扩展功能
文章信息
- 李怀玉, 庄改改, 杨萍, 王安萍
- LI Huaiyu, ZHUANG Gaigai, YANG Ping, WANG Anping
- 并发急性肾损伤早产儿尿中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白水平检测及其临床意义
- Detection of urinary neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin level of premature infants with acute kidney injury and its clinical significance
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(03): 656-660
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 656-660
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190331
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-03-14
近年来,我国早产儿的出生率逐年增加,其生存率也明显提高,但是早产儿急性肾功能损伤(acute renal injury, AKI)的诊断和治疗方面却并未取得相应的进步。早产儿肾组织发育不成熟,在缺氧等疾病因素影响下更容易发展为AKI。早产儿AKI缺乏特异性的早期临床诊断指标,目前临床实践中,其诊断仍主要依据血清肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)和尿量这2个指标,但缺乏特异性和灵敏性,极易导致诊治的延误,从而使AKI的发病率和病死率居高不下。因此寻找能用于AKI早期诊断的某种具有较高灵敏度和特异度的生物标志物成为医学界当前迫切需要解决的问题。近年来已发现一些AKI检测标志物,如β2微球蛋白、胱抑素C(Cys-C)、肾损伤因子1(KIM-1)和尿脂肪酸结合蛋白等。有些已经在临床上得到应用,但是普遍存在敏感性低和特异性差的缺点。中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白(neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, NGAL)是一种相对分子质量较小的多肽,存在于尿液和血浆中,在尿液中纯度较高,检测所需标本量少。健康成人血浆中NGAL水平正常值为6~102 μg·L-1[1],儿童与成人存在差异[2]。然而,NGAL是否能作为一种早产儿AKI诊断标记物,国外虽有报道但尚无多中心、大样本的报道, 国内报道也较少。本研究观察了早产儿AKI早期尿NGAL和Scr水平及其随时间的变化趋势,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料 1.1.1 研究对象本研究采用回顾性研究方法,将2015年10月—2017年7月在本科分娩的胎龄<37周、出生体质量<3 000 g,因窒息缺氧、感染、低出生体质量等24 h内收住本院新生儿重症监护室(NICU)的85例早产儿作为研究对象。
1.1.2 排除标准① 先天性泌尿系统畸形;②患泌尿系感染;③孕母患有急性或慢性肾功能不全和(或)产前72 h内使用过肾毒性药物。
1.1.3 诊断标准依据新生儿AKI分期标准[3-4](表 1)将患儿分为AKI组(30例)和非AKI组(55例)。该研究经本院伦理委员会批准,各研究对象均由患儿监护人签署知情同意书。
| Stage | Scr level |
| 0 | Scr < 0.3 mg·dL-1 |
| 1 | Scr≥0.3 mg·dL-1/ increase to more than or left to 150% to 200% from baseline |
| 2 | Increase to more than 200% to 300% from baseline |
| 3 | Increase to more than 300% from baseline/more than or equal to 2.5 mg·dL-1 or receipt of dialysis |
记录2组早产儿性别、年龄、胎龄、出生体质量、入院时体温、血pH值和Scr水平。生后24、48、72、120和168 h分别采用一次性尿袋留取尿液3~5 mL, 同时采集2 mL静脉血行Scr水平检测。
1.3 尿NGAL水平和Scr水平检测所有留取的尿液标本经3 000 r·min-1离心5 min后取上清液, -80℃冰箱保存,采用ELISA法检测尿NGAL水平,检测试剂盒由上海宝曼公司提供。采集2 mL静脉血, 3 000 r·min-1离心10 min后留取血清采用速率法行Scr水平检测。
1.4 统计学分析采用Excel 2010软件建立数据库,录入原始数据,并进行逻辑查错。采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。2组早产儿的孕周、出生体质量、入住NICU时的年龄、尿NGAL和Scr水平以x±s表示,组间比较采用t检验;重复测量资料的组间比较采用重复测量设计的方差分析。以1-特异度为横坐标,敏感度为纵坐标,绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,曲线下面积(AUC)用于判断各指标的诊断价值。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 2组早产儿基本情况85例早产儿中有30例发生AKI,AKI的发生率为35.29%。2组早产儿的性别、孕周、出生体质量和入住NICU时的年龄比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。见表 2。
