扩展功能
文章信息
- 姚红月, 刘新宇, 刘婉珠
- YAO Hongyue, LIU Xinyu, LIU Wanzhu
- 人参二醇组皂苷对四氯化碳所致大鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用及其机制
- Protective effect of panaxdiol on acute liver damage of rats induced by carbon tetrachloride and its mechanism
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(03): 479-483
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 479-483
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190303
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-08-23
2. 锦州医科大学药理学教研室, 辽宁 锦州 121001
2. Department of Pharmacology, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, China
近年来,病毒、酒精、高脂肪和长期服用药物等多种因素均是造成肝损伤(liver damage,LD)和肝硬化的重要原因,目前肝脏疾病的发生率呈现升高趋势[1-2],因此有关急性和慢性肝脏疾病的研究成为近年的热点和前沿。上述这些因素均会造成患者急性肝功能损伤(acute liver damage,ALD),也是造成急性肝功能衰竭(acute heptic failure, AHF)的主要诱因,甚至可诱发肝部肿瘤的发生[3-4]。目前,AHF治疗难度较大,患者的病死率较高,预后极差,到目前为止仍无疗效确切的、安全可靠的治疗药物[5-6]。人参二醇皂苷(panoxadiol saponins,PDS)对急性重症胰腺炎大鼠多脏器具有保护作用,对感染性休克患者具有治疗和保护作用,PDS还具有抗氧化和抗疲劳等作用。蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B, PKB)又称AKT,是细胞增殖、转录和迁移过程中起重要作用的一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸特性蛋白激酶,在肝脏疾病的发生发展中起重要作用。新近的研究[7-8]也显示:PDS对ALD有治疗作用。为了更好地研究AHF的治疗方法,本实验通过腹腔内注射化学药物四氯化碳(carbon tetrachloride,CCl4)制备大鼠ALD模型,给予待测传统中药PDS,观察其对ALD模型大鼠的保护作用,并对其相关炎症机制进行深入研究。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物、主要试剂和仪器50只SD大鼠,体质量180~220 g,动物合格证号:SCXK(辽) 2007-0009。PDS提取物,本品为淡黄色提取物,经高效液相色谱(HPLC,上海精密仪器仪表公司)测定,纯度达到90%以上,由锦州医学大学实验室自行提纯;白细胞介素12(IL-12)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)均购自BOSTER博士德生物制剂有限公司。全自动血生化分析仪(德国罗氏公司ReflotronPlus快速分析仪),酶标仪(美国Becton dickinson公司)。
1.2 动物分组和处理受试SD大鼠随机分为5组,每组10只,包括对照组,模型组,低、中和高剂量PDS组。除对照组外,其余各组大鼠分别给予60% CCl4橄榄油剂3 mL·kg-1,隔日腹腔注射,共注射3次;对照组大鼠腹腔注射等体积橄榄油[9-10]。制备ALD模型后,对照组和模型组大鼠每日灌胃给予等体积生理盐水,各剂量PDS组大鼠灌胃给予不同剂量(10、20和40 mg·kg-1)PDS,给药时程为2周。
1.3 各组大鼠一般状态的观察给药期间记录各组大鼠外观体征和行为活动,皮毛是否贴身或是否出现稀疏竖散,记录各组大鼠食量、体质量和死亡率。待2周给药结束后,将各组大鼠处死,肉眼观察给药后大鼠的肝脏颜色、大小、光滑度和肝组织韧性。
1.4 各组大鼠肝功能指标的测定末次给药24 h后,采用20%乌拉坦全麻各组大鼠,经颈动脉取血2 mL,采用全自动血生化分析仪测定肝功能指标,包括谷氨酸氨基转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase, AST)、总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)和总蛋白(total protein,TP)。
1.5 各组大鼠肝组织匀浆中IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α水平测定取各组大鼠一部分肝脏,制备肝组织匀浆,采用ELISA法于酶标仪530 nm波长处测定吸光度(A)值,半定量法检测各组大鼠各炎症因子的水平,包括IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α水平。
1.6 Western blotting法测定各组大鼠肝组织中AKT和磷酸化蛋白激酶B(p-AKT)蛋白相对表达水平采用AKT测定试剂盒,按照试剂盒说明书于96孔板内进行梯度加样,制备分离胶与浓缩胶,采用Bio-Rad电泳仪进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,采用湿法转膜。分别加入AKT、p-AKT和β-actin,ECL试剂法显色。采用Image Quant LAS 4000凝胶成像系统获得扫描图像后Image J软件分析条带灰度值,计算蛋白相对表达水平。蛋白相对表达水平=各组蛋白灰度值/β-actin灰度值。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行统计学分析。各组大鼠肝功能指标(ALT、AST、TBIL和TP),肝组织匀浆中IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α水平以及各组大鼠肝组织中AKT和p-AKT蛋白相对表达水平均以x±s表示。两组样本均数比较采用独立样本t检验,多组样本均数比较采用单因素方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组大鼠一般状态在给药期间,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠活动较少,食量明显减少,体质量呈进行性降低,无抵抗力,尿黄,可见皮肤、黏膜出血,多数大鼠出现腹水。实验结束后,剖取大鼠肝脏大体观察:模型组大鼠肝组织表面粗糙,腹膜粘连,且大鼠肝脏肿大或缩小明显,色黄、易出血。与模型组比较,各剂量PDS组大鼠上述症状明显减轻,损伤情况较轻微。
