0 引言
中亚造山带是全球最大的显生宙增生型造山带与大陆成矿域[1-3], 其东部除了受古亚洲洋构造域影响外, 后期还叠加蒙古—鄂霍茨克 (Mongolia-Okhotsk) 构造体制和古太平洋板块 (曾用名Pacific/Izanagi plate) 体制作用, 构造演化独特, 形成了丰富的矿产资源, 并受到广泛关注。矿床作为有效的地球动力学研究探针[4], 也吸引了不同学者从成矿视角进行研究。有学者提出中国东部中生代大规模成矿背景经历了后碰撞造山、构造体制大转折和岩石圈大规模快速减薄[5]; 有学者强调汇聚造山作用的成矿意义[6-7], 认为钼矿主要形成于增生造山和大陆碰撞造山背景[8]; 有学者从矿床类型[9-10]入手, 认为大洋板片部分熔融是斑岩型铜钼矿的主导因素[11], 并将埃达克质岩作为寻找铜金的标志[12]; 也有学者着眼于火山岩[13]、成矿带[14-15], 或典型矿种[16-17], 对中生代局部区域进行更细致的限定。
目前, 国内有关中亚造山带东部成矿特征的研究成果很多, 但大都集中在中国境内; 而对于成矿的研究也多集中于中生代成矿作用, 对古生代成矿作用及成矿作用的长期演化讨论较少。本文收集了过去15年中亚造山带东部, 包括境外, 公开发表的岩浆热液矿床 (包括部分以岩浆热液主导的多成因矿床) 的同位素年龄数据, 以构造单元为基础, 以地质时代为框架, 力求探讨不同时代的成矿分布特征, 为深入分析该地区多种构造体制下长期演化的成矿历史和发育规律及其成矿地球动力学背景提供依据。
1 构造背景中亚造山带东部包括境外蒙古、俄罗斯远东及中国境内的黑龙江—吉林和部分内蒙古—甘肃。构造单元从东到西以断层为界, 划分为:布列亚—佳木斯古陆块 (包含松嫩—张广才岭地块、布列亚地块、佳木斯地块和兴凯地块等中间地块)、南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系 (包含兴安—南蒙古地块和喀拉塔格—旱山地块等中间地块)、萨彦岭—贝加尔造山系 (包含额尔古纳—中蒙古地块、喀拉塔格—旱山地块和阿尔泰—蒙古地块等中间地块)、蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带和中朝古陆北部增生边缘 (本文仅限于辽远地块, 也称白乃庙岛弧带)(图 1)[18-23]。作为南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系和萨彦岭—贝加尔造山系分界的蒙古弧形断裂 (曾用名阿勒泰—满洲里断裂带[172]), 自西到东由蒙古境内戈壁天山断层体系和东戈壁断层带[173](也有学者称之为蒙古主要线性构造[174]), 以及中国境内得尔布干断裂[175]组成。
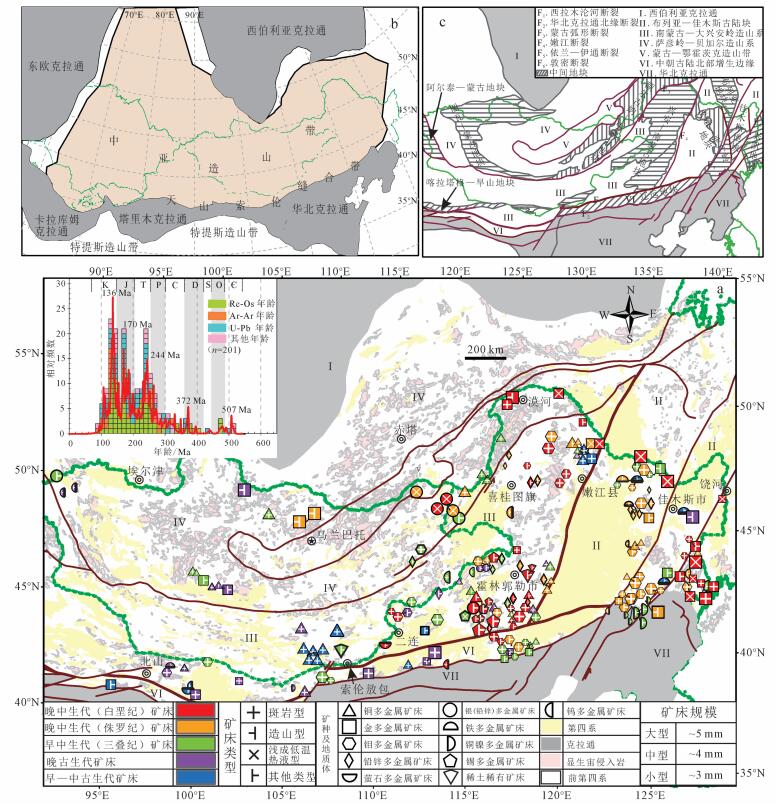
|
| a.据文献[18-20]修编, 部分参考"973"计划"兴蒙造山带构造叠合与大规模成矿作用"项目 (2013CB429800)2015年汇报成果, 其左上角为显生宙矿床成矿年龄直方图 (数据来源和矿床类型详见表 1); b.据文献[169]修编; c.据文献[18-19]修编, 部分中间地块参考[170-171]。 图 1 中亚造山带东部显生宙岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a)、中亚造山带示意图 (b) 及中亚造山带东部构造分区示意图 (c) Figure 1 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution of the Phanerozoic in eastern Central Asian orogenic belt (ECAOB) (a), sketch map of Central Asian orogenic belt (b) and sketch map of tectonics division in ECAOB (c) |
|
|
|
① 曾庆栋.古太平洋构造体系叠加成矿作用2015年“973”计划项目(2013CB429800)汇报成果.北京:北京大学,2015.
① 江思宏.大型金属矿床成矿潜力评估与战略新区预测2015年“973” 计划项目(2013CB429800)汇报成果.北京:北京大学,2015.
① 赵元艺.黑龙江多宝山矿集区2015年“973”计划项目(2013CB429800)汇报成果.北京:北京大学,2015.
① 佘宏全.大兴安岭中北段中生代多金属矿成矿系统研宂2015年“973”计划项目(2013CB429800)汇报成果.北京:北京火学,2015.
① 赵元艺.黑龙江多宝山矿集区2015年“973”计划项目(2013CB429800)汇报成果.北京:北京大学,2015.
中亚造山带东部古亚洲洋形成于新元古代—晚寒武世, 奥陶纪—志留纪处于扩张期, 其中佳木斯地块、松嫩地块和额尔古纳地块自早古生代从西向东依次碰撞, 在晚志留世形成佳蒙地块 (阿穆尔地块), 早泥盆世内蒙古东南部、松辽盆地、佳木斯及俄罗斯的布列亚等地区连为一体[176]。晚古生代 (石炭纪—二叠纪) 构造背景一直存有争议:一种观点认为, 经过连续俯冲增生, 到二叠纪沿着天山—北山—索伦克尔古亚洲洋闭合[173]; 另一种观点认为, 古亚洲洋于泥盆纪闭合[3], 到晚古生代再打开, 形成小洋盆, 早中生代再闭合, 其中, 晚二叠世后古亚洲洋闭合进入板内阶段[177]。多数观点倾向于东亚在晚二叠—早三叠世[178]沿着索伦山—西拉木伦河缝合带自西到东闭合[179-180]。
在早中生代期间, 蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋俯冲闭合, 对大兴安岭特别是北段有影响[181-182]; 晚中生代古太平洋板块向西俯冲[183-184], 中亚造山带经历了侏罗纪多向汇聚造山及其地壳加厚[185]和早白垩世巨量的伸展垮塌[186-187], 这些都主导着区域性的构造、岩浆及成矿作用[173, 175, 180, 188]。
2 数据来源及评价本文收集1 300个矿床, 整理出20002014年公开发表的所有岩浆热液矿床约1 200个同位素年龄数据 (包括同一矿床不同测试方法数据), 从中剔除查不到原始文献和实验测定早于2000年 (除蒙古巴彦洪戈尔4个同位素数据) 的数据, 仅选择与赋矿围岩年龄相近的矿石矿物Re-Os[189]及蚀变矿物40Ar/39Ar数据[190], 和可信度高的锆石U-Pb数据[191-192]及个别其他方法测试数据来限定矿床年龄。最终, 筛选出193个矿床的201个较可靠的年龄数据作为研究对象 (表 1)。
3 成矿作用发育特征本文采用Isoplot4.15[193]进行数据分析, 结果显示, 中亚造山带东部前寒武纪矿床极少 (图 1), 目前缺乏精确同位素年代学研究, 这也可能与后期构造岩浆事件破坏有关。显生宙成矿作用始于晚寒武世, 自晚泥盆世连续成矿, 显示多期次、多阶段特征, 出现6个重要成矿期:古生代早期 (510~473 Ma)、古生代中期 (373~330 Ma)、古生代晚期 (320~253 Ma)、早中生代 (250~210 Ma)、晚中生代早期 (210~167 Ma)、晚中生代晚期 (155~100 Ma), 有5个明显的峰值:507、372、244、170和136 Ma (图 1)。下面以地质时代为序分别论述成矿特点。
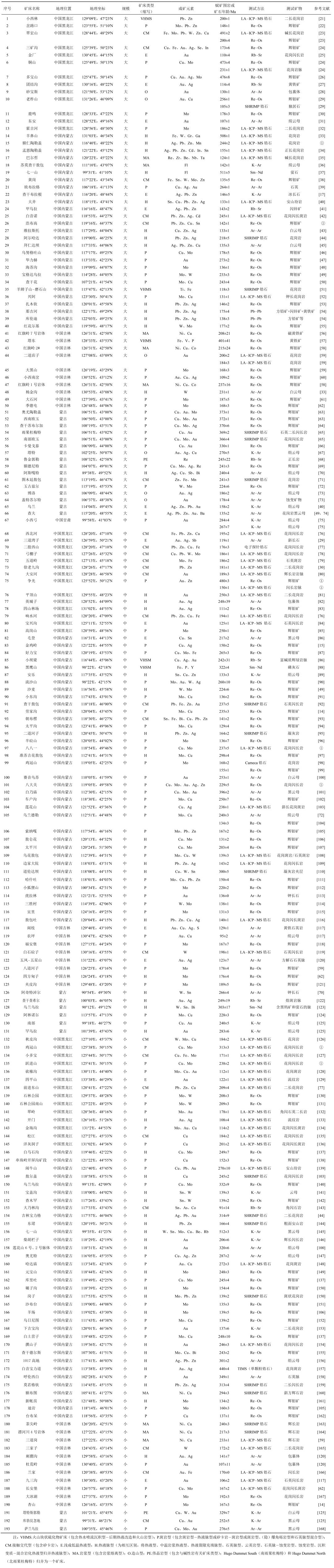
3.1 早—中古生代成矿特点早—中古生代矿床呈点状分布, 以数量少、资源量大、时空分布不连续不均一和多金属成矿为特征。矿床规模以大型超大型矿床为主 (占同期矿床的73%), 矿床类型以热液脉型和斑岩型铁矿铜矿床为主 (图 2)。
|
| 图 2 中亚造山带东部早—中古生代岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a) 及矿床成矿年龄相对频数分布图 (b) Figure 2 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution (a) and mineralization age probability plot of the Early-Middle Paleozoic in ECAOB (b) |
|
|
早古生代发育7个大型铁铜金钨等多金属矿和萤石矿, 呈点状分布, 以矿集区的形式出露在南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系的兴安地块南—北缘和喀拉塔格—旱山地块的北山、布列亚—佳木斯古陆的小兴安岭—张广才岭和佳木斯地块 (图 2a), 成矿作用集中在512~473 Ma, 有3个峰值 (507、490和478 Ma)(图 2b), 矿床类型主要为热液脉型和斑岩型, 均经历了后期热液改造富集。其中, 北山地区七一山矿集区成矿类型为热液脉型, 赋矿岩体存在明显成矿元素分带特征, 从中心向外依次为铷-钨-钼、锡-铁-铜-萤石[194]。钨锡钼矿体主要赋存在似斑状花岗岩体, 萤石主要赋存在黑云母花岗岩, 两类同期 (~512 Ma)[145]花岗岩很好地限定了成矿年龄, 并经历了泥盆纪晚期强烈岩浆改造[194]。佳木斯地块羊鼻山矿集区为沉积变质-热液改造型的铁钨矿, 贫铁矿主要赋存在兴东群大盘道组磁铁石英岩, 富铁钨矿体产于混合岩化片麻状花岗岩与大盘道组碳酸盐岩的接触带, 暗示了后期混合岩化热液作用 (~508 Ma) 对矿体再富集起了关键性作用[33]。小兴安岭矽卡岩型翠宏山矿集区有两期矿化被记录, 铁矿赋存在早古生代碱性花岗岩 (~491 Ma) 和灰岩接触带, 而早侏罗世在矽卡岩接触带又叠加了后期热液作用形成铅锌 (铜) 和钨钼矿[23]。兴安陆块北缘的大兴安岭多宝山矿集区, 主要赋矿围岩为花岗闪长岩和花岗闪长斑岩, 矿石中的辉钼矿Re-Os年龄很好地限定了争光热液型金矿床和铜山多宝山斑岩型铜钼矿床形成于480~473 Ma[26], 侏罗纪又经历了后期热液作用, 形成争光浅部金矿和三矿沟铁铜矿[24]。
3.1.2 泥盆纪成矿特点泥盆纪成矿作用集中在早、晚泥盆世, 有两个峰值 (395和372 Ma), 而中泥盆世是成矿"寂静期"(图 2b), 矿床分布在辽远地块、佳木斯地块以南的张广才岭和南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系的南蒙古岛弧带。其中, 早泥盆世塔东铁矿为海底火山喷流沉积-变质热液改造型, 铁矿赋存在塔东岩群上段的拉拉沟组, 围岩限定成矿年龄为450~426 Ma, 而401 Ma被认为矿体富集时代[195]。白乃庙铜金矿区是辽远地块金属成矿带的重要组成部分, 产出有白乃庙金矿21号脉、26号脉, 铜矿5号矿体和铜钼金矿 (南、北矿带), 富矿石产于花岗闪长斑岩边缘接触带, 从地表到深部, 斑岩型矿体逐渐向绿片岩型矿体过渡; 有学者通过矿石中云母的Ar-Ar年龄和低盐度、低密度和富CO2流体包裹体研究, 强调白乃庙铜金矿区具有早泥盆世造山型成矿特征[196]; 也有学者认为是早志留世华北板块北缘"沟、弧、盆"体系演化和陆缘增生的产物, 并经历了泥盆纪含矿流体富集改造[101]。
晚泥盆世最具代表性的矿产是发育于南蒙的世界性著名超大型奥尤陶勒盖铜金矿区和查干苏布尔加铜钼矿床。矿石辉钼矿Re-Os年龄限定矿床形成于373~366 Ma。该矿带北东延伸数公里, 赋矿围岩石英二长闪长岩、二长花岗斑岩和花岗闪长斑岩与铜金钼矿化存在密切的时空关系, 为铜金钼成矿提供了主要成矿物质和流体来源, 地质构造、蚀变、同位素都指示了一个典型的斑岩成矿体系[63]。
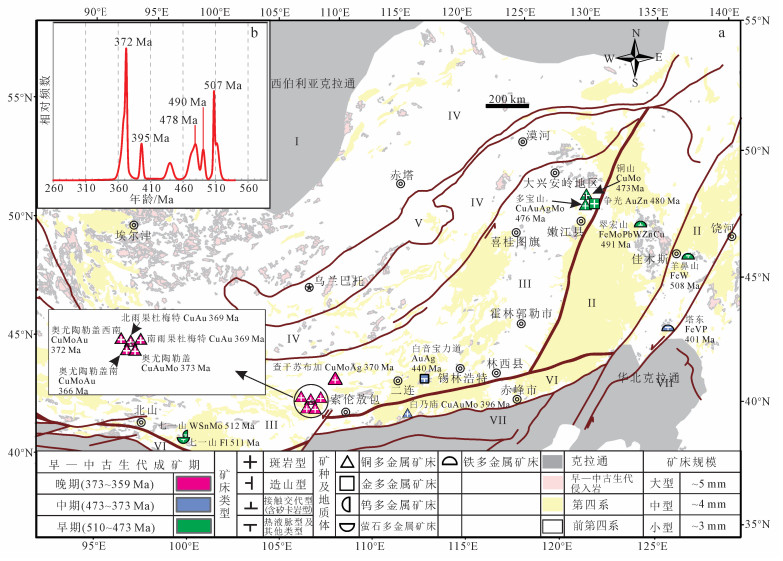
3.2 晚古生代 (石炭纪、二叠纪) 成矿特点中亚造山带东部晚古生代矿床呈带状分布, 以矿床少 (29个矿床)、资源小 (以中小型为主 (占同期矿床83%))、连续成矿、发育斑岩型铜矿和热液脉型或造山型金矿组合为特点。晚古生代矿床集中分布在华北克拉通北缘, 而在中国东北等中间地块较多的区域成矿较弱 (图 3a), 早二叠世首次出现以钼为主的矿床。
|
| 图 3 中亚造山带东部晚古生代岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a) 及矿床成矿年龄相对频数分布图 (b) Figure 3 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution (a) and mineralization ages probability plot of the Late Paleozoic in ECAOB (b) |
|
|
石炭纪矿床主要分布在南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系, 有3个成矿峰值 (349、330和300 Ma)(图 3b)。早、晚石炭世有明显不同的成矿特点。早石炭世 (349~330 Ma) 表现出对泥盆纪成矿作用有明显的继承性, 主要发育斑岩型铜金矿, 分布在南蒙古岛弧带奥尤陶勒盖周边地区。代表性矿床有早石炭世 (330 Ma) 卡曼戈泰大型斑岩型铜金矿, 该矿位于奥尤陶勒盖以北120 km, 与奥尤陶勒盖和查干苏布尔加铜金钼矿带具有相似的成矿特征, 与晚古生代岩体密切相关[10]。因此, 我们认为373~330 Ma代表一个重要的成矿时期。而晚石炭世 (320~300 Ma) 以中小型热液脉型铜银铅锌钨金矿及斑岩型铜钼矿组合为主, 矿床主要分布在南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系兴安地块大兴安岭和北山地区, 反映了成矿作用由蒙古奥尤陶勒盖向东西迁移特征。
3.2.2 二叠纪成矿特点二叠纪成矿作用集中在早—中二叠世, 有3个峰值 (272、264和253 Ma)(图 3b), 主要分布在南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系的大兴安岭南段、辽远陆块、萨彦岭—贝加尔造山系的Dhzid-Selenge和中蒙古微陆块巴彦洪格尔, 以早—中二叠世 (287~260 Ma) 斑岩型铜金钼矿和中—晚二叠世 (270~253 Ma) 造山型金铜矿组合为主。
斑岩型和造山型金矿成矿年龄集中在294~253 Ma, 中亚造山带东部出现由斑岩型金矿向造山型金矿逐步增多的趋势, 从西到东依次出现塔特、流沙山、小西弓、赛音乌苏和老柞山造山型金矿; 而在二叠纪之前, 区域上以铜为主要成矿元素。约298 Ma大兴安岭南段首次出现以钼为主要成矿元素的准苏吉花敖包热液脉型钼铜矿, 可能指示了在石炭纪和二叠纪之交, 中亚造山带东部出现重大体制转变。考虑到北山黑鹰山火山岩型铁矿的形成时代[88], 我们认为322~253 Ma代表一个重要的成矿期。
3.3 早中生代 (三叠纪) 成矿特点三叠纪岩浆热液矿床呈面状分布 (图 4), 以中小型矿床为主 (约占同期70%), 连续成矿, 有4个峰值 (244、238、231和216 Ma)(图 4b), 以发育典型的斑岩型钼铜矿和岩浆熔离型铜镍矿组合为特征。矿床集中分布在额尔古纳—中蒙古地块和兴安地块大兴安岭南段、辽远地块及松嫩—张广才岭地块的小兴安岭—张广才岭 (图 4a), 但额尔古纳—中蒙古地块成矿特点与后者明显不同, 同期兴安地块大兴安岭北段几乎没有成矿作用, 反映了蒙古弧形断裂两侧不同构造体制。
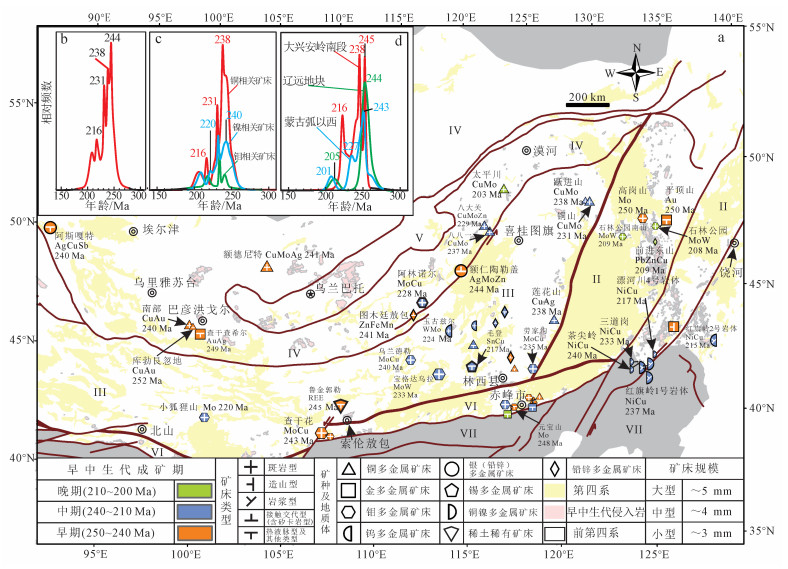
|
| 图 4 中亚造山带东部早中生代岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a) 及三叠纪矿床 (b)、典型矿种 (c)、不同区域矿床 (d) 成矿年龄相对频数分布图 Figure 4 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution of the Early Mesozoic in ECAOB (a) and mineralization ages probability plots of ore deposits (b), associated with Cu/Mo/Ni (c) and in the special area (d) of the Trassic |
|
|
三叠纪主要发育大量斑岩型钼铜矿床、矽卡岩型铅锌多金属矿床和斑岩型铜钼矿床, 而绝大多数铜矿为中小型矿床。其中:与钼相关矿床有3个峰值 (240、231和220 Ma)(图 4c), 矿床类型以斑岩型为主; 与铜有关矿床 (不包含铜镍矿) 成矿峰值为238、231和216 Ma (图 4c), 以斑岩型和热液脉型为主。区域上铜和钼表现出紧密伴生的特征, 但是以钼为主的矿床 (包括钼铜矿、钼金矿和钨钼矿) 主要分布在蒙古弧形断裂以东南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系大兴安岭南段, 而以铜为主的斑岩型矿床主要分布在蒙古弧形断裂以西额尔古纳—中蒙古地块东缘。与镍相关岩浆熔离型矿床紧挨着华北克拉通北缘断裂以北发育, 被不同学者作为古亚洲洋后碰撞的标志[164]; 但对于其成矿年龄有不同的认识。有学者通过辉钼矿Re-Os年龄限定为237~208 Ma[56, 163], 但误差较大; 蚀变矿物Ar-Ar年龄 (230~225 Ma)[197-198]和赋矿围岩U-Pb年龄 (240~213 Ma)[58-59, 163-164, 198-199]指示了铜镍成矿作用集中在240~210 Ma。结合早三叠世 (250~243 Ma) 发育大量与同碰撞花岗岩有关的车户沟斑岩型钼矿[102]、平顶山热液脉型金矿[81]和查干花斑岩型钨钼矿[50]等, 因此, 我们认为三叠纪存在3个不同的成矿期:250~240, 240~210, 210~201 Ma。而三叠纪首次出现单一钼矿, 自东向西分别为早三叠世高岗山[85]、元宝山钼矿[149]和晚三叠世的小狐狸山钼矿[112], 可能指示了一个地块拼合后板内环境。
3.3.2 不同区域成矿特点三叠纪蒙古弧形断裂以西识别出11个矿床, 有3个峰值 (243、227和201 Ma)(图 4d), 集中分布在额尔古纳—中蒙古地块东缘, 自北向南依次发育太平川、八大关、八八一斑岩型铜钼矿和阿林诺尔斑岩型钼铜矿, 而兴安地块大兴安岭北段相邻地区没有成矿作用显示。同期大兴安岭南段矿床集中在中—晚三叠世, 有3个峰值 (245、238和216 Ma)(图 4d), 矿床类型以矽卡岩型、热液脉型和斑岩型为主, 其中钼钨铜矿床与花岗岩类侵入有关, 铅锌铁矿床与中酸性侵入岩有关, 碱性岩与稀有稀土矿床有关。小兴安岭—张广才岭地区早三叠世由斑岩型钼矿床和造山型金矿床组成, 晚三叠世主要形成热液脉型和斑岩型钼钨矿床、矽卡岩型铅锌矿床和岩浆岩熔离型铜镍矿床, 而中三叠世是小兴安岭—张广才岭成矿"寂静期"; 同期额尔古纳—中蒙古地块发育斑岩型铜钼矿床和热液脉型或矽卡型岩铅锌矿床, 可能反映了两者处于不同的构造体制。辽远地块以早—中三叠世斑岩型钼铜矿为主及少量中—晚三叠世蚀变岩型-热液脉型金矿床, 有2个峰值 (244和205 Ma)(图 4d)。
3.4 晚中生代 (侏罗纪—白垩纪) 成矿特点 3.4.1 侏罗纪成矿特点侏罗纪成矿作用呈面状分布 (图 5a), 以"多期多阶段成矿构造-岩浆活动、"逆时针"成矿作用、成矿元素复杂、矿床类型多样"为特征。在张广才岭—小兴安岭和兴凯地块吉黑东部发育大量斑岩型钼矿和矽卡岩型铅锌矿组合, 而蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带最西侧出现造山型金矿和南侧额尔古纳—中蒙古地块出现浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿及斑岩型铜钼矿组合, 显示了不同的构造体制。矿床规模以中小型矿床为主 (约占同期62%), 有5个成矿峰值 (198、186、178、170和155 Ma)(图 5b)。
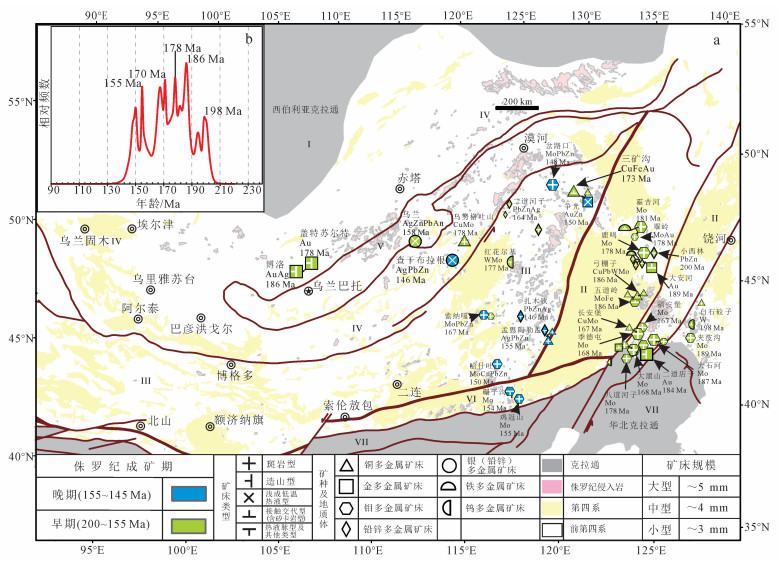
|
| 图 5 中亚造山带东部侏罗纪岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a) 及成矿年龄相对频数分布图 (b) Figure 5 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution (a) and mineralization ages probability plot of the Jurassic in ECAOB (b) |
|
|
与铅锌相关矿床分布在大兴安岭、小兴安岭和乌兰—甲乌拉地区。大兴安岭北段有2个成矿期 (175~164 Ma和150~148 Ma), 发育斑岩型钼铅锌矿床和热液脉型铅锌多金属矿床。而同期额尔古纳地块没有任何成矿作用; 南段 (167 Ma和155~146 Ma) 发育斑岩型钼铜铅锌矿床和热液脉型铅锌银矿床, 而对应的南蒙古地块没有任何成矿作用。乌兰—甲乌拉 (158~146 Ma) 在蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带南侧额尔古纳—南蒙古地块中部发育浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿床。小兴安岭 (200~176 Ma) 发育矽卡岩型铅锌多金属矿床, 显示了"逆时针"的成矿顺序:小兴安岭—大兴安岭北段—大兴安岭南段。
如上分析, 与铜相关矿床在兴凯地块吉黑东部和额尔古纳—南蒙古地块均发育与俯冲有关的斑岩型矿床, 在松嫩地块的小兴安岭和南蒙古—兴安造山系的大兴安岭主要发育矽卡岩型和斑岩型矿床, 显示了其成矿顺序:吉黑东部—小兴安岭—大兴安岭北段—大兴安岭南段。
与钼相关矿床在兴凯地块、张广才岭—小兴安岭发育大量与俯冲有关的斑岩型和矽卡岩型矿床, 在大兴安岭发育大量斑岩型和热液脉型矿床。而同期额尔古纳地块成矿作用较弱, 仅发现斑岩型乌努格吐山铜矿。其中, 翠宏山钨钼矿Re-Os年龄 (辉钼矿) 为 (200±4) Ma, 含矿二长花岗岩U-Pb年龄 (锆石) 为200~193 Ma[23, 200], 而大冰湖钼矿辉钼矿Re-Os年龄为 (192±3) Ma[167], 夹皮沟钼矿Re-Os年龄 (辉钼矿) 为 (200±4) Ma, 含矿二长花岗岩U-Pb年龄 (锆石) 为193 Ma[121]。在误差范围内成矿年龄基本一致, 结合区域上钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os等时线相关系数高度一致[62], 我们认为这是一期成矿事件, 成矿顺序:吉黑东部—张广才岭—小兴安岭—大兴安岭北段—大兴安岭南段—赤峰。综上所述, 侏罗纪明显存在一个"逆时针"成矿顺序, 这在侵入岩岩浆时空格架和与金相关矿床也有同样的反映 (受篇幅限制, 另文详述)。
3.4.1.2 不同区域成矿特点蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带最西侧形成早侏罗世的造山型博洛金银矿和盖特苏尔特金矿, 结合额尔古纳地块南缘早侏罗世斑岩型乌努格吐山铜 (钼) 矿, 可能指示了早侏罗世 (186~178 Ma) 蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋西侧已经碰撞闭合, 而东侧形成晚侏罗世浅成低温热液型乌兰和查干布拉根银铅锌矿[46, 201]。同期大兴安岭成矿特点与之明显不同, 大兴安岭北段以早—中侏罗世形成矽卡岩型铜多金属矿床、热液脉型银铅锌金矿床和钨钼矿床组合为特征, 到晚侏罗世晚期才出现斑岩型钼铅锌矿床; 大兴安岭南段成矿作用集中在晚侏罗世, 以热液脉型银铅锌矿和斑岩型钼铜矿组合为特征。小兴安岭—张广才岭—吉黑东部在早—中侏罗世 (181~167 Ma) 集中发育一系列与斑岩有关的霍吉河钼矿、鹿鸣钼矿、大黑山钼矿、季德屯钼矿、八道河子钼矿等和热液脉型四方甸子钼矿, 赋矿围岩均为钙碱性花岗岩, 指示相似的构造环境[59]。晚三叠世晚期 (约209 Ma), 小兴安岭石林公园南山钼钨矿、石林公园钼矿在成矿大地构造环境、矿区出露地层、岩浆岩、构造与霍吉河和鹿鸣钼铜矿床完全一致, 赋矿围岩均有高分异A2型花岗岩特点[130]。因此, 我们认为210~167 Ma反映了一个重要成矿期。而辽远地块早—中侏罗世没有矿化反映, 晚侏罗世 (155~150 Ma) 出现与A2型花岗岩有关的斑岩型鸡冠山、哈什吐和石英脉型碾子沟等钼铜矿, 及成矿后辉绿岩和石英花岗斑岩岩墙发育[202], 可能反映了区域上的重大体制变化。
3.4.2 白垩纪成矿特点白垩纪矿床成矿作用集中于早白垩世 (图 6), 以有两个成矿期 (早白垩世早期 (145~120 Ma) 和早白垩世晚期 (120~110 Ma))(图 6b) 发育大量浅成低温热液型金矿床和热液脉型-矽卡岩型锡矿床为特征。矿床以中小型为主 (占同期66%), 主要分布在布列亚—佳木斯古陆兴凯地块、兴安地块大兴安岭和额尔古纳地块 (图 6a)。其中, 大兴安岭南段与北段有明显不同的成矿特点, 可能反映了不同的成矿背景; 而金矿集中分布在额尔古纳地块—兴安地块—松嫩地块北缘和兴凯地块周缘。
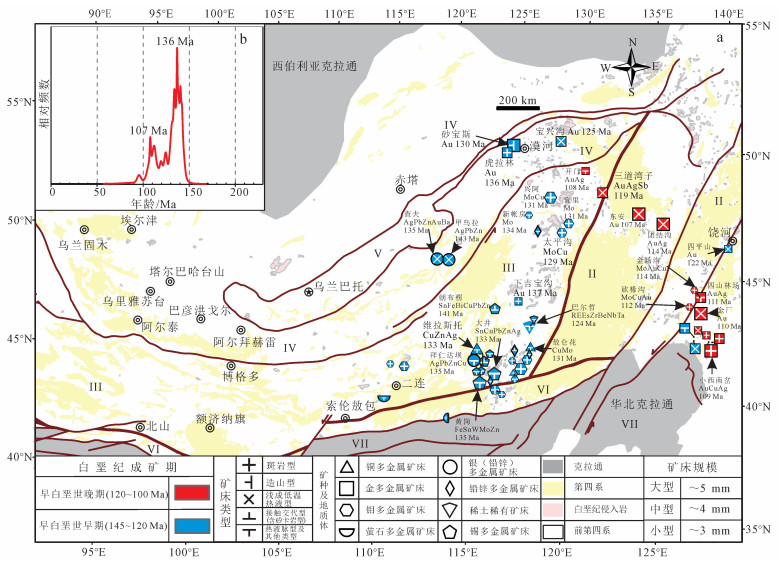
|
| 图 6 中亚造山带东部白垩纪岩浆热液矿床分布图 (a) 及成矿年龄相对频数分布图 (b) Figure 6 Magmatic-hydrothermal deposits distribution (a) and ages probability plot of the Crateceous in ECAOB (b) |
|
|
早白垩世早期 (成矿峰值136 Ma), 矿床呈面状分布。蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带以东的额尔古纳—中蒙古地块最东侧, 在136~125 Ma发育造山型-斑岩型-浅成低温热液型金矿床, 中部在143~135 Ma发育浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿床, 其中砂宝斯造山型金矿形成于130 Ma[28], 可能限定了蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋最东侧闭合的时限。兴安—南蒙古地块大兴安岭南北段有明显不同的成矿特点:北段在134~129 Ma发育斑岩型钼矿, 赋存于二长花岗斑岩里, 在139 Ma发育热液脉型银铅锌矿, 赋存在火山碎屑岩中, 矿体主要分布于NE与NW构造断裂交汇部位[52]; 而南段在141~133 Ma发育独特的热液脉型-矽卡岩型锡矿床, 在139~131 Ma发育大量斑岩型钼多金属矿床, 在142~133 Ma发育热液脉型-矽卡岩型铅锌多金属矿床及少量的铜矿稀土矿床, 并在123.8 Ma发育亚洲最大的稀土矿 (巴尔哲稀土矿)[203]。以上矿床均受NNE向与EW向断裂控制[204], 其中中酸性赋矿围岩与铜银铅锌矿有关, 酸性岩与锡多金属矿有关, 碱性岩与稀有矿化有关。兴凯地块在141~122 Ma发育大量浅成低温热液型金矿, 同期张广才岭—小兴安岭没有任何成矿作用, 显示了大兴安岭北段与兴凯地块有明显不同的成矿背景。结合晚侏罗世斑岩型鸡冠山和石英脉型碾子沟钼铜矿, 额尔古纳地块白垩纪花岗岩集中在130~118 Ma[175], 因此, 我们认为155~120 Ma代表着一个重要的成矿期。
