扩展功能
文章信息
- 王东东, 张宇, 张伟琪, 丁振东, 于洪泉, 齐玲
- WANG Dongdong, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Weiqi, DING Zhendong, YU Hongquan, QI Ling
- SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白在人恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达及其意义
- Expressions of SENP1, SENP2 and SENP6 proteins in human glioma tissue and cells and their mechanisms
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(01): 73-76
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 73-76
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20190114
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-08-08
2. 吉林医药学院病理生理学教研室, 吉林 吉林 132013
2. Department of Pathophysiology, Jilin Medical University, Jilin 132013, China
蛋白翻译后修饰对蛋白功能的发挥起到了极为重要的调节作用[1]。目前研究[2-4]显示:小泛素样相关修饰蛋白(small ubiquitin-related modifier protein,SUMO)修饰作为蛋白质翻译后修饰的一种,与多种肿瘤的发生发展有密切关联。蛋白SUMO化与去SUMO化是一个动态可逆过程,SUMO化可能促进了人胶质瘤的发生[5],但去SUMO化在人胶质瘤组织和细胞中的作用尚不清楚。去SUMO化由SUMO特异性蛋白酶(SUMO-special proteases,SENPs)家族来完成。研究[6-9]表明:SENPs与膀胱癌、肝癌、前列腺癌和乳腺癌的发生有关。但SENPs在人胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达及作用鲜有报道。因此,本实验通过检测SENPs家族中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6在人恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达情况,初步探讨SENPs在人胶质瘤发生过程中的作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 组织标本和细胞人正常脑组织(正常对照组)和恶性胶质瘤组织(恶性胶质瘤组)均由吉林大学第一医院神经外科提供。正常对照组患者8例,年龄45~73岁,平均年龄50.7岁,包括脑外伤3例和脑出血5例,均于死亡24 h内尸解取正常脑组织;恶性胶质瘤组患者10例,年龄49~71岁,平均年龄51.3岁,病理诊断均为Ⅲ-Ⅳ级恶性胶质瘤[5, 10],其中Ⅲ级胶质瘤5例,Ⅳ级胶质瘤5例,均于术后取恶性胶质瘤组织。Cos7细胞(正常细胞对照组)、LN443细胞和U343细胞(恶性胶质瘤细胞组)由吉林大学基础医学院提供。
1.2 主要试剂和仪器SENP1和SENP2抗体购自美国IMGENEX公司,SENP6抗体购自美国ABGENT公司,BCA蛋白测定试剂盒和过硫酸铵购自美国Pierce公司。J-26XP超低温高速离心机购自美国贝克曼公司,超低温冰箱(MDF-U53V)购自日本三洋公司,PLUS 384全自动酶标仪购自美国MDC公司,DNA蛋白电泳系统购自美国Bio-Rad公司,Image-Pro Plus图像分析管理系统购自美国Media Cybernetics公司。
1.3 细胞培养将冻存的Cos7、LN443和U343细胞分别自液氮罐中取出,迅速置入37℃水浴中振荡5 min,离心后将细胞用含10%小牛血清的DMEM培养液或1640培养液混匀,分别置于25 cm2培养瓶中,37℃、5%CO2及饱和湿度下培养,隔日换液。倒置显微镜下观察细胞的形态表现。
1.4 Western blotting法检测组织标本和细胞中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白表达水平准备组织或细胞,冰上破碎后加入50 μL细胞裂解液(裂解液含20nmol·L-1蛋白抑制剂、20nmol·L-1NEM和1%PMSF),继续冰浴10 min,4℃、12000 g离心15 min,离心后弃沉淀,测定上清中样品的蛋白浓度,加入上样缓冲液,准备SDS-PAGE凝胶,上样跑胶分离样品,转膜后封闭1h,分别加入一抗SENP1、SENP2、SENP6和β-actin,4℃孵育过夜。次日二抗室温孵育1h,胶片曝光照相。结果采用Image-Pro Plus图像分析管理系统分析,以特异性条带平均吸光度(A)值与面积的乘积为有效值,代表蛋白表达水平。
1.5 统计学分析采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。组织标本和细胞中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白表达水平以x±s表示,两组间样本均数比较采用t检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白在不同组织中的表达水平与正常对照组比较,恶性胶质瘤组恶性胶质瘤组织中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P < 0.05)。见图 1和表 1。
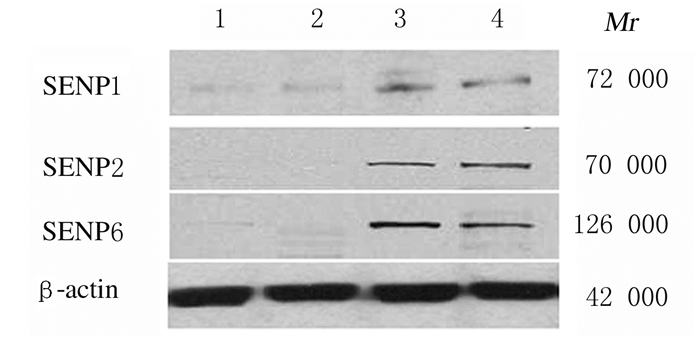
|
| Lane 1, 2: Normal control group; Lane 3, 4: Malignant glioma group. 图 1 SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白在正常脑组织和恶性胶质瘤组织中表达电泳图 Fig. 1 Electrophoregram of expressions of SENP1, SENP2 and SENP6 proteinsin normal brain tissue and malignant glioma tissue |
|
|
| Group | SENP1 | SENP2 | SENP6 |
| Normal control | 0.52±0.08 | 0.23±0.06 | 0.24±0.03 |
| Malignant glioma | 0.65±0.02* | 0.91±0.27* | 1.20±0.35* |
| *P < 0.05 vs normal control group. | |||
与正常细胞对照组比较,恶性胶质瘤细胞组LN443细胞和U343细胞中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P < 0.05)。见图 2和表 2。

|
| Lane 1: Cos 7 cells; Lane 2: LN443 cells; Lane 3: U343 cells. 图 2 SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白在正常细胞和恶性胶质瘤细胞中表达电泳图 Fig. 2 Electrophoregram of expressions ofSENP1, SENP2 and SENP6 proteinsin normal cells and malignant glioma cells |
