扩展功能
文章信息
- 张晓璇, 马征, 于宁, 焦光美, 窦志杰, 赵亮, 高燕军
- ZHANG Xiaoxuan, MA Zheng, YU Ning, JIAO Guangmei, DOU Zhijie, ZHAO Liang, GAO Yanjun
- 丁苯酞对缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马神经元凋亡的抑制作用及其对p38 MAPK信号通路的影响
- Inhibitory effect of butylphthalide on hippocampal neuron apoptosis in ischemic stroke rats and itsinfluence in p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(05): 1086-1091
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1086-1091
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190520
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-10-19
脑血管疾病是严重危害人类健康的常见病和多发病,其中缺血性脑血管疾病所占比例较大,缺血性脑血管疾病的发病率、致残率和死亡率均比较高。缺血性脑卒中引起脑损伤的机制比较复杂,神经元细胞凋亡在脑损伤的发生过程中具有重要作用,在脑缺血早期,缺血区域的病理生理学变化主要为神经元坏死,在脑缺血后期缺血半暗带出现的神经元死亡以细胞凋亡为主,神经元坏死为不可逆的,而神经元凋亡受一些程序调控,对其进行干预可减少神经元凋亡的发生[1-2]。p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases,p38 MAPK)信号通路在神经元凋亡过程中发挥重要的调控作用,p38 MAPK信号通路的激活可促进神经元凋亡,抑制p38 MAPK信号通路可抑制神经元凋亡,减轻脑组织损伤[3]。丁苯酞对急性缺血性脑卒中有明显的治疗效果,对脑组织具有保护作用[4-5],但应用其治疗缺血性脑卒中的具体机制尚不明确。p38 MAPK信号通路在神经元凋亡中的作用在于其对缺血性脑卒中的修复起到了关键作用。本研究探讨丁苯酞对缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马神经元凋亡及p38 MAPK信号通路的影响,阐明丁苯酞治疗缺血性脑卒中的可能机制,为丁苯酞治疗缺血性脑卒中奠定理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、主要试剂和仪器健康清洁级雄性SD大鼠102只,购自上海斯莱克实验动物公司,动物许可证号:SCXK(沪)2007-0005。丁苯酞注射液(石药集团恩必普药业有限公司,批号:618150411),苏木素-伊红(HE)染色试剂盒和原位末端转移酶标记(TUNEL)染色试剂盒等(美国Gibco公司),聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯(BCA)试剂盒、辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记的山羊抗兔抗体、肌动蛋白(β-actin)抗体、兔抗大鼠激活型caspase-3(cleaved caspase-3)单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因(Bcl-2)单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠p38单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠磷酸化-p38(p-p38)单克隆抗体和兔抗大鼠丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)单克隆抗体(美国Sigma公司),cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38和MAPK引物设计与合成均由上海生物工程技术有限公司完成。细胞培养箱(美国Thermo公司), 倒置相差显微镜(日本Olympus公司), 脱色摇床(海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司), 电泳仪(美国Bio-Rad公司)和定量PCR仪(美国ABI公司)。
1.2 实验动物分组和缺血性脑卒中大鼠模型的建立将102只大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和丁苯酞组,每组34只。模型组和丁苯酞组大鼠建立缺血性脑卒中大鼠模型(采用改良Zea-Longa法制备局灶性脑缺血大鼠模型):各组大鼠麻醉成功后,剪开额顶部皮肤,暴露左侧半颅骨和颅骨前囟,采用激光多普勒血流仪记录大鼠左侧大脑中动脉血流情况,左侧大脑中动脉血流数值平稳后将大鼠仰卧位固定于动物手术台上,剪开颈部皮肤,暴露并分离颈总动脉、颈外动脉以及颈内动脉,结扎颈总动脉近心端及颈外动脉,夹闭远端颈内动脉,距颈内动脉分叉1 cm处剪一切口,将尼龙线(头端涂上硅胶)自左侧颈总动脉插入颈内动脉至感到少许阻力,线栓到达大脑中动脉分叉处,栓塞成功的标准为血流仪显示大脑中动脉血流下降至基础值的20%~30%,栓塞成功后固定线栓,缝合伤口,2 h回抽线栓恢复再灌注,大鼠模型制备完成。假手术组大鼠不结扎和插线颈总动脉近心端及颈外动脉,其他手术步骤同模型组。
建模成功的标准:大鼠提尾悬空实验阳性、向对侧转弯、同侧眼裂减小和对侧肢体瘫痪。建模成功后,丁苯酞组大鼠腹腔注射丁苯酞注射液(4.5 mg·kg-1),每天1次,假手术组和模型组大鼠每天相同时间点腹腔注射等量生理盐水,共2周。
