扩展功能
文章信息
- 于秀艳, 张晓伟, 丛占杰, 李铤, 吴雪峰
- YU Xiuyan, ZHANG Xiaowei, CONG Zhanjie, LI Ting, WU Xuefeng
- 乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平检测及其临床意义
- Detection of serum hMAM and CD147 levels of patients with breast cancer and its clinical significance
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(06): 1269-1274
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1269-1274
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180627
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-05-16
人乳腺珠蛋白(human mammaglobin,hMAM)是1996年研究者[1-2]在乳腺癌组织中发现的一种具有高特异性的分泌性球蛋白。国内外研究[3-7]表明:hMAM在乳腺癌患者诊断、治疗和预后中具有重要作用。本课题组前期研究[8-9]显示hMAM mRNA水平检测在诊断乳腺癌微转移中具有重要临床意义。CD147也称为基质金属蛋白酶诱惑因子(extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer,EMMPRIN),CD147通过刺激肿瘤周围纤维母细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs),MMPs可降解肿瘤细胞基底膜及间质,并与CD147形成复合物,使金属蛋白酶降解肿瘤间质的作用进一步加强,促进肿瘤细胞浸润及转移[10]。有关乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平联合检测的研究尚未见报道。本研究主要采用酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)检测乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平,分析其在乳腺癌诊断中的临床意义。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料选择2016年7月—2017年12月在本院乳腺治疗中心行手术治疗、术后经病理确诊的有完整病例的患者作为研究对象(乳腺癌组)。乳腺癌组122例患者均为女性,年龄33~71岁,中位年龄46岁。乳腺癌分子分型依据2013年StGallen乳腺癌会议国际专家共识。按照UICC 2003年制订的乳腺癌TNM分期标准:Ⅰ期24例,Ⅱ期33例,Ⅲ期46例,Ⅳ期19例;雌激素受体(restrogen receptor,ER)阳性79例,孕激素受体(progesterone receptor,PR)阳性76例,人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermalgrowth factor receptor-2,Her-2)阳性81例。同期搜集术后经病理确诊的乳腺纤维腺瘤患者(乳腺纤维腺瘤组)21例,均为女性,年龄28~69岁,中位年龄43岁;选择健康体检者(健康对照组)16人,均为女性,年龄21~75岁,中位年龄49岁,经胸片和B超检查未发现乳腺相关性疾病。乳腺癌组、乳腺纤维腺瘤组和健康对照组研究对象年龄等一般情况比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 纳入和排除标准纳入标准:纳入患者结合临床症状和体征,均经病理学确诊为乳腺癌,术前未接受过放、化疗或生物治疗等干预措施,均具有完整的病历资料。排除标准:排除存在严重心脏和肝肾疾病、自身免疫性疾病、严重并发症及长期嗜酒等情况患者。
1.3 主要试剂和仪器人CD147 ELISA试剂盒(武汉云克隆科技股份有限公司),hMAM ELISA试剂盒(武汉华美生物工程有限公司)。安图PHOMO型酶标仪和安图iWO-960型洗板机购自郑州安图生物工程有限公司。
1.4 标本采集所有研究对象均于术前清晨空腹抽取静脉血3 mL,室温静置30 min后3 500 r·min-1离心5 min,获取血清,-70℃保存待测。
1.5 ELISA法检测乳腺癌组、乳腺纤维腺瘤组和健康对照组研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147水平和阳性表达率血清标本均采用ELISA法测定,操作步骤严格按试剂盒说明书进行。在450 nm波长处测定吸光度(A)值,空白孔作为对照组。分析不同临床病理特征患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平和阳性表达率。hMAM联合CD147检测中任意一个指标阳性即为阳性表达,阳性表达率=阳性表达数/总表达数×100%,hMAM联合CD147检测阳性表达率= hMAM和(或)CD147阳性表达总数/总表达数×100%。
1.6 受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147水平诊断乳腺癌的价值ROC曲线分析研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147水平诊断乳腺癌的cut-off值,计算ROC曲线下面积(AUC)、敏感度和特异度。
1.7 统计学分析采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。各组研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147水平以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析;各组研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147阳性表达率比较采用χ2检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 各组研究对象血清中hMAM和CD147水平乳腺癌组患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平均高于健康对照组和乳腺纤维腺瘤组(P<0.05)。见表 1。
| [x±s,ρB/(μg·L-1)] | |||
| Group | n | hMAM | CD147 |