2.2 各组大鼠肝功能指标与对照组比较,模型组和各剂量PND组大鼠肝功能指标中ALT、AST和TBIL水平明显升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,各剂量PDS组大鼠上述指标明显降低(P < 0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠TP水平明显降低(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,各剂量PDS组大鼠TP水平明显升高(P < 0.01)。见表 1。
| (n=10, x±s) | ||||
| Group | ALT [λB/(IU·L-1)] | AST [λB/(IU·L-1] | TBIL [cB/(μmol·L-1)] | TP [ρB/(g·L-1)] |
| Control | 46.4±12.1 | 63.1±19.4 | 1.63±0.27 | 67.31±7.17 |
| Model | 179.9±11.0* | 203.6±22.5* | 3.63±0.55* | 31.15±2.35* |
| PDS | ||||
| Low dose | 116.6±11.8*△ | 132.9±17.7*△ | 2.51±0.44*△ | 52.00±3.96*△ |
| Middle dose | 103.1±16.9*△ | 120.8±17.1*△ | 1.53±0.31*△ | 58.20±2.70*△ |
| High dose | 99.7±10.2*△ | 121.6±6.9*△ | 1.57±0.12*△ | 61.40±3.70*△ |
| *P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.01 compared with model group. | ||||
与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织匀浆中IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α水平明显升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,各剂量PDS组大鼠上述炎症因子水平明显降低(P < 0.01)。见表 2。
| [n=10, x ±s, ρB/(μg·L-1)] | |||
| Group | IL-12 | IL-6 | TNF-α |
| Control | 7.25±1.68 | 3.96±0.51 | 3.06±0.74 |
| Model | 15.43±3.29* | 6.57±1.24* | 5.39±0.25* |
| PDS | |||
| Low dose | 13.69±2.17△ | 5.17±0.15△ | 4.48±0.28△ |
| Middle dose | 10.61±2.78△ | 4.73±0.48△ | 4.57±0.61△ |
| High dose | 11.37±1.24△ | 4.21±0.64△ | 3.90±0.87△ |
| * P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.01 compared with model group. | |||
与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织中AKT蛋白表达水平明显升高(P < 0.01),而p-AKT蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,各剂量PDS组大鼠肝组织中AKT蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.01),p-AKT蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.01)。见图 1和2。
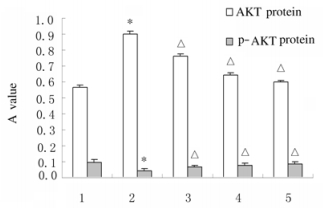
|
| *P < 0.01 compared with control group; △P < 0.01 compared with model group; 1:Control group; 2:Model group; 3:Low dose of PDS group; 4:Middle dose of PDS group; 5:High dose of PND group. 图 1 各组大鼠肝组织中AKT及p-AKT蛋白相对表达水平 Fig. 1 Relative expression levels of AKT and p-AKT proteins in liver tissue of rats in various groups |
|
|
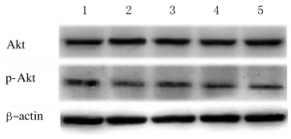
|
| Lane 1:Control group; Lane 2:Model group; Lane 3: Low dose of PDS group; Lane 4: Middle dose of PDS group; Lane 5: High dose of PDS group. 图 2 各组大鼠肝组织中AKT和p-AKT蛋白表达电泳图 Fig. 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of AKT and p-AKT proteins in liver tissue of rats in various groups |
|
|
目前ALD治疗难度大[11],传统中药治疗ALD越来越受到广泛重视。研究[12]显示:该实验中的待测药物PDS对LD有较好的治疗并逆转LD的作用[12]。PDS是人参中的主要活性成分,具有良好的抗氧化、增强免疫力和抗内毒素等多种药理学作用[13]。研究[14]表明:PDS能抑制肿瘤的浸润与转移,是主要的抗癌活性产物。研究[15]显示PDS对梗阻性黄疸(obstructive jaundice,OBJ)造成的ALD具有明显的保护作用。本研究结果显示:PDS处理后ALD大鼠一般状态明显改善,大鼠LD症状明显改善,提示PDS对LD有治疗作用。研究[16]显示:PDS对OBJ大鼠的LD具有保护作用,可改善大鼠肝脏组织病理损伤。
