扩展功能
文章信息
- 商琰红, 潘禹辰, 贾志芳, 王玥琦, 杨娜, 赵丹, 姜晶
- SHANG Yanhong, PAN Yuchen, JIA Zhifang, WANG Yueqi, YANG Na, ZHAO Dan, JIANG Jing
- miR200家族在乳腺癌患者血浆中表达水平的检测及其临床意义
- Detection of expression levels of miR200 family in plasma of breast cancer patients and its significance
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(02): 383-388
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 383-388
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190229
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-05-30
2. 吉林大学第一医院临床研究部, 吉林 长春 130021
2. Department of Clinical Research, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤[1-2],2015年中国乳腺癌的新发人数占女性全部恶性肿瘤发病的15%[3]。乳腺癌的早期诊断和早期治疗可延长患者的生存时间,提高生活质量。微小RNAs(microRNAs,miRNAs)是由18~25个核苷酸组成的一类非编码RNA。microRNA200(miR200)家族包括miR200a、miR200b、miR200c、miR141和miR429 5个成员,与多种恶性肿瘤的进展和预后有关[4-8],有可能作为肿瘤治疗的靶点和预后预测的工具。JIA等[9]研究显示乳腺癌细胞中的miR200a可能作为乳腺癌诊断的生物学指标。石峰等[10]发现:乳腺癌组织中miR200b和miR200c水平明显下降,认为其可能参与了乳腺癌的侵袭和转移过程。miR200在外周血中也有表达,但关于其在外周循环中的表达水平与肿瘤关系的研究报道较少。本研究主要测定miR200在乳腺癌患者和正常人外周血中的表达情况,探讨其在乳腺癌诊断、进展和预后预测中的价值。
1 资料与方法 1.1 研究对象选取2009年11月—2012年11月在河北大学附属医院确诊为乳腺癌患者82例(乳腺癌组),纳入标准为患者需行乳腺癌切除手术,术前未接受放化疗,术后病理诊断为浸润性乳腺癌。收集患者的一般信息、病理诊断和治疗信息。选取同时期于同一医院体检中心进行体检的无乳腺疾病的女性30人为对照组,对照受试对象与乳腺癌组乳腺癌患者年龄分布匹配(±5岁)。所有受试对象均签署知情同意书后纳入研究。本研究方案经河北大学附属医院伦理委员会批准。乳腺癌患者由专业随访员在患者术后第6个月、1年及之后通过电话等方式进行随访,收集患者术后治疗、复发和生存状态等信息。观察终点为乳腺癌引起的死亡。生存时间定义为从手术日期至死亡日期(如果患者死于乳腺癌),或至末次随访日期(如果患者尚存活),或至上一次随访日期(如果失访)之间的时间。截止到2017年8月,共随访74例患者,8例患者失访。
1.2 miRNAs提取和定量收集乳腺癌患者术前和对照组受试对象的EDTA抗凝血,离心后分离血浆于-80℃超低温冰箱中储存备用。采用microRNA提取试剂盒提取血浆样本的miRNAs(miRNeasy Serum/Plasma Kit,德国Qiagen公司)。逆转录合成cDNA(miScript Ⅱ RT Kit,德国Qiagen公司),实时荧光PCR反应监测所有样本中miR200家族成员miR200a、miR200b、miR200c、miR141和miR429的相对表达水平(SYBR GreenPCR Kit,德国Qiagen公司)。考虑到外周血中miRNA的表达水平变异较大,常规用于组织中miRNA表达定量的内参U6不适用于循环miRNAs的定量。因此,本研究采用外加参照方法,在miRNA提取过程中添加人类不表达的线虫微小RNA cel-39,作为miRNA提取、逆转录和定量过程的参照。以上所有miRNAs的引物均购自德国Qiagen公司,所有实验的反应体系、反应条件和操作均按照说明书进行,每个反应重复3次。以ΔCt = Ct cel-39 - CtmiRNA表示血浆标本中miRNAs的相对表达水平,最终结果取3次重复的平均值。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS18.0统计软件进行统计学分析。计量资料如年龄和miR200家族表达水平以x±s表示,组间比较采用两独立样本t检验。计数资料如组织学分级、TNM分期等用N(%)来表示。采用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线评价各血浆miRNAs的诊断价值。采用Cox风险比例模型调整相关影响因素进行生存分析。所有检验均为双侧检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 研究对象的一般特征本研究共纳入乳腺癌患者82例,正常健康对照者30名,全部为女性。乳腺癌组患者平均年龄为(52.27±10.44)岁,对照组受试对象平均年龄为(52.57±9.77)岁。乳腺癌患者TNM分期以Ⅱ期为主(48.8%),其次分别为Ⅰ期(36.6%)、Ⅲ期(12.2%)和Ⅳ期(2.4%);66.7%的患者组织学分级为Ⅱ级,31.9%为Ⅲ级,1.4%为Ⅰ级;雌激素受体(estrogen receptor, ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor, PR)和人表皮生长因子受体2(Her-2)为阳性的患者分别占76.8%、68.3%和25.6%。肿瘤类型以导管腺癌为主(93.5%)。93.7%的患者在术后接受了综合治疗。见表 1。
