扩展功能
文章信息
- 梅冬兰, 韩立赤, 阎振梅, 黄宏伟
- MEI Donglan, HAN Lichi, YAN Zhenmei, HUANG Hongwei
- 应用锥形束CT比较骨性Ⅲ类高角
 与正常
与正常 成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的意义
成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的意义 - Significance of comparison in upper airway morphology and hyoid position between skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle and normal occlusion of adults by cone beam CT
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(04): 899-904
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 899-904
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190427
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-09-24
 与正常
与正常 成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的意义
成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的意义
2. 辽宁省大连市口腔医院正畸科, 辽宁 大连 116021;
3. 陆军特色医学中心教学训练中心, 重庆 400038
 与正常
与正常 成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的差异,初步探讨骨性Ⅲ类高角错
成人上气道形态和舌骨位置的差异,初步探讨骨性Ⅲ类高角错 畸形对成人上气道形态及舌骨位置的影响。方法:
选择在辽宁省大连市口腔医院正畸科就诊的成人患者42例,其中骨性Ⅲ类高角
畸形对成人上气道形态及舌骨位置的影响。方法:
选择在辽宁省大连市口腔医院正畸科就诊的成人患者42例,其中骨性Ⅲ类高角 组和正常
组和正常 组各21例,利用MIMICS 20.0软件测量2组患者CBCT的上气道各分区线距、横截面积、体积和舌骨线距,并对数据进行统计学分析。结果:
与正常
组各21例,利用MIMICS 20.0软件测量2组患者CBCT的上气道各分区线距、横截面积、体积和舌骨线距,并对数据进行统计学分析。结果:
与正常 组比较,骨性Ⅲ类高角
组比较,骨性Ⅲ类高角 组患者鼻咽的最大横向距离(LAT1)、腭咽的最大矢状距离(AP2)和腭咽的体积(VOL2)均增大(P < 0.05),舌咽和喉咽的最大横向距离(LAT3和LAT4)、喉咽的横截面积(CSA4)和体积(VOL4)均减小(P < 0.05)。与正常
组患者鼻咽的最大横向距离(LAT1)、腭咽的最大矢状距离(AP2)和腭咽的体积(VOL2)均增大(P < 0.05),舌咽和喉咽的最大横向距离(LAT3和LAT4)、喉咽的横截面积(CSA4)和体积(VOL4)均减小(P < 0.05)。与正常 组比较,骨性Ⅲ类高角
组比较,骨性Ⅲ类高角 组患者舌骨位置有向前、向上移位的趋势,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:
成人骨性Ⅲ类高角错
组患者舌骨位置有向前、向上移位的趋势,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:
成人骨性Ⅲ类高角错 畸形可使上气道上段腭咽横截面积和体积增大,上气道下段喉咽横截面积和体积减小,并且舌骨有向前、向上移位的趋势。
畸形可使上气道上段腭咽横截面积和体积增大,上气道下段喉咽横截面积和体积减小,并且舌骨有向前、向上移位的趋势。 正常
正常 上气道 舌骨
上气道 舌骨 2. Department of Orthodontics, Dalian Stomatology Hospital, Liaoning Province, Dalian 116021, China;
3. Teaching and Training Center, Army Characteristic Medical Center, Chongqing 400038, China
从19世纪后期,学者们就开始研究颅颌面形态与呼吸功能之间的关系。错









从2016-2018年在辽宁省大连市口腔医院正畸科就诊的患者中随机选择骨性Ⅲ类高角

纳入标准:①年龄18~35岁;②面部基本协调对称,无颅颌面畸形,无唇腭裂手术史,无正畸和正颌治疗史;③无扁桃体、腺样体肥大和手术史;④CBCT影像资料清晰;⑤无明显肥胖,体质量指数18.5~23.9 kg·m-2。骨性Ⅲ类高角