本研究结果显示:PDS能明显减轻CCl4引起的肝脏损害作用,降低ALT和AST水平,升高TP水平,另外也可以通过降低肝组织中炎症介质IL-12、IL-6及TNF-α水平,发挥其保护作用。研究[17]显示:IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α参与了多种炎症反应及随后的炎症级联放大过程,可上调肝脏细胞表面炎症成分和炎症效应,引起相关炎症反应的发生,最终可能诱发AHF。本研究中,各剂量PDS均能明显降低上述炎症因子水平,提示PDS在肝脏疾病中发挥治疗及保护作用。研究[18]显示:PDS对OBJ大鼠LD的保护作用是通过降低氧自由基和炎症因子水平而实现的。XIAO等[19]发现:PDS抗大鼠急性重症胰腺炎中肝脏损伤是通过影响核因子κB(NF-κB)而实现的。研究[20]显示:PDS具有与地塞米松类似的抗炎作用,可通过抑制NF-κB信号通路的活化,进而减少TNF-α和IL-6的产生,上述实验结果在本实验中得到了进一步验证。给予PDS治疗后,大鼠炎症因子IL-12、IL-6和TNF-α水平均降低。本研究结果显示:与对照组比较,PDS组大鼠肝脏组织中AKT蛋白表达水平降低。AKT是一种丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶,在多种细胞和组织的生理以及病理活动中发挥作用,并且可能在肝脏疾病和肝肿瘤中呈高表达[21]。研究[22-23]显示:PDS具有抑制内毒素休克大鼠IL-18表达的作用,进而抑制内毒素诱导的PKB信号转导通路的激活。本研究结果显示:PDS可能通过抑制炎症因子表达,继而影响p-AKT-AKT信号通路蛋白表达,在治疗及预防肝脏疾病中发挥重要作用。
综上所述,PDS具有明显的肝保护作用,该作用可能通过其下调多种炎症因子水平,继而通过影响p-AKT-AKT信号通路发挥其治疗和保护作用。PDS将有可能成为一种较理想的肝病治疗药物。
| [1] | 任仲喜, 王中义, 王贵民, 等. 人参二醇皂苷对大鼠急性重症胰腺炎多脏器损伤时NF-κB的影响[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2011, 15(1): 30–32. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2011.01.010 |
| [2] | YU H S, ZHANG L J, SONG X B, et al. Chemical constituents from processed rhizomes of panax notoginseng[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2013, 38(22): 3910–3917. |
| [3] | EL-AGAMY D S, ALMARAMHY H H, AHMED N, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of vardenafil against cholestatic liver damage in mice:a Mechanistic Study[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 47(2): 523–534. DOI:10.1159/000489986 |
| [4] | SHAH M D, D'SOUZA U J A, IQBAL M. The potential protective effect of Commelina nudiflora L. against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats, mediated by suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Environ Health Prev Med, 2017, 22(1): 66. DOI:10.1186/s12199-017-0673-0 |
| [5] | HE J, BAI K, HONG B, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 53(12): 56–62. |
| [6] | CHEN J, SUN X, XIA T, et al. Pretreatment with dihydroquercetin, a dietary flavonoid, protected against concanavalin A-induced immunological hepatic injury in mice and TNF-α/ActD-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells[J]. Food Funct, 2018, 9(4): 2341–2352. DOI:10.1039/C7FO01073G |
| [7] | BACHMANN M, PFEILSCHIFTER J, MÜHL H. A prominent role of Interleukin-18 in acetaminophen-induced liver injury advocates its blockage for therapy of hepatic necroinflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9(2): 161. |
| [8] | YANG C, LI L, MA Z, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of methyl ferulic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(3): 2228–2238. |
| [9] | 覃俊媛, 谢晓芳, 杨雪, 等. 2个产地赶黄草对四氯化碳致大鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中成药, 2018, 40(7): 1592–1594. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2018.07.031 |
| [10] | 隋菱, 郑静彬, 蔡国弟, 等. 姜黄素对四氯化碳诱导大鼠急性肝损害的保护作用[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2017, 34(11): 1517–1521. |
| [11] | TANG J, HU P, LI Y, et al. Ion imbalance is involved in the mechanisms of liver oxidative damage in rats exposed to glyphosate[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 19(8): 1083. |