3.4.2.2 早白垩世晚期成矿特点早白垩世晚期 (成矿峰值107 Ma), 矿床呈带状分布, 围绕兴安地块—松嫩地块北缘和兴凯地块周缘发育斑岩型-浅成低温热液型金多金属矿床。其中, 兴凯地块在114~106 Ma发育浅成低温热液型-斑岩型金 (钼) 矿床和钼金矿床, 而小兴安岭北侧在114~105 Ma发育浅成低温热液型金 (银) 矿床, 反映了早白垩世晚期整个中亚造山带东部处于统一的成矿环境。
4 重要成矿期成矿背景分析 4.1 古生代早期 (510~473 Ma) 成矿背景位于喀拉塔格—旱山地块内的七一山矿集区, 赋矿围岩为中高钾钙碱性花岗岩, 矿体的εNd(t) 值 (-4.2) 显示了较为古老地壳及一定程度的壳幔混合特征, 可能是早古生代俯冲造山作用的响应[145]。翠宏山矿集区铁矿与A型花岗岩密切相关, 可能指示了兴安地块和松嫩—张广才岭地块拼合背景[23]。羊鼻山矿集区赋矿围岩显示了S型花岗岩特征, 与早奥陶世佳木斯地块与松嫩地块之间的陆陆碰撞有关[33]。多宝山矿集区花岗质岩石具有典型岛弧与同碰撞花岗岩性质, 与兴安和额尔古纳陆块拼合有关[26]。
前人研究认为, 早古生代中亚造山带大约在510 Ma经历了萨拉伊尔运动, 北部的蒙古—阿尔泰古地块、南蒙古地块、额尔古纳—中蒙古地块等中间地块向西伯利亚克拉通挤压拼贴和对接[205], 而在中国东北额尔古纳地块、兴安地块和松嫩地块相继碰撞[206]; 松嫩地块与佳木斯地块沿嘉荫—牡丹江断裂在早古生代开始拼合, 最终在中志留世拼合在一起[207]; 而佳木斯地块麻粒岩相变质作用研究表明, 在约500 Ma, 额尔古纳地块、兴安地块、佳木斯—兴凯地块与西伯利亚板块南缘经历了统一的变质作用[208]。因此, 古亚洲洋开始俯冲、微陆块相互碰撞拼合, 是早古生代成矿动力学背景。
4.2 古生代中期 (373~330 Ma) 成矿背景石炭纪动力学背景有争议, 但多数认为泥盆纪古亚洲洋处于俯冲消减阶段[3]。蒙古大型卡曼戈泰、查干苏布尔加矿和超大型奥尤陶勒盖矿带均位于南蒙古岛弧带[10], 赋矿围岩具有埃达克质岩特征。其中, 查干苏布尔加矿中花岗闪长斑岩和二长花岗岩斑岩主、微量和稀土元素又存在一定差别, 可能是岩浆不同演化阶段的产物, 指示了大洋板片俯冲富集成矿特征[63]。因此, 晚泥盆世—早石炭世成矿作用源于古亚洲洋板块的强烈俯冲。
奥尤陶勒盖超大型铜金矿带的突破, 证实了中亚造山带成矿潜力。近年在南蒙古岛弧带东西两端取得了一些新的进展:在东准发现早、晚泥盆世的蒙西、和尔赛、拉伊克勒克和云英山等斑岩型铜金矿。晚泥盆世东天山黄土坡和三岔口周边发现斑岩型矿点, 说明可能存在一个泥盆纪—石炭纪成矿峰期; 二连—东乌旗与南蒙古相似的地质背景[209], 结合早奥陶世多宝山斑岩型成矿带, 可能暗示存在古生代南蒙古岛弧西延至东准—东天山、东延到多宝山以及东乌旗浅覆盖区找矿的可能。
4.3 古生代晚期 (320~253 Ma) 成矿背景蒙古北部和中部成矿与微陆块碰撞密切相关[10, 210], 西部阿奇特淖尔和乌兰乌拉矿赋存于碱性花岗岩或A型花岗岩[123], 均反映了后碰撞环境。
自约298 Ma开始, 中亚造山带东部由石炭纪之前发育以铜占主导的矿床逐渐转变为二叠纪以后发育以钼占主导的矿床[211], 区域上矿床集中分布在古亚洲洋体制主导下的华北北缘, 而中国东北中间地块较多的区域成矿作用较弱。与S型花岗岩密切相关的道伦达坝铜钨锡矿的发育[110]、西拉木沦河以南赛音乌苏造山型矿床的发现[100]、二连到东乌旗大量碱性岩[212]和大石寨组双峰式火山岩[213]的发现, 以及同期处于活动陆缘环境的中朝古陆北部增生带北缘斑岩型金矿和大量Ⅰ型钙碱性花岗岩的出现[47], 这些都说明古亚洲洋由俯冲增生向板块拼合转变是晚石炭世—二叠纪成矿背景。晚古生代末期强烈的碰撞挤压是造成成矿作用较少的主因, 也与中生代造山带由挤压到伸展的转变期是大规模成矿有利时期的认识一致[214]。
4.4 早中生代 (250~210 Ma) 成矿背景蒙古弧形断裂以西巴彦洪戈尔金矿与磁铁矿系列花岗岩类密切相关, 形成于蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋俯冲碰撞环境[122]; 而紧挨蒙古弧形断裂分布的6个矿床, 赋矿岩体属于过铝质高钾钙碱性Ⅰ型花岗岩, 具有埃达克质特征[215], 反映了俯冲环境。而区域上额尔古纳地块西缘八大关杂岩[216]和北段早中生代花岗岩[175]很好地限定了三叠纪蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋南向俯冲, 结合蒙古杭盖发育一套中三叠世安第斯型陆弧火山岩[168, 182], 因此, 研究区西部250~210 Ma太平川、八大关、八八一斑岩型铜钼等矿床形成于蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋俯冲的陆缘弧环境[140]。
小兴安岭—张广才岭早三叠世斑岩型钼矿与高钾钙碱性S型花岗岩有成因关系, 造山型金矿与Ⅰ型花岗岩有关, 显示壳幔混染的特征[85]。晚三叠世钼钨矿赋矿围岩具有A2型花岗岩特征[217]、华北克拉通北缘断裂发育的铜镍矿与基性超基性岩墙紧密相关, 都反映了板内的后碰撞造山环境[56]。
在古亚洲洋体系下的南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系大兴安岭南段和辽远地块, 钼矿赋矿围岩为高钾钙碱性系列或钙碱性花岗岩[99], 铜锡矿为富钾钙碱性壳源重熔型花岗岩[218], 铁锌矿为钾玄岩—高钾钙碱性系列, 银铅锌矿为高钾钙碱性系列A型花岗岩[42], 造山型金矿为高钾钙碱性、高分异A型花岗岩[154], 这些均反映了板内后造山的伸展环境。
区域上, 中国东北中—晚三叠世广泛发育A型花岗岩[219-220], 晚三叠世吉黑东部发育一套A型流纹岩组合[221], 小兴安岭—张广才岭发育一套双峰式火山岩[222], 被认为与中亚造山带后碰撞伸展的构造环境有关。因此, 我们认为在研究区东部250~240 Ma反映了同碰撞挤压环境, 而240~210 Ma反映了后造山环境。
大兴安岭北段三叠纪几乎没有发现成矿作用, 说明在蒙古弧形断裂以东受古亚洲洋闭合影响, 形成大量板内斑岩型钼铜矿和热液脉型铅锌钨锡矿; 在华北克拉通北缘断裂带发育典型的与后碰撞有关的铜镍矿, 而以西受蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋俯冲影响, 形成代表性陆缘弧环境下斑岩型铜钼矿。
4.5 晚中生代早期 (210~167 Ma) 成矿背景在蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带最西侧, 造山型金矿赋存于高钾钙碱性A型花岗岩中[223], 斑岩型铜钼矿赋存于Ⅰ-S型花岗岩类中, 形成于同碰撞环境[46], 热液型银铅锌矿与高钾钙碱性侵入岩脉群和张裂构造关系密切[17], 结合早—中侏罗世钙碱性火山岩系列分布在额尔古纳地块[224], 这可能反映了蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋西侧在186 Ma之前可能已经闭合, 而后碰撞伸展是蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带和额尔古纳—中蒙古地块成矿的主控因素。
多数学者认为燕山早期吉林东部从南东至北西巨型推覆构造的发育[225], 标志着欧亚大陆与太平洋板块边缘发生构造性质的变换, 大陆东缘由被动陆缘转换成活动陆缘, 伊泽奈崎板块开始向欧亚板块俯冲挤压。
大兴安岭—小兴安岭—张广才岭—吉黑东部含矿岩体以偏铝质—过铝质、高钾钙碱性—钾玄岩系列的Ⅰ型花岗岩为主, 具有与俯冲带相似的地化特征[226]。区域上, 早—中侏罗世 (190~173 Ma) 火山岩主要分布在小兴安岭—张广才岭—吉黑东部。吉黑东部 (敦密断裂东南区) 早—中侏罗世火山岩主要为钙碱性火山岩系列[224], 具有类似于活动陆缘的火成岩组合特征[206]; 小兴安岭—张广才岭则为一套双峰式火成岩组合[227]。结合黑龙江群南北向蛇绿混杂岩中蓝片岩相变质年龄 (165~180 Ma) 的确认[217], 以及小兴安岭—张广才岭花岗岩带的展布方向 (近SN向分布) 与伊泽奈崎板块俯冲形成构造带方向近乎一致, 考虑到早—中侏罗世在西拉木沦河缝合带两侧迄今没有发现任何矿床, 我们推测伊泽奈崎板块向西俯冲挤压是晚三叠世晚期到中侏罗世, 中亚造山带东部布列亚—佳木斯古陆块和南蒙古—大兴安岭造山系成矿背景, 继而佳蒙陆块发生逆时针旋转。
4.6 晚中生代晚期 (155~100 Ma) 成矿背景晚侏罗世晚期, 鸡冠山钼矿区成矿后双峰式岩墙发育[202]。根据A2型花岗岩与哈什吐和碾子沟钼矿体的成因关系[150], 以及南北向挤压断裂对布敦花矿体的限定[98], 结合华北北缘晚侏罗世—早白垩世碱质A2型花岗岩的发育[228], 推测在约155 Ma古太平洋板块转向, 开始向北俯冲。
额尔古纳地块、兴凯地块和兴安—南蒙古地块的大兴安岭及松嫩地块小兴安岭赋矿围岩与准铝质或过铝质高钾钙碱性甚至钾玄岩系列的花岗岩类有关[162]。有学者提出林西早白垩世早期 (约132 Ma) 中基性岩墙群[229]及大兴安岭中南段早白垩世早期 (130~120 Ma) 超基性角闪岩和碱性橄榄玄武岩的存在指示了岩石圈伸展[230], 结合同期上黑龙江盆地漠河逆冲推覆构造带发生左行韧性剪切作用[231], 中国东北早白垩世晚期区域上分布一套碱性、过碱性含晶洞的A型花岗岩类 (如巴尔哲岩体、阿龙山岩体)[220], 萨彦岭—贝加尔造山系蒙古—泛贝加尔地区在150~120 Ma发育过碱性—碱性花岗岩类和双峰式火山岩侵入[232], 变质核杂岩指示了150~120 Ma中下地壳伸展[219], 以及早白垩世伸展盆地的发育[233], 认为中亚造山带东部于晚侏罗世到早白垩世整体处于伸展环境。
有学者对承德地区晚侏罗世火山岩古地磁进行研究, 认为蒙古鄂霍茨克洋在155 Ma仍然打开, 在东部有3 000 km宽[234], 经历了中到晚侏罗世, 向北俯冲的洋壳导致剪式闭合, 最终碰撞在早白垩世[235]。前章所述 (3.4.2白垩纪成矿特点), 结合大兴安岭北段碾子山岩体为新生幔源物质部分熔融的产物, 指示了洋壳到陆壳的再循环[236]; 岔路口矿床赋矿围岩属非常低Sr高Yb型花岗岩, 为高钾钙碱性系列或钾玄岩系列, 亦与后碰撞环境的岩浆活动类型相似[237], 可能指示了蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合对大兴安岭北段构造岩浆成矿作用起主导地位。因此, 我们倾向于早白垩世早期蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合后伸展环境, 对额尔古纳—中蒙古地块和兴安地块大兴安岭北段成矿起主要作用。
考虑到小兴安岭—张广才岭在早白垩世早期没有任何成矿作用, 同期华北克拉通北缘出现与伊泽奈崎板块向北俯冲引起的大规模岩石圈减薄和成矿[238], 所以我们倾向于伊泽奈崎板块向北俯冲是兴安地块大兴安岭南段的主要成矿背景。
松辽盆地以东的兴凯陆块和松嫩地块小兴安岭, 赋矿围岩没有明显选择性, 其中砍椽沟、小西南岔和金厂赋矿围岩具有埃达克质的Ⅰ型花岗岩特征[239], 反映了岛弧或活动陆缘环境[240]; 结合吉黑东部钙碱性火山岩[13], 推测成矿作用与古太平洋板块向北俯冲导致的陆缘弧有密切的成因联系。
早白垩世晚期 (120~100 Ma) 与金相关矿床呈环带状分布, 这可能反映了佳蒙地块受到古太平洋板块向北俯冲后伸展, 加厚岩石圈减薄拆沉, 俯冲后富含铜金残余或停滞大洋板片, 部分熔融及后期岩浆分异成矿[241]; 这也与金矿形成于壳幔混合区, 偏向古老地壳区的认识一致[242]。
5 结论1) 中亚造山带东部成矿作用主要发育于古生代—中生代, 集中于6个主成矿期:510~473、373~330、320~253、250~210、210~167、155~100 Ma。
2) 古生代早期 (510~473 Ma), 主成矿峰值约为507 Ma, 以发育大型斑岩型-热液脉型的铜铁钨金萤石为特征, 主要分布于北山、大兴安岭北段和小兴安岭和佳木斯地块, 形成于古亚洲洋俯冲和微陆块碰撞拼合背景。
中期 (373~330 Ma), 主成矿峰值约为372 Ma, 主要分布于南蒙古奥尤陶勒盖地区, 发育超大型斑岩型铜金矿为代表, 形成于古亚洲洋持续俯冲背景。
晚期 (320~253 Ma), 矿床类型从以斑岩型-热液脉型铜矿为主, 发展到出现大量斑岩型钼矿和造山型金矿, 可能指示着西伯利亚板块与华北板块从俯冲到碰撞的过程。其中, 298 Ma在大兴安岭南段首次出现以钼为主的多金属矿, 可能是该地区碰撞拼合的响应。
3) 早中生代 (250~210 Ma), 主成矿峰值约为244 Ma, 主要发育于额尔古纳—中蒙古地区, 主要形成斑岩型铜矿, 可能与蒙古鄂霍茨克洋俯冲有关; 以东的大兴安岭南段和辽远地块主要形成斑岩型钼矿, 张广才岭发育岩浆熔离型铜镍矿, 可能反映了古亚洲洋闭合后造山伸展环境。
4) 晚中生代早期 (210~167 Ma), 主成矿峰值约为170 Ma。在蒙古—鄂霍茨克造山带两侧形成斑岩型铜钼金矿和造山型金矿, 可能与蒙古鄂霍茨克洋俯冲闭合有关; 以东地区, 在吉黑东部——张广才岭—小兴安岭—大兴安岭发育斑岩型钼铜矿和矽卡岩型铅锌钨金矿组合, 可能与古太平洋板块向西俯冲有关。
晚期 (155~100 Ma), 成矿集中在155~120 Ma (峰值136 Ma)。在额尔古纳—中蒙古地区形成浅成低温热液型金银铅锌矿和造山型金矿, 在大兴安岭北段形成斑岩型钼铜矿, 可能受蒙古鄂霍茨克洋闭合后伸展环境影响; 而以东地区 (如兴凯地块和大兴安岭南段) 形成浅成低温热液型金矿、热液脉型-矽卡岩型锡矿和斑岩型-热液脉型钼矿; 在120~100 Ma (峰值107 Ma), 浅成低温热液型和斑岩型金 (钼) 矿和钼 (金) 矿沿着华北克拉通和佳蒙陆块边缘展布; 它们可能都受古太平洋板块向北俯冲弧后伸展影响。
5) 古亚洲洋构造域控制中亚造山带东部成矿一直持续到晚二叠世 (早三叠世), 并在早侏罗世叠加环太平洋构造域, 而额尔古纳—中蒙古地块成矿作用在三叠纪开始主要受蒙古鄂霍茨克洋构造域限定, 一直持续到早白垩世早期。
致谢: 童英副研究员与作者反复多次讨论成稿, 江思宏研究员和李锦轶研究员给予了悉心指导, 在此表示衷心感谢。| [1] | Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al. Tectonic Models for Accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 31-47. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-022 |
| [2] | Xiao W, Windley B F, Hao J, et al. Accretion Leading to Collision and the Permian Solonker Suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6): 1-8. |
| [3] | Xu B, Zhao P, Wang Y Y, et al. The Pre-Devonian Tectonic Framework of Xing'an-Mongolia Orogenic Belt (XMOB) in North China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 183-196. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.020 |
| [4] | Groves D I, Bierlein F P. Geodynamic Settings of Mineral Deposit Systems[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 19-30. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-065 |
| [5] | 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 171-190. Mao Jingwen, Xie Guiqing, Zhang Zuoheng, et al. Mesozoic Large-Scale Metallogenic Pulses in North China and Corresponding Geodynamic Settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(1): 171-190. |
| [6] | 陈衍景. 大陆碰撞成矿理论的创建及应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(1): 1-17. Chen Yanjing. The Development of Continental Collision Metallogeny and Its Application[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(1): 1-17. |
| [7] | 侯增谦. 大陆碰撞成矿论[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(1): 30-58. Hou Zengqian. Metallogensis of Continental Collision[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 84(1): 30-58. |
| [8] | 陈衍景, 张成, 李诺, 等. 中国东北钼矿床地质[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2012, 42(5): 1223-1268. Chen Yanjing, Zhang Cheng, Li Nuo, et al. Geology of the Mo Deposits in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1223-1268. |
| [9] | Mao J W, Pirajno F, Cook N. Mesozoic Metallogeny in East China and Corresponding Geodynamic Settings:An Introduction to the Special Issue[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 1-7. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.003 |
| [10] | Seltmann R, Porter T M, Pirajno F. Geodynamics and Metallogeny of the Central Eurasian Porphyry and Related Epithermal Mineral Systems:A Review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 810-841. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.030 |
| [11] | Mao J W, Pirajno F, Lehmann B, et al. Distribution of Porphyry Deposits in the Eurasian Continent and Their Corresponding Tectonic Settings[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 576-584. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.002 |
| [12] | 张旗, 秦克章, 王元龙, 等. 加强埃达克岩研究, 开创中国Cu、Au等找矿工作的新局面[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(2): 195-204. Zhang Qi, Qin Kezhang, Wang Yuanlong, et al. Study on Adakite Broadened to Challenge the Cu and Au Exploration in China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(2): 195-204. |
| [13] | 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 339-353. Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Pei Fuping, et al. Mesozoic Tectonic Regimes and Regional Ore-Forming Background in NE China:Constraints from Spatial and Temporal Variations of Mesozoic Volcanic Rock Associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 339-353. |
| [14] | Zeng Q, Liu J, Chu S, et al. Mesozoic Molybdenum Deposits in the East Xingmeng Orogenic Belt, Northeast China:Characteristics and Tectonic Setting[J]. International Geology Review, 2012, 54(16): 1843-1869. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.677498 |
| [15] | Ouyang H, Mao J W, Zhou Z, et al. Late Mesozoic Metallogeny and Intracontinental Magmatism, Southern Great Xing'an Range, Northeastern China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27(3): 1153-1172. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.08.010 |
| [16] | Li J W, Bi S J, Selby D, et al. Giant Mesozoic Gold Provinces Related to the Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 349: 26-37. |
| [17] | Nie F J, Li Q F, Liu C H, et al. Geology and Origin of Ag-Pb-Zn Deposits Occurring in the Ulaan-Jiawula Metallogenic Province, Northeast Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 424-441. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.029 |
| [18] | 李锦轶, 张进, 杨天南, 等. 北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2009, 39(4): 584-605. Li Jinyi, Zhang Jin, Yang Tiannan, et al. Crustal Tectonic Division and Evolution of the Southern Part of the North Asian Orogenic Region and Its Adjacent Areas[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2009, 39(4): 584-605. |
| [19] | 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等. 新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(1): 148-168. Li Jinyi, He Guoqi, Xu Xin, et al. Crustal Tectonic Framework of Northern Xinjiang and Adjacent Regions and Its Formation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(1): 148-168. |
| [20] | 王涛, 张磊, 郭磊, 等. 亚洲中生代花岗岩图初步编制及若干研究进展[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(6): 655-672. Wang Tao, Zhang Lei, Guo Lei, et al. The Progress of Preliminary Compilation of Map of Mesozoic Granitoid of Asia and the Research on Related Key Issues[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(6): 655-672. |
