扩展功能
文章信息
- 李里, 宫亮, 吴玉斌
- LI Li, GONG Liang, WU Yu bin
- 沉默WNT4基因对稳定转染PAX2基因大鼠肾小管上皮细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响
- Effects of WNT4 gene silencing on migration and invasion of renal tubular epithelial cells of rats stably transfected with PAX2 gene
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(06): 1212-1217
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1212-1217
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180618
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-02-05
2. 锦州医科大学附属第一医院耳鼻喉科, 辽宁 锦州 121000;
3. 中国医科大学附属盛京医院小儿肾脏风湿免疫科, 辽宁 沈阳 110004
2. Department of Ear-Nose-Throat, First Affiliated Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, China;
3. Department of Pediatric Nephrology and Rheumatology, Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang 110004, China
配对盒基因2(paired box gene 2, PAX2)是调控肾脏发育的重要调控因子[1-4]。研究[5]表明:在调控后肾脏发育过程中,间充质向上皮细胞转化的重要步骤里WNT4基因发挥重要作用,PAX2基因通过激活该基因完成该过程。如果将PAX2基因敲减可导致细胞停止分化,因此推测WNT4是PAX2的作用基因。本课题组前期研究[6]表明:PAX2基因转染细胞后,激活了WNT通路,WNT4表达水平明显升高,因此认为WNT4基因可能是PAX2基因的靶基因。本课题组前期研究[7]表明:PAX2基因转染肾小管上皮细胞后,可以增加细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,改变其生物学活性。PAX2基因是否通过WNT4基因调控进而调节细胞的生物学活性目前尚无定论。本研究采用RNA沉默技术,沉默WNT4基因后观察细胞生物学活性的改变,探讨PAX2基因是否通过WNT4基因调控细胞的生物学活性。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞、主要试剂和仪器稳定转染PAX2基因的细胞(本课题组前期构建)。WNT4 siRNA(本课题组前期已构建),WNT4兔抗大鼠单克隆抗体购自美国Zymed公司,胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司,Transwell细胞小室购自美国Corning公司。低温高速离心机购自美国Beekman Coulter公司,荧光定量PCR仪购自美国Costar公司。
1.2 WNT4 siRNA的设计和合成本课题组前期已通过实验研究确定3对siRNA,其中最佳为WNT4 siRNA:sense,5′-CACGCACUAAAGGAGAAGUTT- 3′; anti-sense, 5′-ACUUCUCCUUUAGCGCGUGTT- 3′。最佳转染时间为72 h[6]。
1.3 细胞传代培养和分组稳定转染PAX2的大鼠肾小管上皮细胞在37 ℃、5%CO2、饱和湿度条件下,于含10%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养基中培养。每2~3 d传代1次,实验均选用对数生长期细胞。细胞分为稳转组(采用WNT4siRNA处理)和对照组(无特殊处理)。将稳转组细胞分为稳转对照组(不应用WNTsiRNA沉默)和沉默72 h组(应用WNTsiRNA沉默72 h)。
1.4 WNT4 siRNA转染大鼠肾小管上皮细胞取4 μg WNT4siRNA加入无血清高糖DMEM中(每孔总体积250 μL);5 μL脂质体2000加入245 μL高糖无血清DMEM(每孔总体积250 μL)。将2种溶液混合,加入培养板,轻轻混匀。吸弃转染培养基上清,加入含10%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养基,转染72 h收集细胞(沉默72 h组)。
1.5 Western blotting法检测稳转组和对照组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中PAX2和WNT4蛋白相对表达量配制5%SDS-PAGE浓缩胶,采用1 mL加样器将混合液加入玻璃板夹心的凝固分离胶上面,待胶凝固后置于-4℃保存。电泳槽内加入电泳缓冲液后,80 V电压,直至溟酚蓝指示剂迁移至分离胶底部,关闭电源。戴手套取出电泳凝胶,浸泡于电泳缓冲液中,切下目的凝胶条带。将结合了蛋白的PVDF膜采用5-溴-4-氯-3-吲哚基磷醋/四氮唑蓝(BCIP/NBT/uffer,1:1:50)试剂盒显色。测试目的条带的吸光度(A)值,将其与同一样本的β-actinA值的比值进行定量分析,该数值即代表检测样本的蛋白相对表达量。PAX2蛋白相对表达量=PAX2蛋白A值/β-actinA值。WNT4蛋白相对表达量=WNT4蛋白A值/β-actinA值。