1.3 组织标本处理实验结束时,假手术组大鼠均存活;丁苯酞组大鼠死亡2只,予以剔除,32只纳入研究;模型组大鼠建模失败1只,死亡1只,予以剔除,32只纳入研究。假手术组取17只大鼠,模型组和丁苯酞组各取16只大鼠经心脏灌注多聚甲醛固定液后取脑,脑组织经固定、脱水、石蜡包埋,用于HE染色和TUNEL染色;假手术组取17只大鼠,模型组和丁苯酞组各取16只大鼠断头取脑,液氮速冻后保存,用于Western blotting法和RT-PCR法检测。
1.4 大鼠海马CA1区HE染色将各组大鼠石蜡包埋海马组织切成厚度5 μm的切片,进行常规HE染色,显微镜下观察神经元形态学变化,选择海马CA1区明显的层面,400倍高倍视野下观察细胞形态表现,计算每个高倍视野中残留神经元数量。
1.5 大鼠海马CA1区神经元TUNEL染色将各大鼠石蜡包埋海马组织切片脱蜡至水,加入双氧水孵育40 min以消除内源性过氧化酶活性,加入蛋白酶K孵育10 min,TUNEL反应液孵育1 h,POD-转化液孵育30 min,DAB显色10 min,苏木素复染,脱水、透明、封片,高倍显微镜(×400)下观察TUNEL染色情况,TUNEL阳性细胞为细胞核固缩并被染成黄褐色或棕黄色,计算海马CA1区神经元凋亡指数。神经元凋亡指数=TUNEL染色阳性的神经元/总神经元×100%。
1.6 Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38、p-p38和MAPK蛋白表达水平将各组大鼠海马组织放入EP管中,加入蛋白裂解液研磨均匀,提取海马组织总蛋白,采用BCA法测定海马组织蛋白浓度,采用Western blotting法测定大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38、p-p38和MAPK蛋白表达水平,以兔抗大鼠cleaved caspase-3单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠Bax单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠Bcl-2单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠p-p38单克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠p38单克隆抗体和兔抗大鼠MAPK单克隆抗体为一抗,以β-actin为内参,山羊抗兔抗体(HRP标记)为二抗。目标蛋白的相对表达水平=目标蛋白条带灰度值/β-actin条带灰度值。
1.7 RT-PCR法检测各组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38和MAPK mRNA表达水平取各大鼠海马组织在冰上匀浆器中剪碎,加入Trizol提取海马组织中总RNA,采用RT-PCR法测定各组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38和MAPK mRNA水平。PCR反应条件:95℃、5 min;95℃、15 s,60℃、30 s,72℃、15 s,共40个循环;72℃、5 min。以β-actin为内参,大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38、p-p38和MAPK mRNA相对表达水平以2-ΔΔCT表示。
1.8 统计学分析采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析。各组大鼠海马CA1区神经元数量、神经元凋亡指数、cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38、p-p38和MAPK蛋白及mRNA水平以x ±s表示,多组间样本均数比较采用单因素方差分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组大鼠一般情况实验过程中假手术组大鼠无死亡,丁苯酞组大鼠死亡2只,模型组大鼠建模失败1只、死亡1只,予以排除。
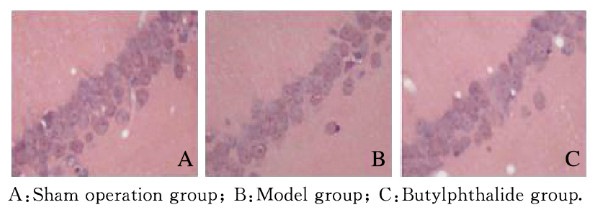
2.2 各组大鼠海马CA1区HE染色结果和CA1区神经元TUNEL染色结果各组大鼠海马CA1区HE染色结果:假手术组大鼠海马CA1区神经元细胞排列整齐,细胞核位于细胞中央,细胞膜完整;模型组大鼠海马CA1区神经元细胞排列紊乱,细胞肿胀破裂,细胞核固缩;丁苯酞组大鼠海马CA1区部分神经细胞结构恢复正常,排列尚完整,细胞膜基本完整。见图 1(插页六)。各组大鼠海马CA1区神经元TUNEL染色结果:假手术组大鼠海马CA1区基本无TUNEL染色阳性神经元;模型组大鼠海马CA1区可见大量TUNEL染色阳性神经元,神经元胞体缩小,细胞核固缩崩解,呈黄褐色或棕黄色颗粒;丁苯酞组大鼠海马CA1区见少量TUNEL染色阳性神经元。见图 2(插页六)。
|
| 图 1 各组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元HE染色结果(×200) Fig. 1 HE staining results of neurons in hippocampus tissue CA1 area of rats in various groups (×200) |
|
|

|
| 图 2 各组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元TUNEI染色(×200) Fig. 2 TUNEL staining results of neurons in hippocampus tissue Cal region of rats in various groups (×200) |
|
|
与假手术组比较,模型组和丁苯酞组大鼠海马CA1区神经元数量明显减少(P<0.01),神经元凋亡指数明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,丁苯酞组大鼠海马CA1区神经元数量明显增加(P<0.01),神经元凋亡指数明显降低(P<0.01)。见表 1。