| Characteristic | Value |
| Age (year) | 52.27±10.44 |
| Histological grading | |
| Ⅰ | 1(1.4%) |
| Ⅱ | 48(66.7%) |
| Ⅲ | 23(31.9%) |
| ER | |
| Positive | 63(76.8%) |
| Negative | 19(23.2%) |
| PR | |
| Positive | 56(68.3%) |
| Negative | 26(31.7%) |
| Her-2 | |
| Positive | 21(25.6%) |
| Negative | 61(74.4%) |
| Triple-negative | |
| Positive | 8(9.8%) |
| Negative | 74(90.2%) |
| Tumor type | |
| Ductal adenocarcinoma | 77(93.9%) |
| Other | 5(6.1%) |
| Surgical procedure | |
| Modified radical mastectomy | 67(81.7%) |
| Other | 15(18.3%) |
| Depth of invasion | |
| T1 | 42(51.2%) |
| T2 | 38(46.3%) |
| T3 | 2(2.4%) |
| Lymph node metastasis | |
| N0 | 49(59.8%) |
| N1 | 22(26.8%) |
| N2 | 4(4.9%) |
| N3 | 7(8.5%) |
| Distant metastasis | |
| M0 | 80(97.6%) |
| M1 | 2(2.4%) |
| TNM stage | |
| Ⅰ | 30(36.6%) |
| Ⅱ | 40(48.8%) |
| Ⅲ | 10(12.2%) |
| Ⅳ | 2(2.4%) |
| Postoperative treatment | |
| Yes | 76(93.7%) |
| No | 6(6.3%) |
乳腺癌组与对照组血浆中miR200家族表达水平见表 2。乳腺癌组患者血浆中miR200b表达水平低于对照组(-5.60±2.27 vs -4.30±1.91,P=0.006),乳腺癌组患者血浆中miR141表达水平低于对照组(-6.73±2.27 vs -5.11±1.56,P < 0.01),但miR200a、miR200c和miR429表达水平在乳腺癌组和对照组间比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.268,P=0.075,P=0.872)。采用ROC曲线评价miR200b和miR141对乳腺癌的诊断价值,miR200b的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.685(P=0.003)。miR141的AUC为0.717(P < 0.01)。如果联用miR200b和miR141,AUC为0.735(P < 0.001)。见图 1。联用miR141和miR200b准确度增加幅度较小,可能由于miR200b和miR141有较强相关性(Pearson检验:r=0.605,P < 0.01)。
| (x±s) | ||||||
| Group | n | miR200a | miR200b | miR200c | miR141 | miR429 |
| Control | 30 | -5.89±1.93 | -4.30±1.91 | -4.02±1.79 | -5.11±1.56 | -7.52±2.66 |
| Breast cancer | 82 | -6.40±2.23 | -5.60±2.27* | -4.98±2.71 | -6.73±2.27* | -7.41±3.32 |
| *P < 0.01 compared with control group. | ||||||
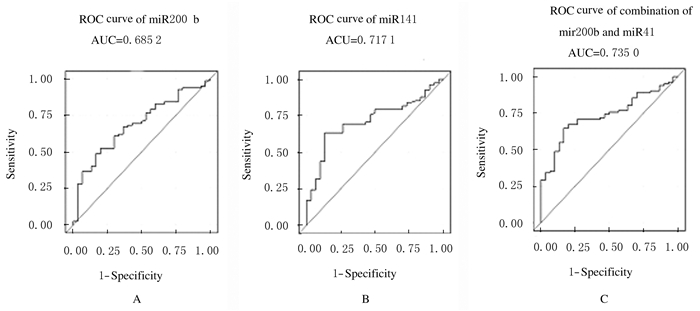
|
| A:MiR200b; B:miR141; C:Combination use of miR200b and miR141. 图 1 miR200b和miR141的ROC曲线 Fig. 1 ROC curves of miR200b and miR141 |
|
|
乳腺癌患者血浆中miR141表达水平随着TNM分期升高而降低(TNM Ⅰ-Ⅱ期:-6.53±2.17;TNM Ⅲ-Ⅳ期:-7.89±2.56),但差异无统计学意义(P=0.055)。乳腺癌患者血浆中miR200b和miR141表达水平与乳腺癌其他临床病理特征无关联(P>0.05)。见表 3。
| (x±s) | |||||||||
| Clinicopathological parameter |
MiR200b | MiR141 | |||||||
| Expressionlevel | t | P | Expressionlevel | t | P | ||||