| [21] | 韩振哲. 小兴安岭东南段早中生代花岗岩类时空演化特征与多金属成矿[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2011: 1-207. Han Zhenzhe. Characteristics of Temporal and Spatial Evolution and Polymetallic Mineralization of Early Mesozoic Granites in Southeasten Xiaoxing'an Mountains[D].Beijing:Chinese University of Geoscience, 2011:1-207. |
| [22] | Liu J, Mao J W, Wu G, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Molybdenite Re-Os Dating of the Chalukou Porphyry Mo Deposit in the Northern Great Xing'an Range, China and Its Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 696-709. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.06.020 |
| [23] | Hu X L, Ding Z J, He M C, et al. Two Epochs of Magmatism and Metallogeny in the Cuihongshan Fe-Polymetallic Deposit, Heilongjiang Province, NE China:Constrains from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Lu-Hf Isotopes[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 143: 116-126. DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.03.027 |
| [24] | Hao Y J, Ren Y S, Duan M X, et al. Metallogenic Events and Tectonic Setting of the Duobaoshan Ore Field in Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 442-458. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.007 |
| [25] | Zhang H F, Li S R, Santosh M, et al. Magmatism and Metallogeny Associated with Mantle Upwelling:Zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf Constraints from the Gold-Mineralized Jinchang Granite, NE China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 54: 138-156. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.03.006 |
| [26] | Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Chu S X, et al. Re-Os and U-Pb Geochronology of the Duobaoshan Porphyry Cu-Mo-(Au) Deposit, Northeast China, and Its Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 895-909. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.007 |
| [27] | Wang Y, Zeng Q, Liu J. Rb-Sr Dating of Gold-Bearing Pyrites from Wulaga Gold Deposit and Its Geological Significance[J]. Resource Geology, 2014, 64(3): 262-270. DOI:10.1111/rge.12040 |
| [28] | 刘军, 武广, 邱华宁, 等. 大兴安岭北部砂宝斯金矿床含金石英脉40Ar/39Ar年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(10): 1-11. Liu Jun, Wu Guang, Qiu Huaning, et al. 40Ar/39Ar Dating of Gold-Bearing Quartz Vein from the Shabaosi Gold Deposit at the Northern End of the Great Xing'an Range and Its Tectonic Sighificance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(10): 1-11. |
| [29] | 薛明轩. 黑龙江省内生金矿成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012: 1-176. Xue Mingxuan. Metallogenesis of Endogenic Gold Deposits in Heilongjiang Province[D].Changchun:Jilin Unversity, 2012:1-176. |
| [30] | Hu X L, Ding Z J, He M C, et al. A Porphyry-Skarn Metallogenic System in the Lesser Xing'an Range, NE China:Implications from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes of the Luming Mo and Xulaojiugou Pb-Zn Deposits[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 90: 88-100. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.04.020 |
| [31] | Zhang Z C, Mao J W, Wang Y B, et al. Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Volcanic Rocks Associated with the Dong'an Adularia-Sericite Epithermal Gold Deposit, Lesser Hinggan Range, Heilongjiang Province, NE China:Constraints on the Metallogenesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2010, 37(3): 158-174. |
| [32] | 张琳琳, 刘翠, 周肃, 等. 小兴安岭霍吉河钼矿区含矿花岗岩类特征及成矿年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3419-3431. Zhang Linlin, Liu Cui, Zhou Su, et al. Characteristics of Ore-Bearing Granites and Ore-Forming Age of the Huojihe Molybdenum Deposit in Lesser Xing'an Range[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(11): 3419-3431. |
| [33] | 赵华雷. 吉黑东部钨矿成因及成矿地球动力学背景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014: 1-150. Zhao Hualei. Ore Genesis and Geodynamic Settings of Tungsten Deposits in Eastern Jilin and Heilongjiang Provinces[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2014:1-150. |
| [34] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古孟恩陶勒盖银多金属矿床及其附近侵入岩的年代学[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1755-1769. Jiang Sihong, Nie Fengjun, Liu Yifei, et al. Geochronology of Intrusive Rocks Occurring in and Around the Mengentaolegai Silver-Polymetallic Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(6): 1755-1769. |
| [35] | Yang W B, Niu H C, Shan Q, et al. Geochemistry of Magmatic and Hydrothermal Zircon from the Highly Evolved Baerzhe Alkaline Granite:Implications for Zr-Ree-Nb Mineralization[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2014, 49(4): 451-470. DOI:10.1007/s00126-013-0504-1 |
| [36] | 许东青, 聂凤军, 钱明平, 等. 苏莫查干敖包超大型萤石矿床的稀土元素地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(1): 29-41. Xu Dongqing, Nie Fengjun, Qian Mingping, et al. Ree Geochemistry and Genesis of Sumochagan Obo Superlarge Fluorite Deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(1): 29-41. |
| [37] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 刘妍, 等. 阿拉善东七一山大型萤石矿床萤石钐-钕同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(1): 10-15. Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, Liu Yan, et al. Sm-Nd Isotopic Dating of Fluorite Separates from Dongqiyishan Fluorite Deposit, Alxa, Western Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2002, 21(1): 10-15. |
| [38] | Zhai D, Liu J, Zhang H, et al. S-Pb Isotopic Geochemistry, U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology of the Huanggangliang Fe-Sn Deposit, Inner Mongolia, NE China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 59: 109-122. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.12.005 |
| [39] | 李俊建, 翟裕生, 桑海清, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善欧布拉格铜-金矿床的成矿时代[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2010, 29(4): 323-327. Li Junjian, Zhai Yusheng, Sang Haiqing, et al. Metallogenic Epoch of the Oubulage Copper-Gold Deposit in the Alashan Area, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2010, 29(4): 323-327. |
| [40] | 江思宏, 梁清玲, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古大井矿区及外围岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时间的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 495-513. Jiang Sihong, Liang Qingling, Liu Yifei, et al. Zircon U-Pb Ages of Themagmatic Rocks Occurring in and Around the Dajing Cu-Ag-Sn Polymetallic Deposit of Inner Mongolia and Constrains to the Ore-Forming Age[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2): 495-513. |
| [41] | 李铁刚, 武广, 刘军, 等. 大兴安岭北部甲乌拉铅锌银矿床Rb-Sr同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(1): 257-270. Li Tiegang, Wu Guang, Liu Jun, et al. Rb-Sr Isochron Age of the Jiawula Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit in Themanzhouli Area and Its Geological Significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(1): 257-270. |
| [42] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 白大明, 等. 内蒙古白音诺尔铅锌矿床印支期成矿的年代学证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(5): 787-798. Jiang Sihong, Nie Fengjun, Bai Daming, et al. Geochronology Evidence for Indosinian Mineralization in Baiyinnuoer Pb-Zn Deposit of Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(5): 787-798. |
| [43] | 潘小菲, 郭利军, 王硕, 等. 内蒙古维拉斯托铜锌矿床的白云母Ar/Ar年龄探讨[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(5): 473-479. Pan Xiaofei, Guo Lijun, Wang Shuo, et al. Laser Microphrobe Ar-Ar Dating of Biotite from the Weilasituo Cu-Zn Polymetallic Deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2009, 28(5): 473-479. |
| [44] | 张万益. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗岩浆活动与金属成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2008: 1-179. Zhang Wanyi.A Dissertation Submitted to Chinese Academy of Geologicak Sciences for Doctoral Degree[D]. Beijing:Chinese Institute of Geoscience, 2008:1-179. |
| [45] | 常勇, 赖勇. 内蒙古银都银铅锌多金属矿床成矿流体特征及成矿年代学研究[J]. 北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 2010, 46(4): 581-593. Chang Yong, Lai Yong. Study on Characteristics of Ore-Forming Fluid and Chronology in the Yindu Ag-Pb-Zn Polymetallic Ore Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2010, 46(4): 581-593. |
| [46] | Chen Z G, Zhang L C, Wan B, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Wunugetushan Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposit in NE China, and Their Geological Significance[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 92-105. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.08.007 |
| [47] | 卿敏, 葛良胜, 唐明国, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特右旗毕力赫大型斑岩型金矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(1): 11-20. Qing Min, Ge Liangsheng, Tang Mingguo, et al. Molybdnite Re-Os Isotope Age of Bilihe Large-Size Porphyry Gold Deposit in Sunid Right Banner of Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(1): 11-20. |
| [48] | Sun J G, Han S J, Zhang Y, et al. Diagenesis and Metallogenetic Mechanisms of the Tuanjiegou Gold Deposit from the Lesser Xing'an Range, NE China:Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Lu-Hf Isotopic Constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 373-388. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.021 |
| [49] | Nie F J, Jiang S H. Geological Setting and Origin of Mo-W-Cu Deposits in the Honggor-Shamai District, Inner Mongolia, North China[J]. Resource Geology, 2011, 61(4): 344-355. DOI:10.1111/rge.2011.61.issue-4 |
| [50] | 蔡明海, 张志刚, 屈文俊, 等. 内蒙古乌拉特后旗查干花钼矿床地质特征及Re-Os测年[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(1): 64-68. Cai Minghai, Zhang Zhigang, Qu Wenjun, et al. Geological Characteristics and Re-Os Dating of the Chaganhua Molybdenum Deposit in Urad Rear Banner, Western Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 64-68. |
| [51] | 李大新, 赵一鸣, 丰成友, 等. 内蒙古羊蹄子山-磨石山锐钛矿矿床富矿层和花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(4): 449-458. Li Daxin, Zhao Yiming, Feng Chengyou, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Dating of Mesoproterozoic Anatase-Rich Ore Beds and Granite in Yangtizishan-Moshishan Anatase Deposit, Inner Mongolia, and Its Geological Significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(4): 449-458. |
| [52] | 张成, 李诺, 陈衍景, 等. 内蒙古兴阿钼铜矿区侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(1): 217-230. Zhang Cheng, Li Nuo, Chen Yanjing, et al. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Hf Isotopic Compositions of the Intrusive Rocks in the Xing'a Mo-Cu Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(1): 217-230. |
| [53] | 张梅, 翟裕生, 沈存利, 等. 大兴安岭中南段铜多金属矿床成矿系统[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 819-831. Zhang Mei, Zhai Yusheng, Shen Cunli, et al. Metallogenic System of Copper Polymetallic Deposits in the Middle-Southern Part of Da Hinggan Mountains, China[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(5): 819-831. |
| [54] | 赵丕忠, 王永, 韩凤彬, 等. 大兴安岭北段库伦迪-那吉河铅锌银矿成矿流体特征与矿床成因[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(5): 751-761. Zhao Pizhong, Wang Yong, Han Fengbin, et al. Ore-Forming Fluid Characteristics and Genesis of the Kulundi-Najihe Lead-Zinc-Silver Deposit in Northern Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(5): 751-761. |
| [55] | 向安平, 王亚君, 秦大军, 等. 内蒙古红花尔基钨多金属矿床成岩成矿年代学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(2): 428-439. Xiang Anping, Wang Yajun, Qin Dajun, et al. Metallogenic and Diagenetic Age of Honghuaerji Tungsten Polymetallic Deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2014, 33(2): 428-439. |