|
|
| Group | SENP1 | SENP2 | SENP6 |
| Cos7 cells | 0.26±0.06 | 0.58±0.04 | 0.80±0.19 |
| Ln443 cells | 1.44±0.15* | 1.11±0.13* | 1.64±0.21* |
| U343 cells | 1.06±0.16* | 0.91±0.03* | 1.41±0.12* |
| *P < 0.05 vs Cos7 cells group. | |||
目前,对哺乳动物细胞SENPs家族的6个成员中SENP1的研究较多。有研究[11-12]表明:在前列腺癌形成过程中,SENP1mRNA和蛋白的表达水平均增加,SENP1可以通过调节基质金属蛋白酶2(MMP2)和基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP9)的表达来影响前列腺癌细胞的转移能力。而在结肠癌中,SENP1则可以通过调控低氧诱导因子1α(HIF-1α)/血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)途径来参与肿瘤血管的增生[13]。在肺癌组织中,SENP1可以下调γ-H2AX蛋白表达而促进DNA损伤[14]。也有研究[15]表明:SENP1通过调控MMP9对胰腺导管癌的转移和侵袭能力发挥着重要的作用。ZHANG等[16]发现:抑制胶质瘤细胞中SENP1的表达可以抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖,降低细胞的侵袭和转移能力。本实验同时检测了恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中SENP1蛋白的表达水平,结果表明:与正常对照组和正常细胞对照组比较,恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中SENP1蛋白的表达水平均明显升高。在胶质瘤细胞中的表达结果与ZHANG等[16]对胶质瘤细胞的研究结论一致,而在胶质瘤组织中的表达水平结果进一步验证了SENP1促进了胶质瘤的发生。因此,本研究在组织学和细胞学水平进一步验证了SENP1与胶质瘤发生的关系。
在蛋白的去SUMO化修饰过程中,SENP2也可能参与了肿瘤的形成过程。研究[17]显示:膀胱癌T24细胞稳定表达SENP2时,细胞的增殖、侵袭和转移能力均明显降低,而SENP2低表达则可引起MMP13活化,从而促进肿瘤细胞的迁移。当肝癌HepG2细胞和胃癌AGS细胞沉默SENP2表达时,反而促进了细胞的增殖及成瘤能力,深入研究[18-19]显示:SENP2通过介导NDRG2肿瘤抑制基因或调控Wnt/β-catenin信号转导途径来影响肿瘤的发生发展。虽然SENP2在肝癌、胃癌和膀胱癌中可能有抗肿瘤形成的作用,但本研究结果显示:SENP2在恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达均明显升高。有关神经退行性病变的研究[20]显示:SENP2表达下调或缺失会引起严重的神经功能障碍,而胶质瘤发生过程中会出现神经元功能的改变,这可能会引起SENP2的异常改变,从而导致SENP2的表达与其他肿瘤不一致。本研究结果显示:在胶质瘤的发生过程中SENP2可能起到了改变神经元功能的特殊作用,但其具体的作用机制还需要进一步的研究。
目前,SENP6在各种肿瘤发生中的作用还鲜有报道。研究[21]显示:SENP6在肝细胞癌HepG2细胞中高表达,沉默SENP6后如果用一定剂量的放射线作用于HepG2细胞,则可引起核因子κB(NF-κB)活化水平增加并激活NF-κB通路,进而促进HepG2细胞凋亡。本研究结果显示:SENP6在恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达水平均明显增加,提示SENP6可能对促进恶性胶质瘤的发生起到了重要的作用,但表达异常的SENP6调节恶性胶质瘤发生的具体机制尚不明确,仍需进一步深入研究。
综上所述,本研究检测了去SUMO化修饰蛋白SENPs家族成员SENP1、SENP2和SENP6在恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中的表达水平,结果显示:在恶性胶质瘤组织和细胞中SENP1、SENP2和SENP6蛋白表达水平均明显增加,提示SENP1、SENP2和SENP6可能对恶性胶质瘤的发生起到明显的促进作用。恶性胶质瘤发生时涉及了明显的蛋白SUMO化和去SUMO化,但究竟哪些蛋白发生了SUMO化或去SUMO化修饰改变,还需要更多的研究来进一步证明。
| [1] | PEEK J, HARVEY C, GRAY D, et al. SUMOtargeting of a stress-tolerant Ulp1 SUMO protease[J]. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(1): e0191391. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0191391 |
| [2] | LIU K, ZHANG J, WANG H. Small ubiquitin-like modifier/sentrin-specific peptidase 1 associates with chemotherapy and is a risk factor for poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2018, 32(9): e22611. DOI:10.1002/jcla.2018.32.issue-9 |
| [3] | DE ANDRADE J P, LORENZEN A W, WU V T, et al. Targeting the SUMO pathway as a novel treatment for anaplastic thyroid cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(70): 114801–114815. |
| [4] | YANG Y, XIA Z, WANG X, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting protein SUMOylation as novel anticancer compounds[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2018, 94(2): 885–894. |
| [5] | 齐玲, 王玮瑶, 郑中华, 等. SUMO及SUMO化修饰蛋白在恶性胶质瘤发生中的作用[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2016, 42(1): 7–10. |
| [6] | DONG B, GAO Y, KANG X, et al. SENP1 promotes proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through activation of glycolysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(49): 80435–80449. |
| [7] | JIN Z L, PEI H, XU Y H, et al. The SUMO-specific protease SENP5 controls DNA damage response and promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2016, 20(17): 3566–3573. |