| Group | n | Gender(Male/Female) | Gestational age(week) | Bodyweight(m/g) | Age at NICU(t/min) |
| Non-AKI | 55 | 36/19 | 34.21±1.25 | 2 180.65±398.09 | 21.76±6.29 |
| AKI | 30 | 23/7 | 33.40±2.74 | 1 980.69±557.27 | 23.00±6.93 |
| t | 1.149 | -1.508 | -1.900 | 0.827 | |
| P | 0.284 | 0.141 | 0.061 | 0.411 |
生后24、48、72和120 h时,2组早产儿各时间点尿NGAL水平比较差异有统计学意义(F=62.710,P < 0.01)。AKI组早产儿尿NGAL水平明显高于非AKI组(P < 0.05)。时间点与患者分组因素之间存在交互效应(F=52.042,P < 0.05)。2组早产儿出生后各时间点尿NGAL水平见表 3。
| [x±s, ρB/(ng·dL-1)] | ||||||
| Group | n | Level of urinary NGAL | ||||
| (t/h) 24 | 48 | 72 | 120 | 168 | ||
| AKI | 30 | 308.84±1.30 | 11.80±0.23 | 14.31±2.06 | 11.46±3.13 | 7.80±1.37 |
| Non-AKI | 55 | 6.74±0.34 | 8.07±1.54 | 7.60±1.53 | 7.29±1.08 | 7.56±1.33 |
| t | 8.710 | 11.410 | 7.060 | 7.090 | 0.750 | |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.460 | |
2组早产儿生后各时间点Scr水平比较差异均有统计学意义(F=27.332,P < 0.05)。AKI组早产儿Scr水平在48 h时开始升高,72 h时达最高峰值,72 h后呈下降趋势,而非AKI组早产儿生后Scr水平呈轻度降低趋势。生后48、72和120h时AKI组早产儿Scr水平明显高于非AKI组(P < 0.05)。各时间点与分组因素之间存在交互效应(F=48.136,P < 0.05)。见表 4。
| [x±s, cB/μmol·L-1)] | ||||||
| Group | n | Level of Scr | ||||
| (t/h) 24 | 48 | 72 | 120 | 168 | ||
| AKI | 30 | 0.65±0.23 | 0.85±0.29 | 1.20±0.51 | 1.01±0.58 | 0.56±0.17 |
| Non-AKI | 55 | 0.64±0.14 | 0.64±0.15 | 0.56±0.08 | 0.54±0.09 | 0.52±0.13 |
| t | 0.26 | 36.89 | 6.73 | 29.77 | 1.00 | |
| P | 0.82 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.32 | |
生后24 h时,尿NGAL的AUC为0.937(95%CI:0.870~1.000),Scr的AUC为0.446(95%CI:0.309~0.583), 两者比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。尿NGAL水平的临界值为6.95 ng·dL-1时,诊断AKI的敏感性和特异性分别为0.900和0.836。生后48 h时Scr水平诊断AKI的敏感性及特异性均低于尿NGAL水平。生后72和120 h时二者诊断价值相当。ROC曲线见图 1。
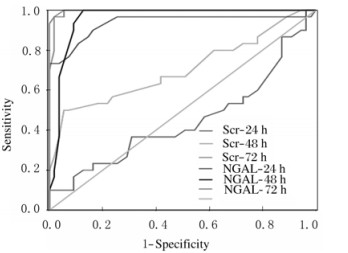
|
| 图 1 尿NGAL水平和血清Scr水平对早产儿AKI诊断价值的ROC曲线 Fig. 1 ROC curves of urinary NGAL and Scr levels in diagnosis of AKI of premature infants |
|
|
在儿童及新生儿[5-6]危重症中AKI是导致死亡的独立危险因素,使患儿发生慢性肾脏疾病的风险增加[7],为了降低死亡率及促进肾功能恢复,目前建议在亚临床AKI阶段提供尽早的干预措施,如严密的监测及液体平衡[8]。但是关于早产儿AKI发病率并无很权威的数据,主要是因为针对这个群体AKI缺乏统一的定义,之前基于Scr和尿量评估所进行的相关研究同质性较差[9]。因此,探索早期AKI生物学标记物在促进AKI研究中发挥了显著的作用。
研究[10]显示:儿童心脏手术后发生急性肾功能衰竭的患者在手术后2 h血、尿NGAL水平明显升高,而Scr水平则在1~3 d后明显升高。BAUMERT等[11]在一项新生儿(n=43)的前瞻性队列研究中发现:AKI组、非AKI组和对照组新生儿出生时脐血、生后24 h脐带血人和肽素、Scr水平均无变化,而AKI组新生儿NGAL水平较其他2组升高,提示NGAL具有高度特异性,即使对于亚临床型AKI患者NGAL水平也是一种有价值的标志物。HANNAD等[12]在对早产儿的病例对照研究中发现:使用尿生物学标志物诊断新生儿AKI较目前基于Scr水平的判断可提前24 h。