排除标准:①颜面部明显不对称,有唇腭裂手术史,有正畸和正颌治疗史;②有扁桃体、腺样体肥大和手术史;③肥胖,体质量指数(BMI)大于24 kg·m-2;④骨性Ⅲ类高角
所有研究对象均由辽宁省大连市口腔医院放射科同一名医生拍摄CBCT,扫描时要求患者站立,眼耳平面(FH平面)与地面平行,上下唇自然闭合,双侧后牙处于最大牙尖交错位,不咀嚼,不吞咽,不说话,呼气末屏住呼吸。扫描的数据保存为DICOM格式,再导入三维重建MIMICS 20.0软件进行重建测量。本研究所有CBCT资料均由同一个人进行测量。第一次定点后每个测量值测量2次取均值,间隔2周后,从研究样本中随机抽取10例患者,再次定位测量,同样进行2次测量取均值,2次测量结果进行两独立样本t检验,P>0.05代表测量结果可靠。
1.3 上气道3D模型的建立原始数据导入MIMICS 20.0软件后,调整阈值,最低阈值为-1424,最高阈值为-550,消除多余的噪点,生成蒙罩1,对其行Calculate 3D from mask命令,生成上气道3D模型。见图 1(插页八)。

|
| 图 1 上气道三维重建模型 Fig. 1 Upper airway 3D reconstruction model |
|
|
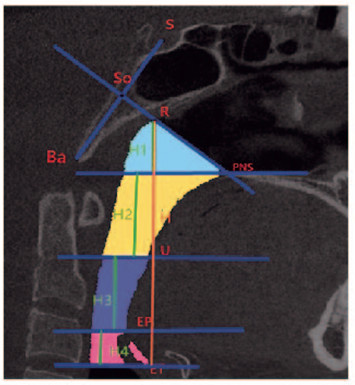
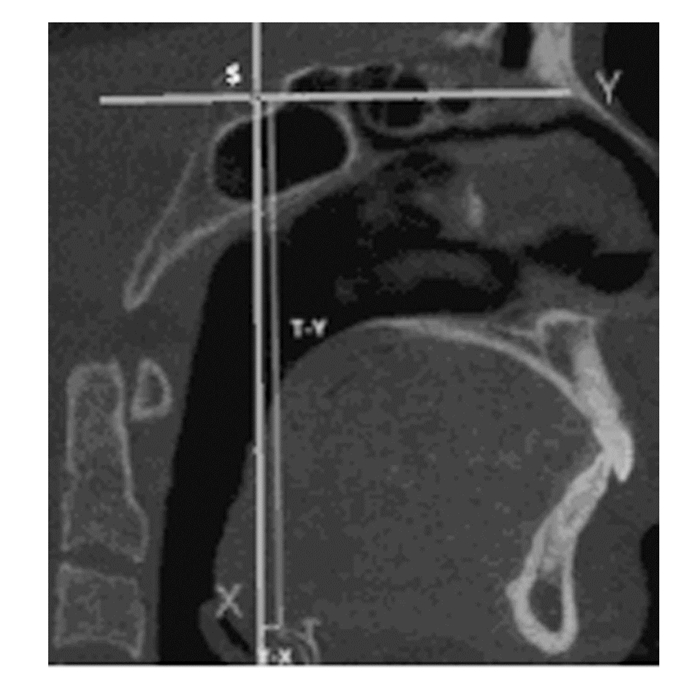
标志点及平面的确定参考以往的文献[5], 上气道标志点及参考平面共13个,包括蝶鞍点(S)、颅底点(Ba)、S点与Ba点连线的中点(So)、后鼻棘点(PNS)、So点与PNS点连线与鼻咽上界的交点(R)、腭垂尖点(U)、会厌顶点(EP)、会厌基点(ET)、鼻咽前界(过R点和PNS点且垂直于正中矢状面的平面)、鼻咽下界及腭咽上界(过PNS点平行于FH平面的平面)、腭咽下界及舌咽上界(过U点平行于FH平面的平面)、舌咽下界及喉咽上界(过EP点平行于FH平面的平面)和喉咽下界(过ET点平行于FH平面的平面)。见图 2~4(插页八)。舌骨的标志点及参考线共3个,包括舌骨的最高点(T)、过S点与眶耳平面平行的Y轴和过S点与眶耳平面垂直的X轴。见图 5。
|
| 图 2 正中矢状面上气道分区和高度测量 Fig. 2 Upper airway partition and height measurement in sagittal plane |
|
|
|
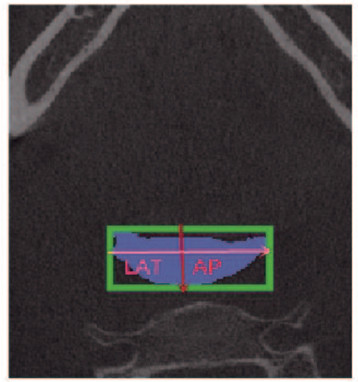
| 图 3 上气道横截面LAT和AP测量 Fig. 3 Measurement of LAT and AP of cross section of upper airway |
|
|
|
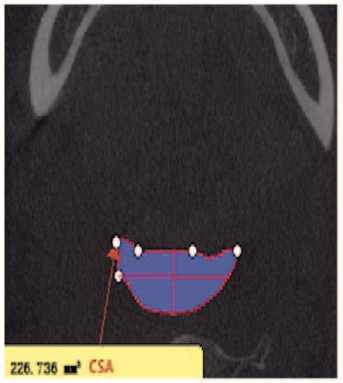
| 图 4 上气道CSA测量 Fig. 4 Measurement of CSA of upper airway |
|
|
|
| 图 5 正中矢状面舌骨位置的测量 Fig. 5 Measurement of hyoid position in sagittal plane |
|
|
上气道测量项目:利用MIMICS 20.0软件的容积计算对3D模型的上气道鼻、腭、舌、喉咽体积和总体积进行测量(VOL1、VOL2、VOL3、VOL4和VOL)。见图 1(插页八)。利用MIMICS 20.0软件的线距测量鼻咽长度(H1)、腭咽长度(H2)、舌咽长度(H3)、喉咽长度(H4)和上气道总长度(H)。见图 2(插页八)。利用MIMICS 20.0软件的截面图测量各分界的最大横向距离(LAT)和最大矢状距离(AP)。见图 3(插页八)。利用横截面测量各分界的横截面积(CSA)。见图 4(插页八)。舌骨的测量项目:舌骨最高点T至Y轴的距离(T-Y),T点至X轴的距离(T-X)。见图 5。
1.6 统计学分析采用SPSS20.0统计软件进行统计学分析。对正常