| Healthy control | 16 | 5.15±2.41 | 99.17±30.44 |
| Breast fibroadenoma | 21 | 4.67±2.33 | 94.01±21.06 |
| Breast cancer | 122 | 8.64±5.01*△ | 162.41±53.27*△ |
| * P < 0.05 vs healthy control group; △ P < 0.05 vs breast fibroadenoma group. | |||
乳腺癌组患者血清中hMAM和CD147阳性表达率高于健康对照组(χ2=15.275, P<0.01;χ2=13.748, P<0.01)和乳腺纤维腺瘤组(χ2=13.748, P<0.01;χ2=17.423, P<0.01),乳腺癌组患者血清中hMAM联合CD147检测阳性表达率高于健康对照组(χ2 =13.079, P<0.01)和乳腺纤维腺瘤组(χ2 = 26.347, P<0.01)。见表 2。
| [n(η/%)] | ||||
| Group | n | hMAM | CD147 | hMAM + CD147 |
| Healthy control | 16 | 1(6.25) | 3(18.75) | 3(18.75) |
| Breast fibroadenoma | 21 | 2(9.52) | 6(28.57) | 7(33.33) |
| Breast cancer | 122 | 75(61.48)*△ | 85(69.67)*△ | 103(84.43)*△ |
| * P < 0.05 vs healthy control group; △ P < 0.05 vs breast fibroadenoma group. | ||||
是否有淋巴结转移患者hMAM和CD147阳性表达率比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),不同年龄、肿瘤大小和PR情况患者血清中hMAM和CD147阳性表达率比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同表达分期、ER和Her-2情况患者血清中hMAM阳性表达率比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),而CD147阳性表达率比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随着分期增加,乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM和CD147阳性表达率均呈递增趋势。见表 3。
| [n(η/%)] | |||||
| Clinicopathological feature | n | hMAM | P | CD147 | P |
| Age(year) | |||||
| ≤ 50 | 48 | 31(64.58) | 32(68.75) | 0.570 | 0.858 |
| >50 | 74 | 44(59.46) | 52(70.27) | ||
| Tumor size(d/cm) | |||||
| ≤ 2 | 43 | 24(55.81) | 28(65.12) | 0.343 | 0.419 |
| >2 | 79 | 51(64.56) | 57(72.15) | ||
| TNM stage | |||||
| Ⅰ | 24 | 11(45.83) | 11(45.83) | 0.136 | 0.039 |
| Ⅱ | 33 | 18(54.55) | 21(63.64) | ||
| Ⅲ | 46 | 32(69.57) | 36(78.26) | ||
| Ⅳ | 19 | 14(73.68) | 17(89.47) | ||
| Lymphatic metastasis | |||||
| Yes | 69 | 51(73.91) | 58(84.06) | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| No | 53 | 24(45.28) | 27(50.94) | ||
| ER | |||||
| Negtive | 43 | 25(58.14) | 24(55.81) | 0.576 | 0.014 |
| Positive | 79 | 50(63.29) | 61(77.22) | ||
| PR | |||||
| Negtive | 46 | 27(58.70) | 33(71.74) | 0.624 | 0.699 |
| Positive | 76 | 48(63.16) | 52(67.42) | ||
| Her-2 | |||||
| Negtive | 41 | 24(58.54) | 23(56.10) | 0.635 | 0.020 |
| Positive | 81 | 51(62.96) | 62(76.54) | ||
hMAM的AUC为0.809,95% CI:0.703~0.916;CD147的AUC为0.721,95% CI:0.582~0.861。hMAM的cut-off值为6.51μg·L-1,筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为61.1%和87.5%;CD147的cut-off值为144.92 ng·L-1,筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为73.6%和68.7%。hMAM联合CD147的AUC为0.880,95% CI:0.798~0.962,筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为80.6%和81.2%。见图 1和表 4。
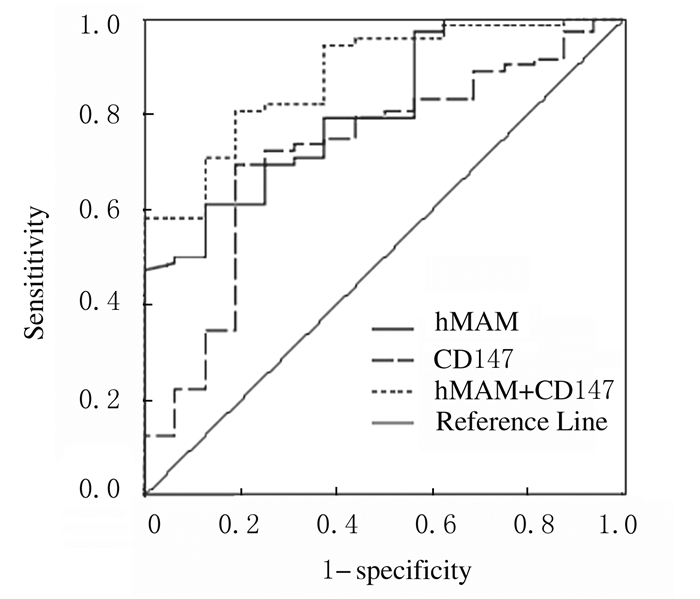
|
| 图 1 hMAM和CD147的ROC曲线 Figure 1 ROC curves of hMAM and CD147 |
|
|
| Marker | AUC | Sensitivity(η/%) | Specificity(η/%) | Cut-off value | 95% CI |
| hMAM | 0.809 | 61.1 | 87.5 | 6.51 | 0.703-0.916 |
| CD147 | 0.721 | 73.6 | 68.7 | 144.92 | 0.582-0.861 |
| hMAM+CD147 | 0.880 | 80.6 | 81.2 | - | 0.798-0.962 |
| “-”:No data. | |||||