本研究结果显示:2组早产儿生后各时间点尿NGAL水平比较差异有统计学意义;AKI组早产儿生后24 h尿NGAL水平升高,72 h达最高峰值,72 h后呈下降趋势;非AKI组早产儿生后24和48 h尿NGAL水平轻度升高,48 h后变化不明显;AKI组早产儿在生后24、48、72和120 h NGAL水平均高于非AKI组。因NGAL在泌尿系统主要表达于肾脏近曲小管上皮细胞,而肾小球及肾单位的其他部分尚未见表达,提示NGAL与肾小管关系密切。在正常生理情况下,NGAL水平非常低,主要刺激肾祖细胞向肾小管上皮细胞分化,以维持肾脏正常的生长发育。当肾缺氧缺血或毒素导致急性肾小管损伤时,NGAL被诱导呈高表达[13], 能直接从尿液中检测出来。KAMIANOWSKA等[14]首次证实:宫内发育迟缓(IUGR)的小于胎龄儿尿NGAL水平及NGAL/Cr比值高于正常妊娠的适龄胎龄儿,这可能提示IUGR新生儿存在亚临床肾损伤。SONG等[15]比较了窒息早产儿生后不同时间尿NGAL、KIM-1、Cys-C与Scr水平的变化,发现尿NGAL水平升高先于血Scr,且NGAL水平升高程度明显高于同时间的KIM-1与Cys-C水平,提示NGAL较其他标志物能更有效地诊断早产儿AKI。本研究中2组患儿生后24 h时Scr水平比较差异无统计学意义,而尿NGAL水平明显升高,提示在AKI诊断中NGAL较Scr更敏感,可作为早产儿AKI早期的诊断指标,这与DAVID等[16]和BAUMERT等[17]研究结果相似。
本研究中ROC曲线检测结果显示:生后24 h时尿NGAL的临界值为6.95 ng·dL-1时,诊断AKI的敏感性和特异性分别为0.900和0.736;生后48 h时尿NGAL的临界值为6.95 ng·dL-1时,诊断AKI的敏感性和特异性分别为1.000和0.873,诊断价值均高于同期Scr水平。这与已有研究[18-20]的结果相似。这种细微的差别可能来自于研究的人群、纳入对象的数量及其他影响尿NGAL的因素(如肾毒性药物、脓毒症等)不同有关。
综上所述,尿NGAL作为有代表性的生物标记物,可以高效预测早产儿AKI。尿NGAL检测取材方便,对早产儿无创伤,与Scr比较,尿NGAL能更早地预测早产儿AKI,但该结论需大样本和多中心研究结果进行证实。
| [1] | 刘梦婕, 蒋洪敏. 血清中性粒细胞明胶酶相关性脂质运载蛋白在健康成年人中的参考值范围调查[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2014, 35(6): 689–652. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2014.06.015 |
| [2] | 赵琦, 黄松, 叶辉, 等. 儿童血浆和尿液中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白正常参考值的建立[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2017, 38(8): 1032–1037. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2017.08.008 |
| [3] | SELEWSK D T, COMELL T T, HEUNG M, et al. Validation of the KDIGO acute kidney injury criteria in a pediatric critical care population[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2014, 40(10): 1481–1488. DOI:10.1007/s00134-014-3391-8 |
| [4] | DAVID T S, JENNIFER R C, JENNIFER G J, et al. Neonatal acute kidney injury[J]. Pediatrics, 2015, 136(2): 463–473. DOI:10.1542/peds.2014-3819 |
| [5] | CANETE P, FERNANDEZ A, SOLIS A, et al. Incidence and prognosis of acute kidney injury after cardiac arrest in children[J]. Nephron, 2019, 141(1): 18–23. DOI:10.1159/000493471 |
| [6] | SHALABY M A, SAWAN Z A, NAWAWI E, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of neonatal acute kidney injury:a prospective cohort study[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2018, 33(9): 1617–1624. DOI:10.1007/s00467-018-3966-7 |
| [7] | MINA H, PATRIC D B, PETER J G, et al. Early urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in preterm infants[J]. Pediat Res, 2016, 80: 218–223. DOI:10.1038/pr.2016.70 |
| [8] | CHO M H, KANG H G. Acute kindey injury ang continuous renal replacement therapy in children:what pediatricians need to know[J]. Korean J Pediatr, 2018, 61(11): 339–347. DOI:10.3345/kjp.2018.06996 |
| [9] | NADA A, BONACHEA E M, ASKENAZI D J. Acute kidney injury in the fetus and neonate[J]. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017, 22(2): 90–97. DOI:10.1016/j.siny.2016.12.001 |
