2. 中山大学广东省地质过程与矿产资源探查重点实验室, 广州 510275;
3. 中国地质大学(武汉)资源学院, 武汉 430074;
4. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室, 武汉 430074
2. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Geological Process and Mineral Resources Exploration, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China;
3. Resources Faculty, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China;
4. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China
0 引言
化探数据是矿产勘查和矿产资源定量预测与评价的重要数据源之一,通过对其进行一定的数据处理以识别、提取有用的找矿信息,尤其是对于水系沉积物化探数据,可以有助于快速、经济、有效地圈定找矿靶区。因此,在勘查地球化学和成矿预测中,化探数据处理和找矿信息提取一直以来都是一个较为重要的研究方向。早在20世纪七八十年代,国内外学者就将统计分类分析的思想用于化探的异常识别与提取[1-6],如聚类分析、对应分析、判别分析等,之后其应用越来越广泛,已经成为一种常规的化探数据处理方法,并且取得了一定的效果[5, 7-9]。但是,传统的分类分析方法大多是基于比较严格的正态或混合正态分布假定的[5, 8-11],如k-means方法[12],其对数据统计分布律的依赖性比较强,而很多实际化探数据通常情况下并不满足这个假定条件[8-9, 13-15],故其对这类数据的分类分析效果往往不太理想,甚至很差。因此,近年来,很多学者都在不断尝试和探索新的方法手段用于化探数据处理及其异常识别,如小波[16-20]、分形[13-14, 21-28]、非负矩阵分解[29-30]、希尔伯特黄变换[31]和盲信号处理及盲提取[31-32]等。
投影寻踪分类(projection pursuit classification, PPC)的基本原理是根据一定的准则,以高维空间中某一单位向量为投影方向,将高维数据投影到低维子空间上,以寻找出能够反映高维数据结构或特征的投影值,从而达到研究分析高维数据及对其进行系统分类和模式识别的目的[33-38]。其核心思想是投影寻踪(projection pursuit, PP),最初由Friedman等[39]提出。
投影寻踪分类[34, 36-37]是一种探索性数据分析与模式识别方法,它属于非参数统计模型,不受分布律的限制[34, 37, 40]。该模型是基于原数据结构与特征投影的分类方法[41-43],对数据的局部结构特征刻画较好,所以它的分类识别效果通常好于传统分类分析方法。因此,该模型自提出以来,已得到了广泛的应用,涉及到水资源与环境评价[44-50]、农业灌溉制度优化评价[44, 51-52]、遥感影像分类[41, 53-56]、地质灾害评价[57-59]、地震预报[60]、经济财务评价[61-62]以及精神分裂症的诊断[63]等多指标评价和分类识别领域,并且都取得了良好的应用效果。
以上研究表明,投影寻踪分类的思想作为多元数据分析的一种方法,克服了传统分类分析思想的一些不足,取得了优于传统方法的良好效果[15]。这种方法很好地契合了地学中找矿信息识别和提取的难题,在对多元化探数据进行处理分析、遥感蚀变信息提取等领域值得借鉴。因此,本文将其引入并与基于实数编码的遗传算法(real coded genetic algorithm, RCGA)[35, 64-70]相结合,用于化探异常的识别与提取中。
1 基于RCGA的PPC模型 1.1 投影寻踪分类模型用于化探异常识别与提取的PPC模型可概括为以下4个步骤来实现[35, 46-47, 51-52, 71]。
1) 原始化探数据的归一化处理。设第i个化探样品中第j种元素的含量为x*(i, j)(i=1, 2, 3, …, m; j=1, 2, 3, …, n),为了消除各元素含量值量纲的不一致,进行数据归一化处理:
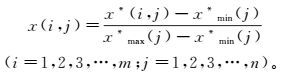 (1)
(1) 式中:x*(j)和xmin*(j)分别为样品中第j种元素含量的最大值和最小值;x(i, j)为原始化探数据归一化处理后的值。
2) 构造化探数据处理的投影目标函数Q(a)。投影寻踪方法就是把n维化探数据x(i, j)(i=1, 2, 3, …, m; j=1, 2, 3, …, n)(归一化后)投影到单位向量a={a(1), a(2), a(3), …, a(n)}(|a|=1) 的方向上,得到其投影值z(i):
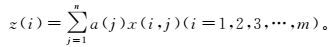 (2)