| TNM stage |
Ⅰ-Ⅱ Ⅲ-Ⅳ |
70 12 |
-5.57±2.25 -5.78±2.44 |
0.09 | 0.769 | -6.53±2.17 -7.89±2.56 |
3.81 | 0.055 | |
| Histological grading |
Ⅰ-Ⅱ Ⅲ |
49 23 |
-5.81±2.24 -4.81±1.97 |
3.34 | 0.072 | -6.78±2.38 -6.66±2.37 |
0.04 | 0.846 | |
| ER | Positive Negative |
63 19 | -5.45±2.24 -6.10±2.33 |
1.19 | 0.278 | -6.59±2.36 -7.20±1.94 |
1.05 | 0.308 | |
| PR | Positive Negative |
56 26 | -5.45±2.25 -5.98±2.32 |
0.95 | 0.332 | -6.65±2.31 -6.91±2.20 |
0.22 | 0.639 | |
| Her-2 | Positive Negative |
21 61 | -5.35±2.61 -5.69±2.15 |
0.35 | 0.555 | -6.73±2.13 -6.73±2.33 |
0.00 | 0.999 | |
| Tumor type |
Ductal adenocarcinoma Other |
77 5 |
-5.57±2.26 -6.05±2.54 |
0.45 | 0.652 | -6.74±2.30 -6.53±1.93 |
0.20 | 0.843 | |
| Vascular invasion* | Positive Negative |
32 44 |
-5.65±2.25 -5.63±2.38 |
0.00 | 0.968 | -6.82±2.56 -6.73±2.02 |
0.03 | 0.869 | |
| Neural invasion* |
Positive Negative |
20 56 |
-5.72±2.83 -5.61±2.12 |
0.03 | 0.859 | -6.47±2.27 -6.88±2.55 |
0.49 | 0.484 | |
| *:The data of vascular invasion and neural invasion were absent in pathological data of 6 patients.Therefore, the results of 76 patients were reported on the two indicators of vascular invasion and neural invasion. | |||||||||
截止2017年8月(中位随访时间为72.4个月),82例患者中有5例患者(6.1%)死于乳腺癌,8例患者失访,69例患者仍存活,5年生存率为96.1%。以中位数为界,将miR200家族5个成员的血浆表达水平分为低和高表达组,分析miR200家族表达水平与乳腺癌患者术后总生存期关系的结果显示:miR200家族的表达水平与乳腺癌患者术后总生存期无关联(P>0.05)。见表 4。
| microRNA | Classification1 | n | Death | 5-year survival rate | Log-rank P | HR (95%CI)2 |
| miR200a |
≤-6.13 >-6.13 |
41 41 |
3 2 |
94.6% 97.4% |
0.611 | 0.69(0.10-4.65) |
| miR200b |
≤-5.35 >-5.35 |
41 41 |
3 2 |
94.6% 97.4% |
0.551 | 0.58(0.09-3.72) |
| miR200c |
≤-4.78 >-4.78 |
41 41 |
3 2 |
94.6% 97.4% | 0.596 | 0.67(0.10-4.44) |
| miR141 |
≤-6.72 >-6.72 |
41 41 |
3 2 |
94.6% 97.4% |
0.549 | 0.65(0.09-4.30) |
| miR429 |
≤-7.00 >-7.00 |
41 41 |
2 3 |
94.4% 97.5% |
0.730 | 1.72(0.25-11.91) |
| 1:According to the median of expression level, the patients were divided into low expression group and high expression group;2:Hazard ratio(HR)was calculated after adjusted age, TNM stage, histological grading, vascular invasion, neural invasion, ER, PR and Her-2. | ||||||
在过去的20年里,全球范围内乳腺癌患者绝对数量上升了1.4倍,大多数国家和地区乳腺癌发病率升高了30%~40%[11]。在我国,乳腺癌发病率也明显升高[12]。虽然近几年在诊断技术和抗癌药物方面的研究进展迅猛,但是乳腺癌的早期诊断依然存在困难;乳腺癌患者若不能做到早期发现,将会失去手术特别是保乳手术的机会, 且辅助治疗效果相对较差, 常预后不佳。因此探索乳腺癌早期、无创诊断方法,将有助于延长患者的生存时间,改善生活质量。