| [10] | TANG R, AO X, ZHONG Y, et al. Values of combination of urinary L-FABP and NGAL in early diagnosis of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in children[J]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi, 2017, 19(7): 770–775. |
| [11] | BAUMERT M, SURMIAK P, WIECEK A, et al. Serum NGAL and copeptin levels as predictors of acute kidney injury in asphyxiated neonates[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2017, 21(4): 658–664. DOI:10.1007/s10157-016-1320-6 |
| [12] | HANNA M, BROPHY P D, GIANNONE P J, et al. Early urinay biomarkers of acute kidney injury in preterm infants[J]. Pediat Res, 2016, 80(2): 218–223. DOI:10.1038/pr.2016.70 |
| [13] | 刘颖, 柳云恩, 刘学磊, 等. 创伤性休克对兔肾组织不同时相NGAL、Kim-1与HSP70表达影响[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学, 2017, 5(1): 13–17. |
| [14] | KAMIANOWSKA M, SZCZEPANSKI M, KULIKOWSKA E E, et al. The tubular damage markers:neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 in newborns with intrauterine growth restriction[J]. Neonatology, 2018, 115(2): 169–174. |
| [15] | SONG Y, SUN S Z, YU Y H, et al. Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for renal injury in asphyxiated preterm infants[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 13(4): 1245–1248. DOI:10.3892/etm.2017.4107 |
| [16] | DAVID J A, RAJESH K, NEHA P, et al. Acute kidney injury urine biomarkers in very low-birth-weight infants[J]. CJASN, 2016, 11(9): 1527–1535. DOI:10.2215/CJN.13381215 |
| [17] | BAUMERT M, SUMIAK P, WIEEK A, et al. Serum NGAL and copeptin levels as predictors of acute kidney injury in asphyxiated neonates[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2017, 21(4): 658–664. DOI:10.1007/s10157-016-1320-6 |
| [18] | PIOTR S, MABGORZATAB, Hunley H, et al. umbilical neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin level as an early predictor of acute kidney injury in neonates with hypoplastic left heart syndrom[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2015, 6(6): 1–6. |
| [19] | 佘萍莉, 刘丹, 王露, 等. 血和尿中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白在早期诊断新生儿急性肾损伤中的价值[J]. 广东医学, 2016, 37(13): 1979–1981. |
| [20] | KARI J A, SHALABY M A, SOFYANI K, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and serum cystatin C measurements for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in children admitted to PICU[J]. World J Pediatr, 2018, 14(2): 134–142. DOI:10.1007/s12519-017-0110-x |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