(2) 投影时,要求投影值{z(i)|i=1, 2, 3, …, m}的空间散布特征为:局部尽可能密集,而在整体上各点团之间尽可能散开。因此,Friedman等[39]将投影目标函数定义为
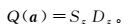 (3)
(3) 式中,Sz和Dz分别为投影值z(i)的标准差和局部密度。即
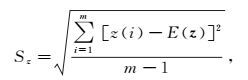 (4)
(4) 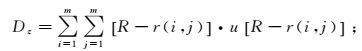 (5)
(5) 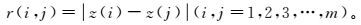 (6)
(6) 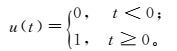 (7)
(7) 式中:E(z)为投影值{z(i)|i=1, 2, 3, …, m}的平均值;R为局部密度的窗口半径,可以通过实验来决定;r(i, j)表示第i个化探样品投影值与第j个化探样品投影值之间的距离;u(t)为跳跃函数。
3) 优化投影目标函数。当化探数据给定时,投影目标函数Q(a)只随投影方向a的变化而变化。不同的投影方向反映了数据的不同结构特征,最佳投影方向就是最大可能暴露高维数据某类特征结构的投影方向。因此,可以通过求解投影指标函数最大化问题来估计最佳投影方向。目标函数和约束条件分别为
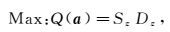 (8)
(8) 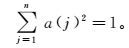 (9)
(9) 这是一个以a={a(1), a(2), a(3), …, a(n)}(|a| =1) 为优化变量的复杂非线性优化问题,用传统的寻优方法比较困难。这里选择基于实数编码的遗传算法来解决此高维全局寻优问题。
4) 对化探样品的分类和异常识别与提取。把第3) 步求得的最佳投影方向a*代入(2) 式后可得到各个化探样品的最佳投影值z*(i),根据z*(i)值的大小来对化探样品进行分类和异常识别与提取。
1.2 基于实数编码的遗传算法RCGA较传统的二进制编码遗传算法具有编码效率高、搜索空间大、计算精度高等特点,其计算具体实现步骤如下[35, 64-70]。
1) 优化变量的实数编码,产生初始种群。在优化变量的取值区间[0, 1],随机生成N组均匀分布的随机变量yi(0)(yi1, yi2, yi3, …, yij, …, yin)(i=1, 2, 3, …, N; j=1, 2, 3, …, n),N为种群规模,n为优化变量的数目,yi(0)表示父代染色体。
2) 计算目标函数值。将步骤1) 中的yi(0)代入目标函数求出对应的函数值,按照函数值由大到小将染色体进行排序,形成yi(1)。
3) 计算基于序的适应度评价函数f的值。设定参数α∈(0, 1),则
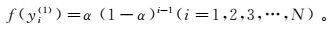 (10)
(10) 4) 选择操作。旋转赌轮N次,得到一个新的种群yi(2),其具体过程表述如下。
① 计算yi(1)中每个染色体yi的累积概率:
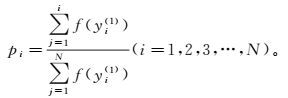 (11)
(11) ② 从区间[0, pi]中产生一个随机数pr,若pi-1<pr≤pi(p0=0),则选择第i个染色体yi。
③ 重复步骤①②,直到有N个染色体被复制,组成新的种群yi(2)。
5) 交叉操作,产生种群yi(3)。定义pc为交叉概率,其具体过程如下。
① 从i=1到N重复:从[0, 1]中产生pr,若pr<pc,则从yi(2)中选择染色体yi用于交叉操作。用y′1, y′2, y′3, …表示选择得到的染色体。
② 将y′1, y′2, y′3, …随机配对:(y′1, y′2), (y′3, y′4), (y′5, y′6), …。
③ 产生随机数λ∈(0, 1),按下列形式在配对染色体y′i和y′j之间进行交叉操作,并产生2个属于种群yi(3)的染色体yi和yj:
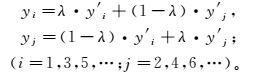 (12)
(12) 6) 变异操作,产生种群yi(4)。定义pm为变异概率,从i=1到N重复:从[0, 1]中产生pr,若pr<pm,则从yi(3)中选择染色体,用y′i表示,进行变异操作,产生属于种群yi(3)的染色体yi:
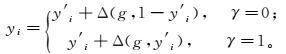 (13)
(13) 式中:γ是值为0或1的随机数;Δ(g, t)=t(1-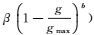
7) 进化迭代。对种群yi(4)按其目标函数值从大到小进行排序,即转入步骤2) 进入下一次进化迭代,重新进行评价、选择、交叉和变异计算,如此循环,直到达到预先设定的终止条件:前面Ne个优秀个体收敛或达到最大进化代数gmax(当达到最大进化代数时终止,考虑寻优结果可能失败,可能需要初始化重新计算)。