| (x ±s) | |||
| Group | n | Number of neurons (×400 field of view) | Apoptotic index (η/%) |
| Sham operation | 17 | 48.35±2.14 | 5.29±4.25 |
| Model | 16 | 26.47±1.35* | 49.27±1.54* |
| Butylphthalide | 16 | 41.13±3.24*△ | 22.14±1.34*△ |
| * P<0.01 compared with sham operation group; △ P<0.01 compared with model group. | |||
与假手术组比较,模型组和丁苯酞组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、p-p38和MAPK蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白水平明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,丁苯酞组大鼠海马组织cleaved caspase-3、Bax、p-p38和MAPK蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。见表 2。
| (x ±s) | |||||||
| Group | n | Cleaved caspase-3 protein | Bax protein | Bcl-2 protein | p38 protein | p-p38 protein | MAPK protein |
| Sham operation | 17 | 0.18±0.03 | 0.23±0.04 | 0.64±0.06 | 0.52±0.02 | 0.17±0.01 | 0.19±0.01 |
| Model | 16 | 0.75±0.11* | 0.57±0.08* | 0.11±0.04* | 0.53±0.11 | 0.64±0.17* | 0.77±0.12* |
| Butylphthalide | 16 | 0.46±0.05*△ | 0.38±0.04*△ | 0.24±0.03*△ | 0.51±0.12 | 0.30±0.07*△ | 0.44±0.05*△ |
| * P<0.01 compared with sham operation group;△ P<0.01 compared with model group. | |||||||
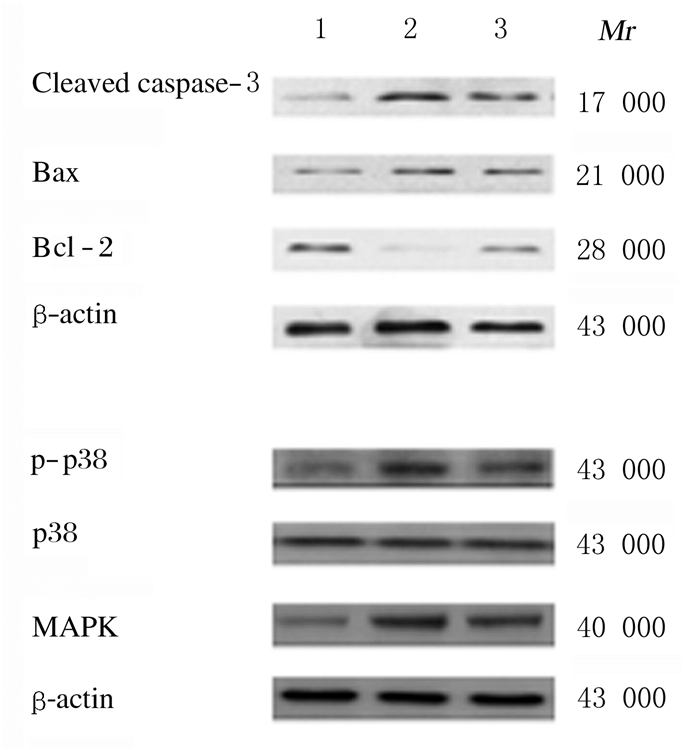
与假手术组比较,模型组和丁苯酞组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax和MAPK mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),Bcl-2 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,丁苯酞组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax和MAPK mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),Bcl-2 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。见图 3和表 3。
|
| Lane 1: Sham operation group; Lane 2: Model group; Lane 3: Butylphthalide group. 图 3 Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马组织中cleaved caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p-p38、p38和MAPK蛋白表达电泳图 Fig. 3 Electrophoregram of expressionsof cleaved caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, p-p38, p38, and MAPK proteins in hippocampus tissue of rats in various groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|
| (x ±s) | ||||||
| Group | n | Cleaved caspase-3 mRNA | BaxmRNA | Bcl-2mRNA | p38 mRNA | MAPK mRNA |
| Sham operation | 17 | 1.00±0.00 | 1.00±0.00 | 1.00±0.00 | 1.00±0.00 | 1.00±0.00 |
| Model | 16 | 2.14±0.05* | 2.42±0.12* | 0.43±0.05* | 0.98±0.15 | 2.52±0.35* |
| Butylphthalide | 16 | 1.47±0.03*△ | 1.67±0.08*△ | 0.74±0.06*△ | 1.01±0.13 | 1.64±0.24*△ |
| * P<0.01 compared with sham operation group; △ P<0.01 compared with model group. | ||||||
细胞凋亡的诱导和调控比较复杂,caspases为凋亡的最后执行因子,凋亡的实施通过caspases的激活而完成的,caspase-3为caspases级联反应下游的关键因子,在凋亡程序的启动中起枢纽作用,caspase-3可水解脱氧核糖核酸酶的抑制蛋白,使脱氧核糖核酸酶活化进入细胞核、使DNA断裂从而导致细胞凋亡;caspase-3还可裂解Bcl-2,使其失去活性从而发挥促凋亡作用;脑缺血可通过多种途径激活caspase-3,进而引起神经元凋亡[6-7]。