hMAM在正常乳腺上皮组织中表达水平较低,而在乳腺癌组织中呈高表达,是乳腺癌特异的肿瘤标志物[4, 11],hMAM在其他肿瘤,如胃癌、卵巢癌、直肠癌和前列腺癌等组织中均不表达[12-14]。乳腺癌患者外周血中循环肿瘤细胞hMAM水平升高[15-16],hMAM阳性表达率也与乳腺癌骨髓转移和不良预后有关[17]。体外细胞实验[18-19]表明:对CD147基因进行干扰可以抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭,对CD147进行糖基化位点突变可以抑制肿瘤细胞增殖;Dimas等[20]进行Meta分析结果显示:CD147在乳腺癌患者预后中具有重要临床意义;Luz等[21]研究显示CD147作为乳腺癌诊断和预后标记物,具有较好的开发前景。
本研究采用ELISA法测定乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM和CD147水平结果显示:hMAM筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为61.1%和87.5%,提示hMAM对诊断乳腺癌具有高特异性[4];CD147筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为73.6%和68.7%,二者联合筛查乳腺癌敏感度和特异度分别为80.6%和81.2%。田英等[22]研究显示:不同淋巴结转移和肿瘤大小乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM水平比较差异均有统计学意义,不同年龄、月经状况、组织学分级、ER、PR、Her-2、P53、Ki-67和分子分型患者血清中hMAM水平比较差异无统计学意义;杨超等[23]发现:有腋窝淋巴结转移的乳腺癌患者血清hMAM阳性表达率明显高于无淋巴结转移的患者,但hMAM水平比较差异无统计学意义。不论乳腺癌患者血清中是否存在ER、原癌基因Cerb-2表达及是否绝经,其hMAM水平及阳性表达率差异均无统计学意义。印滇等[12]研究显示:不同淋巴结转移乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM水平比较差异有统计学意义,而是否存在ER以及是否绝经乳腺癌患者hMAM水平和阳性表达率比较差异均无统计学意义。不同年龄、病理分型、肿瘤大小、分级和淋巴结转移状态乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM水平比较差异无统计学意义。本研究结果显示:不同淋巴结转移状态乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM阳性表达率比较差异有统计学意义,不同年龄、肿瘤大小、不同分期、ER、Her-2和PR乳腺癌患者血清中hMAM阳性表达率比较差异均无统计学意义。hMAM与乳腺癌患者病理临床特征的关系在不同研究的结论中存在差异,还需大量实验数据验证。不同淋巴结转移状态、分期、ER和Her-2乳腺癌患者血清中CD147阳性表达率比较差异有统计学意义,不同年龄、肿瘤大小和PR乳腺癌患者血清中CD147阳性表达率比较差异均无统计学意义,与Xue等[24]的研究结果一致。本研究结果显示:随着乳腺癌分期增加,hMAM和CD147阳性表达率均呈递增趋势。
本研究结果显示:乳腺癌组患者hMAM和CD147水平明显高于乳腺纤维腺瘤组和健康对照组,表明hMAM和CD147水平与乳腺癌发生具有一定关联,可作为乳腺癌早期筛查的标志物。乳腺癌组患者hMAM和CD147阳性表达率明显高于乳腺纤维腺瘤组和健康对照组,且二者联合检测时其阳性表达率更高。
综上所述,hMAM作为乳腺癌高特异性肿瘤标记物,有望成为早期乳腺癌筛查和诊断的一种重要指标,而hMAM和CD147联合检测可以提高乳腺癌筛查阳性率,该方法也具有相对较高的敏感性和特异性,具有一定的临床意义,其在乳腺癌治疗及预后中的临床价值还需大量的随访数据和更多高质量的研究证据来证实。
| [1] | Watson MA, Fleming TP. Mammaglobin, a mammary-specific member of the uteroglobin gene family is overexpressed in human breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 1996, 56(4): 860–865. |
| [2] | Becker RM, Darrow C, Zimonjie DB, et al. Identification of mammaglobin B, a novel member of the uteroglobin gene family[J]. Genomics, 1998, 54(1): 70–78. DOI:10.1006/geno.1998.5539 |
| [3] | Oloomi M, Moazzezy N, Bouzari S. Modulation of molecular biomarker expression in response to chemotherapy in invasive ductal carcinoma[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2018, 2018: 7154708. |
| [4] | Li C, Zhang T. Human mammaglobin:A specific marker for breast cancer prognosis[J]. J Buon, 2016, 21(1): 35–41. |
| [5] | Lv X, Feng X, Hao X, et al. Anti-hMAM monoclonal antibodies evaluated in breast and non-breast tissues for differential diagnosis implication[J]. Tumori, 2016, 2016(3): 264–269. |
| [6] | 武帅, 王斌, 刘赟. 人乳腺珠蛋白在乳腺癌组织中的表达及意义[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2017, 17(9): 1299–1300. |
| [7] | 刘震, 马德寿, 沈国双. hMAM在乳腺癌前哨淋巴结中的表达及其临床意义分析[J]. 现代免疫学, 2017, 37(5): 395–398. |
| [8] | 鲍慧铮, 陈力, 李思莹, 等. CK19联合hMAM检测乳腺癌循环肿瘤细胞的临床价值[J]. 肿瘤, 2014, 34(2): 153–157. |
| [9] | 于秀艳, 张晓伟, 野丽莉, 等. hMAM联合MMP-9和C-erbB2 mRNA表达检测在乳腺癌外周血微转移诊断中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2017, 43(5): 1009–1014. |