| [56] | Lü L S, Mao J W, Li H B, et al. Pyrrhotite Re-Os and SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Hongqiling Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits in Northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 106-119. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.02.003 |
| [57] | 邵建波, 张希友, 王洪涛, 等. 吉林省塔东大型铁矿地球化学特征及黄铁矿Re-Os同位素定年[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(1): 83-98. Shao Jianbo, Zhang Xiyou, Wang Hongtao, et al. Geochemistry and Pyrite Re-Os Dating of the Tadong Iron Deposit in Jilin Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(1): 83-98. |
| [58] | 郝立波, 吴超, 孙立吉, 等. 吉林红旗岭铜镍硫化物矿床Re-Os同位素特征及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2014, 44(2): 507-517. Hao Libo, Wu Chao, Sun Liji, et al. Re-Os Isotope Characteristics of Hongqiling Cu-Ni Sufide Deposit in Jilin Province and Its Significance[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(2): 507-517. |
| [59] | 汪志刚. 吉林东部中生代内生金属矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012: 1-219. Wang Zhigang. Study of Metallogenesis of Mesozoic Endogenetic Metal Deposits in the Eastern Part of Jilin Province[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2012:1-219. |
| [60] | 宫瑞清, 邓志平, 王承洋, 等. 吉林小西南岔金-铜矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素定年研究及其地质意义[J]. 吉林地质, 2012, 31(2): 14-20. Gong Ruiqing, Deng Zhiping, Wang Chengyang, et al. The Re-Os Isotope Dating of Molybdenite and Its Geological Significance of Xiaoxinancha Gold-Copper Deposit[J]. Jilin Geology, 2012, 31(2): 14-20. |
| [61] | 王辉, 任云生, 侯鹤楠. 延边大石河钼矿床成因及成矿时代[J]. 矿物学报, 2011(增刊1): 96-97. Wang Hui, Ren Yunsheng, Hou Henan. Metallogenic Age and Genesis of Dashihe Molybdenite Deposit, Jilin Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011(Sup.1): 96-97. |
| [62] | 张勇. 吉林省中东部地区侏罗纪钼矿床的地质、地球化学特征与成矿机理研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013: 1-157. Zhang Yong. Research on Characteristics of Geology, Geochemistry and Metallogenic Mechanism of the Jurassic Molybdenum Deposits in the Mid-East Area of Jilin[D].Changchun:Jilin Unversity, 2013:1-157. |
| [63] | Khashgerel B E, Rye R O, Hedenquist J W, et al. Geology and Reconnaissance Stable Isotope Study of the Oyu Tolgoi Porphyry Cu-Au System, South Gobi, Mongolia[J]. Economic Geology, 2006, 101(3): 503-522. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.101.3.503 |
| [64] | 侯万荣, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 蒙古国查干苏布尔加大型铜-钼矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 307-320. Hou Wanrong, Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, et al. The Geology and Ore-Forming Mechanism of the Tsagaan Suvarga Large-Size Cu-Mo Porphyry Deposit in Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 307-320. |
| [65] | Wainwright A J, Tosdal R M, Wooden J L, et al. U-Pb (Zircon) and Geochemical Constraints on the Age, Origin, and Evolution of Paleozoic Arc Magmas in the Oyu Tolgoi Porphyry Cu-Au District, Southern Mongolia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(3): 764-787. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.012 |
| [66] | Kirwin D J, Wilson C C, Turmagnai D, et al. Exploration History, Geology, and Mineralization of the Kharmagtai Gold-Copper Porphyry District, South Gobi Region, Mongolia[C]//Seltmann R, Gerel O, Kirwin D J. Geodynamics and Metallogeny of Mongolia with a Special Emphasis on Copper and Gold Deposits:Iagod Guidebook Series. London:Centre for Russian and Central Eurasian Mineral Sudies, Natural History Museum, 2005, 11:193-201. |
| [67] | Oyungerel S, Lee I. Sericite K-Ar Dating and Sulfur Isotope Study in Tavt Gold Deposit in the Northern Mongolia[C/OL].AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, 2012:2849[2015-10-23].http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2012AGUFM.V43C2849O |
| [68] | Munkhtsengel B, Iizumi S. Petrology and Geochemistry of the Lugiin Gol Nepheline Syenite Complex, South Mongolia Geodynamics and Metallogeny of Mongolia with a Special Emphasis on Copper and Gold Deposits[J]. Iagod Guidebook Series, 2005, 11: 203-214. |
| [69] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 苏永江, 等. 蒙古国额尔登特特大型铜-钼矿床年代学与成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 289-306. Jiang Sihong, Nie Fengjun, Su Yongjiang, et al. Geochronology and Origin of the Erdenet Superlarge Cu-Mo Deposit in Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 289-306. |
| [70] | Pavlova G G, Borisenko A S. the Age of Ag-Sb Deposits of Central Asia and Their Correlation with Other Types of Ore Systems and Magmatism[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 35(2): 164-185. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.11.006 |
| [71] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 苏永江, 等. 蒙古国图木尔廷敖包大型锌矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 321-330. Jiang Sihong, Nie Fengjun, Su Yongjiang, et al. The Geological Features and Origin of the Tumurtin Ovoo Large-Scale Zinc Deposit, Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 321-330. |
| [72] | Nie F J, Chen X H, Jiang S H, et al. Annual Report for the Integrated Studies on Balchas-Junggar-South Mongolia Metallogenic Belt and Exploration Techniques[J]. Intern Sci Tectonic Rep Inst Mineral Res, 2010, 12: 1-224. |
| [73] | Cluer J, Kotlyar B, Gantsetseg O, et al. Geology of the Boroo Gold Deposit, Northern Mongolia[J]. Seg-Iagod Guidbook Series, 2005, 11: 105-117. |
| [74] | 聂凤军, 刘勇, 刘翼飞, 等. 中蒙边境查夫-甲乌拉地区中生代银多金属矿床成矿作用[J]. 吉林大学学报 (地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1715-1725. Nie Fengjun, Liu Yong, Liu Yifei, et al. Ore-Forming Processes of Silver-Polymetallic Deposits Occurring Within Tsav-Jiawula Region along China-Mongolian Border[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(6): 1715-1725. |
| [75] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等. 北山地区金属矿床成矿规律及找矿方向[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 1-427. Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, Bai Daming, et al. Metallogenic Studies and Ore Prospecting in the Conjunction Area of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Gansu Province and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Beishan Mt), Northwest China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002: 1-427. |
| [76] | 陈静. 黑龙江小兴安岭区域成矿背景与有色、贵金属矿床成矿作用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2011: 1-161. Chen Jing.Metallogenic Setting and Metallogenesis of Nonferrous-Precious Metals in Lesser Hinggan Mountain, Heilongjiang Province[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2011:1-161. |
| [77] | 张振庭. 黑龙江省伊春地区铅锌多金属矿产预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2010: 1-165. Zhang Zhenting. Forecast of Lead Zinc Polymetallic Ore in Yichun of Heilongjiang[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2010:1-165. |
| [78] | 魏连喜. 黑龙江省有色、贵金属成矿规律及定量预测研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013: 1-201. Wei Lianxi. Study on Metallogenic Regularity and Quantitative Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Precious Metals in Heilongjiang Province[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2013:1-201. |
| [79] | 史鹏会, 杨言辰, 叶松青, 等. 黑龙江五道岭钼铁矿床地质地球化学特征及成因[J]. 世界地质, 2012, 31(2): 262-270. Shi Penghui, Yang Yanchen, Ye Songqing, et al. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Ferromolybdenum Deposit in Wudaoling, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Global Geology, 2012, 31(2): 262-270. |
| [80] | 唐臣, 柴鹏, 孙景贵, 等. 黑龙江伊春大安河金矿床区辉长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(2): 173-179. Tang Chen, Chai Peng, Sun Jinggui, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Age of Gabbro in Da'anhe Gold Deposit and Its Geological Implications of Yichun, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Global Geology, 2011, 30(2): 173-179. |
| [81] | 包真艳, 王建, 杨言辰, 等. 黑龙江平顶山金矿赋矿花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(3): 407-420. Bao Zhenyan, Wang Jian, Yang Yanchen, et al. U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Ore-Hosting Granites from the Pingdingshan Gold Deposit, Heilongjiang Province, and Its Geological Implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 407-420. |
| [82] | 赵羽军, 崔培龙, 王清海, 等. 黑龙江宁安英城子热液金矿床流体包裹体的氩同位素激光探针定年与成矿时代讨论[J]. 世界地质, 2010, 29(2): 201-208. Zhao Yujun, Cui Peilong, Wang Qinghai, et al. 40Ar/39Ar Laser Probe Dating of Fluid Inclusions and Discussion on Metallogenic Epoch of Yingchengzi Epithemal Au Deposit in Ning'an Area of Heilongjiang[J]. Global Geology, 2010, 29(2): 201-208. |
| [83] | 黄永卫.黑龙江省东南部完达山-太平岭一带浅成低温热液矿床区域成矿规律及找矿前景研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学,2010:1-180. Huang Yongwei. Study on Metallogenetic Regularities and Ore-Forming Forecast of Epithermal Gold Deposits in Wanda Mountain and Taiping Mountain Belts in Southeast of Heilongjiang Province[J].Beijing:China University of Geoscience, 2010:1-180. |
| [84] | 李向文, 杨言辰, 王献忠, 等. 黑龙江省塔河县宝兴沟金矿床地质特征及成矿构造环境[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(6): 1700-1710. Li Xiangwen, Yang Yanchen, Wang Xianzhong, et al. Geologic Characteristics and Metallogenic Tectonic Environment of the Baoxianggou Gole Deposit in Tahe, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(6): 1700-1710. |
| [85] | 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 刘瑞萍, 等. 黑龙江高岗山斑岩型钼矿床成岩成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(5): 624-635. Zhang Yongmei, Gu Xuexiang, Liu Ruiping, et al. Geochronology of Instrusive Rocks and Associated Ores of the Gaogangshan Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(5): 624-635. |
| [86] | 聂凤军. 中蒙边境中东段金属矿床成矿规律和找矿方向[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-574. Nie Fengjun. Metallogenic Studies and Prospecting Orientation in Central and Eastern Segements Along China-Mongolia Border[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 1-574. |
| [87] | Zeng Q D, Sun Y, Duan X X, et al. U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology of the Haolibao Porphyry Mo-Cu Deposit, NE China:Implications for a Late Permian Tectonic Setting[J]. Geological Magazine, 2013, 150(6): 975-985. DOI:10.1017/S0016756813000186 |
| [88] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古黑鹰山富铁矿床磷灰石钐-钕同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(2): 134-140. Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, Liu Yan, et al. Sm-Nd Isotopic Dating of Apatite Separates from Heiyingshan High-Grade Iron Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(2): 134-140. |
| [89] | Ishihara D, Mizuta T, Ishikawa Y, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Igneous Rocks and Tin-Copper Mineralization[J]. Project Final Report of Chinese Research Center for Mineral Resources Exploration, 2001, 4: 115-138. |
| [90] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 赵省民, 等. 内蒙古流沙山金(钼)矿床地质特征及矿床类型的划分[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002, 30(1): 1-7. Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, Zhao Xingmin, et al. Geological Features and Metallogenic Type of the Liushashan Gold (Molybdenum) Deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2002, 30(1): 1-7. |
| [91] | 聂凤军, 张万益, 杜安道, 等. 内蒙古小东沟斑岩型钼矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(7): 898-905. Nie Fengjun, Zhang Wanyi, Du Andao, et al. Re-Os Isotopic Dating on Molybdenite Separates from the Xiaodonggou Porphyry Mo Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(7): 898-905. |
| [92] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 内蒙古查干敖包石英闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2008, 27(3): 177-184. Zhang Wanyi, Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age of Quartz Diorite in Qagan Obo of Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2008, 27(3): 177-184. |