1.3 RCGA-PPC模型在MATLAB中的实现基于上述计算原理和建模方法,RCGA-PPC模型在MATLAB中具体实现方法如图 1所示。本文基于MATLAB软件平台开发了用于化探异常识别与提取的RCGA-PPC软件模块(图 2)。该软件模块主要由4个部分构成:数据显示、数据预览、变量选择以及模型参数设置。软件模块左上部分的表格用于显示打开的原始化探数据,左下部分的图形窗口可用于预览选定某个元素含量(即原始数据)的分布特征,右上部分的列表框用于选择RCGA-PPC模型中用到的变量(即元素),右下部分的文本框主要用于输入RCGA-PPC模型中相应的各项参数,如局部密度窗口、种群规模、优秀个体数目、交叉概率、变异概率等。
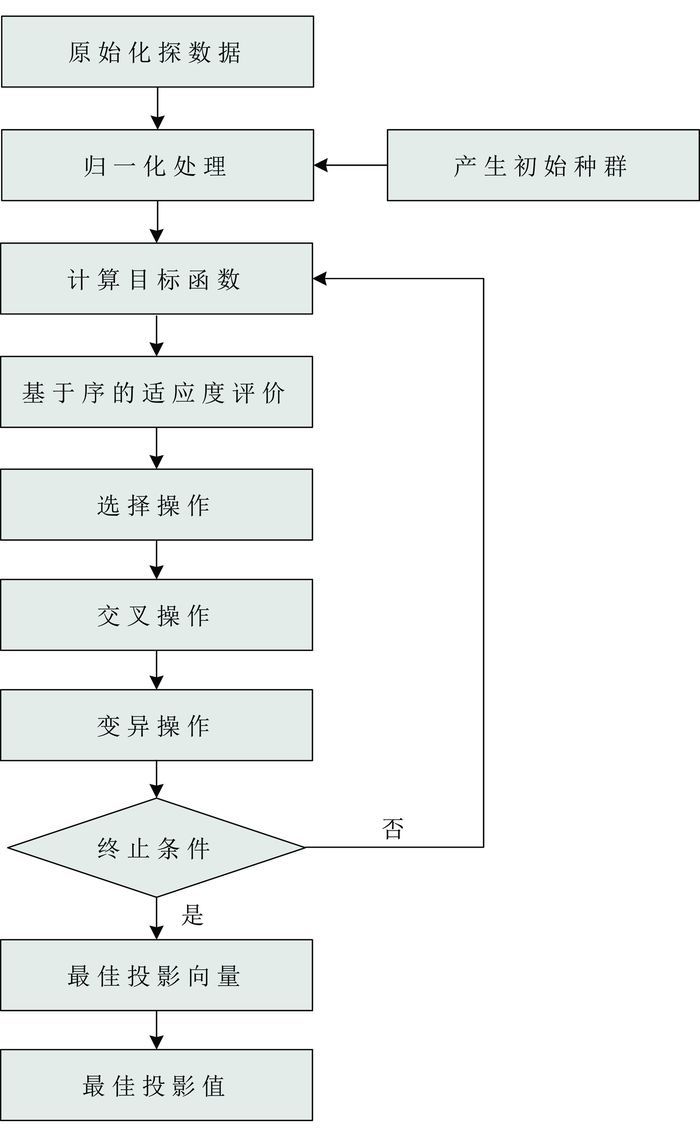
|
| 图 1 用于化探异常识别与提取的RCGA-PPC模型实现的流程图 Figure 1 Flow chart of RCGA-PPC model applying to geochemical anomaly identification and extraction |
|
|
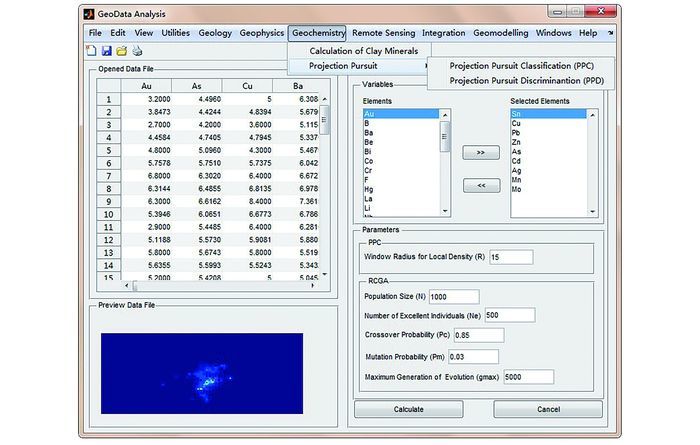
|
| 图 2 基于MATLAB的RCGA-PPC化探异常识别与提取的软件模块 Figure 2 Software package for geochemical anomaly identification and extraction using the RCGA-PPC model based on MATLAB |
|
|
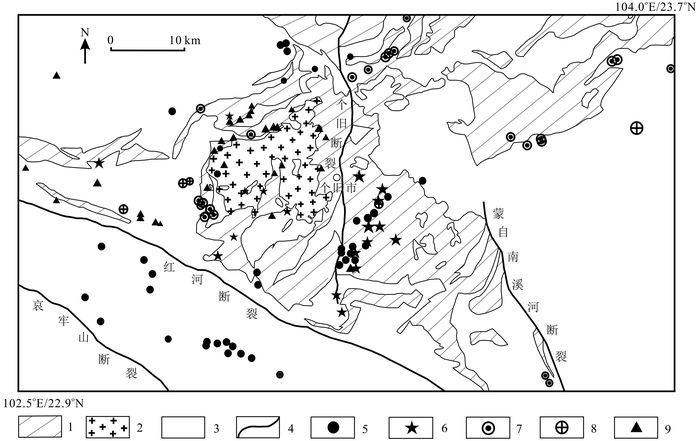
研究区位于云南个旧锡铜多金属矿化集中区,面积约10 920 km2。成矿地质条件较为复杂,不同方向的深大断裂相互交织、叠加,形成了本区复杂的构造格局,使得整个滇东南成矿区处于多条深大断裂的交汇部位[72-73]。区内主要发育哀牢山断裂、红河断裂、个旧断裂和蒙自南溪河断裂等一系列主断裂及其次级断裂构造(图 3)。主要含矿地层为个旧组[72-74]。出露的主要岩体为个旧岩体,与成矿关系密切[73, 75]。
|
| 1.个旧组;2.个旧岩体;3.其他地层;4.断裂;5. Cu矿床(点);6. Sn矿床(点);7. Mn矿床(点);8. Ag矿床(点);9. Pb-Zn矿床(点)。 图 3 云南个旧锡铜多金属成矿区矿产地质略图 Figure 3 Simplified geological map of Sn-Cu polymetallic mineralization district in Gejiu, Yunnan |
|
|
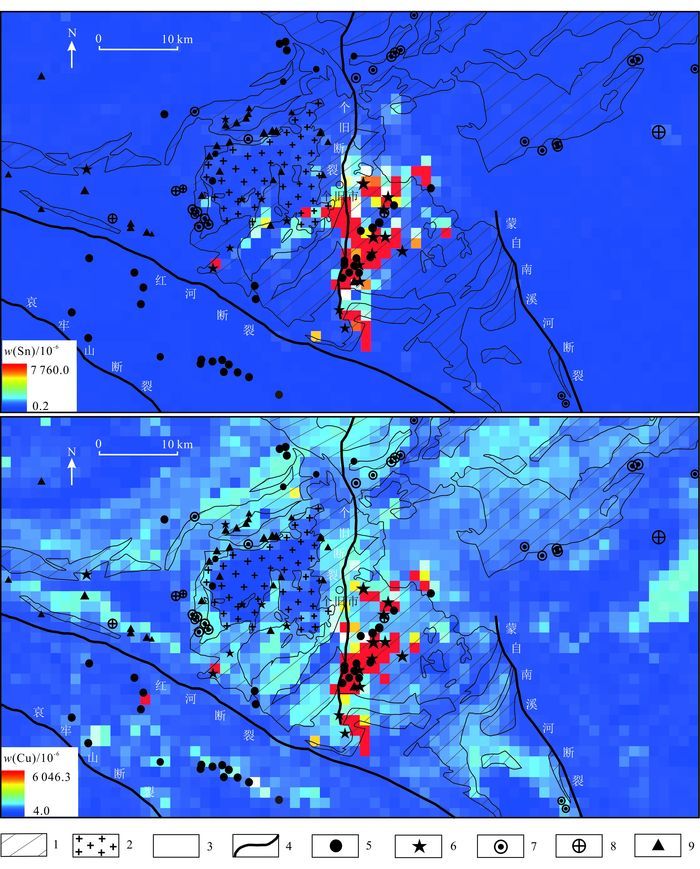
区内共有2 729个1:20万水系沉积物地球化学采样单元,每个采样单元分析了Sn、Cu、Pb、Zn、Mn、Ag、As、Au等39种元素(或氧化物)。在进行化探异常识别和提取时,本文选择了其中2种主要成矿元素Sn、Cu(图 4)以及与成矿关系密切的Pb、Zn、As、Cd等9种主要元素进行计算[72-73, 76-77]。
|
| 1.个旧组;2.个旧岩体;3.其他地层;4.断裂;5. Cu矿床(点);6. Sn矿床(点);7. Mn矿床(点);8. Ag矿床(点);9. Pb-Zn矿床(点)。 图 4 研究区Sn、Cu原始地球化学数据分布图 Figure 4 The raw geochemical data of Sn and Cu in the study area |
|
|
对于RCGA中初始种群规模N、交叉概率pc和变异概率pm等有关参数的选择以及PPC模型中局部密度窗口半径R等参数的确定,付强等[35]进行了系统的总结并做过专门的研究工作,给出了这些参数的经验取值范围;笔者也曾对此做过较为详细的探讨[78]。本文在参考前人应用及给定经验取值范围的基础上[35, 47, 51, 67-69, 71],通过多次试验,选择始种群规模N=1 000,pc=0.85,pm=0.03,gmax=5 000,优秀个体数Ne=500,R=15进行计算。
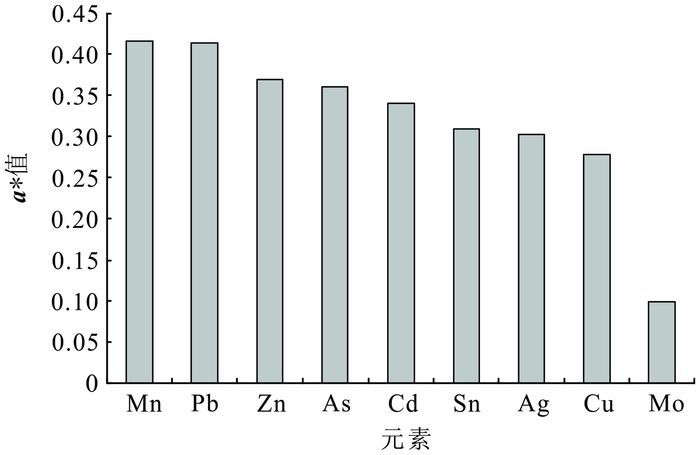
利用RCGA-PPC模型分别对个旧水系沉积物地球化学数据进行处理和异常的识别、提取,得到最佳投影方向向量a*和最佳投影值z*,结果如图 5和图 6所示。
|
| 图 5 RCGA-PPC模型得到的最佳投影方向向量 Figure 5 Projection direction vector in RCGA-PPC model |
|
|