2005年MISKA[13]发现:miRNAs参与细胞的分化、增殖和凋亡过程,在肿瘤的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用,miRNAs可作为潜在的生物标志物来评估肿瘤。miR200家族包括miR200a、miR200b、miR200c、miR141和miR4295个成员。研究[14-15]显示:miR200家族在肿瘤的发生发展过程中起抑癌基因作用,其通过抑制Suz12蛋白的形成、降低癌基因CDH1的水平、抑制肿瘤干细胞形成和干性维持而与肿瘤发生有关联。miR200家族也可通过抑制细胞周期相关基因如CDK6和PLCG1将细胞周期阻滞在G1期而影响肿瘤细胞的增殖[16]。同样,miR200家族通过作用于转录因子ZEB1和ZEB2,调节上皮细胞钙黏蛋白表达,影响上皮间质转化过程而抑制肿瘤的迁移和侵袭[17-18]。YE等[19]研究显示:miR200家族在乳腺癌组织中表达水平降低,且乳腺癌组织中表达水平较低者预后更差,乳腺癌组织中miR200的表达水平是乳腺癌预后的独立预测因素。
在循环miR200家族表达方面,ANTOLÍN等[20]对比了55例乳腺癌患者和20名对照者miR200家族表达水平发现:乳腺癌患者miR141表达水平明显降低。本研究结果显示:乳腺癌组患者血浆中miR141表达水平低于对照组,miR141用于乳腺癌诊断的AUC为0.717,与ANTOLÍN等[20]的研究结果相似。本研究结果显示:乳腺癌组患者血浆miR200b表达水平也降低,但是联用miR141和miR200b诊断乳腺癌时,AUC为0.735,准确度增加幅度较小,可能源于miR200b和miR141同作为miR200家族成员,表达有关联。
综上所述,miR200家族分子miR200b和miR141在乳腺癌患者血浆中表达水平下降,miR200b和miR141有可能作为生物学标志物用于乳腺癌的早期诊断。
| [1] | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(1): 5–29. DOI:10.3322/caac.21254 |
| [2] | ZUO T T, ZHENG R S, ZENG H M, et al. Female breast cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2017, 8(3): 214–218. DOI:10.1111/tca.2017.8.issue-3 |
| [3] | CHEN W, ZHENG R, BAADE P D, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115–132. DOI:10.3322/caac.21338 |
| [4] | VOLINIA S, GALASSO M, SANA M E, et al. Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(8): 3024–3029. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1200010109 |
| [5] | BLENKIRON C, GOLDSTEIN L D, THORNE N P, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of human breast cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype[J]. Genome Biol, 2007, 8(10): R214. DOI:10.1186/gb-2007-8-10-r214 |
| [6] | ZHENG R Z, LIU Y H, ZHANG X L, et al. miRNA-200c enhances radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer by cell cycle arrest and targeting P21[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 90: 517–523. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.006 |
| [7] | BHARDWAJ M, SEN S, CHOSDOL K, et al. MiRNA-200c and miRNA-141 as potential prognostic biomarkers and regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in eyelid sebaceous gland carcinoma[J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2017, 101(4): 536–542. DOI:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-309460 |
| [8] | KNUDSEN K N, LINDEBJERG J, NIELSEN B S, et al. MicroRNA-200b is downregulated in colon cancer budding cells[J]. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12(5): e0178564. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0178564 |
