扩展功能
文章信息
- 于雷, 唐庚, 方芳, 李鑫, 龚守良, 王志成, 王剑锋
- YU Lei, TANG Geng, FANG Fang, LI Xin, GONG Shouliang, WANG Zhicheng, WANG Jianfeng
- 低剂量辐射诱导小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α和XBP1 mRNA及其蛋白的表达
- Expressions of IRE1α and XBP1 mRNA and proteins in mouse testis cells induced by low dose ionizing radiation
- 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(05): 919-923
- Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 919-923
- 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20180506
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-10-20
2. 吉林大学公共卫生学院卫生部放射生物学重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130021;
3. 吉林大学中日联谊医院放疗科, 吉林 长春 130033
2. Key Laboratory of Radiobiology, Ministry of Health, School of Public Health, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;
3. Department of Radiotherapy, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130033, China
2011年日本福岛核电站泄漏事件后,辐射高本底环境是否影响人类健康再次引起广泛关注,其焦点是致癌问题。低剂量辐射(low dose radiation,LDR)的生物效应区别于高剂量诱导的损伤,但LDR诱导的效应仍不确定[1-2]。LDR诱导的损伤效应主要依据是线性无阈模型(linear no threhold, LNT),任何剂量的电离辐射都有致癌的可能性[3-4]。但也有学者[5-6]认为:LDR可诱导适应性反应和兴奋性效应。睾丸是辐射敏感的器官,极低剂量就能引起睾丸生精细胞凋亡[7-8],并且具有一定的剂量和时程-效应规律性。前期研究[9]显示:LDR能够诱导小鼠睾丸生精细胞内质网应激的发生,并且启动了凋亡信号通路。肌醇需求酶1(inositol-requiring enzyme-1, IRE1)是一种定位在内质网膜的具有激酶和核酸内切酶活性的双功能酶,可以被内质网应激激活,从而激活多条下游信号通路,其中X盒结合蛋白1(X box-binding protein-1, XBP1)是最早发现并且最受关注[10],是重要的内质网应激信号调节通路。本实验旨在通过检测LDR后小鼠睾丸细胞中肌醇需求酶1α(inositol-requiring enzyme-1α, IRE1α)、Total-XBP1(T-XBP1)、spliced XBP1(S-XBP1)mRNA及蛋白的表达,阐明IRE1-XBP1通路的激活在LDR诱导小鼠睾丸内质网应激信号调控中的作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物和照射处理方法50只健康雄性ICR小鼠,体质量(18±2)g,由吉林大学白求恩医学部实验动物中心提供,动物合格证号:SXCK(吉)203-00007,随机分为10组,每组5只。时程-效应实验为75 mGy照射后0、3、6、12和24 h处死动物,剂量-效应实验为0、50、75、100和200 mGy照射后12 h处死动物。应用国产固定式X射线深部治疗机(XSZ-220/20X型,丹东市康嘉仪器设备有限公司)进行全身照射,电压180 kV,电流15 mA,剂量率为12.5 mGy·min-1。
1.2 主要试剂和仪器TRIzol(美国Invitrogen公司),焦碳酸二乙酯(DEPC, 上海生工生物公司),反转录试剂盒(加拿大MBI Fermentas公司),IRE1α、T-XBP1、S-XBP1和GAPDH引物及real time PCR试剂盒(大连宝生物公司),ECL发光试剂盒, IRE1α、T-XBP1、S-XBP1(兔抗鼠多克隆)和GAPDH(山羊抗鼠多克隆)一抗(美国Santa Cruz公司),辣根过氧化酶标记的抗兔及抗山羊二抗(北京中杉金桥公司),其他试剂为国产分析纯;PCR仪(美国Perkin-Elmer公司),Mx3000P real time PCR仪(美国Stratagene公司),Mini-PROTEAN 3 Dodeca微型电泳槽(美国Bio-Rad公司)。
1.3 实时定量PCR法检测小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平IRE1α引物:5′-CATGAGGAACAAGAAGCACCACTA-3′(上游序列),5′-TCGCTGTGTGAAGTACTGAATGAA-3′(下游序列);T-XBP1引物:5′-TGGGCATTCTGGACAAGTT-3′(上游序列),5′-GAAAGGGAGGCTGGTAAGG-3′(下游序列);S-XBP1引物:5′-CTGAGTCCGAATCAGGTGCAG-3′(上游序列),5′-GTCCTAGGGAAGATGTTCTGG-3′(下游序列);GAPDH引物:5′-AAATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTG-3′ (上游序列),5′- TGAAGGGGT-CGTTGATGG-3′(下游序列)。用TRIzol试剂提取各组睾丸细胞中总RNA后,采用反转录试剂盒合成互补DNA(cDNA),MX3000P real time PCR系统进行PCR扩增并分析。每组随机选择5只小鼠左侧睾丸样本,每个样本设3个复孔。每个样本的mRNA表达水平用各自内参照GAPDH表达水平进行标准化,以目的mRNA与GAPDH mRNA比值为该基因的相对表达水平,同时将对照组目的mRNA相对表达水平设定为1[8]。
1.4 Western blotting法检测小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1蛋白表达强度将上述5只小鼠右侧睾丸组织提取总蛋白并进行蛋白定量。每个样品取20 μg上样,SDS聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳时,浓缩胶采用60 V恒压,分离胶采用90 V恒压。蛋白转移至硝酸纤维膜上,膜经新鲜配制的封闭液(1×TBS,5%脱脂奶粉,0.05% Tween-20)常温封闭1 h,加入按一定比例稀释后的IRE1α、T-XBP1、S-XBP1和GAPDH一抗,4℃过夜,用含0.05% Tween 20的TBST洗涤2次,每次15 min,加入按一定比例稀释的辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记的二抗,37℃震荡孵育1 h;用ECL发光试剂盒进行发光,X射线片曝光显影,照相后进行分析,结果以条带灰度值表示蛋白表达强度。实验重复3次。