| [10] | Zucker S, Hymowitz M, Rollo EE, et al. Tumorigenic potential of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer[J]. Am J Pathol, 2001, 158(6): 1921–1928. DOI:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64660-3 |
| [11] | 冀峰, 吕复君, 李延翠. hMAM mRNA表达情况与乳腺癌的关系[J]. 癌症进展, 2018, 16(3): 315–317. |
| [12] | 印滇, 王亚非, 杨莉, 等. hMAM水平与乳腺癌早期诊断和癌微转移的相关性及临床意义研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2015, 14(18): 1512–1515. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2015.18.010 |
| [13] | Al Joudi FS. Human mammaglobin in breast cancer:a brief review of its clinical utility[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2014, 139(5): 675–685. |
| [14] | Goedegebuure PS, Watson MA, Viehl CT, et al. Mammaglobin-based strategies for treatment of breast cancer[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2004, 4(6): 531–542. DOI:10.2174/1568009043332862 |
| [15] | Strati A, Markou A, Parisi C, et al. Gene expression profile of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer by RT-qPCR[J]. BMC Cancer, 2011, 11(1): 422. DOI:10.1186/1471-2407-11-422 |
| [16] | Zhao S, Yang H, Zhang M, et al. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) detected by triple-marker EpCAM, CK19, and hMAM RT-PCR and their relation to clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2013, 65(2): 263–273. DOI:10.1007/s12013-012-9426-2 |
| [17] | Liu Y, Ma L, Liu X, et al. Expression of human mammaglobin as a marker of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2012, 3(3): 550–554. DOI:10.3892/etm.2011.429 |
| [18] | Yang J, Wang R, Li H, et al. Lentivirus mediated RNA interference of EMMPRIN (CD147) gene inhibits the proliferation, matrigel invasion and tumor formation of breast cancer cells[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2016, 17(2): 237–247. DOI:10.3233/CBM-160636 |
| [19] | 赵超悦, 宋润敏, 秦晖, 等. EMMPRIN糖基化突变质粒的构建及功能检测[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2014, 40(3): 583–587. |
| [20] | Dimas DT, Perlepe CD, Sergentanis TN, et al. The prognostic significance of Hsp70/Hsp90 expression in breast cancer:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Anticancer Res, 2018, 38(3): 1551–1562. |
| [21] | Luz M, Perez M, Azzalis L, et al. Evaluation of MCT1, MCT4 and CD147 genes in peripheral blood cells of breast cancer patients and their potential use as diagnostic and prognostic markers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(4): 170–180. DOI:10.3390/ijms18040170 |
| [22] | 田英, 姜专基, 张志艳. 乳腺癌患者血清hMAM检测的临床意义研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2013, 34(3): 302–304. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2013.03.019 |
| [23] | 杨超, 康炜, 李建华, 等. 血清乳腺珠蛋白与乳腺癌的相关性及临床意义探讨[J]. 检验医学, 2014, 29(1): 61–64. |
| [24] | Xue S, Li SX, Wu ZS, et al. Expression of CD147, matrix metalloproteinases and transforming growth factor beta1 in breast cancer[J]. Chin J Path, 2009, 38(8): 524–528. |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