1.6 Realtime PCR法检测稳转对照组和沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4 mRNA相对表达量将各组细胞中加入1 mL RZ裂解液,充分混匀,充分振荡,缓慢加入0.5倍体积无水乙醇,混匀,室温放置2 min,4℃、12 000 r·min-1离心2 min,所得即为样本总RNA。在波长260 nm处测定待测RNA样品A值。反转录合成cDNA:加入1 μL(200 U)TIANScript M-MLV,采用移液器轻轻混匀。42℃温浴50 min。95℃加热5 min终止反应。按照试剂盒要求,配制20 μL PCR反应液(冰上操作),引物序列见表 1。反应条件为95℃、10 min,95℃、10 s,60℃、20 s, 35个循环;72℃、30 s,4℃、5 min,4个循环;熔解曲线条件(由机器自行设定):95℃、15s,60℃、1 min,95℃、15s。采用相对定量方法RQ=2-△△Ct计算WNT4基因mRNA的相对表达量。ΔΔCt=(实验样品Ct-内参基因Ct)-(基准样品Ct-内参基因Ct)。
| Gene | Sequence(5′-3′) | Length(bp) | Temperture(θ/℃) | Size(bp) |
| WNT4-F | TTCGGGAAGGTGGTGACACAAG | 22 | 64.4 | 211 |
| WNT4-R | ACAGTGAGAAGGCTACGCCATAGG | 24 | 64.0 | |
| β-actin-F | CGGGACCTGACTGACTACCTCA | 22 | 61.4 | 546 |
| β-actin-R | CTCGTCATACTCCTGCTTGCTG | 22 | 60.2 |
采用pipette tip造成细胞划痕,将前1天采用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化的肾小管上皮细胞接种到培养板中,待细胞聚集达80%~90%,采用pipette tip造成细胞划痕后,加入培养基于细胞表面洗涤2次,之后于培养基中继续培养,10和18 h后显微镜下照相,观察愈合情况,计算细胞迁移率。细胞迁移率=(0 h划痕宽度-10 h或18 h划痕宽度)∕0 h划痕宽度×100%。
1.8 Transwell实验检测稳转对照组和沉默72h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的穿膜细胞数将50μL Matrigel (1g·L-1)均匀铺在Transwell的8μm孔径聚碳酸酷微孔滤膜上。将600μL含胎牛血清的NIH3T3细胞的上清中加入Transwell下室各孔。将不含血清的200μL稳转对照组和沉默72 h组细胞悬液加入Transwell上室,培养48 h。将Transwell小室取出。固定染色后,在200倍倒置显微镜下,随机选取16个高倍视野计数穿膜细胞数并照相。以每个高倍镜下穿膜细胞数表示细胞侵袭能力。
1.9 统计学分析采用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行统计学分析。各组细胞中PAX2、WNT4蛋白和WNT4 mRNA相对表达量,细胞迁移率,穿膜细胞数以x±s表示,组间两两比较时先行多样本方差齐性检验,若方差齐则行LSD-t检验。以α=0.05为检验水准。
2 结果 2.1 稳转组和对照组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中PAX2和WNT4蛋白相对表达量稳转组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中PAX2蛋白相对表达量为1.12±0.14,对照组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中PAX2蛋白相对表达量为0.87±0.05,组间比较差异有统计学意义(t=376.6,P<0.05)。见图 1。
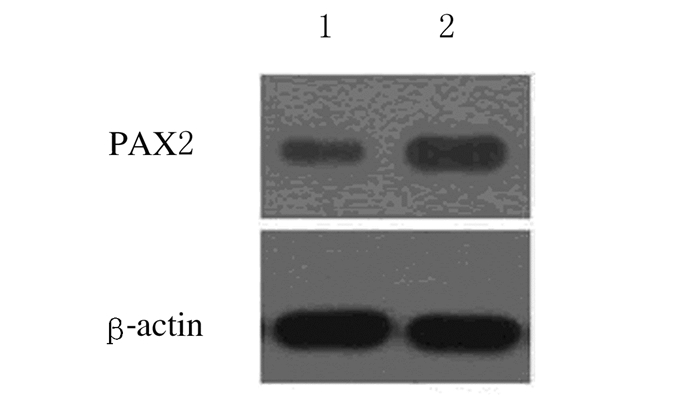
|
| Lane 1:Stably transfected group; Lane 2: Control group. 图 1 Western blotting法检测2组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中PAX2蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 1 Electrophoregram of expressions of PAX2 protein in renal tubular epithelial cells of rats in two groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|
稳转组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4蛋白相对表达量为1.03±0.15,对照组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4蛋白相对表达量为0.85±0.11,组间比较差异有统计学意义(t=368.7,P<0.05)。见图 2。
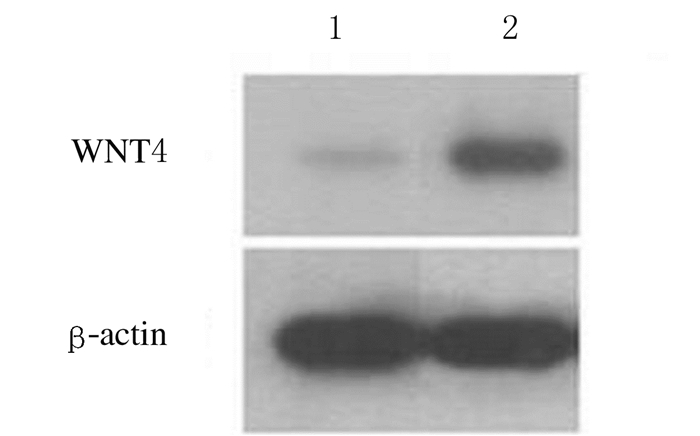
|