上气道长度:与正常



| (n=21, x±s, l/mm) | |||||
| Group | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H |
| Normal occlusion | 13.53±1.98 | 26.74±3.66 | 23.50±4.41 | 11.40±2.35 | 75.76±5.63 |
| Skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle | 14.75±3.03 | 26.22±3.52 | 23.29±3.71 | 10.21±2.47 | 75.00±6.74 |
| t | 1.55 | -0.468 | -0.167 | -1.608 | -0.397 |
| P | 0.13 | 0.642 | 0.868 | 0.116 | 0.694 |
| H1:Length of nasopharynx; H2:Length of velopharyngeal; H3: Length of glossopharynx; H4:Length of laryngopharynx; H:Total length. | |||||
上气道横截面形态指标:与正常



| (n=21, x±s, l/mm) | ||||||||
| Group | LAT1 | LAT2 | LAT3 | LAT4 | AP1 | AP2 | AP3 | AP4 |
| Normal occlusion | 34.62±6.24 | 26.05±6.60 | 31.70±3.73 | 33.72±3.52 | 25.66±4.36 | 12.24±3.09 | 13.71±2.83 | 15.33±3.87 |
| Skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle | 39.13±6.17 | 28.59±5.14 | 28.97±3.09 | 30.52±3.13 | 24.98±4.00 | 14.80±3.95 | 14.47±4.17 | 15.89±4.98 |
| t | 2.353 | 1.291 | -2.574 | -2.623 | -0.527 | 2.346 | 0.693 | 0.411 |
| P | 0.024 | 0.204 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.601 | 0.024 | 0.493 | 0.683 |
| LAT1:Maximum lateral distance ofnasopharynx; LAT2:Maximum lateral distance ofvelopharyngeal; LAT3:Maximum lateral distance ofglossopharynx; LAT4:Maximum lateral distance oflaryngopharynx; AP1:Maximum anterior-posterior distance of nasopharynx; AP2:Maximum anterior-posterior distance of velopharyngeal; AP3:Maximum anterior- posterior distance of glossopharynx; AP4:Maximum anterior-posterior distance of laryngopharynx. | ||||||||
上气道横截面积:与正常