| [93] | 聂凤军, 张万益, 杜安道, 等. 内蒙古朝不楞矽卡岩型铁多金属矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2007, 28(4): 315-323. Nie Fengjun, Zhang Wanyi, Du Andao, et al. Re-Os Isotopic Age Dating of Molybdenite Separates from the Chaobuleng Skarn Iron-Polymetallic Deposit, Dong Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 315-323. |
| [94] | 王圣文, 王建国, 张达, 等. 大兴安岭太平沟钼矿床成矿年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 1913-1923. Wang Shengwen, Wang Jianguo, Zhang Da, et al. Geochronological Study on Taipinggou Molybdenum Deposit in DaHinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(11): 1913-1923. |
| [95] | 李进文, 梁玉伟, 王向阳, 等. 内蒙古二道河子铅锌矿成因研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1745-1754. Li Jinwen, Liang Yuwei, Wang Xiangyang, et al. the Origin of the Erdaohezi Lead-Zinc Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(6): 1745-1754. |
| [96] | 闫聪, 孙艺, 赖勇, 等. 内蒙古半拉山钼矿LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb与辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其成矿动力学背景[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(4): 616-634. Yan Cong, Sun Yi, Lai Yong, et al. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb and Molybdenite Re-Os Isotope Ages and Metallogenic Geodynamic Setting of Banlashan Mo Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(4): 616-634. |
| [97] | 刘翼飞, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗准苏吉花钼矿床成岩成矿年代学及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(1): 119-128. Liu Yifei, Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, et al. Geochronology of Zhunsujihua Molybdenum Deposit in Sonid Left Banner, Inner Mongolia, and Its Geological Significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2012, 31(1): 119-128. |
| [98] | Ouyang H G, Wu X L, Mao J W, et al. The Nature and Timing of Ore Formation in the Budunhua Copper Deposit, Southern Great Xing'an Range:Evidence from Geology, Fluid Inclusions, and U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 63: 238-251. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.05.016 |
| [99] | Wu H Y, Zhang L G, Wan B, et al. Re-Os and 40Ar/39Ar Ages of the Jiguanshan Porphyry Mo Deposit, Xilamulun Metallogenic Belt, NE China, and Constraints on Mineralization Events[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2011, 46(2): 171-185. DOI:10.1007/s00126-010-0320-9 |
| [100] | Hart C J, Goldfarb R J, Qiu Y, et al. Gold Deposits of the Northern Margin of the North China Craton:Multiple Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic Mineralizing Events[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3/4): 326-351. |
| [101] | 冯晓曦, 姚书振, 段明, 等. 内蒙古白乃庙铜(钼)矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(1): 132-141. Feng Xiaoxi, Yao Shuzhen, Duan Ming, et al. Re-Os Dating of Molybdenite from the Bainaimiao Cu(Mo) Deposit in Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2015, 45(1): 132-141. |
| [102] | 孟树, 闫聪, 赖勇, 等. 内蒙古车户沟钼铜矿成矿年代学及成矿流体特征研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(1): 255-269. Meng Shu, Yan Cong, Lai Yong, et al. Study on the Mineralization Chronology and Characteristics of Mineralization Fluid from the Chehugou Porphyry Mo-Cu Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(1): 255-269. |
| [103] | 周振华, 武新丽, 欧阳荷根. 内蒙古莲花山铜银矿斜长花岗斑岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年、Hf同位素研究及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6): 1472-1485. Zhou Zhenhua, Wu Xinli, Ouyang Hegen. LA-MC-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotope Study of the Plagioclase Granite Porphyry in the Lianhuashan Cu-Ag Deposit of Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Significance[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(6): 1472-1485. |
| [104] | 陶继雄, 钟仁, 赵月明, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗乌兰德勒钼(铜)矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 413-422. Tao Jixiong, Zhong Ren, Zhao Yueming, et al. Geological Characteristics and Ore-Prospecting Criteria of the Ulandler Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit in Sonid Left Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 413-422. |
| [105] | 杨梅珍, 侯坤, 陆建培, 等. 东乌珠穆沁旗索纳嘎钼铅锌多金属矿床成岩成矿年代学[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(6): 1327-1337. Yang Meizhen, Hou Kun, Lu Jianpei, et al. Chronology of Molybdenum-Lead-Zinc Polymetallic Deposit of Suo Naga, Dong Ujimqin Banner Region[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(6): 1327-1337. |
| [106] | Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Zhang Z L. Re-Os Geochronology of Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit in South Segment of Da Hinggan Mountains, Northeast China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2010(4): 392-401. |
| [107] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 卢百志, 等. 内蒙古太平川铜钼矿成矿斑岩时代、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(5): 1437-1449. Chen Zhiguang, Zhang Lianchang, Lu Baizhi, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Taipingchuan Copper-Molybdenum Deposit in Inner Mongolia, and Its Geological Significances[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(5): 1437-1449. |
| [108] | 刘翠, 邓晋福, 许立权, 等. 大兴安岭-小兴安岭地区中生代岩浆-构造-钼成矿地质事件序列的初步框架[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(3): 166-178. Liu Cui, Deng Jinfu, Xu Liquan, et al. A Preliminary Frame of Magma-Tectonic-Mo Metallogenic Events of Mesozoic Era in Da Hinggan Mountains and Xiao Hinggan Mountains Areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(3): 166-178. |
| [109] | 阮班晓, 吕新彪, 刘申态, 等. 内蒙古边家大院铅锌银矿床成因:来自锆石U-Pb年龄和多元同位素的制约[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(3): 501-514. Ruan Banxiao, Lü Xinbiao, Liu Shentai, et al. Genesis of Bianjiadayuan Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit in Inner Mongolia:Constraints from U-Pb Dating of Zircon and Multi-Isotope Geochemistry[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(3): 501-514. |
| [110] | 薛怀民, 郭利军, 侯增谦, 等. 大兴安岭西南坡成矿带晚古生代中期未变质岩浆岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 811-823. Xue Huaimin, Guo Lijun, Hou Zengqian, et al. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Ages of the Middle Neopaleozoic Unmetamorphosed Magmatic Rocks in the Southwestern Slope of the Da Hinggan Mountains, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2010, 29(6): 811-823. |
| [111] | Zhai D G, Liu J J, Wang J P, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Molybdenite Re-Os Geochronology, and Whole-Rock Geochemistry of the Hashitu Molybdenum Deposit and Host Granitoids, Inner Mongolia, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 144-160. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.008 |
| [112] | 彭振安, 李红红, 屈文俊, 等. 内蒙古北山地区小狐狸山钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(3): 510-516. Peng Zhen'an, Li Honghong, Qu Wenjun, et al. Molybdenite Re-Os Age of Xiaohulishan Molybdenum Deposit in Beishan Area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [113] | 王科强, 黄辉, 王治华, 等. 内蒙古额尔古纳虎拉林金矿床钾长石40Ar-39Ar年龄及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊2): 41-46. Wang Keqiang, Huang Hui, Wang Zhihua, et al. 40Ar-39Ar Age of Potassium Feldspar of Hunalin Gold Deposit and Its Significance, Ergun of Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(Sup.2): 41-46. |
| [114] | 周勇.内蒙古化德县三胜村钨钼矿床的成矿作用[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院,2013:1-81. Zhou Yong.The Mineralization of Sansheng W-Mo Deposit in Huade, Inner Mongolia[D].Beijing:Chinese Science Institute of Geoscience, 2013:1-81. |
| [115] | Wu C, Jiang T, Liu W, et al. Early Cretaceous Adakitic Granites and Mineralization of the Yili Porphyry Mo Deposit in the Great Xing'an Range:Implications for the Geodynamic Evolution of Northeastern China[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 57(9/10): 1152-1171. |
| [116] | 董旭舟, 周振华, 王润和, 等. 内蒙古敖包吐铅锌矿床花岗岩类年代学及其地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(2): 323-338. Dong Xuzhou, Zhou Zhenhua, Wang Runhe, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Granite in Aobaotu Pb-Zn Deposit,Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Geology, 2014, 33(2): 323-338. |
| [117] | Han S J, Sun J G, Bai L A, et al. Geology and Ages of Porphyry and Medium-to High-Sulphidation Epithermal Gold Deposits of the Continental Margin of Northeast China[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(3): 287-310. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.695472 |
| [118] | 李立兴, 松权衡, 王登红, 等. 吉林福安堡钼矿中辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及成矿作用探讨[J]. 岩矿测试, 2009, 28(3): 283-287. Li Lixing, Song Quanheng, Wang Denghong, et al. Re-Os Isotopic Dating of Molybdenite from the Fu'anpu Molybdenum Deposit of Jilin Province and Discussion on Its Metallogenesis[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(3): 283-287. |
| [119] | 赵华雷, 任云生, 鞠楠, 等. 延边白石砬子钨矿床成矿岩体的年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(6): 1726-1744. Zhao Hualei, Ren Yunsheng, Ju Nan, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Metallogenic Intrusion in Baishilazi Tungsten of Eastern Yanbian Area, Northeast China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(6): 1726-1744. |
| [120] | 赵羽军, 孙景贵, 王清海, 等. 吉林延边地区浅成热液金(铜)矿床的40Ar/39Ar激光探针测年与成矿时代讨论[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 156-169. Zhao Yunjun, Sun Jinggui, Wang Qinghai, et al. 40Ar/39Ar Laser Probe Dating and Discussion on Metallogenic Epoch of Epithermal Au-Cu Deposit in Yanbian Area of Jilin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2): 156-169. |
| [121] | 王辉, 任云生, 孙振明, 等. 吉林汪清夹皮沟斑岩型钼矿床的形成时代与成矿构造背景[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(3): 489-500. Wang Hui, Ren Yunsheng, Sun Zhenming, et al. Metallogenic Epoch and Tectonic Setting of Jiapigou Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit in Wangqing Area, Jilin Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(3): 489-500. |
| [122] | Jargalan S, Fujimaki H, Ohba T. Petrologic Characteristics and Rb-Sr Age Dating of Lamprophyre Dikes of Tsagaan Tsahir Uul Gold Deposit, Mongolia[J]. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 2007, 102(3): 163-173. DOI:10.2465/jmps.060322b |
| [123] | Kempe U, Belyatsky Bv. Direct Isotope Dating of W (-Y) Mineralization at Kyzyltau (Mongolian Altai):Preliminary Results[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 42(5): 470-480. |
| [124] | 薛静, 聂凤军, 戴塔根, 等. 蒙古国阿林诺尔钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 350-356. Xue Jing, Nie Fengjun, Dai Tagen, et al. Re-Os Isotopic Dating of Molybdenite from the Aryn Nuur Mo Deposit in Mongolia and Its Geological Implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 350-356. |
| [125] | Watanabe Y, Turmagnai D, Byambasuren D, et al. Geology and K-Ar Ages of the South, Huh Bulgiin Hundii, Saran Uul, Taats Gol and Han Uul Deposits in the Bayankhongor Region, Mongolia[J]. Resource Geology, 1999, 49(3): 123-130. DOI:10.1111/rge.1999.49.issue-3 |
| [126] | 王林, 杨言辰, 张国宾, 等. 黑龙江秋皮沟铜矿床年代学与地球化学特征及成因[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(1): 24-34. Wang Lin, Yang Yanchen, Zhang Guobin, et al. Chronology, Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Qiupigou Copper Deposit in Heilongjiang[J]. Global Geology, 2013, 32(1): 24-34. |
| [127] | 白令安, 孙景贵, 张勇, 等. 大兴安岭地区内生铜矿床的成因类型、成矿时代与成矿动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 468-482. Bai Ling'an, Sun Jinggui, Zhang Yong, et al. Genetic Type,Mineralization Epoch and Geodynamical Setting of Endogenous Copper Deposits in the Great Xing'an Range[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2): 468-482. |