| Lane 1:Stably transfected group; Lane 2: Control group. 图 2 Western blotting法检测2组肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of WNT4 protein in renal tubular epithelial cells of rats in two groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|
Realtime PCR结果表明:沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4mRNA相对表达量为0.47±0.02,稳转对照组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4mRNA相对表达量为0.87±0.05,组间比较差异有统计学意义(t=264.5,P<0.05)。见图 3。
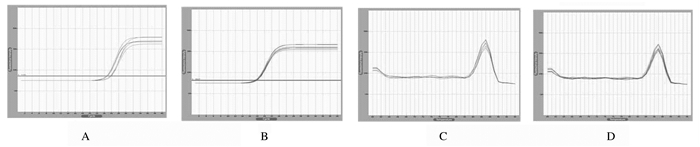
|
| A, C: WNT4 melting curve; B, D:β-actin amplification curve; A, C: Silening 72 h group; B, D:Stably transfected control group. 图 3 Real time PCR法检测稳转对照组和沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞中WNT4 mRNA的表达 Figure 3 Relative expression amounts of WNT4 mRNA in renal tubular epithelial cells of rats in stably transfected control and silence 72 h groups detected by Real time PCR method |
|
|
沉默10 h后稳转对照组和沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的细胞迁移率分别为(43.12±7.13)%和(35.31±6.54) %,组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。沉默18 h后,稳转对照组和沉默72 h组细胞迁移率分别为(83.72±7.12)%和(40.31±7.14) %,组间比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=497.5,P<0.05)。见图 4。
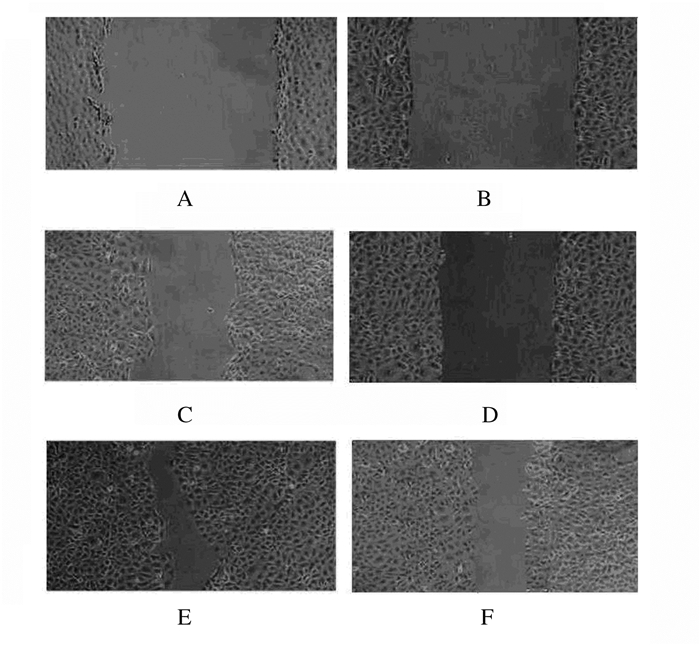
|
| A, B:0 h; C, D:10 h; E, F:18 h; A, C, E:Stably transfected control group; B, D, F: Silencing 72 h group. 图 4 不同时间点稳转对照组和沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的细胞迁移情况(×100) Figure 4 Migration of renal tubular epithelial cells of rats in stably transfected control and silencing 72 h groups at different time points |
|
|
稳转对照组和沉默72 h组细胞培养48 h后,2组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的穿膜细胞数分别为(46.33±3.63)和(38.00±8.14)个;与稳转对照组比较,沉默72 h组大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的穿膜细胞数明显减少,组间比较差异有统计学意义(t=291.6,P < 0.05)。见图 5(插页四)。
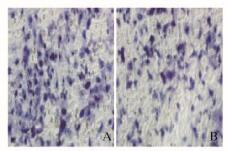
|
| A:Control group; B: Experiment group. 图 5 稳转对照组(A)和沉默72 h组(B)大鼠肾小管上皮细胞的穿膜细胞形态表现(HE,×200) Figure 5 Morphology of transmembrane cells of renal tubular epithelial cells of rats in transfected control(A) and silencing 72 h(B) groups (HE, ×200) |
|
|
本研究利用本课题组前期构建的PAX2基因稳定转染细胞系,通过转染鉴定及WMT4蛋白检测发现:PAX2和WNT4蛋白表达水平明显升高,表明PAX2基因转染后激活了WNT4基因的表达,这与本课题组前期研究[6]结果一致。PAX2可激活WNT4基因,提示WNT4基因可能是PAX2基因的靶基因[8-11]。
本课题组前期研究[7]已经证实:PAX2基因可以提高细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。目前研究[12-13]显示:PAX2基因可以通过调节LSD1及EPHA2调控细胞侵袭程度。研究[14]显示:胎鼠中WNT4表达水平较高,在正常成熟大鼠的肾脏组织中WNT4处于失活状态。研究者[15-16]在高表达PAX2基因的UUO大鼠肾脏组织中发现WNT4基因表达水平明显升高,将WNT阻断后,肾脏纤维化程度减轻。研究者[16-17]观察到WNT4基因可促进肾间质细胞合成α-SMA和Ⅰ型胶原。