在RCGA-PPC模型得到的a*所反映出的组合元素关系中,Mn、Pb、Zn所对应的a*值较大(图 5),说明这些元素对z*的贡献也较大,而Sn和Cu两种主要成矿元素所对应的值较小,其相应的对z*的贡献也变小。可以认为该方法有效地增强了除Sn、Cu两种主要成矿元素以外其他与成矿有关的元素(组合)(如Mn、Pb、Zn等元素)所引起的异常,如个旧岩体西侧和北侧主要分布Mn、Pb-Zn矿床(点)的区域(图 4)。由图 6可以看出,RCGA-PPC模型中z*值较高的地区与该区域实际矿床(点)吻合情况较好。除个旧岩体东侧个旧断裂附近具有明显的高z*异常外,在个旧岩体的北侧、西侧、南侧及其他一些在原始地球化学数据分布图中有具弱异常或无异常的区域(如图 6中A、B、C和D等区域),也明显现出一定强度和一定范围的局部高z*异常。

|
| 1.个旧组;2.个旧岩体;3.其他地层;4.断裂;5. Cu矿床(点);6. Sn矿床(点);7. Mn矿床(点);8. Ag矿床(点);9. Pb-Zn矿床(点)。 图 6 研究区RCGA-PPC模型得到的最佳投影值 Figure 6 Projection values calculated by the RCGA-PPC model in the study area |
|
|
进行化探异常识别与提取时,首先结合成矿地质特征,选取针对某一特定勘查区域有效的化探指示元素(组合),即,挑选具有明显地质意义的元素组合,这样既使得后续使用RCGA-PPC模型进行化探数据处理结果的地质意义更明显,有效避免了化探数据处理的盲目性,同时也减少了数据量,提高了数据处理的效率。在此基础上,将RCGA-PPC模型用于化探异常识别,这样可以较为准确地提取出综合地球化学异常。本文以云南个旧地区1:20万的水系沉积物地球化学数据为例,系统分析了利用RCGA-PPC模型进行化探异常识别与提取的过程,并在MATLAB软件平台上实现了该方法,且取得了较好的效果。由此可知:PPC模型有可能成为一种新的并且有效的化探多元素综合异常识别与提取方法,开辟了一种新的综合识别找矿信息的方法。
当然,本文将RCGA-PPC模型用于化探数据处理和异常识别中,还是一种初步的尝试和探讨,一些参数的选择,如局部密度的窗口半径等,笔者和前人都曾做过有益的探讨研究,但是,目前尚缺乏理论计算依据,通常情况下,主要是参考前人研究的经验值范围和通过多次试验以获得较为可靠的参数。因此,将RCGA-PPC模型用于化探数据处理和异常识别可能还需要对这些问题进行更为细致的研究,这样RCGA-PPC模型用于化探数据处理和异常识别的效果可能会更好。在实际应用RCGA-PPC模型进行化探异常提取时,为了合理确定最佳投影值的异常下限,至少可以考虑运用以下2种方法:其一为比较传统的异常下限划分方法,即μ±nσ(μ和σ分别为最佳投影值的均值和方差);这种方法比较简单易用,往往也可以取得比较好的效果,因为经过投影变换之后,一般最佳投影值会很接近正态分布[26, 78]。另一种比较有效的方法就是利用t统计量分析最佳投影值与已知矿床(点)之间空间相关性的大小来划分异常下限[26-27];与前者相比,这种方法的计算过程相对复杂些,但结果通常较前者更合理。
致谢: 云南省地质调查院提供了文中使用的水系沉积物地球化学数据,在此表示感谢。| [1] | David M, Campiglio C, Darling R. Progress in R-and Q-Mode Analysis: Correspondence Analysis and Its Application to the Study of Geological Processes[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1974, 13(1): 131-146. |
| [2] | Armour B A, Olesen B L. Condensing Multi-Element Reconnaissance Geochemical Data from South Greenland Using Empirical Discriminant Analysis[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1984, 21(1/2/3): 395-404. |
| [3] | Castillo M R, Howarth R J. Application of the Empirical Discriminant Function to Regional Geochemical Data from the United Kingdom[J]. Geological Society of America, 1976, 87(11): 1567-1581. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1976)87<1567:AOTEDF>2.0.CO;2 |
| [4] |
黄意信. 相似性判别分析方法[J].
地质与勘探, 1975, 8: 56-68.
Huang Yixin. The Discriminant Analysis Method Based on Similarity[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1975, 8: 56-68. |