| [128] | 刘莉.黑龙江省穆棱市砍椽沟钼铜矿床成矿地质条件及找矿远景评价[D].长春:吉林大学,2010:1-67. Liu Li. Ore-Forming Geological Conditions and Propecting of Kanchuangou Mo-Cu Deposit in Muling Area, Heilongjiang[D].Changchun:Jilin Univerisity, 2010:1-67. |
| [129] | Zhang G B, Yang Y C, Wang J, et al. Geology, Geochemistry, and Genesis of the Hot-Spring-Type Sipingshan Gold Deposit, Eastern Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(4): 482-495. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.727572 |
| [130] | 孙珍军, 孙丰月, 孙国胜, 等. 小兴安岭北麓石林公园区钼钨矿化成矿地球化学特征及年代学[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(增刊 3): 25-37. Sun Zhenjun, Sun Fengyue, Sun Guosheng, et al. Geochemical Features and Geochronology of the Shilin Park Mo-W Mineralization in the Northern Foot of Lesser Xing'an Range[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(Sup. 3): 25-37. |
| [131] | Sun W D, Ling M X, Yang X Y, et al. Ridge Subduction and Porphyry Copper-Gold Mineralization:An Overview[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(4): 475-484. DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-0024-0 |
| [132] | 杨言辰, 韩世炯, 孙德有, 等. 小兴安岭-张广才岭成矿带斑岩型钼矿床岩石地球化学特征及其年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 379-390. Yang Yanchen, Han Shijiong, Sun Deyou, et al. Geological and Geochemical Features and Geochronology of Porphyry Molybdenum Deposits in the Lesser Xing'an Range-Zhangguangcai Range Metallogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2): 379-390. |
| [133] | 唐臣, 杨帆, 孙景贵, 等. 大兴安岭旁开门金银矿床赋矿围岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(4): 532-537. Tang Chen, Yang Fan, Sun Jinggui, et al. U-Pb Dating of Zircons from Host Rocks of Pankaimen Gold-Silver Deposit in Great Xing'an Range and Its Geological Implications[J]. Global Geology, 2011, 30(4): 532-537. |
| [134] | 孙景贵, 张勇, 邢树文, 等. 兴蒙造山带东缘内生钼矿床的成因类型、成矿年代及成矿动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4): 1317-1332. Sun Jinggui, Zhang Yong, Xing Shuwen, et al. Genetic Types, Ore-Forming Age and Geodynamic Setting of Endogenic Molybdenum Deposits in the Eastern Edge of Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(4): 1317-1332. |
| [135] | 唐忠.黑龙江松江Cu-W-Zn多金属矿床特征及成矿条件[D].长春:吉林大学,2012:1-63. Tang Zhong. The Characteristics and Metallogenic Condition of Songjiang Cu-W-Zn Polymetallic Deposit in Heilongjiang Province[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2012:1-63. |
| [136] | 吕俊超, 杨言辰, 韩世炯, 等. 黑龙江洋灰洞子铜矿床花岗闪长斑岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(1): 59-75. Lü Junchao, Yang Yanchen, Han Shijiong, et al. Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Granodiorite Porphyry in the Yanghuidongzi Copper Deposit,Heilongjiang Province,and Its Geological Implications[J]. Global Geology, 2014, 33(1): 59-75. |
| [137] | 孙燕, 刘建明, 曾庆栋, 等. 内蒙东部白土营子钼铜矿田的矿床地质特征、辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(1): 241-254. Sun Yan, Liu Jianming, Zeng Qingdong, et al. Geological Characteristics and Molybdenite Re-Os Ages of the Baituyingzi Mo-Cu Field, Eastern Inner Mongolia and Their Geological Implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(1): 241-254. |
| [138] | 毛景文, 周振华, 武广, 等. 内蒙古及邻区矿床成矿规律与成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(4): 716-730. Mao Jingwen, Zhou Zhenhua, Wu Guang, et al. Metallogenic Regularity and Minerogenetic Series of Ore Deposits in Inner Mongolia and Adjacent Areas[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(4): 716-730. |
| [139] | 白令安.大兴安岭中北部热液铜矿床的成矿机制与资源预测[D].长春:吉林大学,2013:1-145. Bai Ling'an. Study on Metallogenic Mechanism and Resource Forecast of Hydrothermal Cu Deposits in the Central and North of the Great Xing'an Range, NE China[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2013:1-145. |
| [140] | 聂凤军, 屈文俊, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古额勒根斑岩型钼(铜)矿化区辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(6): 638-646. Nie Fengjun, Qu Wenjun, Liu Yan, et al. Re-Os Isotopic Age Dating of Molybdenite Separates from Elegen Porphyry Mo (Cu) Mineralized Area, Northwestern Alxa, Western Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(6): 638-646. |
| [141] | Wang J B, Wang Y W, Wang L J, et al. Tin-Polymetallic Mineralization in the Southern Part of the Da Hinggan Mountains, China[J]. Resource Geology, 2001, 51(4): 283-291. DOI:10.1111/rge.2001.51.issue-4 |
| [142] | 王明艳, 何玲. 内蒙古查木罕钨钼多金属矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(1): 49-56. Wang Mingyan, He Ling. Re-Os Dating of Molybdenites from Chamuhan W-Mo Deposit, Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(1): 49-56. |
| [143] | 王玉往, 王京彬, 王莉娟. 内蒙古大乃林沟角闪石岩岩石学特征[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(3): 1-6. Wang Yuwang, Wang Jingbin, Wang Lijuan. The Petrologic Characteristics of Hornblendite in Danailingou, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Review, 2000, 46(3): 1-6. |
| [144] | 张斌. 内蒙古东珺铅锌银矿矿床地质特征及其成因研究[D].北京:中国地质科学院,2011:1-80. Zhang Bin. The Geological Features and Genesis of the Dongjun Lead-Zinc-Silver Deposit in Inner Mongolia, China[D].Beijing:Chinese Science Institute of Geoscience, 2011:1-80. |
| [145] | 沈存利, 张梅, 于玺卿, 等. 内蒙古钼矿找矿新进展及成矿远景分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(4): 561-575. Shen Cunli, Zhang Mei, Yu Xiqing, et al. New Progresses in Exploration of Molybdenum Deposits and Analysis of Mineralization Prospect in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(4): 561-575. |
| [146] | 佘宏全, 徐贵忠, 周瑞, 等. 内蒙东部红花沟金矿田早中生代构造-岩浆活动及对金成矿的控制作用[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(4): 408-416. She Hongquan, Xu Guizhong, Zhou Rui, et al. Tectonic and Magmatic Activities in Early Mesozoic and Their Controlling on Gold Mineralization in Honghuagou Gold Ore Field, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2000, 14(4): 408-416. |
| [147] | 张万益, 聂凤军, 刘妍, 等. 内蒙古奥尤特铜-锌矿床绢云母40/Ar-39Ar同位素年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(5): 592-598. Zhang Wanyi, Nie Fengjun, Liu Yan, et al. 40Ar-39Ar Geochronology of the Aououte Cu-Zn Deposit in Inner Mongolia and Its Significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(5): 592-598. |
| [148] | Liu J M, Zhao Y, Sun Y L, et al. Recognition of the Latest Permian to Early Triassic Cu-Mo Mineralization on the Northern Margin of the North China Block and Its Geological Significance[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 17(1): 125-134. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.07.007 |
| [149] | Cunningham D, Davies S, Mclean D. Exhumation of a Cretaceous Rift Complex Within a Late Cenozoic Restraining Bend, Southern Mongolia:Implications for the Crustal Evolution of the Gobi Altai Region[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2009, 166(2): 321-333. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492008-082 |
| [150] | Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Zhang Z L, et al. Geology and Geochronology of the Xilamulun Molybdenum Metallogenic Belt in Eastern Inner Mongolia, China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2011, 100(8): 1791-1809. DOI:10.1007/s00531-010-0617-z |
| [151] | Shu Q H, Lai Y, Wang C, et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes of the Haisugou Porphyry Mo Deposit, Northeast China, and Their Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 777-791. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.05.015 |
| [152] | Jiang S H, Niu S Y, Hou W R, et al. Summary of Study on Metallogenesis of the Au and Ag-Polymetallic Deposits Occurring in East-Central Inner Mongolia[R]. Beijing:Institute of Mineral Resources, 2012:1-531. |
| [153] | 祝洪臣, 张炯飞, 权恒. 下吉宝沟金矿的发现及其地质特征[J]. 贵金属地质, 2000, 9(2): 65-72. Zhu Hongchen, Zhang Jiongfei, Quan Heng. The Geological Characteristics of Xiajibaogou Gold Deposit[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 2000, 9(2): 65-72. |
| [154] | 孙珍军.华北克拉通北缘赤峰-朝阳地区金矿成矿作用研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2013:1-206. Sun Zhenjun. Study on Gold Deposits Mineralization in Chifeng-Chaoyang Region, Northern Margin of North China Craton[D].Changchun:Jilin University, 2013:1-206. |
| [155] | 蔡明海, 彭振安, 屈文俊, 等. 内蒙古乌拉特后旗查干德尔斯钼矿床地质特征及Re-Os测年[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(3): 377-384. Cai Minghai, Peng Zhen'an, Qu Wenjun, et al. Geological Characteristics and Re-Os Dating of Molybdenites in Chagandeersi Molybdenum Deposit, Western Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(3): 377-384. |
| [156] | 王治华, 常春郊, 王梁, 等. 内蒙古1017高地银多金属矿床40Ar/39Ar年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(6): 589-598. Wang Zhihua, Chang Chunjiao, Wang Liang, et al. 40Ar/39Ar Age and Its Geological Significance of 1017 Highland Ag Polymetallic Deposit in Dong Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geochimica, 2013, 42(6): 589-598. |
| [157] | 张炯飞, 庞庆邦, 朱群, 等. 内蒙古白音宝力道花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb定年:白音宝力道金矿成矿主岩的形成时代[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(2): 189-192. Zhang Jiongfei, Pang Qingbang, Zhu Qun, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Bayan Bold Granite-Porphyry in Inner Mongolia:The Age of the Host Rock of the Bayan Bold Gold Deposit[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2004, 23(2): 189-192. |
| [158] | 李俊建, 骆辉, 周学武, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善呼伦西白金矿的成矿时代[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(2): 193-196. Li Junjian, Luo Hui, Zhou Xuewu, et al. Metallogenic Epoch of Hulunxibai Gold Deposit in Alashan Area, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Geoscience, 2004, 18(2): 193-196. |
| [159] | 云飞, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 内蒙古莫若格钦地区二长闪长岩锆石SHRIM PU-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(3): 504-510. Yun Fei, Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age of Monuogechin Monzodiorite of Inner Mongolia and Its Geological Significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(3): 504-510. |
| [160] | Peng R M, Zhai Y S, Li C S, et al. The Erbutu Ni-Cu Deposit in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt:A Permian Magmatic Sulfide Deposit Related to Boninitic Magmatism in an Arc Setting[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108(8): 1879-1888. DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.8.1879 |
| [161] | 佘宏全, 李红红, 李进文, 等. 内蒙古大兴安岭中北段铜铅锌金银多金属矿床成矿规律与找矿方向[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(10): 1456-1472. She Hongquan, Li Honghong, Li Jinwen, et al. The Metallogenetical Characteristics and Prospecting Direction of the Copper-Lead-Zinc Polymetal Deposits in the Northern-Central Daxing'anling Mountain, Inner Monglia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(10): 1456-1472. |
| [162] | Zhou Z H, Mao J W, Wu X L, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry Constraints of the Early Cretaceous Taibudai Porphyry Cu Deposit, Northeast China, and Its Tectonic Significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 103: 212-228. |
| [163] | 郝立波, 孙立吉, 赵玉岩, 等. 吉林红旗岭镍矿田茶尖岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2013, 38(2): 233-240. Hao Libo, Sun Liji, Zhao Yuyan, et al. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating of Chajian Mafic-Ultramafic Rocks in Hongqiling Mine Field, Jilin Province, and Its Implications[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 38(2): 233-240. |
| [164] | Wu F Y, Wilde S, Zhang G L, et al. Geochronology and Petrogenesis of the Post-Orogenic Cu-Ni Sulfide-Bearing Mafic-Ultramafic Complexes in Jilin Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5): 781-797. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00114-7 |
