3-Ⅱ, and P62 proteins; 1:Control group; 2:Model group; 3:DXMS group; 4-6:10, 20, and 40 μmol·L-1 baicalin groups; *P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 compared with model group. 图 5 各组RSC-364细胞中Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、Beclin1、LC3-Ⅱ和P62蛋白表达水平 Fig. 5 Expression levels of Atg5, Atg7, Atg12, Beclin1, LC3-Ⅱ, and P62 proteins in RSC-364 cells in various groups |
|
|
RA是一种因免疫耐受机制而产生的慢性变态反应性疾病[11],其主要特征为滑膜增生和炎性细胞浸润。研究[7]已证实:RASFs大量增殖是RA发病的关键因素之一。近年来,常采用体外培养大鼠滑膜RSC-364细胞经LPS诱导,促使细胞增殖并分泌大量炎性因子作为细胞水平炎症模型。本研究结果显示:LPS诱导后,模型组RSC-364细胞大量增殖;给予黄芩苷后,LPS诱导的RSC-364细胞存活率明显降低,其增殖明显受到抑制,提示黄芩苷可抑制LPS诱导的RSC-364细胞增殖;与相关文献[12]报道的结果一致。
自噬是生物体中进化保守的溶酶体降解的途径[13],其能调控细胞存活、增殖和凋亡等,以维持细胞内平衡。自噬失调与其自身免疫性疾病发病机制有关[14],RA发病过程中存在自噬途径的失调。研究[9]显示:RASFs通过各种途径激活自噬,以维持细胞内环境稳定,促使滑膜细胞的大量增殖,导致关节炎症反应加重。
PI3k/Akt/mTOR信号通路在细胞自噬中发挥着重要作用[10]。PI3k和Akt是mTOR重要的上游调控因子,PI3k可以激活Akt,活化的Akt进一步磷酸化mTOR[15]。mTOR作为自噬启动阶段的关键调节因子,活化后可抑制自噬的发生[16]。Beclin 1是启动自噬的关键,在哺乳动物细胞中,Beclin 1表达上调可以激活自噬[17]。Atg5和Atg7对自噬小体的延伸起重要作用,Atg7启动Atg5- Atg12结合以及LC3-Ⅰ脂化反应形成LC3-Ⅱ [12, 18]。P62水平经常被用作自噬活动的标志,其充当信号转导分子和自噬选择性底物,连接多泛素化蛋白及其相关蛋白细胞器到自噬体进行降解[19]。
本研究结果显示:模型组RSC-364细胞中PI3k、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平降低,Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、Beclin1和LC3-ⅡmRNA及蛋白表达水平升高,P62蛋白表达水平较低,提示LPS诱导的RSC-364细胞中可通过抑制PI3k/Akt/mTOR信号通路激活自噬;给予黄芩苷后,黄芩苷组RSC-364细胞中自噬通路PI3k、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平升高,Atg5、Atg7、Atg12、Beclin1和LC3-ⅡmRNA及蛋白表达水平降低,P62蛋白表达水平升高,提示黄芩苷可通过促进PI3k/Akt/mTOR信号通路抑制LPS诱导的RSC-364细胞自噬。
综上所述,黄芩苷可能通过激活PI3k/Akt /mTOR信号通路抑制LPS诱导的RSC-364细胞自噬,从而抑制炎性RSC-364细胞增殖。
| [1] |
LEE W, KU S K, BAE J S. Anti-inflammatory effects of Baicalin, Baicalein, and Wogonin in vitro and in vivo[J]. Inflammation, 2015, 38(1): 110-125. |
| [2] |
WANG CC, SONG Y, WANG X, et al. Baicalin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis through the suppression of Janus kinase 1(JAK1)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3(STAT3) signaling in mice[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24(1): 9213-9222. |
| [3] |
DING Y, DOU J, TENG Z, et al. Antiviral activity of baicalin against influenza A (H1N1/H3N2) virus in cell culture and in mice and its inhibition of neuraminidase[J]. Arch Virol, 2014, 159(12): 3269-3278. DOI:10.1007/s00705-014-2192-2 |
| [4] |
GAO C, ZHOU Y, LI H, et al. Antitumor effects of baicalin on ovarian cancer cells through induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of cell migration in vitro[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(6): 8729-8434. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7757 |
| [5] |
WANG H Z, WANG H H, HUANG S S, et al. Inhibitory effect of baicalin on collagen-induced arthritis in rats through the nuclear factor-B pathway[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2014, 350(2): 435-443. DOI:10.1124/jpet.114.215145 |
| [6] |
YANG X, YANG J, ZOU H J. Baicalin inhibits IL-17-mediated joint inflammation in murine adjuvant-induced arthritis[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2013, 2013(1): 268065. |
| [7] |
VALERIA M, SERENA R, ANTONELLA C, et al. Autophagy induces protein carbamylation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2018, 57(11): 2032-2041. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/key174 |
| [8] |
KATO M, OSPELT C, GAY R E, et al. Dual role of autophagy in stress-induced cell death in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66(1): 40-48. |
| [9] |
ZHU L, WANG H Z, WU Y, et al. The autophagy level is increased in the synovial tissues of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and is correlated with disease severity[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2017, 2017(6): 7623145. |
| [10] |
冯楠楠, 王冰洁, 朱启航, 等. 玉米赤霉烯酮通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路诱导大鼠睾丸支持细胞自噬及对细胞周期分布的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2018, 41(4): 708-714. |
| [11] |
VOMERO M, MANGANELLI V, BARBATI C, et al. Reduction of autophagy and increase in apoptosis correlates with a favorable Clinical outcome in patients with Rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF drugs[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2019, 21(1): 39. |
| [12] |
PEETERS J G C, De GRAEFF N, LOTZ M, et al. Increased autophagy contributes to the inflammatory phenotype of juvenile idiopathic arthritis synovial fluid T cells[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2017, 56(10): 1694-1699. DOI:10.1093/rheumatology/kex227 |
| [13] |
TONG W W, ZHANG C, HONG T, et al. Silibinin alleviates inflammation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and has a therapeutic effect on arthritis in rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 3241. |
| [14] |
MARINO G, NISO-SANTANO M, BAEHRECKE E H, et al. Self-consumption:the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 15(2): 81-94. |
| [15] |
XU K, CAI Y S, LU S M, et al. Autophagy induction contributes to the resistance to methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells through high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015, 17(1): 374. DOI:10.1186/s13075-015-0892-y |
| [16] |
RAYCHAUDHURI S K, RAYCHAUDHURI S P. mTOR signaling cascade in psoriatic disease:double kinase mTOR inhibitor a novel therapeutic target[J]. Indian J Dermatol, 2014, 59(1): 67-70. |
| [17] |
TANG J, LU X J, CHEN F F. Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on the associated genes expression of autophagy signaling pathway of carassius auratus lymphocytes in vitro[J]. Front Physiol, 2018, 9: 1748. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2018.01748 |
| [18] |
KIM E K, KWON J E, LEE S Y, et al. IL-17-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction impairs apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through activation of autophagy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(1): e2565. |
| [19] |
洪永桃.自噬在类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞中的作用及甲氨蝶呤对自噬的影响[D].南充: 川北医学院, 2015.
|
 2020, Vol. 46
2020, Vol. 46