| [5] |
赵鹏大, 胡旺亮, 李紫金.
矿床统计预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994.
Zhao Pengda, Hu Wangliang, Li Zijin. Statistical Prediction for Mineral Deposits[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. |
| [6] |
罗长清. 聚类分析在某地化探异常评价中的应用效果[J].
物化探计算技术, 1984, 6(1): 77-80.
Luo Changqing. Application of the Cluster Analysis to the Evaluation of the Geochemical Prospecting Anomalies[J]. Computation Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1984, 6(1): 77-80. |
| [7] | Ji H J, Zeng D M, Shi Y X, et al. Semi-Hierarchical Correspondence Cluster Analysis and Regional Geochemical Pattern Recognition[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 93(2): 109-119. DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2006.10.002 |
| [8] |
陈永良, 李学斌. 基于核函数理论的系统聚类分析[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(5): 1211-1216.
Chen Yongliang, Li Xuebin. Kernel-Based Hierarchical Cluster Analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(5): 1211-1216. |
| [9] |
陈永良, 路来君, 李学斌. 多元地球化学异常识别的核马氏距离方法[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1): 396-408.
Chen Yongliang, Lu Laijun, Li Xuebin. Kernel Mahalanobis Distance for Multivariate Geochemical Anomaly Recognition[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(1): 396-408. |
| [10] | Gordon A D. A Review of Hierarchical Classification[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1987, 150(2): 119-137. DOI:10.2307/2981629 |
| [11] | Cormack R M. A Review of Classification[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1971, 134(3): 321-367. DOI:10.2307/2344237 |
| [12] | Hartigan J A, Wong M A. A K-Means Clustering Algorithm[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1979, 28(1): 100-108. |
| [13] | Cheng Q M, Agterberg F P, Ballantyne S B. The Separation of Geochemical Anomalies from Background by Fractal Methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51(2): 109-130. DOI:10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2 |
| [14] |
成秋明. 多维分形理论和地球化学元素分布规律[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25(3): 311-318.