| [165] | 任云生, 牛军平, 王辉, 等. 吉林四平孟家岭含钨花岗岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2009, 29(3): 100-105. Ren Yunsheng, Niu Junping, Wang Hui, et al. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age and Its Geological Significance of Tungsten-Bearing Mengjialing Granitic Intrusion in Siping Area, Jilin Province[J]. Jmineral Petrol, 2009, 29(3): 100-105. |
| [166] | 闻爽, 李碧乐, 李立宝, 等. 吉林省兰家金矿南泉眼闪长岩U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(2): 305-315. Wen Shuang, Li Bile, Li Libao, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age and Geochemistry of Nanquanyan Dirorite in the Lanjia Gold Deposit, Jilin Province[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(2): 305-315. |
| [167] | 邸新, 毕小刚, 贾海明, 等. 蛟河地区前进岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及其与吉中-延边地区钼矿成矿作用的关系[J]. 吉林地质, 2011, 30(4): 25-28. Di Xin, Bi Xiaogang, Jia Haiming, et al. Qianjin Rock Zircon U-Pb Ages of Jiaohe Region to the Molybdenum Mineralization of Central Part of Jilin Province-Yanbian Region[J]. Jilin Geology, 2011, 30(4): 25-28. |
| [168] | Orolmaa D, Erdenesaihan G, Borisenko A, et al. Permian-Triassic Granitoid Magmatism and Metallogeny of the Hangayn (Central Mongolia)[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2008, 49(7): 534-544. DOI:10.1016/j.rgg.2008.06.008 |
| [169] | Jahn B M. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and Growth of the Continental Crust in the Phanerozoic[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2004, 226(1): 73-100. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.226.01.05 |
| [170] | 王鸿祯, 何国琦, 张世红. 中国与蒙古之地质[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 1-13. Wang Hongzhen, He Guoqi, Zhang Shihong. Geology of Mongolia and China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 1-13. |
| [171] | 张兴洲, 杨宝俊, 吴福元, 等. 中国兴蒙-吉黑地区岩石圈结构基本特征[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(4): 816-823. Zhang Xingzhou, Yang Baojun, Wu Fuyuan, et al. the Lithosphere Structure in the Hingmong-Jihei (Hinggan-Mongolia-Jilin-Heilongjiang) Region, Northeastern China[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(4): 816-823. |
| [172] | 李述靖. 蒙古弧地质构造特征及形成演化概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998. Li Shujing. Geological Features of Mongolia Arc Structure and Its Formation and Evolution[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998. |
| [173] | Xiao W J, Mao Q G, Windley B F, et al. Paleozoic MulTiple Accretionary and Collisional Processes of the Beishan Orogenic Collage[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(10): 1553-1594. DOI:10.2475/10.2010.12 |
| [174] | PerellÓ J, Cox D, Garamjav D, et al. Oyu Tolgoi, Mongolia:Siluro-Devonian Porphyry Cu-Au-(Mo) and High-Sulfidation Cu Mineralization with a Cretaceous Chalcocite Blanket[J]. Economic Geology, 2001, 96(6): 1407-1428. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.96.6.1407 |
| [175] | Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic Granitoids in Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 1-30. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014 |
| [176] | Wang C W, Sun Y W, Li N, et al. Tectonic Implications of Late Paleozoic Stratigraphic Distribution in Northeast China and Adjacent Region[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2009, 52(5): 619-626. DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0062-7 |
| [177] | 张晋瑞, 初航, 魏春景, 等. 内蒙古中部构造混杂带晚古生代-早中生代变质基性岩的地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1935-1947. Zhang Jinrui, Chu Hang, Wei Chunjing, et al. Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic Meta-Basic Rocks in the MÉLange Zones, Central Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(7): 1935-1947. |
| [178] | Wu F Y, Zhao G C, Sun D Y, et al. The Hulan Group:Its Role in the Evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 30(3): 542-556. |
| [179] | Han G, Liu Y, Neubauer F, et al. Provenance Analysis of Permian Sandstones in the Central and Southern Da Xing'an Mountains, China:Constraints on the Evolution of the Eastern Segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 580: 100-113. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.041 |
| [180] | Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China):Implications for the Continental Growth of Central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4): 370-395. DOI:10.2475/ajs.304.4.370 |
| [181] | 李锦轶, 莫申国, 和政军, 等. 大兴安岭北段地壳左行走滑运动的时代及其对中国东北及邻区中生代以来地壳构造演化重建的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 157-168. Li Jinyi, Mo Shenguo, He Zhengjun, et al. The Timing of Crustal Sinistral Strike-Slip Movement in the Northern Great Khing'an Ranges and Its Constraint on Reconstruction of the Crustal Tectonic Evolution of NE China and Adjacent Areas Since the Mesozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 157-168. |
| [182] | Tomurtogoo O, Windley B F, Kröner A, et al. Zircon Age and Occurrence of the Adaatsag Ophiolite and Muron Shear Zone, Central Mongolia:Constraints on the Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean, Suture and Orogen[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2005, 162(1): 125-134. DOI:10.1144/0016-764903-146 |
| [183] | Seton M, Flament N, Whittaker J, et al. Ridge Subduction Sparked Reorganization of the Pacific Plate-Mantle System 60-50 Million Years Ago[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(6): 1732-1740. DOI:10.1002/2015GL063057 |
| [184] | Li J, Yuen D A. Mid-Mantle Heterogeneities Associated with Izanagi Plate:Implications for Regional Mantle Viscosity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 385: 137-144. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2013.10.042 |
| [185] | 董树文, 李廷栋, 钟大赉, 等. 侏罗纪/白垩纪之交东亚板块汇聚的研究进展和展望[J]. 中国科学基金, 2009, 23(5): 281-286. Dong Shuwen, Li Tingdong, Zhong Dalai, et al. Recent Progress and Perspective of the Research on JK East Asian Multi:Direction Convergent Tectonics[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2009, 23(5): 281-286. |
| [186] | Wang T, Zheng Y D, Zhang J J, et al. Pattern and Kinematic Polarity of Late Mesozoic Extension in Continental NE Asia:Perspectives from Metamorphic Core Complexes[J]. Tectonics, 2011, 30(6): 1-27. |
| [187] | Wang T, Guo L, Zhang L, et al. Timing and Evolution of Jurassic-Cretaceous Granitoid Magmatisms in the Mongol-Okhotsk Belt and Adjacent Areas, NE Asia:Implications for Transition from Contractional Crustal Thickening to Extensional Thinning and Geodynamic Settings[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 365-392. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.005 |
| [188] | Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhang X Z, et al. The Onset of Pacific Margin Accretion in NE China:Evidence from the Heilongjiang High-Pressure Metamorphic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 478(3): 230-246. |
| [189] | Stein H, Markey R, Morgan J, et al. The Remarkable Re-Os Chronometer in Molybdenite:How and Why It Works[J]. Terra Nova, 2001, 13(6): 479-486. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2001.00395.x |
| [190] | Gao H. System Blank Level and Small Sample Dating in the All-Aotomatic 40Ar/39Ar Laser Probe Dating System[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26: 39-43. |
| [191] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. A Mineralogical Study of Zircon and Constraintes on Interpretation of U-Pb Age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. |
| [192] | Belousova E, Griffin W L, O'reilly S Y, et al. Igneous Zircon:Trace Element Composition as an Indicator of Source Rock Type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7 |
| [193] | Ludwig K. User'S Manual for Isoplot, Version 3.70:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 2008, 4: 1-76. |
| [194] | 杨岳清, 吕博, 孟贵祥, 等. 内蒙古东七一山花岗岩地球化学、锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及岩体形成环境探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2013, 34(2): 163-175. Yang Yueqing, Lü Bo, Meng Guixiang, et al. Geochemistry, SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating and Formation Environment of Dongqiyishan Granite, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 163-175. |
| [195] | Wang F, Xu W L, Gao F H, et al. Precambrian Terrane Within the Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China:Evidence from U-Pb Ages of Detrital Zircons from the Dongfengshan and Tadong Groups[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(1): 402-413. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.017 |
| [196] | 聂凤军, 江思宏, 张义, 等. 中蒙边境及邻区斑岩型铜矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(2): 176-189. Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, Zhang Yi, et al. Geological Features and Origin of Porphyry Copper Deposits in China-Mongolia Border Region and Its Neighboring Areas[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2004, 23(2): 176-189. |
| [197] | 刘金玉, 郗爱华, 葛玉辉, 等. 红旗岭3号含矿岩体地质年龄及其岩石学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(2): 321-326. Liu Jinyu, Xi Aihua, Ge Yuhui, et al. Mineralization Age of the No. 3 Ore-Bearing Intrusion and Its Petrological Significance in Hongqiling Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposits, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(2): 321-326. |
| [198] | 郗爱华, 顾连兴, 李绪俊, 等. 吉林红旗岭铜镍硫化物矿床的成矿时代讨论[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(5): 54-59. Xi Aihua, Gu Lianxing, Li Xujun, et al. Discussion on Metallogenic Epoch of Hongqiling Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposit, Jilin Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(5): 54-59. |
| [199] | 冯光英, 刘燊, 冯彩霞, 等. 吉林红旗岭超基性岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、Sr-Nd-Hf同位素特征及岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6): 1594-1606. Feng Guangying, Liu Shen, Feng Caixia, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age, Sr-Nd-Hf Isotope Geochemistry and the Petrogenesis of the Ultramafic Pluton in Hongqiling, Jilin Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(6): 1594-1606. |
| [200] | 邵军, 李秀荣, 杨宏智. 黑龙江翠宏山铅锌多金属矿区花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(2): 163-170. Shao Jun, Li Xiurong, Yang Hongzhi. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Dating of Granite in the Cuihongshan Polymetallic Deposit and Its Geological Implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 163-170. |
| [201] | Goldfarb R J, Taylor R D, Collins G S, et al. Phanerozoic Continental Growth and Gold Metallogeny of Asia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(1): 48-102. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.03.002 |
| [202] | Wu H F, Zhang L C, Pirajno F, et al. The Jiguan-shan Porphyry Mo Deposit in the Xilamulun Metallogenic Belt, Northern Margin of the North China Craton, U-Pb Geochronology, Isotope Systematics, Geochemistry and Fluid Inclusion Studies:Implications for a Genetic Model[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 56: 549-565. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.02.004 |
| [203] | Yang Y T. An Unrecognized Major Collision of the Okhotomorsk Block with East Asia During the Late Cretaceous, Constraints on the Plate Reorganization of the Northwest Pacific[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2013, 126: 96-115. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.07.010 |
| [204] | 赵一鸣. 大兴安岭及其邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律与远景评价[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1997: 1-318. Zhao Yiming. Copper Polymetal Deposits Metallogenic Regularity and Prospective Evaluation[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1997: 1-318. |