| (n=21, x±s, S/mm2) | ||||
| Group | CSA1 | CSA2 | CSA3 | CSA4 |
| Normal occlusion | 610.98±111.77 | 225.37±102.22 | 302.57±96.18 | 317.41±104.72 |
| Skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle | 636.42±156.10 | 334.19±152.73 | 323.30±116.65 | 266.21±49.35 |
| t | 0.607 | 2.713 | 0.628 | -2.027 |
| P | 0.547 | 0.010 | 0.533 | 0.049 |
| CSA1:CSA of nasopharynx; CSA2:CSA of velopharyngeal; CSA3:CSA of glossopharynx; CSA4: CSA of laryngopharynx. | ||||
上气道体积:与正常



| (n=21, x±s, V/mm3) | |||||
| Group | VOL1 | VOL2 | VOL3 | VOL4 | VOL |
| Normal occlusion | 5249.99±1 255.79 | 8 474.67±3 570.06 | 6 074.17±2 647.23 | 3 601.68±1 331.97 | 23 685.41±7 216.65 |
| Skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle | 6 678.24±3 114.87 | 11 365.31±4 820.31 | 6 042.74±2 292.79 | 2 793.11±1 031.16 | 25 764.80±6 660.94 |
| t | 1.949 | 2.208 | 0.090 | -2.200 | 0.970 |
| P | 0.058 | 0.033 | 0.929 | 0.034 | 0.338 |
| VOL1:Volume of nasopharynx; VOL2:Volume of velopharyngeal; VOL3:Volume of glossopharynx; VOL4:Volume of laryngopharynx; VOL:Total volume. | |||||


与正常



| (n=21, x±s, l/mm) | ||
| Group | T-X | T-Y |
| Normal occlusion | 9.40±6.51 | 102.18±8.33 |
| Skeletal class Ⅲ malocclusion of high-angle | 10.54±5.07 | 101.12±8.26 |
| t | 0.636 | 0.414 |
| P | 0.528 | 0.680 |
| T-X:Distance from the highest point of hyoid toX-axis; T-Y:Distance from the highest point of hyoid toY-axis. | ||
上气道形态对口颌呼吸健康至关重要,已发现上气道的形态与患者性别、年龄、肥胖以及颅面部的矢状向、垂直向的发育等均有密切关联[6-7]。李志敏等[8]研究颅面部矢状向的发育对上气道形态影响发现:骨性Ⅲ类错






本研究对成年骨性Ⅲ类高角









有学者[19-20]报道:在不同程度的睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(OSAHS)患者中上气道中下段存在缩小的情况,并且随着OSAHS程度的加重,上气道中下段减小更加明显。本研究骨性Ⅲ类高角