Cheng Qiuming. Multifractal Theory and Geochemical Element Distribution Pattern[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 25(3): 311-318. |
| [15] | Xiao F, Chen J G. Fractal Projection Pursuit Classification Model Applied to Geochemical Survey Data[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2012, 45: 75-81. |
| [16] | Zhang L P, Bai G P, Xu Y X. A Wavelet-Analysis-Based New Approach for Interference Elimination in Geochemical Hydrocarbon Exploration[J]. Mathematical Geology, 2003, 35(8): 939-952. DOI:10.1023/B:MATG.0000011587.46835.f8 |
| [17] | Su S, Mcardle B H, Rodgers K A, et al. Wavelet Analysis of Variations in Geochemical and Microfossil Data Across the Cretaceous/Tertiary Boundary at Flaxbourne River, New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 2003, 46(2): 199-208. DOI:10.1080/00288306.2003.9515004 |
| [18] | Zhang L P, Ruan T J. Application of Wavelet Analysis to Interference Elimination for Geochemical Hydrocarbon Exploration[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 11(1): 89-91. |
| [19] |
黄厚辉, 郭科, 唐菊兴. 基于小波多尺度分析的异常下限确定方法[J].
地质找矿论丛, 2007, 22(4): 311-313.
Huang Houhui, Guo Ke, Tang Juxing. The Wavelet Theory-Based Multi-Scale Analysis Method to Determine the Lower Limit of Element Geochemical Anomalies[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2007, 22(4): 311-313. |
| [20] |
陈建国, 夏庆霖. 利用小波分析提取深层次物化探异常信息[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 1999, 24(5): 509-512.
Chen Jianguo, Xia Qinglin. Wavelet-Based Extraction of Geophysical and Geochemical Anomaly Information[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1999, 24(5): 509-512. |
| [21] |
李庆谋, 成秋明. 分形奇异(特征)值分解方法与地球物理和地球化学异常重建[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(1): 109-118.
Li Qingmou, Cheng Qiuming. Fractal Singular-Value (Egin-Value) Decomposition Method for Geophysical and Geochemical Anomaly Reconstruction[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(1): 109-118. |
| [22] | Cheng Q M. Mapping Singularities with Stream Sediment Geochemical Data for Prediction of Undiscovered Mineral Deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1): 314-324. |
| [23] | Cheng Q M, Agterberg F P. Singularity Analysis of Ore-Mineral and Toxic Trace Elements in Stream Sediments[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2009, 35(2): 234-244. |
| [24] |
成秋明. 多重分形与地质统计学方法用于勘查地球化学异常空间结构和奇异性分析[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2001, 26(2): 161-166.
Cheng Qiuming. Multifractal and Geostatistic Methods for Characterizing Local Structure and Singularity Properties of Exploration Geochemical Anomalies[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2001, 26(2): 161-166. |
| [25] |
陈志军. 多重分形局部奇异性分析方法及其在矿产资源信息提取中的应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2007
Chen Zhijun. Multifractal Theory Based Local Singularity Analysis Method and Its Application in Spatial Information Extraction for Mineral Exploration[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2007. |
| [26] | Xiao F, Chen J G, Zhang Z Y, et al. Singularity Mapping and Spatially Weighted Principal Component Analysis to Identify Geochemical Anomalies Associated with Ag and Pb-Zn Polymetallic Mineralization in Northwest Zhejiang, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 122: 90-100. DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.04.010 |
| [27] | Xiao F, Chen J G, Agterberg F P, et al. Element Behavior Analysis and Its Implications for Geochemical Anomaly Identification: A Case Study for Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposits in Eastern Tianshan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 145: 1-11. DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.04.008 |
| [28] | Xie S Y, Cheng Q M, Ke X Z, et al. Identification of Geochemical Anomaly by Multifractal Analysis[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 19(4): 334-342. DOI:10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60066-7 |
| [29] |
张生元, 黄锐, 徐德义, 等. 非负矩阵分解方法在水系沉积物地球化学数据处理中应用[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(2): 347-352.
Zhang Shengyuan, Huang Rui, Xu Deyi, et al. Application of Non-Negative Matrix Factorization in Stream Sediment Geochemical Data Processing[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(2): 347-352. |
| [30] | Heslop D, Dobeneck T V, Höcker M. Using Non-Negative Matrix Factorization in The "Unmixing" of Diffuse Reflectance Spectra[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 241(1): 63-78. |
| [31] |
陈建国, 肖凡, 陈志军, 等. 希尔伯特-黄变换与独立分量分析在深层次找矿信息提取中的应用[C]//地球资源环境定量化理论与应用. 广州: 中山大学, 2009: 195
Chen Jianguo, Xiao Fan, Chen Zhijun, et al. Hilbert-Huang Transformation and Independent Component Analysis Applied in Deep Mineralization Associated Geoinformation Extraction[C]//Quantitative Theory and Applications for Earth Resources and Environment. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2009: 195. |
| [32] |
连盈盈. 盲提取在地球化学异常识别中的应用[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009
Lian Yingying. BSE Applied to Distinguish Geochemical Anomaly from Background[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009. |
| [33] | Jimenez L O, Landgrebe D A. High Dimensional Feature Reduction Via Projection Pursuit[C]//Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 1994. California: IEEE, 1995: 1145-1147. |
| [34] | Friedman J H. Exploratory Projection Pursuit[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1987, 82(1): 249-266. |
| [35] |
付强, 赵小勇.