| [9] | MING J, ZHOU Y, DU J Z, et al. Identification of miR-200a as a novel suppressor of connexin 43 in breast cancer cells[J]. Biosci Rep, 2015, 35(5): e00251. DOI:10.1042/BSR20150153 |
| [10] | 石峰, 闫凤彩, 宋清坤, 等. MiR-200b及miR-200c在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达及意义[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2017, 24(12): 926–929. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2017.12.010 |
| [11] | 郑莹, 吴春晓, 张敏璐. 乳腺癌在中国的流行状况和疾病特征[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2013, 23(8): 561–569. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2013.08.001 |
| [12] | 柏尚柱. 乳腺癌在中国的流行状况和疾病特征[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘:电子版, 2017, 17(41): 253, 256. |
| [13] | MISKA E A. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2005, 15(5): 563–568. DOI:10.1016/j.gde.2005.08.005 |
| [14] | ILIOPOULOS D, LINDAHL-ALLEN M, POLYTARCHOU C, et al. Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to Polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 39(5): 761–772. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.013 |
| [15] | LIM Y Y, WRIGHT J A, ATTEMA J L, et al. Epigenetic modulation of the miR-200 family is associated with transition to a breast cancer stem-cell-like state[J]. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 10): 2256–2266. |
| [16] | UHLMANN S, ZHANG J D, SCHWÄGER A, et al. miR-200bc/429 cluster targets PLCγ1 and differentially regulates proliferation and EGF-driven invasion than miR-200a/141 in breast cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(30): 4297–4306. DOI:10.1038/onc.2010.201 |
| [17] | WELLNER U, SCHUBERT J, BURK U C, et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2009, 11(12): 1487–1495. DOI:10.1038/ncb1998 |
| [18] | GREGORY P A, BERT A G, PATERSON E L, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2008, 10(5): 593–601. DOI:10.1038/ncb1722 |
| [19] | YE F, TANG H L, LIU Q, et al. MiR-200b as a prognostic factor in breast cancer targets multiple members of RAB family[J]. J Transl Med, 2014, 12(1): 1–10. DOI:10.1186/1479-5876-12-1 |
| [20] | ANTOLÍN S, CALVO L, BLANCO-CALVO M, et al. Circulating miR-200c and miR-141 and outcomes in patients with breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2015, 15: 297. DOI:10.1186/s12885-015-1238-5 |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