1.5 统计学分析采用SPSS24.0统计软件进行统计学分析。小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1mRNA表达水平以x±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
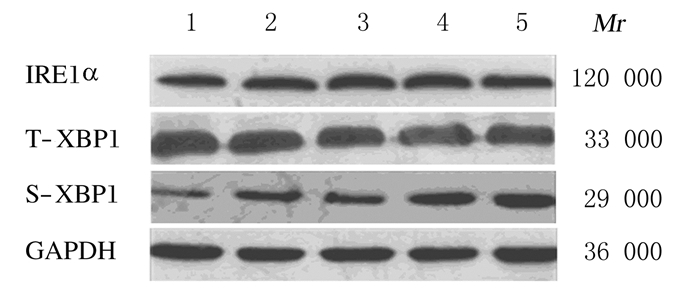
2 结果 2.1 75 mGy X射线照射后不同时间小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1mRNA表达水平和蛋白表达强度除3 h组小鼠睾丸细胞中T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平降低外,其他各时间组IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平均随时间延长而升高,并在6 h达到峰值,而后逐渐降低。与0 h组比较,6、12和24 h组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1αmRNA表达水平及6和12 h组T-XBP1、S-XBP1mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);与0 h组比较,不同时间组IRE1α和S-XBP1蛋白表达强度增加,6和12 h组IRE1α蛋白表达强度及24 h组S-XBP1蛋白表达强度最高,而T-XBP1蛋白表达强度稍有降低。见表 1和图 1。
| (n=5, x±s) | |||
| Group | IRE1α mRNA | T- XBP1 mRNA | S-XBP1 mRNA |
| 0 h | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 h | 1.37±0.33 | 0.69±0.21 | 0.63±0.32 |
| 6 h | 3.75±0.58* | 2.37±0.20** | 2.14±0.29* |
| 12 h | 3.13±0.36** | 2.37±0.72* | 1.58±0.16* |
| 24 h | 1.54±0.10** | 2.18±0.17 | 0.91±0.10 |
| *P < 0.05,** P < 0.01 vs 0 h group. | |||
|
| Lane 1:0 h group; Lane 2:3 h group; Lane 3:6 h group; Lane 4:12 h group; Lane 5:24 h group. 图 1 Western blotting法检测75 mGy X射线照射后不同时间各组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 1 Electrophoregram of expressions of IRE1α, T-XBP1 and S-XBP1proteins in mouse testis cells at different time after 75 mGy X-ray irradiation in various groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|
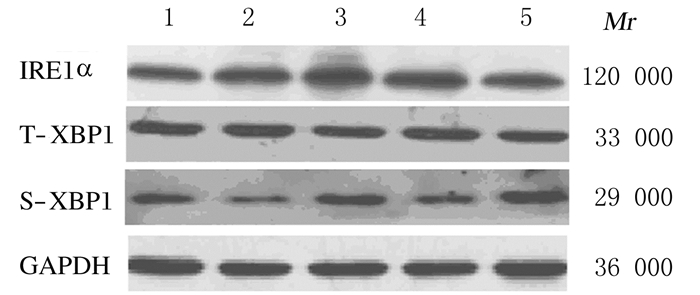
0~200 mGy X射线全身照射后12 h,随照射剂量的增加,各组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平升高,75 mGy组升高达峰值后逐渐降低,甚至降至0 mGy组以下。与0 mGy组比较,75和200 mGy组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1αmRNA表达水平、75 mGy组T-XBP1和S-XBP1mRNA表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。与0 h组比较,各剂量组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α和S-XBP1蛋白表达强度升高,75 mGy组IRE1α蛋白表达强度、75和200 mGy组S-XBP1蛋白表达强度升高最明显,而T-XBP1蛋白表达强度无明显变化。见表 2和图 2。
| (n=5, x±s) | |||
| Group | IRE1α mRNA | T-XBP1 mRNA | S-XBP1 mRNA |
| 0 mGy | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 50 mGy | 1.34±0.11 | 1.42±0.46 | 1.39±0.27 |
| 75 mGy | 3.13±0.36** | 2.37±0.72* | 1.58±0.16* |
| 100 mGy | 1.08±0.43 | 0.64±0.29 | 0.58±0.28 |
| 200 mGy | 1.12±0.07* | 0.85±0.36 | 0.83±0.40 |
| *P < 0.05,** P < 0.01 vs 0 mGy group. | |||
|
| Lane 1:0 mGy group; Lane 2:50 mGy group; Lane 3:75 mGy group; Lane 4:100 mGy group; Lane 5:200 mGy group. 图 2 Western blotting法检测不同剂量X射线照射后12 h各组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1蛋白表达电泳图 Figure 2 Electrophoregram of expressions of IRE1α, T-XBP1 and S-XBP1 proteins in mouse testis cells 12 h after different doses of X-ray irradiation in various groups detected by Western blotting method |
|
|