Bcl-2为一种癌基因,对细胞凋亡具有抑制作用[8];Bax为Bcl-2家族成员之一,是人体重要的凋亡基因,可与Bcl-2形成二聚体而对Bcl-2产生抑制作用[9]。Bax和Bcl-2间的平衡关系对细胞凋亡具有调控作用,脑缺血时脑组织中Bax和Bcl-2平衡失调,Bax水平升高、Bcl-2水平降低,从而引起神经元凋亡的发生[10]。
丁苯酞是治疗脑梗死的Ⅰ类新药,对缺血性脑梗死的治疗效果比较显著,可通过多个环节阻断缺血性脑损伤[11],其机制可能通过重构缺血区域微循环、调节缺血区域血流量,增加脑组织能量代谢,减轻神经细胞凋亡,促进脑损伤的修复[12-13],但丁苯酞对缺血性脑梗死的脑保护作用机制尚不清楚。本研究通过建立缺血性脑卒中大鼠模型,给予丁苯酞治疗后,缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马组织中存活神经元数量增加、凋亡神经元细胞减少、cleaved caspase-3和Bax水平下降,Bcl-2水平升高。缺血性脑卒中海马组织中Bax水平升高,在线粒体外膜发生寡聚体化,影响线粒体膜的通透性,使细胞色素C进入细胞质,激活caspase-3级联反应,且Bax与Bcl-2形成二聚体抑制Bcl-2产生,Bax和Bcl-2间的平衡被打破,从而诱导神经元凋亡;丁苯酞可能通过抑制上述反应发挥抑制神经元凋亡的作用,从而在缺血性脑损伤中发挥脑保护作用。
神经元凋亡受多种信号通路调控,p38 MAPK信号通路在神经元凋亡过程中发挥重要作用,脑缺血后p38 MAPK信号通路被激活,引起神经元凋亡[14-15]。p38 MAPK信号通路被激活后可直接激活Bax,激活的Bax转移并插入线粒体外膜,使细胞色素C进入细胞质激活caspase-3级联反应,并抑制Bcl-2产生,从而诱导细胞凋亡;磷酸化的p38可激活NF-κB,激活的NF-κB与多种靶基因结合,对细胞核凋亡相关基因的表达发挥调节作用,从而诱导神经元凋亡[16-18]。本研究结果显示:缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马组织中p-p38和MAPK蛋白表达水平升高,丁苯酞治疗可降低缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马组织中p-p38和MAPK的表达。
综上所述,丁苯酞通过抑制缺血性脑卒中大鼠海马神经元凋亡发挥脑保护作用,其机制可能与丁苯酞抑制p38 MAPK信号通路有关。
| [1] | ZHOU L, ZHANG J, WANG C, et al. Tanshinone inhibits neuronal cell apoptosis and inflammatory response in cerebral infarction rat model[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2017, 30(2): 123–129. DOI:10.1177/0394632017703274 |
| [2] | 余婷, 韩亚非. 苦参素对慢性脑缺血大鼠海马CA1区神经元凋亡保护作用的研究[J]. 天津中医药, 2018, 35(11): 863–867. DOI:10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2018.11.17 |
| [3] | LIU X, ZHANG J, WANG SB, et al. Astragaloside Ⅳ attenuates the H2O2-induced apoptosis of neuronal cells by inhibiting α-synuclein expression via the p38 MAPK pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2017, 40(6): 1772–1780. |
| [4] | JIANG Y, SUN LY, XUAN XY, et al. Impacts of N-Butylphthalidethalexpression of growth factors in rats with focal cerebral ischemia[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2016, 16(2): 102–107. |
| [5] | 刘颖丽, 杨立彬, 张舒石, 等. 丁苯酞注射液治疗老年急性脑梗死患者的疗效及其对脑血流动力和脑血管储备能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2017, 43(2): 344–348. |
| [6] | CHEN B, WANG GX, LI WW, et al. Memantine attenuates cell apoptosis by suppressing the calpain-caspase-3 pathway in an experimental model of ischemic stroke[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 351(2): 163–172. |
| [7] | LI D, AI YQ. Hydrogen saline suppresses neuronal cell apoptosis and inhibits the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase caspase-3 signaling pathway following cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(4): 5321–5325. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7294 |