PAX2是否通过WNT4来调控细胞的迁移和侵袭能力目前尚无报道。本课题组将WNT4基因沉默,观察细胞迁移和侵袭能力的变化,结果表明:划痕18 h后,沉默72 h组细胞迁移率较稳转对照组明显降低,沉默72 h组穿膜细胞数较稳转对照组减少,提示沉默WNT4后,稳定转染PAX2细胞的迁移和侵袭能力减弱。本研究结果与Chen等[18]的研究结果相似,在胸腺瘤的研究中发现WNT4基因通过改变肿瘤细胞侵袭程度而发挥重要作用。在氧化损伤过程中,WNT4参与调节细胞迁移侵袭。本课题组沉默了PAX2激活的WNT4基因后,细胞侵袭和迁移能力减弱,说明PAX2可能通过调控WNT4基因来改变肾小管上皮细胞生物学活性[19-20]。
综上所述,PAX2基因转染正常肾小管上皮细胞后使得细胞迁移和侵袭能力增强,并激活了WNT4表达,沉默WNT4后出现了细胞迁移和侵袭能力较沉默前减弱,因此推测WNT4基因可能是PAX2调控细胞生物学活性的主要基因。
| [1] | Kahraman K, Kiremitci S, Taskin S, et al. Expression pattern of PAX2 in hyperplastic and malignant endometrium[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2012, 286(1): 173–178. DOI:10.1007/s00404-012-2236-3 |
| [2] | El-Nahas AM. Plasticity of kidney cells:Role in kidney remodeling and scarring[J]. Kindey Int, 2003, 64(5): 1553–1563. DOI:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00255.x |
| [3] | Narlis M, Grote D, Gaitan Y, et al. Pax2 and pax8 regulate branching morphogenesis and nephron differentiation in the developing kidney[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2007, 18(4): 1121–1129. DOI:10.1681/ASN.2006070739 |
| [4] | Torban E, Goodyer P. What PAX genes do in the kidney[J]. Exp Nephrol, 1998, 6(1): 7–11. DOI:10.1159/000020498 |
| [5] | Torban E, Dziarmaga A, Iglesias D, et al. PAX2 activates WNT4 expression during mammalian kidney development[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(18): 12705–12712. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M513181200 |
| [6] | 李里, 南晓娟, 吴玉斌. WNT4基因沉默对PAX2诱导肾小管上皮细胞间充质转分化的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2013, 39(4): 720–725. |
| [7] | 李里, 宫亮, 吴玉斌. PAX2稳转细胞系构建及对细胞迁移和侵袭能力的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015, 18(35): 4325–4329. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.35.013 |
| [8] | Lyons JP, Mueller UW, Ji H, et al. Wnt-4 activates the canonical beta-catenin-mediated Wnt pathway and binds Frizzled-6 CRD:functional implications of Wnt/beta-catenin activity in kidney epithelial cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2004, 298(2): 369–387. DOI:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.036 |
| [9] | Liu Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21(2): 212–222. DOI:10.1681/ASN.2008121226 |
| [10] | Chilosi M, Poletti V, Zamo A, et al. Aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Am J Pathol, 2003, 162(5): 1495–1502. DOI:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64282-4 |