随着核电和核技术应用越来越广泛,由此产生的辐射对人体健康的影响也日渐增加,尤其是LDR所引发的问题已经成为放射医学领域的研究热点。过去20多年来,LDR的生物学效应特别是导致生殖及遗传效应引起诸多研究者的关注。睾丸组织是辐射敏感器官,睾丸细胞群主要包括精原细胞、精母细胞、精子细胞和精子,以及Lydig和Sertoli细胞;其中,精原细胞及精母细胞对辐射敏感,而精子细胞和精子以及Lydig和Sertoli细胞则表现为辐射抵抗。因此,LDR诱导睾丸细胞的凋亡以精原细胞和精母细胞为主,很少涉及到精子细胞和精子以及Lydig和Sertoli细胞,这一点本研究前期的相关研究已经证实[7]。睾丸组织是辐射敏感器官,低至100 mGy的单次剂量照射损伤分裂中的精原细胞,导致生精障碍[11-12]。在放射治疗中睾丸组织分次照射生精小管损伤也会增加,主要可能是由于干细胞的重复激活导致的,对于生精上皮来说,多种低程度的遗传损伤甚至比高程度的损伤更严重[13]。因此,研究LDR对睾丸生殖损伤则有望提出相应的新理论和新机制。
内质网是真核细胞中蛋白质合成、折叠和分泌的重要细胞器,内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件, 因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。在氧化应激、缺氧和电离辐射等条件下,内质网内未折叠和错误折叠的蛋白明显增多,超出了内质网处理能力时,细胞会激活相关的信号级联反应来应对条件的变化,并恢复内质网良好的环境,这种情况被称为内质网应激,当应激发生程度较低时则细胞可以正常分裂,恢复生命;而当应激过载时则激活下游凋亡通路信号分子,诱导细胞凋亡。参与内质网应激的信号调控的3个重要的跨膜蛋白分别为:双链RNA依赖的蛋白激酶样内质网激酶(PKR-like ER kinase,PERK)、活化转录因子6(activating transcription factor-6,ATF6)和IRE1,均可与下游相应的分子构成独立的或互为网状的信号通路。IRE1被激活后能够切割下游XBP1 mRNA(T-XBP1)形成切割体mRNA(S-XBP1),进而导致该通路的激活[14-18]。本课题组前期研究显示:LDR能够诱导睾丸细胞发生内质网应激,并且激活了PERK-CHOP凋亡通路[8],但是内质网应激能否激活ATF6和IRE1通路尚不明确。本实验通过检测75 mGy照射后0~24 h和0~200 mGy照射后12 h各组小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达强度变化来判断发生内质网应激的可能,结果显示:75 mGy照射后0~24 h,随着时间延长,小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达强度逐渐增加,分别在6和/或12 h达到峰值而后降低;T-XBP1和S-XBP1与IRE1α mRNA表达时程变化趋势相似,S-XBP1蛋白随时间延长逐渐增加,但是在照射后24 h表达最高,而T-XBP1蛋白表达有降低趋势但不明显;0~200 mGy照射后12 h,随着剂量的增加,小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α、T-XBP1和S-XBP1 mRNA表达水平的变化趋势基本一致,即75 mGy照射后其表达水平最高,而后逐渐减低甚至降至0 mGy组水平以下。IRE1α和S-XBP1蛋白表达强度分别在75和200 mGy照射后达最强,而T-XBP1蛋白表达强度无明显的变化。本研究结果表明:LDR能够诱导小鼠睾丸细胞中IRE1α mRNA表达水平及蛋白表达强度增加,进而切割T-XBP1 mRNA形成S-XBP1 mRNA。理论上T-XBP1 mRNA被切割后其表达减少,但是其表达也随着时间延长而增加,可能与辐射后时间不同有关[19-20]。本研究结果提示:LDR能够诱导小鼠睾丸细胞IRE1-XBP1内质网应激通路的激活。本结果为研究LDR诱导睾丸细胞凋亡机制提供了必要的补充,为电离辐射防护政策和法规的制订提供了实验数据。
| [1] | Doss M. Linear no-threshold model vs.radiation hormesis[J]. Dose Response, 2013, 11(3): 480–497. |
| [2] | Morgan WF, Bair WJ. Issues in low dose radiation biology:the controversy continues.A perspective[J]. Radiat Res, 2013, 179(5): 501–510. DOI:10.1667/RR3306.1 |
| [3] | Till JE, Beck HL, Grogan HA, et al. A review of dosimetry used in epidemiological studies considered to evaluate the linear no-threshold (LNT) dose-response model for radiation protection[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2017, 7(5): 1–17. |
| [4] | Sun Y, Hawkins PG, Bi N, et al. Serum microRNA signature predicts response to high-dose radiation therapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018, 100(1): 107–114. DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.08.039 |
| [5] | Zhao Y, Kong C, Chen X, et al. Repetitive exposure to low-dose X-irradiation attenuates testicular apoptosis in type 2 diabetic rats, likely via Akt-mediated Nrf2 activation[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2016, 422(6): 203–210. |
| [6] | Jiang X, Hong Y, Zhao D, et al. Low dose radiation prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(1): 332–345. |
| [7] | Liu G, Gong P, Zhao H, et al. Effect of low-level radiation on the death of male germ cells[J]. Radiat Res, 2006, 165(4): 379–389. DOI:10.1667/RR3528.1 |