| [8] | MIRECKA A, MORAWIEC Z, WOZNIAK K. Genetic polymorphism of SUMO-Specific cysteine proteases-SENP1 and SENP2 in breast cancer[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2016, 22(4): 817–823. DOI:10.1007/s12253-016-0064-7 |
| [9] | JIANG Q F, TIAN Y W, SHEN Q, et al. SENP2 regulated the stability of β-catenin through WWOX in hepatocellular carcinoma cell[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(10): 9677–9682. DOI:10.1007/s13277-014-2239-8 |
| [10] | 齐玲, 沈楠, 王玮瑶, 等. SENP蛋白在胶质瘤中表达与临床病理分级相关性[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2015, 31(9): 1219–1221. |
| [11] | WANG Q, XIA N, LI T, et al. SUMO-specific protease 1 promotes prostate cancer progression and metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(19): 2493–2498. DOI:10.1038/onc.2012.250 |
| [12] | CHENG J, BAWA T, LEE P, et al. Role of desumoylation in the development of prostate cancer[J]. Neoplasia, 2006, 8(8): 667–676. DOI:10.1593/neo.06445 |
| [13] | XU Y, ZUO Y, ZHANG H, et al. Induction of SENP1 in endothelial cells contributes to hypoxia-driven VEGF expression and angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285(47): 36682–36688. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M110.164236 |
| [14] | WANG R T, ZHI X Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Inhibition of SENP1 induces radiosensitization in lung cancer cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2013, 6(4): 1054–1058. DOI:10.3892/etm.2013.1259 |
| [15] | ZHANG Q S, ZHANG M, HUANG X J, et al. Downregulation of SENP1 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and promotes apoptosis in human glioma cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 12(1): 217–221. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.4558 |
| [16] | MA C, WU B, HUANG X, et al. SUMO-specific protease 1 regulates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting MMP-9[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(12): 12729–12735. DOI:10.1007/s13277-014-2598-1 |
| [17] | TAN M Y, MU X Y, LIU B, et al. SUMO-specific protease 2 suppresses cell migration and invasion through inhibiting the expression of MMP13 in bladder cancer cells[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2013, 32(3): 542–548. DOI:10.1159/000354458 |
| [18] | HU X Y, LIU Z, ZHANG K L, et al. SUMO-specific protease 2-mediated deSUMOylation is required for NDRG2 stabilization in gastric cancer cells[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2017, 21(1): 195–201. DOI:10.3233/CBM-170651 |
| [19] | SHEN H J, ZHU H Y, YANG C, et al. SENP2 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by modulating the stability of beta-catenin[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2012, 13(8): 3583–3587. DOI:10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.8.3583 |
| [20] | FU J, YU H M, CHIU S Y, et al. Disruption of SUMO-specific protease 2 induces mitochondria mediated neurodegeneration[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10(10): e1004579. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004579 |
| [21] | QIAN J, LUO Y, GU X, et al. Inhibition of SENP6-induced radiosensitization of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by blocking radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2013, 28(3): 196–200. DOI:10.1089/cbr.2012.1288 |
 2019, Vol. 45
2019, Vol. 45