| [11] | Jiang F, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B. Gene expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation[J]. J Hepatol, 2006, 45(3): 401–409. DOI:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.03.016 |
| [12] | Patel D, Shimomura A, Majumdar S, et al. The histone demethylase LSD1 regulates inner ear progenitor differentiation through interactions with Pax2 and the NuRD repressor complex[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): e0191689. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0191689 |
| [13] | Ma X, Ma Z, Jiao X, et al. Functional non-coding polymorphism in an EPHA2 promoter PAX2 binding site modifies expression and alters the MAPK and AKT pathways[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9992. |
| [14] | Nguyen HT, Thomson AA, Kogan BA, et al. Expression of the Wnt gene family during late nephrogenesis and complete ureteral obstruction[J]. Lab Invest, 1999, 79(6): 647–658. |
| [15] | He W, Dai C, Li Y, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes renal interstitial fibrosis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2009, 20(4): 765–776. DOI:10.1681/ASN.2008060566 |
| [16] | Surendran K, McCaul SP, Simon TC. A role for Wnt-4 in renal fibrosis[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2002, 282(3): F431–F441. DOI:10.1152/ajprenal.0009.2001 |
| [17] | Surendran K, Schiavi S, Hruska KA. Wnt-dependent beta-catenin signaling is activated after unilateral ureteral obstruction, and recombinant secreted frizzled-related protein 4 alters the progression of renal fibrosis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2005, 16(8): 2373–2384. DOI:10.1681/ASN.2004110949 |
| [18] | Chen Y, Zhang P, Tang P, et al. Wnt4 overexpression promotes thymoma development through a JNK-mediated planar cell polarity-like pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(1): 83–90. |
| [19] | Wang L, Qing L, Liu H, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate oxidative stress-induced islet endothelium apoptosis and functional impairment via Wnt4-β-catenin signaling[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 8(1): 188–122. DOI:10.1186/s13287-017-0640-0 |
| [20] | 雷蕾, 李良平, 张虎. 血清胱抑素C联合尿中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白对肝硬化腹水继发急性肾损伤的诊断价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(1): 101–105. |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