投影寻踪模型原理及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
Fu Qiang, Zhao Xiaoyong. The Principles and Applications of Project Pursuit Model[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. |
| [36] | Friedman J H, Stuetzle W, Schroeder A. Projection Pursuit Density Estimation[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1984, 79(387): 599-608. DOI:10.1080/01621459.1984.10478086 |
| [37] | Huber B P. Projection Pursuit[J]. The Annals Statistics, 1985, 13(2): 435-475. DOI:10.1214/aos/1176349519 |
| [38] | Flick T E, Jones L K, Priest R G, et al. Pattern Classification Using Projection Pursuit[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1990, 23(12): 1367-1376. DOI:10.1016/0031-3203(90)90083-W |
| [39] | Friedman J H, Tukey J W. A Projection Pursuit Algorithm for Exploratory Data Analysis[J]. IEE Transactions on Computers, 1974, 23(9): 881-890. |
| [40] | Friedman J H. A Recursive Partitioning Decision Rule for Nonparametric Classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 1977, 26(4): 404-408. |
| [41] | Jimenez L O, Landgrebe D A. Hyperspectral Data Analysis and Supervised Feature Reduction via Projection Pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(6): 2653-2667. DOI:10.1109/36.803413 |
| [42] | Jimenez L O, Landgrebe D A. Unsupervised Classification in High Dimensional Space: Geometrical, Statistical, and Asymptotical Properties of Multivariate Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on System Man and Cybernetics: Part C:Applications and Reviews, 1998, 28(1): 39-54. DOI:10.1109/5326.661089 |
| [43] | Lee E, Cook D, Klinke S, et al. Projection Pursuit for Exploratory Supervised Classification[J]. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2005, 14(4): 831-846. DOI:10.1198/106186005X77702 |
| [44] | Fu Q, Fu H. Application of PPE Model Based on RAGA in the Investment Decision-Making of Water Saving Irrigation Project[J]. Nature and Science, 2003, 1(1): 57-61. |
| [45] |
肖长来, 危润初, 梁秀娟, 等. 基于投影寻踪聚类模型的龙坑水源地地下水水质评价[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(增刊1): 248-252.
Xiao Changlai, Wei Runchu, Liang Xiujuan, et al. Assessment of Water Quality of Groundwater in Longkeng Based on Projection Pursuit Cluster Model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(Sup.1): 248-252. |
| [46] | Fu Q, Zu W. Study on PPE Model Based on RAGA to Evaluation the Water Quality[J]. Nature and Science, 2004, 2(4): 8-34. |
| [47] |
王顺久. 水资源开发利用综合研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2003
Wang Shunjiu. Research on the Utilization of Water Resources[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2003. |
| [48] | Wang S J, Yang Z F, Ding J. Projection Pursuit Cluster Model and Its Application in Water Quality Assessment[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 16(6): 994-995. |
| [49] | Zhang C, Dong S. A New Water Quality Assessment Model Based on Projection Pursuit Technique[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(Sup.1): S154-S157. |
| [50] |
舒栋才, 樊明兰, 林三益. 基于免疫进化算法的投影寻踪聚类及其在地下水动态分类中的应用[J].
四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2004, 36(1): 15-18.
Shu Dongcai, Fan Minglan, Lin Sanyi. Applying Projection Pursuit Cluster Based on Immune Evolutionary Algorithmin Groundwater Regime Classification[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2004, 36(1): 15-18. |
| [51] |
付强, 金菊良, 梁川. 基于实码加速遗传算法的投影寻踪分类模型在水稻灌溉制度优化中的应用[J].
水利学报, 2002, 33(10): 39-45.
Fu Qiang, Jin Juliang, Liang Chuan. Application of Projection Pursuit Model to Optimize Paddy Irrigation Schedule[J]. Shuili Xuebao, 2002, 33(10): 39-45. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2002.10.007 |
| [52] |
张军, 梁川, 赵燮京, 等. 基于RAGA的PPC模型在节水灌溉多方案择优中的应用[J].
中国农村水利水电, 2006, 12: 13-15.
Zhang Jun, Liang Chuan, Zhao Xiejing, et al. Application of PPC Model Based on RAGA in the Water-Saving Irrigation Scheme Selection[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2006, 12: 13-15. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2006.12.004 |
| [53] | Trizna D B, Bachmann C, Sletten M, et al. Projection Pursuit Classification of Multiband Polarimetric SAR Land Images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(11): 2380-2386. DOI:10.1109/36.964974 |
| [54] | Chiang S S, Chang C I, Ginsberg I W. Unsupervised Target Detection in Hyperspectral Mages Using Projection Pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(7): 1380-1391. DOI:10.1109/36.934071 |
| [55] | Ifarraguerri A, Chang C I. Unsupervised Hyperspe-ctral Image Analysis with Projection Pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(6): 2529-2538. DOI:10.1109/36.885200 |
| [56] |
林伟, 田铮. 极化SAR图像的聚类序列投影寻踪模型方法[J].
电波科学学报, 2006, 21(5): 682-686.
Lin Wei, Tian Zheng. Sequential Projection Pursuit Clustering Model for POL-SAR Data Unsupervised Classification[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2006, 21(5): 682-686. |
| [57] |
谷复光, 王清, 张晨. 基于投影寻踪与可拓学方法的泥石流危险度评价[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(2): 373-377.
Gu Fuguang, Wang Qing, Zhang Chen. Debris Flow Risk Assessment by PPC and Extenics[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(2): 373-377. |
| [58] |
倪长健, 王顺久, 丁晶. 边坡稳定性评价的投影寻踪聚类模型[J].
岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(16): 2687-2689.
Ni Changjian, Wang Shunjiu, Ding Jing. Projection Pursuit Cluster Model for Slope Stability Evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(16): 2687-2689. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.005 |
| [59] |
王园, 王沁, 何蕴龙, 等. 西安地裂与地面沉降灾害投影寻踪分析预测[J].
工程地质学报, 1999, 7(1): 30-34.