本研究结果中骨性Ⅲ类高角错

本研究通过建立骨性Ⅲ类高角



| [1] | KAUR S, RAI S, KAUR M. Comparison of reliability of lateral cephalogram and computed tomography for assessment of airway space[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2014, 17(5): 629–636. DOI:10.4103/1119-3077.141431 |
| [2] | JIANG YY. Correlation between hyoid bone position and airway dimensions in Chinese adolescents by cone beam computed tomography analysis[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45(7): 914–921. DOI:10.1016/j.ijom.2016.02.005 |
| [3] | DALMAU E, ZAMORA N, TARAZONA B, et al. A comparative study of the pharyngeal airway space, measured with cone beam computed tomography, between patients with different craniofacial morphologies[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2015, 43(8): 1438–1446. DOI:10.1016/j.jcms.2015.06.016 |
| [4] | ZHONG Z, TANG Z H, GAO X M, et al. A comparison study of upper airway among different skeletal craniofacial patterns in nonsnoring Chinese children[J]. Angle Orthod, 2010, 80(2): 267–274. DOI:10.2319/030809-130.1 |
| [5] | WEN X, WANG XY, QIN SQ, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of upper airway morphology in skeletal Class Ⅲ patients with and without mandibular asymmetry[J]. Angle Orthod, 2017, 87(4): 526–533. DOI:10.2319/120116-866.1 |
| [6] |
任少春, 门海艳, 李洪发, 等.
成人骨性Ⅱ类错 口咽气道形态的CBCT研究[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2017, 23(4): 364–368. 口咽气道形态的CBCT研究[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2017, 23(4): 364–368.
|
| [7] |
杨莉, 韩蓓蕾, 邓海艳, 等.
矢状骨面型错 畸形对成年人上气道影响的CBCT研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2017, 37(2): 144–148. 畸形对成年人上气道影响的CBCT研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2017, 37(2): 144–148.
|
| [8] |
李志敏, 武杰, 门海燕, 等.
成人骨性Ⅲ类错 口咽气道容积大小和舌骨位置的锥形束CT研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2015, 24(3): 351–355. 口咽气道容积大小和舌骨位置的锥形束CT研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2015, 24(3): 351–355.
|
| [9] | IWASAKI T, HAYASAKI H, TAKEMOTO Y, et al. Oropharyngeal airway in children with Class Ⅲ malocclusion evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2009, 136(3): 318.e1-318.e9;discussion 318-9. |
| [10] | 杨芳, 闫英剑, 张明烨, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类不同垂直骨面型成人上气道形态三维测量分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2013, 22(2): 289–293. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-6455.2013.02.019 |
| [11] | 曹安怡, 羊晓, 葛红珊, 等. 高角成人口咽气道形态与颌骨形态间的关系[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2017, 25(8): 510–514. |
| [12] | 詹宇婷, 汪美霞, 陶长绣. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征发病机制研究[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2015, 27(12): 1658–1660. |
| [13] | 徐蓉, 吴绯红, 苏筱芮, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征上气道舌骨位置改变的研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2015, 31(19): 3216–3219. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2015.19.031 |
| [14] | 车蓓, 顾月光, 马俊青, 等. 下颌后缩患者上气道三维结构和舌骨位置的分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 39(4): 532–535. |
| [15] | 郭涛, 丁寅. 不同垂直骨面型成年患者上气道形态和舌骨位置差异的研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2006, 22(1): 25–29. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2006.01.007 |
| [16] | PARK JE, BAE SH, CHOI JY, et al. The structural changes of pharyngeal airway contributing to snoring after orthognathic surgery in skeletal class Ⅲ patients[J]. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg, 2017, 39(1): 22. DOI:10.1186/s40902-017-0120-6 |
| [17] | 王明洁.成人骨性Ⅲ类上气道结构的CBCT三维测量分析[D].郑州: 郑州大学, 2017. |
| [18] |
杨莉, 韩蓓蕾, 邓海艳, 等.
矢状骨面型错 畸形对成年人上气道影响的CBCT研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2017, 37(2): 144–148. 畸形对成年人上气道影响的CBCT研究[J]. 口腔医学, 2017, 37(2): 144–148.
|
| [19] | 梁秀妮, 陆钊群, 吴平安, 等. OSAHS患者上气道容积与多导睡眠图部分参数的相关性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(18): 1409–1413. |
| [20] |
孟怡彤, 张晓东.
OSAHS患者与个别正常 志愿者上气道二维三维测量的差异性研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2018, 32(5): 269–273. 志愿者上气道二维三维测量的差异性研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2018, 32(5): 269–273.
|
| [21] | IRANI S K, OLIVER D R, MOVAHED R, et al. Pharyngeal airway evaluation after isolated mandibular setback surgery using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2018, 153(1): 46–53. DOI:10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.05.031 |
| [22] |
聂萍, 陶丽, 朱妍菲, 等.
2种不同正颌术式对骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形患者上气道形态的影响[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2018, 27(3): 280–284. 畸形患者上气道形态的影响[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2018, 27(3): 280–284.
|
| [23] | YANG YX, YANG K, ZHAO Y. Three-dimensional changes in the upper airway of skeletal class Ⅲ patients after different orthognathic surgical procedures[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 76(1): 155–164. DOI:10.1016/j.joms.2017.06.025 |
| [24] | 韩蓓蕾, 邓海艳, 杨莉, 等. 不同垂直骨面型女性青少年上气道形态和舌骨位置的锥体束CT分析[J]. 广东医学, 2017, 38(7): 1024–1028. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2017.07.012 |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