| [8] | JI W, LIU HZ, LIU C, et al. Up-regulation of MCM3 relates to neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury in adult rats[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2017, 37(4): 683–693. |
| [9] | CAKIR Z, FUNK K, LAUTERWASSER J, et al. Parkin promotes proteasomal degradation of misregulatedBAX[J]. J Cell Sci, 2017, 130(17): 2903–2913. DOI:10.1242/jcs.200162 |
| [10] | SUN X Z, LIAO Y, LI W, et al. Neuroprotective effects of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides against oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2017, 12(6): 953–958. DOI:10.4103/1673-5374.208590 |
| [11] | ZHOU J, ZHANG Y H, SONG H Z, et al. 5d, a novel analogue of 3-n-butylphthalide, decreases NADPH oxidase activity through the positive regulation of CK2 after ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(26): 39444–39457. |
| [12] | 毛西京, 王敏, 于挺敏, 等. 丁苯酞对血管性痴呆大鼠海马CA1区脑源性神经营养因子表达的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2017, 43(5): 857–861. |
| [13] | 刘昌亚, 胡学斌, 熊志勇, 等. 丁苯酞注射液对动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血早期脑损伤的作用与机制探讨[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2018, 13(07): 692–695. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5765.2018.07.011 |
| [14] | ZHANG P, HONG J, YOON I N, et al. Clostridium difficiletoxin A induces reactive oxygen species production and p38 MAPK activation to exert cellular toxicity in neuronal cells[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2017, 27(6): 1163–1170. DOI:10.4014/jmb.1702.02041 |
| [15] | ZHAO B S, PAN Y Y, WANG Z X, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen pretreatment improves cognition and reduces hippocampal damage via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in a rat model[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2017, 58(1): 131–138. DOI:10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.131 |
| [16] | 谢君, 张智博. 细胞内丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路与脑缺血后神经元凋亡[J]. 国际脑血管病杂志, 2015, 23(6): 464–468. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4165.2015.06.008 |
| [17] | LI W, LI D Y, ZHAO S M, et al. Rutin attenuates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis via modulating JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in the hippocampi of neonatal rats[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 13(5): 2056–2064. DOI:10.3892/etm.2017.4173 |
| [18] | 杨擎, 李娜, 隋欣, 等. 五味子乙素靶向调节Aβ及下游NF-κB/TNF-α信号通路保护受损神经元的分子机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(5): 2064–2069. |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