| [12] | ALDABA-MURUATO L R, MUÑOZ-ORTEAG M H, MACIAS-PÉREZ JR, et al. Adrenergic regulation during acute hepatic infection with Entamoeba histolytica in the hamster:involvement of oxidative stress, Nrf2 and NF-KappaB[J]. Parasite, 2017, 24: 46. DOI:10.1051/parasite/2017048 |
| [13] | WANG W W, ZHANG Y, HUANG X B, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation prevents hepatic encephalopathy in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic dysfunction[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(38): 6983–6994. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6983 |
| [14] | GIL-FARINA I, DI SCALA M, SALIDO E, et al. Transient expression of transgenic IL-12 in mouse liver triggers unremitting inflammation mimicking human autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Immunol, 2016, 197(6): 2145–2156. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.1600228 |
| [15] | LIAO C C, DAY Y J, LEE H C, et al. Baicalin attenuates IL-17-mediated acetaminophen-induced liver injury in a mouse model[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0166856. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0166856 |
| [16] | LI S Q, ZHU S, HAN H M, et al. IL-6 trans-signaling plays important protective roles in acute liver injury induced by acetaminophen in mice[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2015, 29(6): 288–297. DOI:10.1002/jbt.2015.29.issue-6 |
| [17] | HUBER Y, GEHRKE N, BIEDENBACH J, et al. Voluntary distance running prevents TNF-mediated liver injury in mice through alterations of the intrahepatic immune milieu[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(6): e2893. DOI:10.1038/cddis.2017.266 |
| [18] | YAN B, CHEN Z H, ZHAI X G, et al. Microbial carbonylation and hydroxylation of 20(R)-panaxadiol by Aspergillus niger[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2018, 32(7): 782–787. |
| [19] | XIAO Q, YE Q F, WANG W, et al. Mild hypothermia pretreatment protects against liver ischemia reperfusion injury via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(5): 7520–7526. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7501 |
| [20] | XU S Z, WU L W, ZHANG Q H, et al. Pretreatment with propylene glycol alginate sodium sulfate ameliorated concanavalin A-induced liver injury by regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in mice[J]. Life Sci, 2017, 15(185): 103–113. |
| [21] | ZHANG Y, WEI Z K, LIU W J, et al. Melatonin protects against arsenic trioxide-induced liver injury by the upregulation of Nrf2 expression through the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(3): 3773–3780. |
| [22] | LI Y, TONG L Q, ZHANG J Y, et al. Galangin alleviates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model by mediating the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(3): 1354–1363. DOI:10.1159/000495553 |
| [23] | 张欣, 王文俊, 翟嵩, 等. 模式识别分子Mindin蛋白在CCl4诱导急性肝损伤小鼠模型中的表达[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(2): 368–371. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.025 |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