| [8] | Elmhiri G, Gloaguen C, Grison S, et al. DNA methylation and potential multigenerational epigenetic effects linked to uranium chronic low-dose exposure in gonads of males and females rats[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2018, 282(2): 64–70. |
| [9] | 方芳, 龚平生, 宋祥福, 等. 低剂量电离辐射诱导小鼠睾丸细胞内质网应激及PERK-CHOP信号通路的激活[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2012, 18(9): 777–782. |
| [10] | Jiang M, Yu S, Yu Z, et al. XBP1(X-box-binding protein-1)-dependent o-glcNAcylation is neuroprotective in ischemic stroke in young mice and its impairment in aged mice is rescued by thiamet-G[J]. Stroke, 2017, 48(6): 1646–1654. DOI:10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.016579 |
| [11] | 杨艳明, 方芳, 刘念, 等. 低剂量电离辐射诱导小鼠睾丸细胞中caspase-9表达的变化[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2014, 34(3): 185–187. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5098.2014.03.007 |
| [12] | Grewenig A, Schuler N, Rübe CE. Persistent DNA damage in spermatogonial stem cells after fractionated low-dose irradiation of testicular tissue[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2015, 92(5): 1123–1131. DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.04.033 |
| [13] | Tröndle I, Westernströer B, Wistuba J, et al. Irradiation affects germ and somatic cells in prepubertal monkey testis xenografts[J]. Mol Hum Reprod, 2017, 23(3): 141–154. |
| [14] | Tavernier SJ, Osorio F, van ders Sarren L, et al. Regulated IRE1-dependent mRNA decay sets the threshold for dendritic cell survival[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2017, 19(6): 698–710. DOI:10.1038/ncb3518 |
| [15] | Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE, Glimcher LH. Tumorigenic and immunosuppressive effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancer[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(4): 692–706. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.004 |
| [16] | Iurlaro R, Muñoz-Pinedo C. Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. FEBS J, 2016, 283(14): 2640–2652. DOI:10.1111/febs.13598 |
| [17] | Zhang B, Wang Y, Pang X, et al. ER stress induced by ionising radiation in IEC-6 cells[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2010, 86(6): 429–435. DOI:10.3109/09553001003668014 |
| [18] | Homma T, Fujii J. Heat stress promotes the down-regulation of IRE1α in cells:An atypical modulation of the UPR pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 349(1): 128–138. DOI:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.10.006 |
| [19] | Son B, Kwon T, Lee S, et al. CYP2E1 regulates the development of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via ER stress-and ROS-dependent mechanisms[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2017, 313(5): L916–L929. DOI:10.1152/ajplung.00144.2017 |
| [20] | Peschek J, Acosta-Alvear D, Mendez AS, et al. A conformational RNA zipper promotes intron ejection during non-conventional XBP1 mRNA splicing[J]. EMBO Rep, 2015, 16(12): 1688–1698. DOI:10.15252/embr.201540955 |
 2018, Vol. 44
2018, Vol. 44