Wang Yuan, Wang Qin, He Yunlong, et al. Analysis and Prediction of Ground Fractures and Surface Subsidence Hazard in Xi'an City Using Projection Tracing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1999, 7(1): 30-34. |
| [60] |
王琼, 朱令人. 投影寻踪聚类在新疆地震预报中的应用[J].
内陆地震, 2005, 19(1): 8-15.
Wang Qiong, Zhu Lingren. Application of the Projection Pursuit Cluster on the Earthquake Prediction in Xinjiang[J]. Inland Earthquake, 2005, 19(1): 8-15. |
| [61] | Jiang F Z, Yang X F. The Application of Projection Pursuit Classification in the Process of Strategy Selection and Evaluation Based on the Real Coded Accelerating Genetic Algorithm[J]. Chinese Business Review, 2008, 7(1): 41-45. |
| [62] |
舒栋才. 基于免疫进化算法的投影寻踪聚类在公司债券财务质量评级中的应用[J].
计算机工程与应用, 2004, 40(15): 226-229.
Shu Dongcai. Applying PPC based on IEA in Enterprises Bond Financial Quality Evaluation Grading[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2004, 40(15): 226-229. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2004.15.070 |
| [63] | Demirci O, Clark V P, Calhoun V D. A Projection Pursuit Algorithm to Classify Individuals Using FMRI Data: Application to Schizophrenia[J]. NeuroImage, 2008, 39(4): 1774-1782. DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.012 |
| [64] |
周明, 孙树栋.
遗传算法原理及其应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2000.
Zhou Ming, Sun Shudong. The Principles and Applications of Genetic Algorithms[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2000. |
| [65] | Munteanu C, Lazarescu V. Improving Mutation Capabilities in a Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the First European Workshops on Evolutionary Image Analysis, Signal Processing and Telecommunications. Sweden: Springer-Verlag, 1999: 138-149. |
| [66] | Kaelo P, Ali M M. Integrated Crossover Rules in Real Coded Genetic Algorithms[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 176(1): 60-76. DOI:10.1016/j.ejor.2005.07.025 |
| [67] | Deep K, Thakur M. A New Crossover Operator for Real Coded Genetic Algorithms[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, 188(1): 895-911. DOI:10.1016/j.amc.2006.10.047 |
| [68] | Blanco A, Delgado M, Pegalajar M C. A Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm for Training Recurrent Neural Networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2001, 14(1): 93-105. DOI:10.1016/S0893-6080(00)00081-2 |
| [69] | Deep K, Thakur M. A New Mutation Operator for Real Coded Genetic Algorithms[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, 193(1): 211-230. DOI:10.1016/j.amc.2007.03.046 |
| [70] | Ha J, Kung Y, Fung R, et al. A Comparison of Fitness Functions for the Identification of a Piezoelectric Hysteretic Actuator Based on the Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2006, 132(2): 643-650. DOI:10.1016/j.sna.2006.02.022 |
| [71] | Fu Q, Xie Y G, Wei Z M. Application of Projection Pursuit Evaluation Model Based on Real-Code Acceleration Genetic Algorithm in Evaluation Wetland Soil Quality Variations in the Sanjiang, China[J]. Pedosphere, 2003, 13(3): 249-256. |
| [72] |
成秋明, 赵鹏大, 陈建国, 等. 奇异性理论在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用:成矿弱信息提取和复合信息分解[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(2): 232-242.
Cheng Qiuming, Zhao Pengda, Chen Jianguo, et al. Application of Singularity Theory in Prediction of Tin and Copper Mineral Deposits in Gejiu District, Yunnan, China: Weak Information Extraction and Mixing Information Decomposition[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(2): 232-242. |
| [73] |
薛传东. 个旧超大型锡铜多金属矿床时空结构模型[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2002
Xue Chuandong. The Space-Time Structure Model of the Gejiu Superlarge Tin-Copper-Polymetallic Deposit[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2002. |
| [74] |
陈守余, 赵鹏大, 张寿庭, 等. 个旧超大型锡铜多金属矿床成矿多样性与深部找矿[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(2): 319-324.
Chen Shouyu, Zhao Pengda, Zhang Shouting, et al. Mineralizing Multiformity and Deep Prospecting of Gejiu Super Sn-Cu Multi-metal Deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(2): 319-324. |
| [75] |
徐启东, 夏庆霖, 成秋明. 云南个旧矿集区区域构造-岩浆演化与锡铜多金属成矿系统[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(2): 307-313.
Xu Qidong, Xia Qinglin, Cheng Qiuming. Tectonic-Magmatic Evolution Related to Metallogenic System in Gejiu Ore-Concentration Area, Southeast Yunnan of China[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(2): 307-313. |
| [76] |
贾润幸. 云南个旧锡矿集中区地质地球化学研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2005
Jia Yunxing. The Geological and Geochemical Research on Gejiu Tin-Polymetallic District, Yunan[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2005. |
| [77] |
秦德先, 黎应书, 范柱国, 等. 个旧锡矿地球化学及成矿作用演化[J].
中国工程科学, 2006, 8(1): 30-39.
Qin Dexian, Li Yingshu, Fan Zhuguo, et al. The Geochemistry and Mineralization Evolvement of Gejiu Tin Ore Deposits[J]. Engineering Science, 2006, 8(1): 30-39. |
| [78] |
肖凡. 基于RAGA的PPC模型在个旧化探资料处理中的应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2008
Xiao Fan. Study of PPC Model Based on RAGA and Its Application for Geochemical Data Processing in Gejiu[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2008. |