| [205] | 苑凤华, 彭玉鲸, 周晓东. 中国东北兴蒙-吉黑造山带贝加尔运动、萨拉伊尔运动、兴凯运动及泛非运动等之比较[J]. 吉林地质, 2012, 31(4): 1-13. Yuan Fenghua, Peng Yujing, Zhou Xiaodong. Comparison of Baikalian Orogeny, Salair Orogeny, Xingkai Orogeny, and Pan-African Orogeny of Xingmeng-Jihei Orogenessi Zone in the Northeast China[J]. Jilin Geology, 2012, 31(4): 1-13. |
| [206] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 兴蒙造山带东段斑岩型Cu,Mo矿床成矿时代及其地球动力学意义[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(20): 2407-2417. Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, Zhou Changyong, et al. Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposits in the Eastern Xing'an Mongolian Orogenic Belt:Mineralization Ages and Their Geodynamic Implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(20): 2407-2417. |
| [207] | 许文良, 王枫, 孟恩, 等. 黑龙江省东部古生代-早中生代的构造演化:火成岩组合与碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(5): 1378-1389. Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Meng En, et al. Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution in the Eastern Heilongjiang Province, NE China:Evidence from Igneous Rock Association and U-Pb Geochronology of Detrital Zircons[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1378-1389. |
| [208] | Wilde S A, Wu F Y, Zhang X Z. Late Pan-African Magmatism in Northeastern China:SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Evidence from Granitoids in the Jiamusi Massif[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1/2/3/4): 311-327. |
| [209] | 王守光, 黄占起, 苏新旭, 等. 一条值得重视的跨国境成矿带:南戈壁-东乌旗铜多金属成矿带[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 249-255. Wang Shouguang, Huang Zhanqi, Su Xinxu, et al. A Notable Metallogenic Belt Striding Across the Border Between China and Mongolia-South Gobi-Dongwuqi Copper-Polymetallic Metallogenic Belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(1): 249-255. |
| [210] | 张长青, 张承帅, 王义天, 等. 蒙古国巴彦洪戈尔地区金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 357-364. Zhang Changqing, Zhang Chengshuai, Wang Yitian, et al. The Geological Characteristics and Metallogenesis of Gold Deposits in Bayanhongor Area, Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 357-364. |
| [211] | Sinclair W. Porphyry Deposits Mineral Deposits of Canada:A Synthesis of Major Deposit-Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods[J]. Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposits Division, Special Publication, 2007, 5: 223-243. |
| [212] | 童英, 洪大卫, 王涛, 等. 中蒙边境中段花岗岩时空分布特征及构造和找矿意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 395-412. Tong Ying, Hong Dawei, Wang Tao, et al. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Granitoids in the Middle Segment of the Sino-Mongolian Border and Its Tectonic and Metallogenic Implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 395-412. |
| [213] | Zhang X, Zhang H, Tang Y, et al. Geochemistry of Permian Bimodal Volcanic Rocks from Central Inner Mongolia, North China:Implication for Tectonic Setting and Phanerozoic Continental Growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(3): 262-281. |
| [214] | 陈衍景. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6): 1181-1196. Chen Yanjing. Orogenic-Type Deposits and Their Metallogenic Model and Exploration Potential[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1181-1196. |
| [215] | 刘翼飞, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 蒙古国阿林诺尔钼矿床赋矿花岗岩年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 343-349. Liu Yifei, Nie Fengjun, Jiang Sihong, et al. The Geochronology and Geochemical Features of Ore-Hosting Granite in the Aryn Nuur Molybdenum Deposit, Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 343-349. |
| [216] | 曾维顺, 周建波, 董策, 等. 蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋俯冲的记录:额尔古纳地区八大关变质杂岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1948-1960. Zeng Weishun, Zhou Jianbo, Dong Ce, et al. Subduction Record of Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean:Constrains from Badaguan Metamorphic Complexes in the Erguna Massif, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(7): 1948-1960. |
| [217] | Wu F Y, Yang J H, Lo C H, et al. The Heilong-jiang Group:A Jurassic Accretionary Complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the Western Pacific Margin of Northeastern China[J]. Island Arc, 2007, 16(1): 156-172. DOI:10.1111/iar.2007.16.issue-1 |
| [218] | 张晓玲, 张文山. 内蒙古毛登锡铜钼多金属矿床花岗岩及火山角砾熔岩地质特征及找矿意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊1): 337-338. Zhang Xiaoling, Zhang Wenshan. Geologic Features of Granites and Volcanic Breccia of Maodeng Sn-Cu-Mo Polymetallic Deposit, Inner Mongolia and Its Prospecting Significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(Sup.1): 337-338. |
| [219] | Wang T, Guo L, Zheng Y, et al. Timing and Processes of Late Mesozoic Mid-Lower-Crustal Extension in Continental NE Asia and Implications for the Tectonic Setting of the Destruction of the North China Craton:Mainly Constrained by Zircon U-Pb Ages from Metamorphic Core Complexes[J]. Lithos, 2012, 154: 315-345. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.07.020 |
| [220] | Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H, et al. A-Type Granites in Northeastern China:Age and Geochemical Constraints on Their Petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1): 143-173. |
| [221] | Xu W L, Ji W Q, Pei F P, et al. Triassic Volcanism in Eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China:Chronology, Geochemistry, and Tectonic Implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 392-402. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.07.001 |
| [222] | Wang F Y, Xu W L, Meng E, et al. Late Triassic Bimodal Magmatism in the Lesser Xing'an-Zhangguangcai Range, NE China:Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2011, 75: 2116. |
| [223] | Khishgee C, Akasaka M, Ohira H, et al. Gold Mineralization of the Gatsuurt Deposit in the North Khentei Gold Belt, Central Northern Mongolia[J]. Resource Geology, 2014, 64(1): 1-16. DOI:10.1111/rge.2014.64.issue-1 |
| [224] | 许文良, 葛文春, 裴福萍, 等. 东北地区中生代火山作用的年代学格架及其构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3): 286-287. Xu Wenliang, Ge Wenchun, Pei Fuping, et al. Geochronolog Framework of the Mesozoic Volcanism in the Northeast China and Its Tectonic Significance[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(3): 286-287. |
| [225] | 张宏远, 侯泉林, 曹代勇. 胶东东部中生代走滑逆冲构造带的构造年代学制约[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2006, 36(7): 593-600. Zhang Hongyuan, Hou Quanlin, Cao Daiyong. Mesozoic Strike-Slip Thrust Belt in Eastern Jiaodong Construction and Its Geochronological Constraints[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2006, 36(7): 593-600. |
| [226] | Maghsoudi A, Yazdi M, Mehrpartou M, et al. Porphyry Cu-Au Mineralization in the Mirkuh Ali Mirza Magmatic Complex, NW Iran[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 932-941. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.002 |
| [227] | Yu J J, Wang F, Xu W L, et al. Early Jurassic Mafic Magmatism in the Lesser Xing'an-Zhangguangcai Range, NE China, and Its Tectonic Implications:Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Chronology and Geochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2012(142/143): 256-266. |
| [228] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 吴华英, 等. 内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带碾子沟钼矿区A型花岗岩地球化学和构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(4): 879-889. Chen Zhiguang, Zhang Lianchang, Wu Huaying, et al. Geochemistry Study and Tectonic Background of A Style Host Granite in Nianzigou Molybdenum Deposit in Xilamulun Molybdenum Metallogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(4): 879-889. |
| [229] | 李益龙, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等. 华北-西伯利亚板块对接带早白垩纪的裂解:来自西拉木伦断裂带中性岩墙群的锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学证据[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(6): 921-932. Li Yilong, Zhou Hanwen, Zhong Zengqiu, et al. Extension of Suture Zone between North China and Siberia Craton in Early Cretaceous:Insights from Geochronology and Geochemistry of Intermediate Dykes from Xar Moron Fault Belt in Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(6): 921-932. DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2010.107 |
| [230] | 翟德高, 刘家军, 杨永强, 等. 内蒙古黄岗梁铁锡矿床成岩、成矿时代与构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 513-523. Zhai Degao, Liu Jiajun, Yang Yongqiang, et al. Petrogenetic and Metallogentic Ages and Tectonic Setting of the Huanggangliang Fe-Sn Deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2012, 31(4): 513-523. |
| [231] | 武广, 陈衍景, 赵振华, 等. 大兴安岭北端洛古河东花岗岩的地球化学、SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(2): 233-247. Wu Guang, Chen Yanjing, Zhao Zhenhua, et al. Geochemistry, Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age and Petrogenesis of the East Luoguhe Granites at the Northern end of the Great Hinggan Range[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(2): 233-247. |
| [232] | Jahn B M, Litvinovsky B, Zanvilevich A, et al. Pe-ralkaline Granitoid Magmatism in the Mongolian-Transbaikalian Belt:Evolution, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3): 521-539. |
| [233] | Meng Q R. What Drove Late Mesozoic Extension of the Northern China-Mongolia Tract?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 369(3): 155-174. |
| [234] | Pei J L, Sun Z M, Liu J, et al. A Paleomagnetic Study from the Late Jurassic Volcanics (155 Ma), North China:Implications for the Width of Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 510(3): 370-380. |
| [235] | Metelkin D V, Vernikovsky V A, Kazansky A Y, et al. Late Mesozoic Tectonics of Central Asia Based on Paleomagnetic Evidence[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 18(2): 400-419. |
| [236] | Wei C S, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F, et al. Oxygen and Neodymium Isotope Evidence for Recycling of Juvenile Crust in Northeast China[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(4): 375-378. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0375:OANIEF>2.0.CO;2 |
| [237] | 刘军, 武广, 王峰, 等. 大兴安岭北段岔路口斑岩钼矿床成矿年代学、岩石地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(6): 1093-1116. Liu Jun, Wu Guang, Wang Feng, et al. Geochronology and Petrogeochemistry of Chalukou Porphyry Mo Deposit inNorthern Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(6): 1093-1116. |
| [238] | 翟明国, 孟庆任, 刘建明, 等. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折峰期的主要地质效应和形成动力学探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 285-297. Zhai Mingguo, Meng Qingren, Liu Jianming, et al. Geological Features of Mesozoic Tectonic Regime Inversion in Eastern North China and Implication for Geodynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 285-297. |
| [239] | Zhang H D, Zhang H F, Santosh M, et al. Fluid Inclusions from the Jinchang Cu-Au Deposit, Heilongjiang Province, NE China:Genetic Style and Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 82: 103-114. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.12.017 |
| [240] | Wu F Y, Li X H, Yang J H, et al. Discussions on the Petrogenesis of Granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
| [241] | Sun W D, Zhang H, Ling M X, et al. The Genetic Association of Adakites and Cu-Au Ore Deposits[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53(5/6): 691-703. |
| [242] | Richards J P. Postsubduction Porphyry Cu-Au and Epithermal Au Deposits:Products of Remelting of Subduction-Modified Lithosphere[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(3): 247-250. DOI:10.1130/G25451A.1 |


